Module 1.1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
oikos
The term “ecology” is from which Greek word?
house or habitation
What does oikos mean?
Haeckel
Who coined the term ecology?
Ecosystem
This is a model for the cycles of matter and energy that include organic entities and their linkages to the inorganic.
Resilience
A measure of the degree of change a system can undergo while still maintaining its basic elements or relationships.
Stability
A measure of the speed with which a system returns to equilibrium after absorbing disturbances.
Natural
Semi-natural
Artificial
What are the 3 types of ecosystems?
Natural Ecosystems
Not perceptibly altered by humans
The actual and historical role of humans in the functioning of the ecosystem is nil or almost nil. Species composition and species numbers are uninfluenced. Geomorphic, ecological, and biological processes are almost undisturbed by humans.
Examples are: Highest parts of mountains, Undisturbed parts of the seas, lakes, rivers, tundras, etc, and Primeval natural forest ecosystems.
Semi-natural Ecosystems
Altered by human actions, but which retain significant native elements
May range from unaltered species composition to just using the natural background-soil and or water by man.
Almost all ecosystems resulting from “traditional” forms of agricultural land use as steppes, puszta's and wooded meadows fall in this category.
Artificial ecosystems
Human-made system of plants, animals and people living in an area together with their surroundings
Zoo parks often create artificial ecosystems by placing animals in human-made areas similar to their natural habitat. People can also create lakes in the middle of desserts and keep penguins in warm climates, but only if they create an artificial ecosystem.
Family
The basic foundation of social organization comprised of individuals associated by blood relationship, legal union, adoption, or consensual affiliation.
Organizations
These can be a random group of people who come together spontaneously to address a short-term need, such as collecting litter along a specific stretch of road.
Or, it might be a carefully collected, aligned, and integrated group of people who came together for the long term to address a long-term need, such as stopping poverty in a certain country.
Community according to the theory of human ecology
The structure of relationships through which a localized population meets its daily requirements’. It points out its key role of providing support to its members for its survival by forming relationship of care.
Systems theory
This theory identifies community as the amalgamation of different units or sub-systems that jointly work towards achievement of community goals.
Human Settlements
The totality of the human community – whether city, town, or village – with all the social, material, organizational, spiritual, and cultural elements that sustain it.
Nature
Man
Society
Shells
Networks
What comprises human settlements?
Actor based model
Ecosystem-based model
Social system with the ecosystems model
Human ecosystems model
What are the 4 Human Ecological Frameworks?
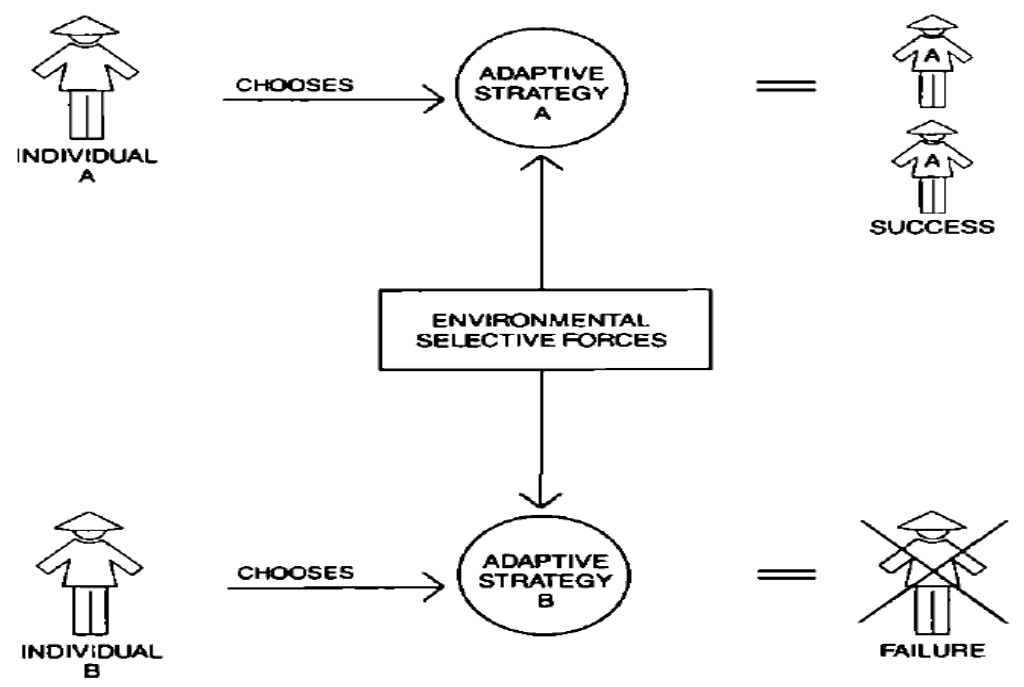
Actor-based model
What human ecological framework is this?
