1.2 water
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
bonds between the hydrogen atom and oxygen atom in water molecules
covalent bonds
draw a water molecule

is water a polar or non polar molecule
polar
bonds that form between water molecules
hydrogen bonds
molecules with an unevenly distributed electrical charge
polar molecules
what gives water its fluidity
hydrogen bonds constantly forming and reforming between water molecules
why is water known as a universal solvent for polar molecules
because of its polarity
why do most inorganic ions dissolve well in water
because the positive or negative charges of the ions are attracted to the charge of water molecules
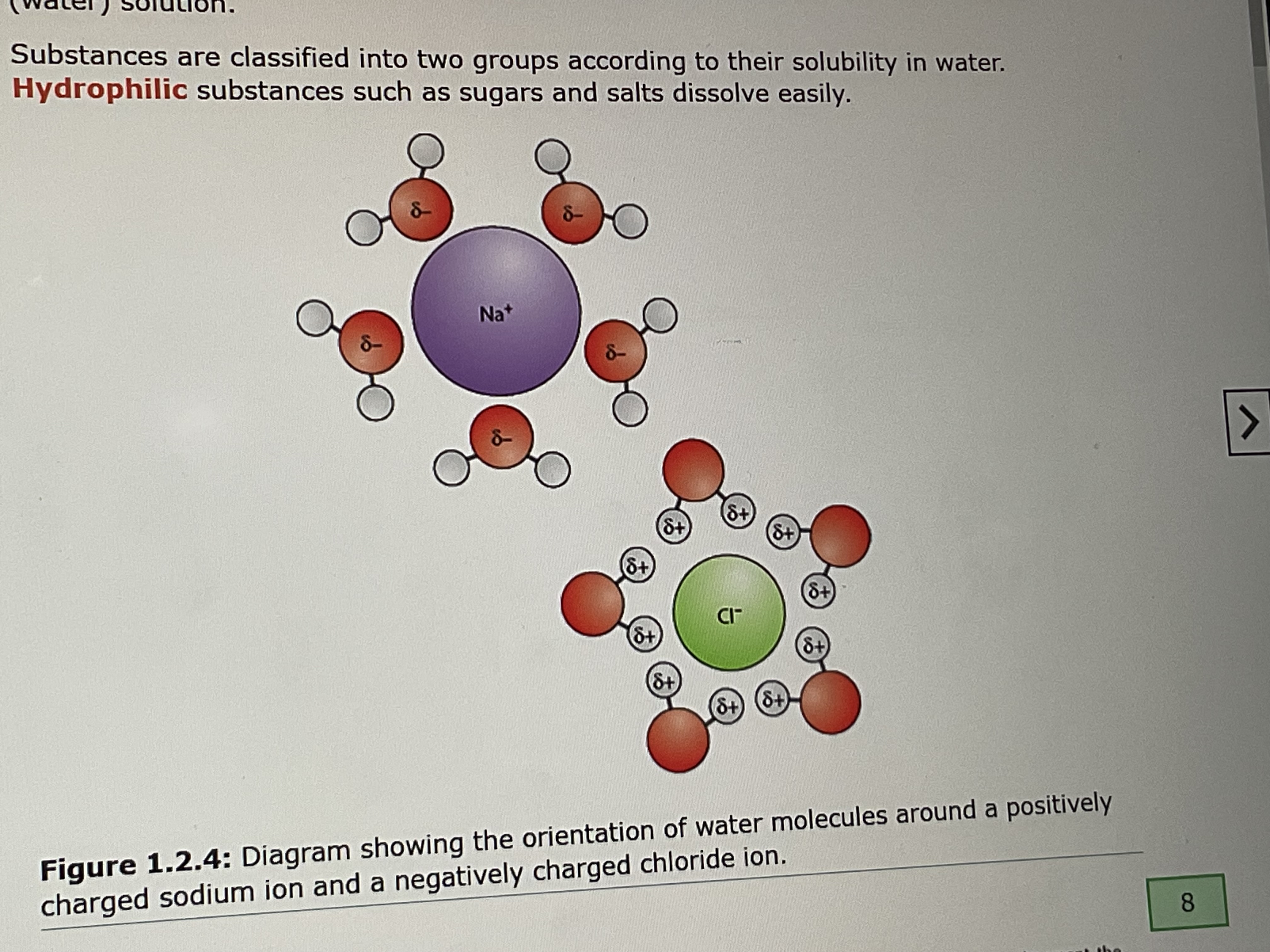
water and salt which is solvent and solute
water - solvent, salt - solute
positive and negative charges of water molecules attract ions with opposite charges so
ions position themselves between water molecules and dissolve
what is soluble in water
polar organic molecules
why is water the medium in which most biochemical reactions take place
because almost all substances involved dissolve well in water
what are the 2 groups when talking about solubility in water
hydrophilic and hydrophobic
what does hydrophilic mean
water loving, dissolvable
what does hydrophobic mean
after hating, undissolvable
why are non polar substances not soluble in water
because water molecules would rather remain hydrogen-bonded to each other
substances formed in or are needed for metabolism
metabolites
molecules that have both polar and non polar regions
amphipathic molecules
properties of a complex system that arise from simple interactions of individual component parts
emergent properties
what do the polar properties of molecules give water
cohesion of its molecules to one another
adhesion of its molecules to other molecules
high specific heat capacit
surface tension
what allows water to form droplets and gives it surface tension
cohesive forces
hydrogen bonding holding water tg in a network
cohesion
why is cohesion responsible for surface tension
because at the surface of water, there is a greater attraction of water molecules to one another
what occurs between water molecules and different molecules that causes water to attract to and stick to the walls of its container
adhesion
adhesive forces is
water being attracted to other polar or charged molecules
what creates the upward force on the edges of liquid
adhesion
what is it called when adhesive forces to the sides of the container are stronger than the cohesive force between molecules, and water is drawn upward against the pull of gravity
capillary action
what is high specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1cm³ by 1C
why is water a more stable environment for living things than air
because the temperature of water varies less than the temperature of air
properties that materials or liquids have that are related to their ability to conduct heat
thermal properties
what gives water a high specific heat capacity
a large amount of energy is needed to break the many weak hydrogen bonds between the water molecules