Atomic Theory
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Antoine Lavoisier (1785)
Law of Conservation of Mass - matter is not created/destroyed during chemical reaction; reactants equals products
Joseph Proust (1799)
Law of Definite Proportions - elements in substances always combine in definite proportions by mass
John Dalton (1803)
Atomic Theory - all matter is made of atoms, all atoms in an element are the same but different with different elements, atoms combine in fixed proportions to make compounds, chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms, not creating/destroying
J.J. Thomson (1897)
Cathode ray has electrons, calculated ratio of electron mass to it charge
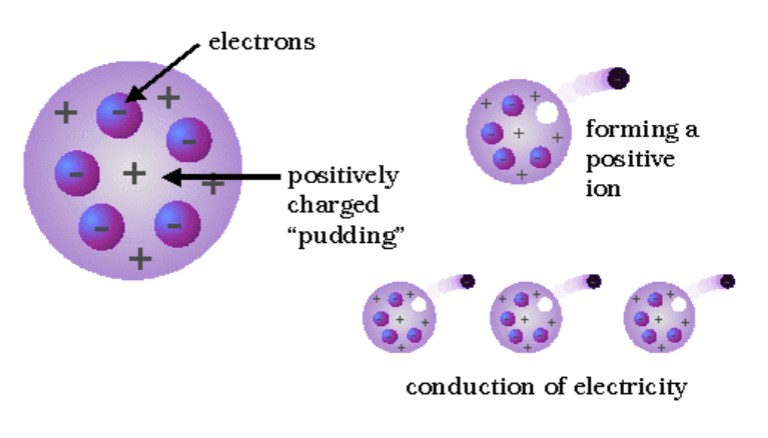
Plum Pudding Model
Thomson - negatively charged electrons scattered in positive sponge-like structure
Robert Millikan (1909)
Oil drop experiment - determined charge of electron
Ernest Rutherford (1911)
Gold foil experiment; devised Nuclear Theory of the Atom - all positive charge and nearly all mass of an atom are in a tiny nucleus, electron has almost no mass but occupy nearly all the volume of atom; discovered proton
Neils Bohr (1922)
Proposed Planetary model of atom - similar to solar system, sun is nucleus, electrons are planets
Relative masses and charges
Proton - 1 amu +1, Neutron - 1amu 0, Electron 5×10^-4 = 0 -1
Atomic Number
number of protons (same as electrons)
Mass Number
number of protons + neutrons (neutrons = mass # - atomic #)
Ions
charged particles formed when atom loses/gains an electron
Cations
positive, loss of electron
Anion
negative, gains electron
Isotopes
different atoms of same element with different mass numbers