MED CHEM EXAM 1
1/426
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
427 Terms
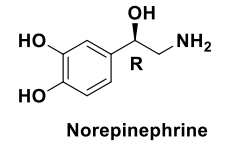
Norepinephrine Synthesis
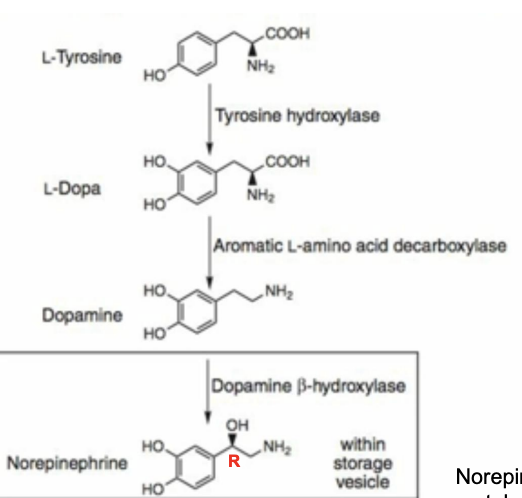
Norepinephrine Synthesis
Tyrosine → (Hydroxylation) → L-Dopa → (Decarboxylation) → Dopamine → (Hydroxylation) → Norepinephrine
Ortho vs Meta vs Para
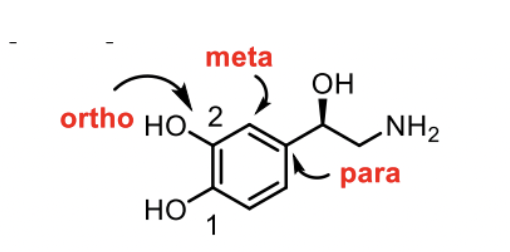
ROMP
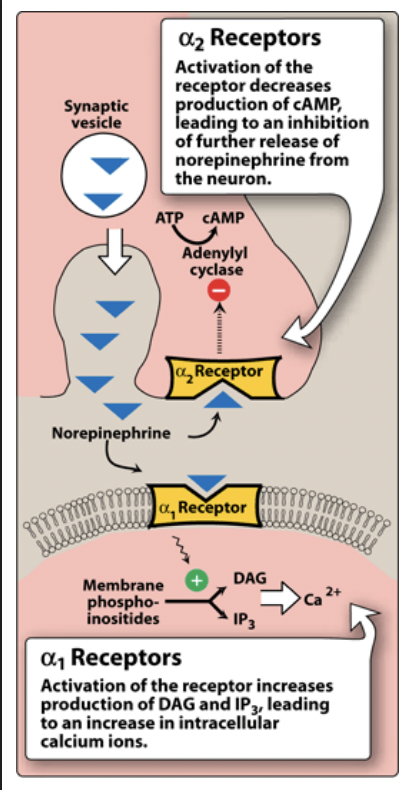
Activation of α2 receptor inhibits the ________
enzyme adenylate cyclase.
Inactivation of adenylate cyclase → decreases cAMP → → inhibition of further release of norepinephrine (uses negative feedback).
Epinephrine (EPI) has a poor oral bioavailability due to extensive metabolism by ______
MAO and COMT
Norepinephrine
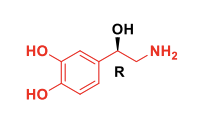
Epinephrine
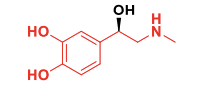
Epinephrine MOA
Think of sympathetic signaling!
Activates a1 → Vasoconstriction → Good for hypotension
Activates a1 → Vasoconstriction → Good for nasal decongestant (dilation)
Why should catecholamines like NE and Epinephrine be stored away from light?
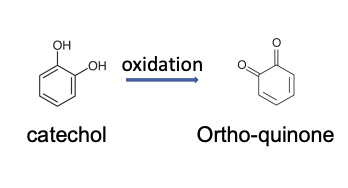
Bases and lights cause it to oxidize, leading to an ortho-quinone, which then can react with your DNA=bad.
That is why they are always formulated with antioxidants.
Why would you use Epinephrine?
