Lipolysis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is lipolysis?
The process of hydrolyzing (breaking down) triglycerides into glycerol and free FA which are used for energy
Where does lipolysis occur?
In adipose tissue
What are the 5 steps in lipolysis?
Activation of Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL)
Triglyceride Hydrolysis
Release and transport of FFAs
Glycerol utilisation
Fatty acid oxidation
Activation of Hormone Sensitive Lipase
During fasting, what occurs to increase cAMP levels
cAMP then causes what activation train
During fasting, what occurs to increase cAMP levels: Glucagon and epinephrine bind to their receptors on adipocytes
cAMP then causes what activation train: Activates protein kinease A (PKA) which phosphorylates and activates HSL
Triglyceride Hydrolysis
What occurs?
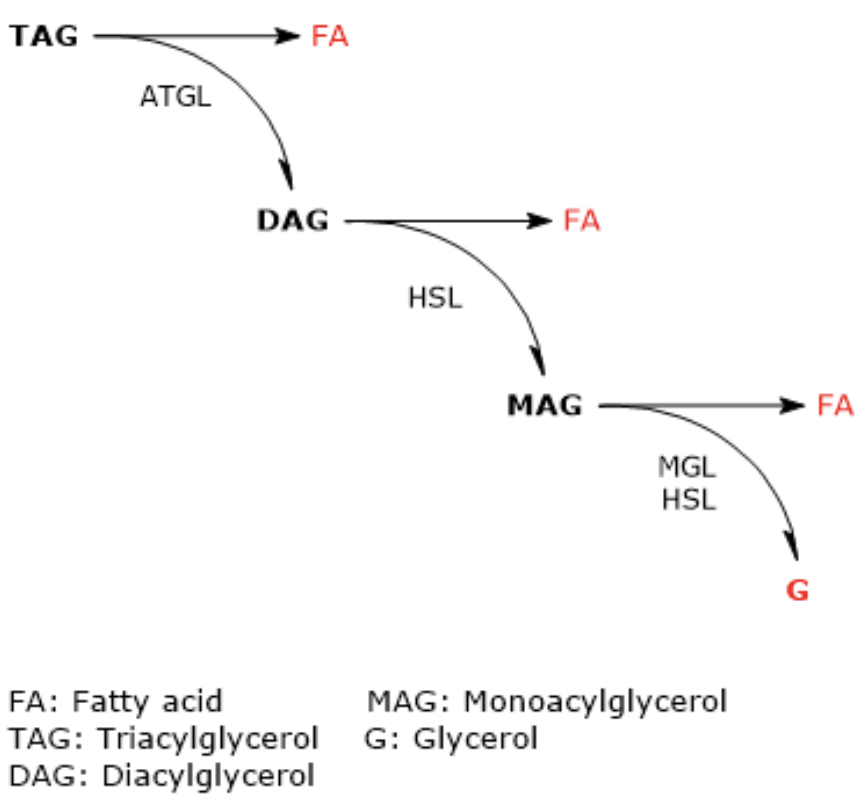
ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase
HSL: Hormone sensitive lipase
MGL: Monoacylglycerol lipase
ATGL: Triglyceride → Diglyceride + FFA
HSL: Diglyceride → Monoglyceride + FFA
MGL: Monoglyceride → Glycerol + FFA
Release and Transport of FFA
How is FFA transported?
Diffused out of adipocytes and bind to albumin in bloodstream for transport to energy demanding tissues
Glycerol Utilisation
Transported to
How is it used?
Transported to: Liver
Used by: Entering gluconeogenesis or glycolysis after conversion to glycerol-3-phosphate by glycerol kinase
Fatty Acid Oxidation
FFA activated to
Transported to
Undergo
Generating
FFA activated to: Fatty acyl-CoA
Transported to: Mitochondria via carnitine shuttle
Undergo: Beta-oxidation
Generating: Acetyl-CoA, NADH and FADH2 for ATP production by krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
Regulation of lipolysis
How is it activated?
Glucagon, epinephrine, norepinephrine by cAMP/PKA pathway
Cortisol because it enhances expression of lipolytic enzymes
Regulation of lipolysis
How is it inhibited?
Insulin because it stimulates phosphodiesterase activity to degrade cAMP, reducing HSL activation
High glucose and TG availability