Organic Compounds and Carbohydrates Overview
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Inorganic Compounds
Compounds that don't contain carbon.
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon, derived from living things.
Polymerization
Process of joining smaller compounds to form larger ones.
Monomer
Subunit serving as the building block of a polymer.
Polymer
Large molecule made of many identical monomers.
Covalent Bond
Strong bond formed by sharing electron pairs.
Condensation Reaction (Dehydration Synthesis)
Reaction building molecules by losing water.
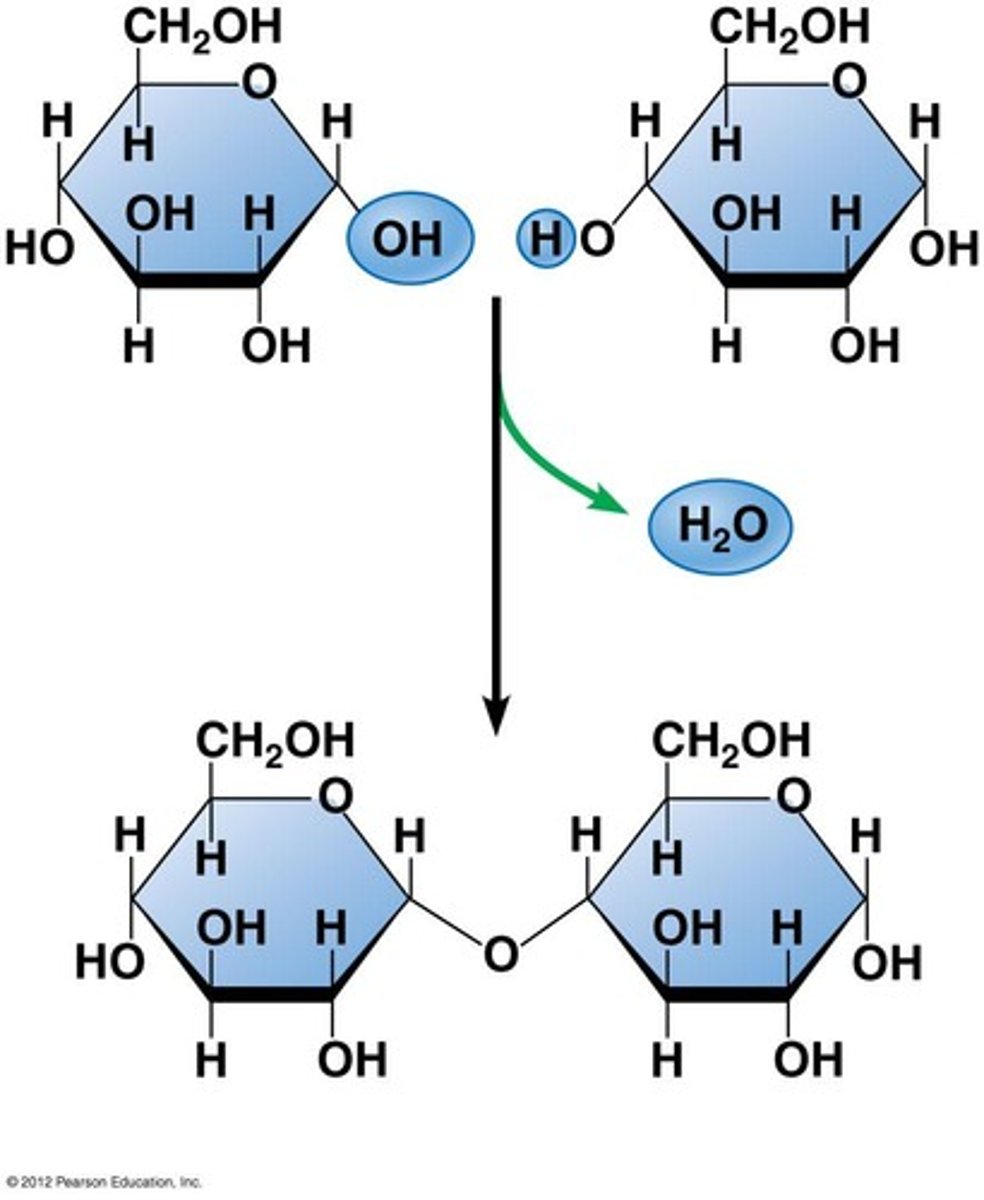
Hydrolysis
Reaction breaking molecules by adding water.