Causes vasoconstriction (leading to hypertension in the sympathetic response) and also dilating blood vessels in mucus membranes (dilate to increase airflow). You want it’s vasodilatory effect.
Thus it also used for allergic rhinitis when the airways close up why? To cause bronchodilation!
What is the problem with ortho-quinone?
Toxic and it can react with DNA, protein, GSH and others.
Epinephrine and all other catechols are chemically susceptible to _______
oxygen and other oxidizing agents, especially in the presence of base and/or light, quickly decomposing to inactive quinones.
All catechol-containing drugs are stabilized with ______
antioxidants and dispensed in air-tight amber containers.
Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is used to treat a number of conditions, including ___________
anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, asthma, and superficial bleeding

Anaphylaxis
A severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
The reaction can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to an allergen.
Symptoms include a skin rash, nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing, and shock.
If not treated right away, usually with epinephrine, it can result in unconsciousness or deat
Epinephrine infusions may also be used for symptomatic _____
bradycardia.
Since it causes your HR to go up, and bradycardia is when your HR is too SLOW.
Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia, or abnormal heart rhythm, that occurs when the heart beats slower than ______
60 beats per minute (bpm).
Epinephrine (Epi Pen) usually is administered slowly by intravenous (IV) injection to relieve a__________ not controlled by other treatments
acute asthmatic attacks
Phenylethanolamine
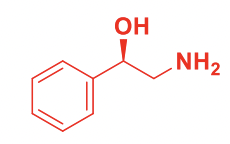
Common structure for 1 of 2 classes of a1 agonists
Alpha 1 agonists are spilt into what two classes?
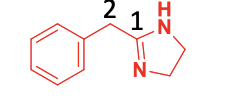
2-arylimidazoline
Phenylethanolamine
2-arylimidazoline
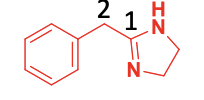
Common structure for 1 of 2 classes of a1 agonists
a1 agonist MOA
Stimulates phospholipase C activity.
What is it used for? Vasoconstriction, mydriasis; used for the treatment of hypotension, nasal decongestants, and during eye exams.
-azoline
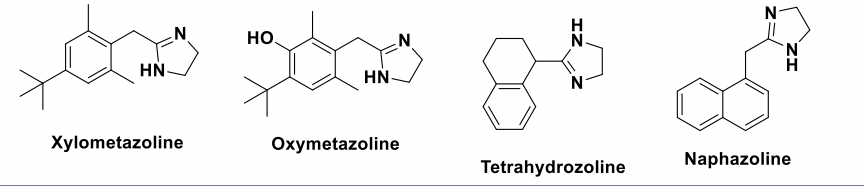
Alpha 1 agonists that are apart of the 2-arylimidazoline class
Phenylethanolamine Alpha 1 Agonists
2-arylimidazoline Alpha 1 agonists
Suffix: “azoline”
Phenylephrine Structure
Class: Alpha 1 agonists with the phenylethanolamine backbone.
Phenylephrine
Very frequently found in over-the-counter (OTC) decongestants in cold medications
Short duration of action of less than 4 hrs
Class: Alpha 1 agonists with the phenylethanolamine backbone.
Structure:
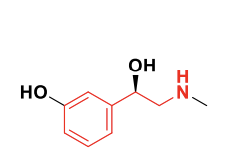
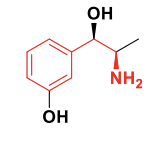
Metaraminol
Alpha 1 agonist used for the treatment of hypotension
Class: Alpha 1 agonists with the phenylethanolamine backbone.
Midodrine
Alpha 1 agonist for orthostatic hypotension
Do=A prodrug that does require conversion to the active metabolite, desglymidodrine
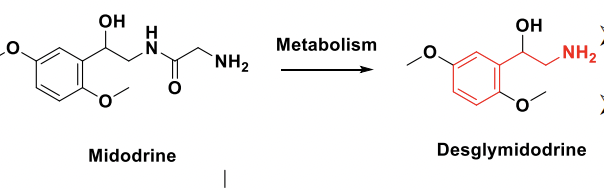
Midodrine Structure
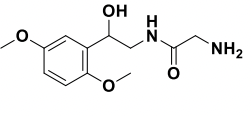
Key: Midodrine does require metabolism to its active metabolite, desglymidodrine
Class: Alpha 1 agonists with the phenylethanolamine backbone.
