Cellular Respiration: Processes and Energy Production
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Catabolism
Breakdown of molecules to release energy.
Cellular respiration
Process of converting glucose into energy.
Intermediate compound
Substance formed during metabolic reactions.
Enzyme
Protein that catalyzes biochemical reactions.
Energy release
Energy produced at each reaction step.
Controlled energy production
Regulated release of energy during respiration.
Respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP.
Heat generation
60% of energy lost as heat.
Body temperature maintenance
Heat from respiration keeps body temperature stable.
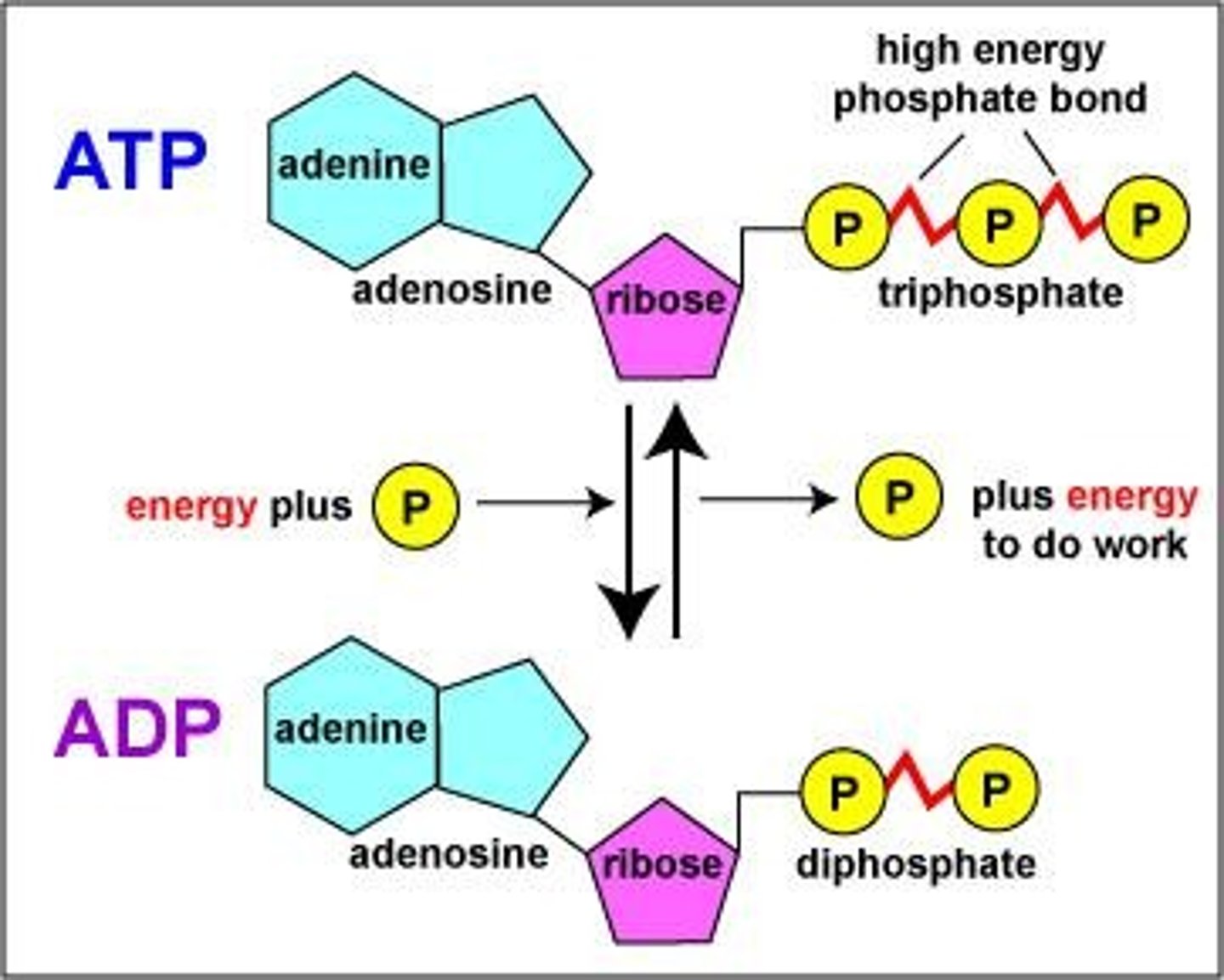
ATP
Energy currency of the cell, formed from ADP.
