Cyber Week5 - MLS,CovertChannels,PowerAttacks
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What does the ‘dominates’ relation signify
It means a classification is “at least as sensitive” as another
Reflexive (each classification dominates itself)
Asymmetric (different classifications cannot both dominate the other)
Transitive (If A > B and B > C, then A > C)
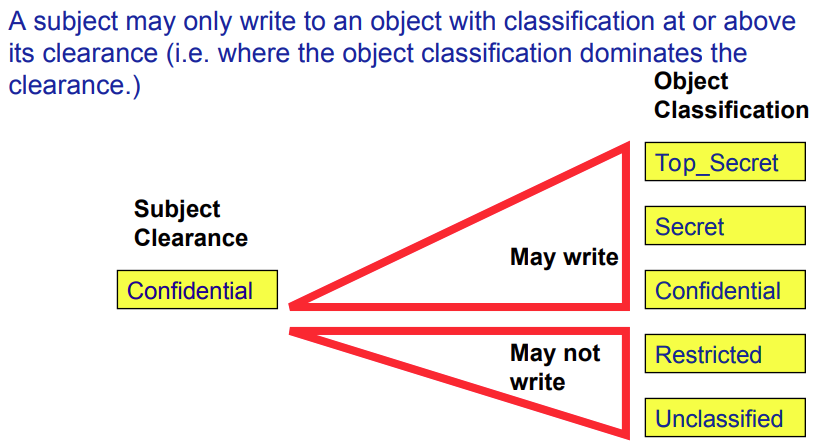
In MLS what is classification and clearance
Objects are assigned a classification indicating the sensitivity of their data.
Subjects are assigned a clearance - a classification which indicates the most sensitive data they can read/write.
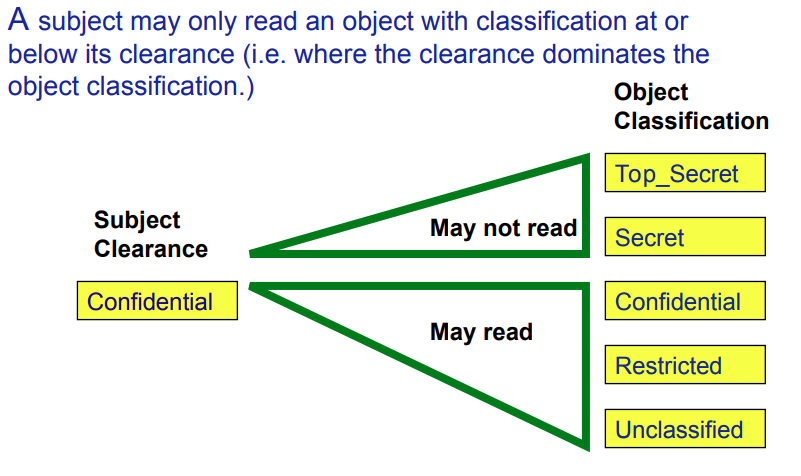
Why is the No Read-Up rule not enough to provide security on its own?
A user may read contents of a secret file and copy them to an Unclassified file