Midodrine Metabolism
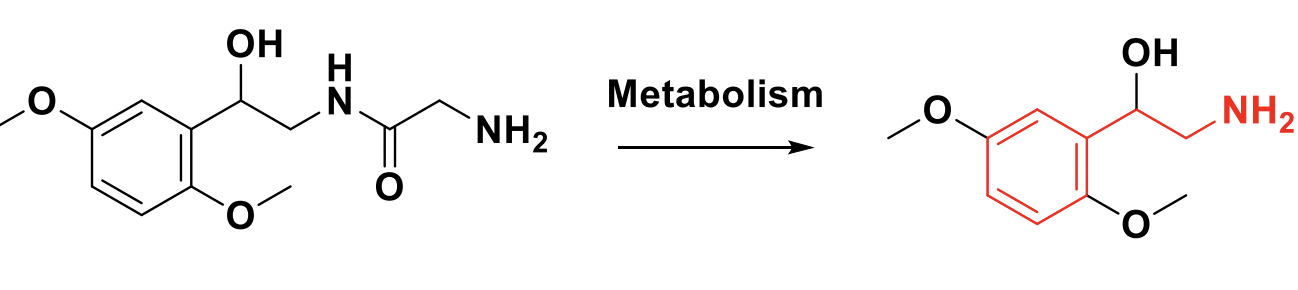
Class: Alpha 1 agonists with the phenylethanolamine backbone.

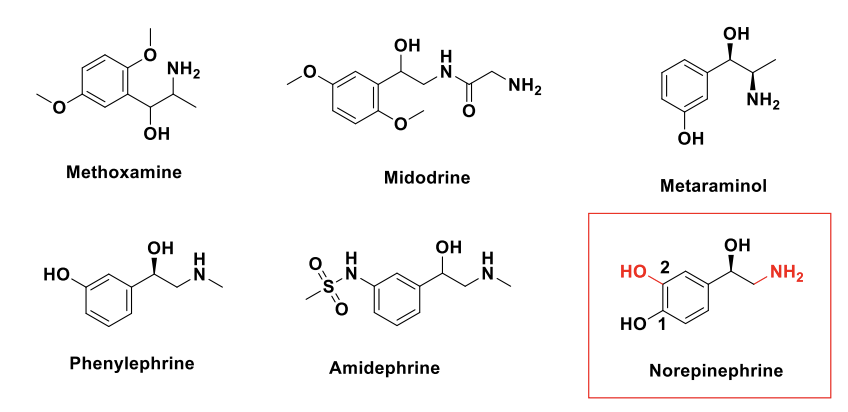
Alpha 1 Agonists Class w/ phenylehtanolamine backbone
Methoxamine
Midodrine
Metaminol
Phenylephrine
Amidephrine
NE (Why? The structure is essentially NE minus the two OHs on the catechol!)
Imadazole vs Imidazoline pKAs
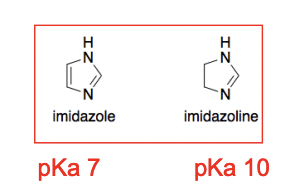
Alpha 1 2-aryl imidazoline agonists need a lip_____
ophillic substitution at the ortho position of the phenyl ring
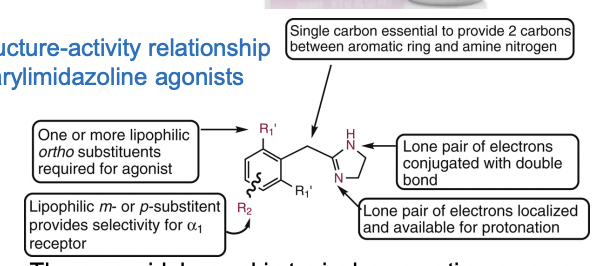
Structure-activity relationship of arylimidazoline agonists
Lipophilic ortho position is required.
Lipophilic meta/para substitution helps to provide selectivity for the alpha 1 receptor.