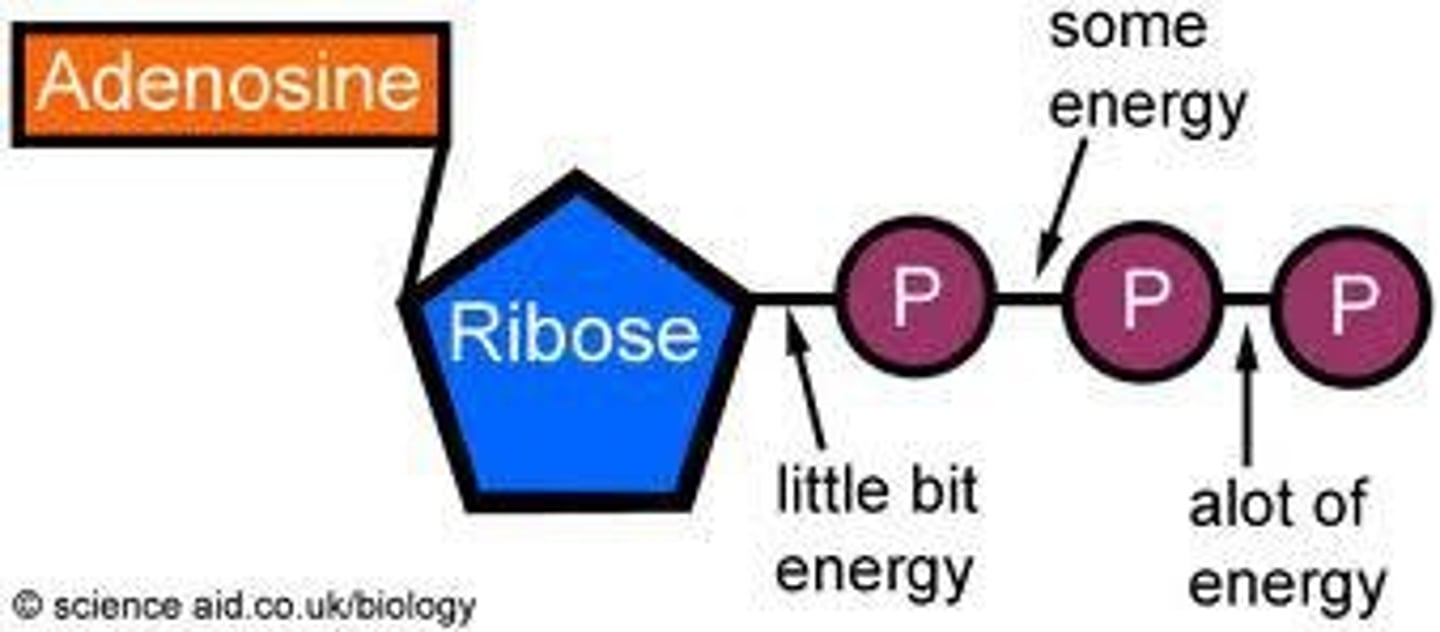
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, precursor to ATP.
ADP/ATP cycle
Recycling of ADP to store energy.
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration without oxygen, low energy yield.