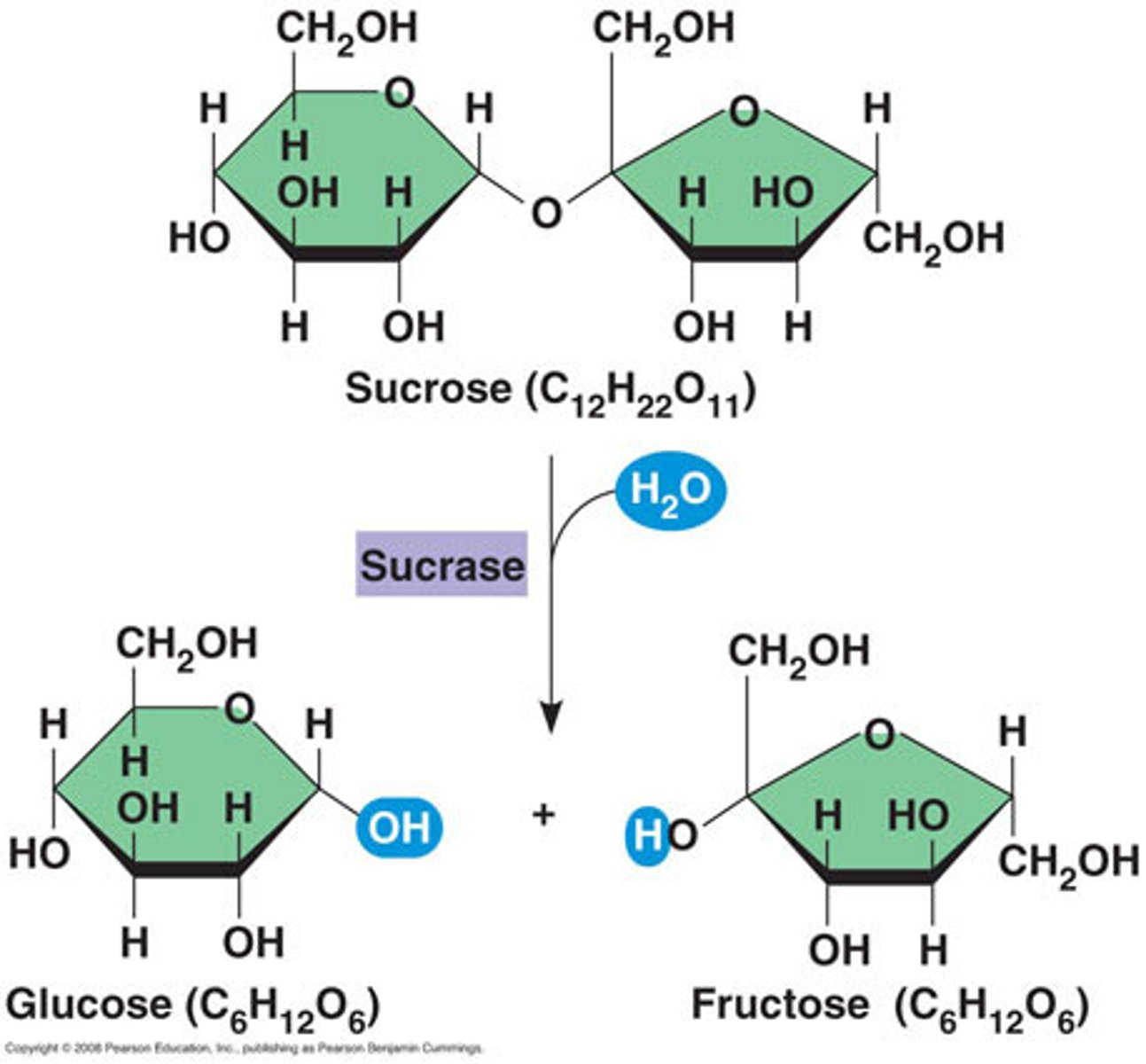
Carbohydrates
Sugars and starches used for energy or structure. 1:2:1 Ratio C,H,O
Monosaccharide
Simple sugars.
Examples: glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharide
Formed from two monosaccharides combining. Examples: sucrose, maltose, lactose
Polysaccharide
Formed from many monosaccharides combining. Ex: cellulose, starch, glycogen
Glucose
Monosaccharide; major source of blood sugar.
Fructose
Fruit sugar; isomer of glucose.
Galactose
Sugar found in milk.
Sucrose
Disaccharide found in table sugar.
Lactose
Disaccharide found in milk.
Maltose
Disaccharide found in wheat products.
Starch
Polysaccharide; glucose storage in plants.
Cellulose
Indigestible polysaccharide providing plant cell structure.
Chitin
Polysaccharide in insect and mushroom exoskeletons.
Glycogen
Polysaccharide; glucose storage in animals.
Deoxyribose
Monosaccharide part of DNA.
Ribose
Monosaccharide part of RNA.