Mixed-acting agonists
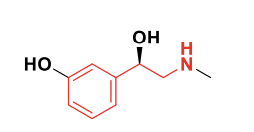
Ephedrine
Pseudoephedrine
MOA: Bind to both alpha and beta adrenoreceptors and displace NE from synaptic vesicles or inhibit their uptake, thus increasing NE concentration at the adrenergic receptors.
Used in cold medications with antihistamines.
Ephedrine
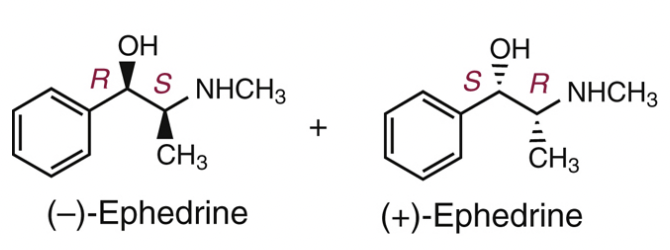
Not a substrate for COMT nor MAO. Why? The alpha methyl group sterically hinders its metabolism.
Class: Mixed acting sympathomimetic (targets alpha, beta receptors, and also increases NE concentration).
What is ephedrine regulated?
Ephedrine → Methamphetamine (Meth)
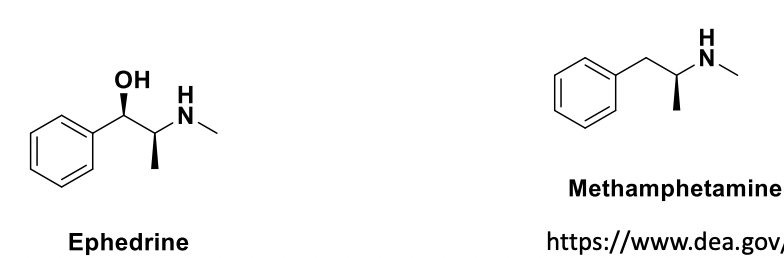
Loratadine Structure
Antihistamine

Diphenhydramine Structure
Antihistamine

Pseudoephedrine Use
Nasal decongestant (in combo OTC products e.g., Claritin-D)
Structure:
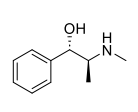
Used in products like Zyrtec-D (Allergy + Sinus) and Advil Cold and Sinus.
Arylimidazoline adrenergic agonists are highly ionic in nature.
They are widely used in topical preparations as nasal decongestants and eye drops for conditions associated with the common cold, influenza, sinusitis, allergic and nonallergic rhinitis, and upper respiratory track infections
Ephedrine is not a substrate for ___ and ___
COMT; MAO
Not for MAO because of the presence of an alpha-methyl group which sterically hinders metabolism by MAO.
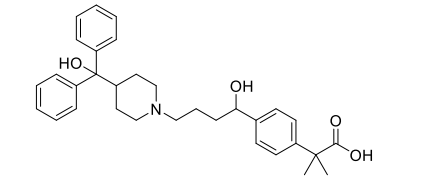
Fexofenadine Structure
Certizine Structure
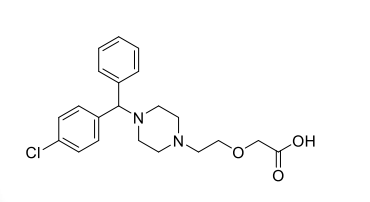

Mixed-acting sympathomimetics are common ingredients in many ______ with oral decongestant formulations
cold medications
Mixed-acting sympathomimetics:
Ephedrine
Pseudoephedrine
Ibuprofen Structure
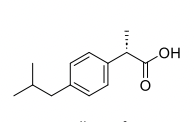
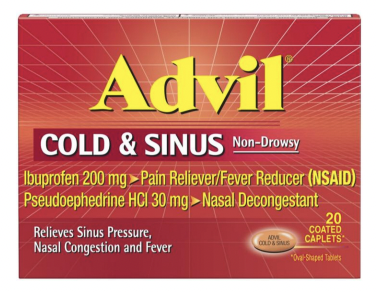
α2 agonist Uses
Antihypertensive, treatment of glaucoma, sedative & treatment of opiate dependence and alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