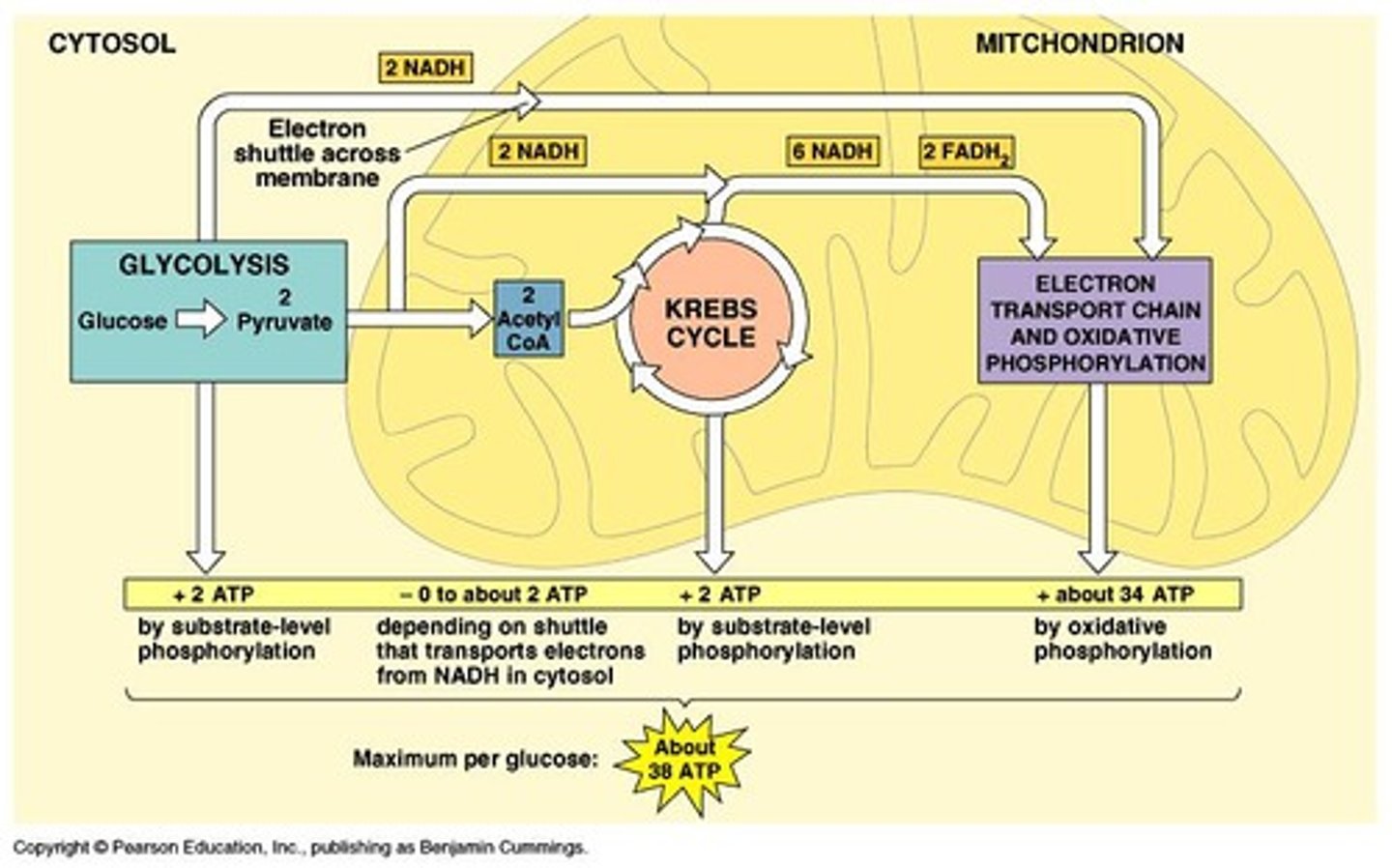
Glycolysis
First phase of glucose breakdown, produces pyruvic acid.
Lactic acid
Product of anaerobic respiration, causes muscle fatigue.
Oxygen debt
Deficit of oxygen after intense exercise.
Recovery oxygen
Increased breathing post-exercise to repay oxygen debt.
Aerobic respiration
Respiration in presence of oxygen, high energy yield.