**Even though it’s in the brain! Activates the receptor to lead to a decrease in NE which decreases BP.
Alpha 2 agonists Structures
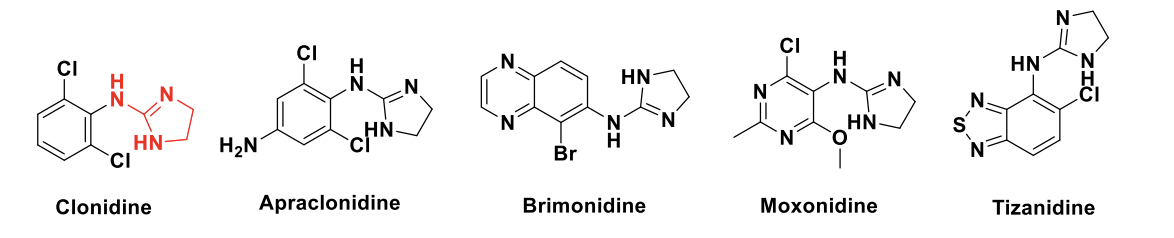
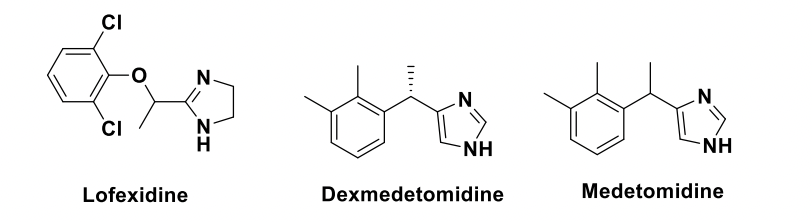
Suffix “idine”, all contain the aminoadamine backbone.
Alpha 2 agonists Nomenclature Exceptions
Monoxide → HT
Guanfacine → HT
Guanabenz → HT
Methyldopa → HT
Mnemonic: Asma and Aliza (a2) watched “Good Morning Ginny”.

Clonidine
Used for hypertension
Tablets, Injection, Transdermal System
Due to it’s CNS Side Effects it cannot treat gluacoma
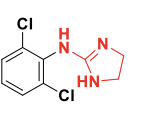
Clonidine
Class: Alpha 2 agonist with a 2-aminoimidazoline backbone.
Used for Hypertension
So it’s an alpha 2 agonist, think about how Clonidine affects the brain, so the “inidine” suffixes all pertain to that drug class.
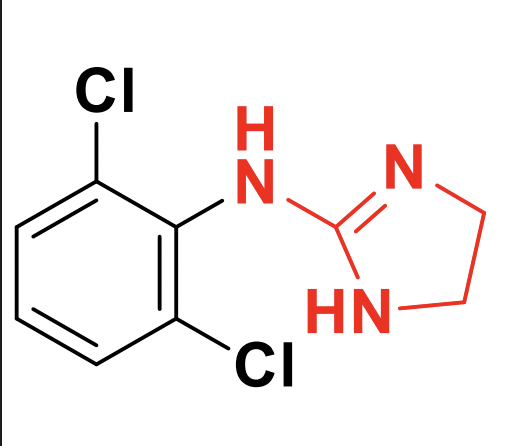
Apraclonidine vs Clonidine
Apraclonidine contains an NH2 polar group, which will cause it to be highly ionized at a physiological pH, so it’s less likely to cross the BBB.
Clonidine=cutesy and demure; it will cross the blood-brain barrier → HT
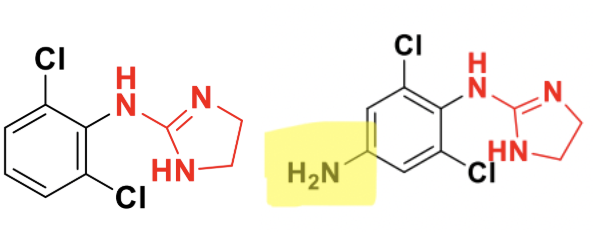
Brimonidine does a little bit of both → crosses the BBB for fatigue and glaucoma use
Suffix: -nidine
Alpha 2 agonists
Apraclonidine
Brimonidine
Alpha 2 agonists used to treat glaucoma
-nidine: Alpha 2 agonists
Apraclonidine vs Brimonidine
Apraclonidine: Poor BBB penetration → fewer CNS effects
Brimonidine: Crosses BBB → may cause fatigue/drowsiness
Why? Apraclonidine is highly ionized at a normal pH (can’t cross) and Brimonidine is very lipophillic
2-Arylimidazoline VS 2-aminoimidazoline

Outlier: Lofexidine which is an alpha 2 agonist but doesn’t have the 2-aminoimadzoline backbone
2-Arylimidazoline vs 2-aminoimidazoline Clinical Use
2-Arylimidazoline: Alpha 1 agonist for nasal decongestant (the other class for alpha 1 was for hypotension also).
2-aminoimidazoline: Alpha 2 agonist for hypertension, glaucoma
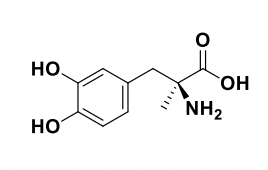
Methyldopa
Also like midodrine both are prodrugs that need to be converted to their activie metabolite
But methyldopa is alpha 2, hypertension and midodrine is alpha 1 for hypotension
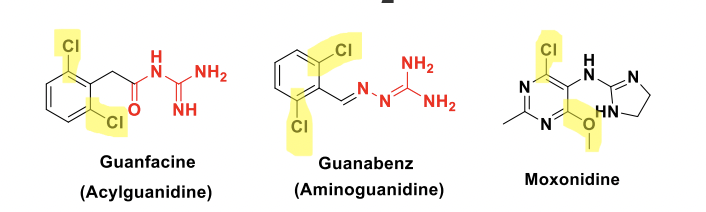
Guanfacine, guanabenz, and moxonide are used for the treatment of _____
hypertension
All alpha 2 agonists!
What does the 2-arylimidazoline vs 2-aminoimidazoline rings require for activity?
2-arylimidazoline: Liophilic ortho substitution and needs an Imidazoline Ring
2-aminoimidazoline: Phenyl needs one ortho Chlorine or Methy,l but the Imidazoline Ring not required
Tizanidine
“idine” → Alpha 2 agonist
Used for muscle spasticity due to spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis
Tizanidine readily crosses the ________ reducing spasticity by increasing presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons
BBB where it functions as a α2 -adrenergic agonist
“idine” → Alpha 2 agonist

Tizanidine
Alpha 2 agonist that readily crosses the BBB and is used for the treatment of muscle spasticity.
All alpha 2 agonist have the 2-aminoimidazoline backbone except….
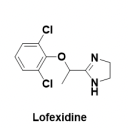
Also…Guanfacine, Guanabenz, Moxonidine, Methyldopa
Lofexidine is an agonist of α2 adrenergic receptor and used for the treatment of _____ symptoms in adults (approved in 2018)
opioid withdrawal
“idine” → Alpha 2 agonist
Does not have a 2-aminoimidazoline backbone!

Guanfacine Structure
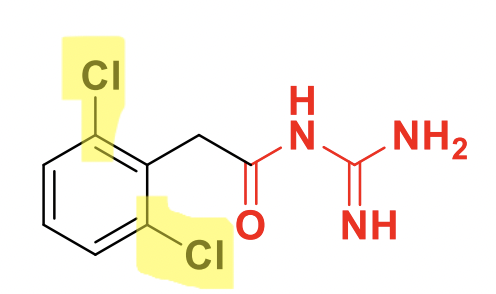
Used for Hypertension
Class: Alpha 2 agonist, but does not contain the 2-aminoimidazole backbone like lofexidine.
**Open ring analog of clonidine.
Systolic vs Diastolic Pressure
Systolic → Blood pumped out of the heart
Diastolic → Resting state between heartbeats
Guanabenz Structure
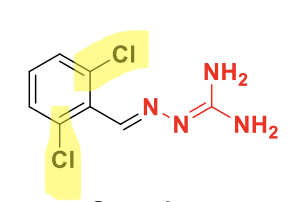
Used for Hypertension
Class: Alpha 2 agonist, but does not contain the 2-aminoimidazole backbone like lofexidine.