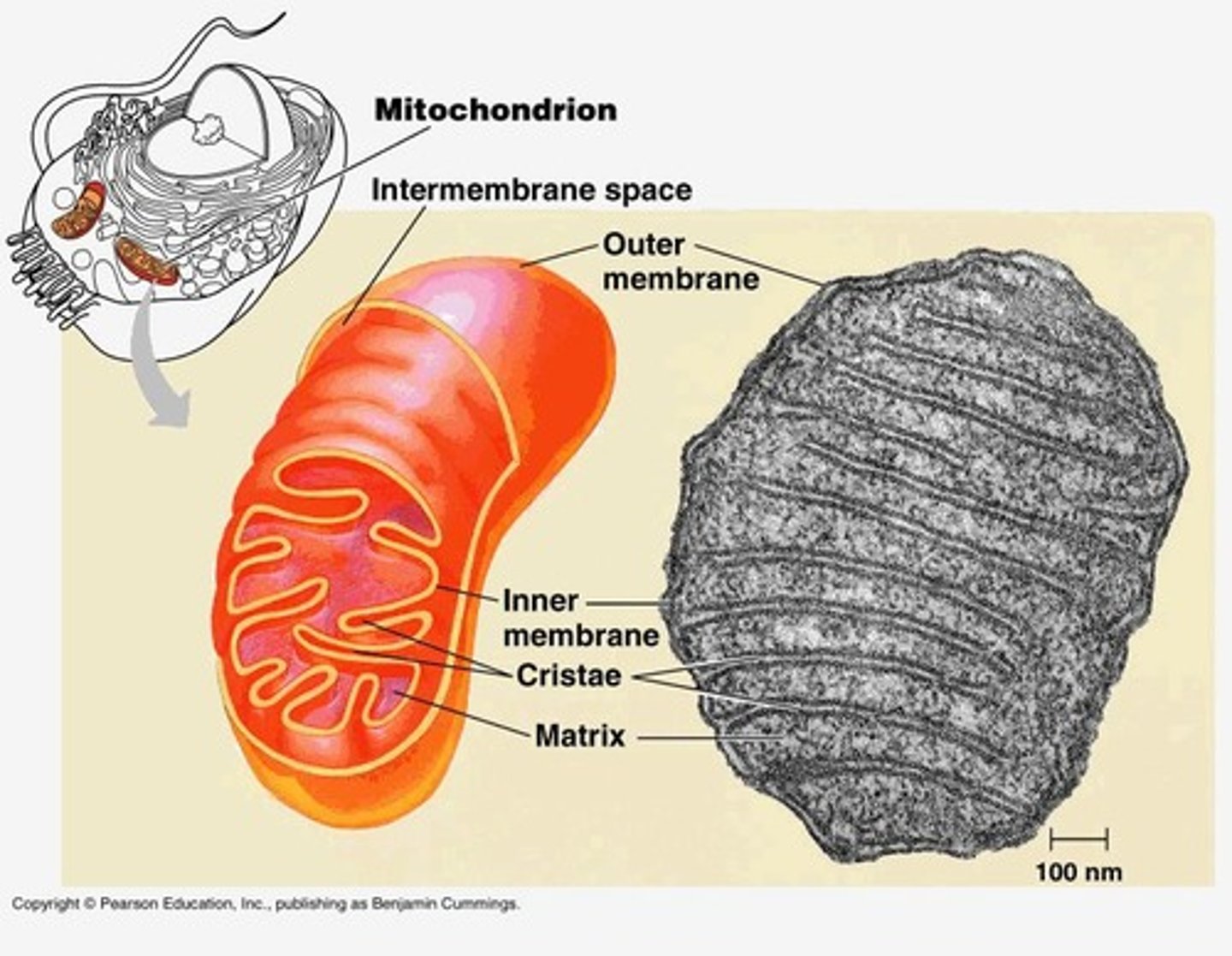
Mitochondrion
Cell organelle where aerobic respiration occurs.
Citric acid cycle
First step in aerobic respiration, produces ATP.
Electron transport chain
Second step in aerobic respiration, produces ATP.
Total ATP yield
Up to 38 ATP from one glucose molecule.
Energy used by cells
ATP needed for various cellular functions.
Active transport
Movement of substances against concentration gradient.
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins, used for energy.
Fatty acids
Components of lipids, alternative energy source.
Glycerol
Part of lipids, can be used for energy.
Anabolism
Synthesis of larger molecules from smaller ones.
Chemical bonds
Connections between atoms in molecules, require energy.
Glycogen
Stored form of glucose in the liver.