**Open ring analog of clonidine.
Moxonidine Structure
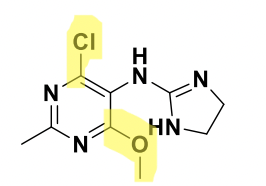
Used for Hypertension
Class: Alpha 2 agonist, but does not contain the 2-aminoimidazole backbone like lofexidine
What do the structures of Guanfacine, guanabenz, and moxonide reveal for alpha 2 agonists?
The imidazoline ring was not necessary for the activity, but the phenyl ring requires at least one ortho chlorine or methyl group
Methyldopa
Used for the treatment of hypertension
An alpha 2 agonist that does require conversion to its active metabolite to be selective for the alpha 2 agonist.
Dexmedetomidine is an agonist of α2 adrenergic receptor which was approved for the ____
sedation purpose (approved in 2020)
“idine” → Alpha 2 agonist
Also decreases blood pressure and heart rate!!

What do the structures of Guanfacine, guanabenz indicate for alpha 2 agonist?
The imidazoline ring was not necessary for the activity, but the phenyl ring requires at least one ortho chlorine or methyl group.
Is methyldopa the active form of the drug?
No, it’s the active metabolite that is so.
What part of molecules does COMT metabolize?
The catecholamine
For Sudafed, by not having a catecholamine means that it will not be metabolized by COMT but since it has a methyl it will be by MAO.
Apraclonidine vs Clonidine
Apraclonidine: Contains an NH2 group which is polar
This means that it will not cross the BBB like clonidine making it a better candidate for glaucoma (in the eye) than clonidine.
“pril”
ACE inhibitors
“sartan”
ARBs
Normal HT
Less than 120 (Systolic)
Less than 80 (Diastolic)
Anything higher than these values is HT
140/90 mmHG
High Blood Pressure
What is the first line of therapies for patients with high blood pressure?
Thiazide Diuretics
Calcium Channel Blockers
Angiotensin-Converting Enzymes
** Beta-blockers if this treatment options fail
ABCD
First line therapies for hypertension
A: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors)
B: Beta Blockers
C: Calcium Channel Blockers
D: Diuretics
ARBs suffix
“sartan”
Calcium Channel Blockers suffix
“dipine”
Diuretics Suffix
“ide”
Beta Agonists Classes

____ β-blockers are often preferred in patients with respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD due to their reduced effect on bronchoconstriction compared to non-selective β-blockers.
Selective
Dobutamine
β1 adrenergic agonist used as a cardiac stimulant after surgery or congestive heart failure (IV only)
Dobutamine Structure
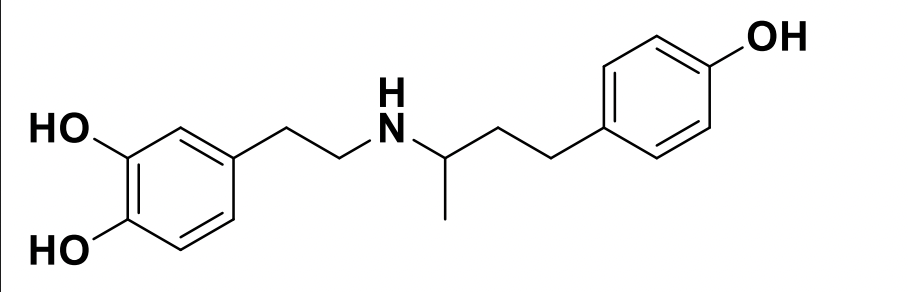
Only B1 agonist.
Catechol Structure allows it to be quickly degraded by COMT, which is used as a cardiac stimulant after congestive heart failure.
How does the structure of dobutamine effect it’s metabolism?
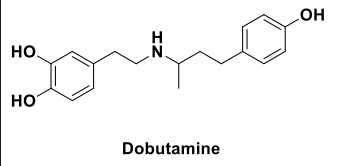
Contains a catechol: Metabolized by COMT
Thus, it has a short duration of action and no oral activity.
Dobutamine is an example of what?
Beta 1 agonist
All SABAs are resistant to COMT metabolism except what?
Isoetharine
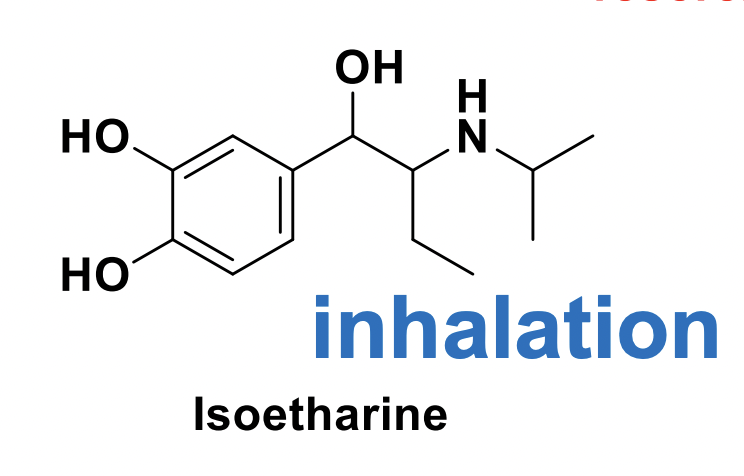
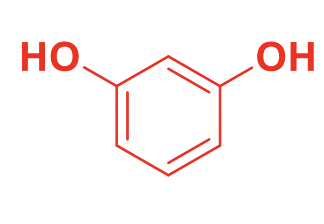
What is the common structure in short-acting Beta agonists (SABAs)?
Resorcinol
This prevents COMT metabolism and allows SABA to be slowly metabolized by MAO.
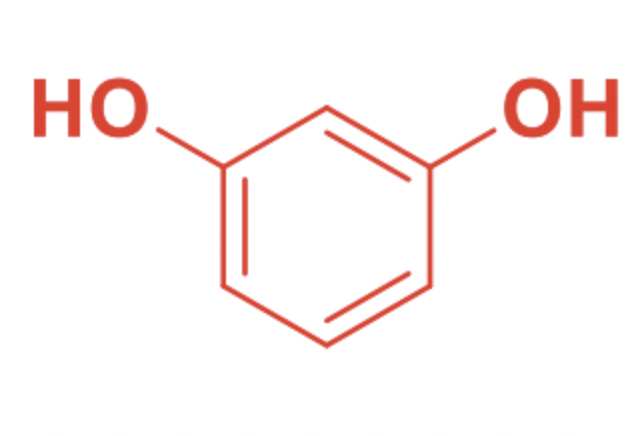
This indicates that the structure is what?
SABA (Resorcinol)
Structures of SABAs
It contains a Resorcinol that is not metabolized by COMT but by MAO.
But also, the MAO metabolism is slow because the nitrogens are very sterically hindered, making it harder for them to be metabolized.
Exception: Isoetharine
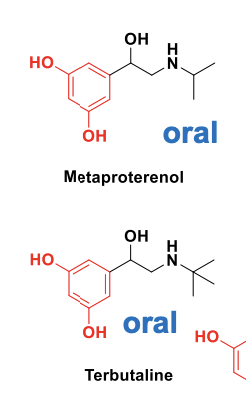
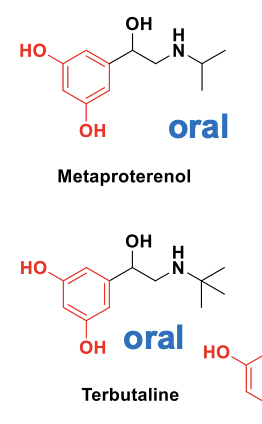
Metaproterenol vs Terbutaline
Short-acting β2 agonists → Used for COPD/Asthma
Terbutaline: Can be used for long-term treatment since the nitroge
is more sterically hindered, increasing the time it takes for MAO metabolism to occur.
How can albuterol be administered?
Inhaled or orally
What makes levalbuterol so special?
This is the R enantiomer of albuterol.
Meaning that compared to the structure of epinephrine, this will be bind to the B2 receptors more potently because it structure is similar to that of epinephrine (natural sympathetic analog which triggers bronchodilation).