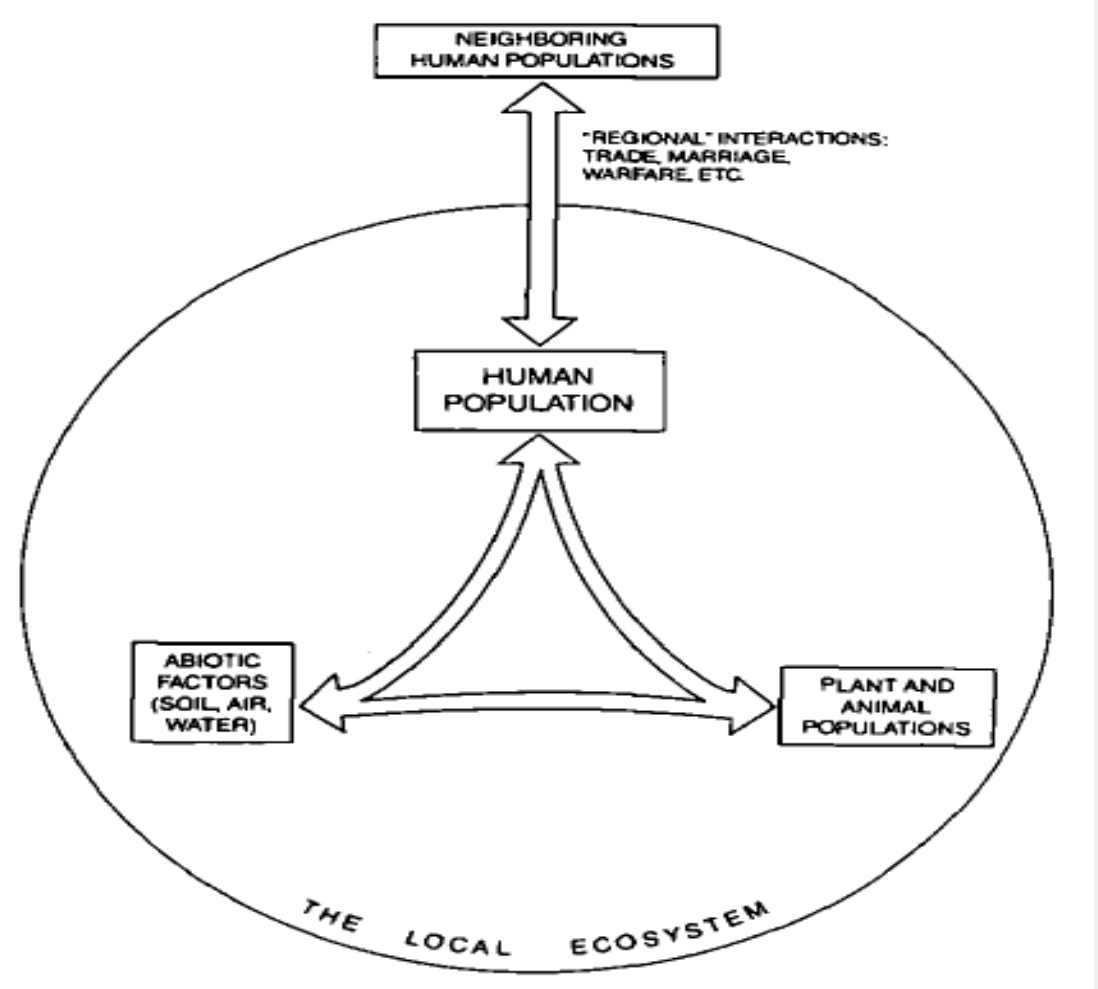
Ecosystem-based model
What human ecological framework is this?
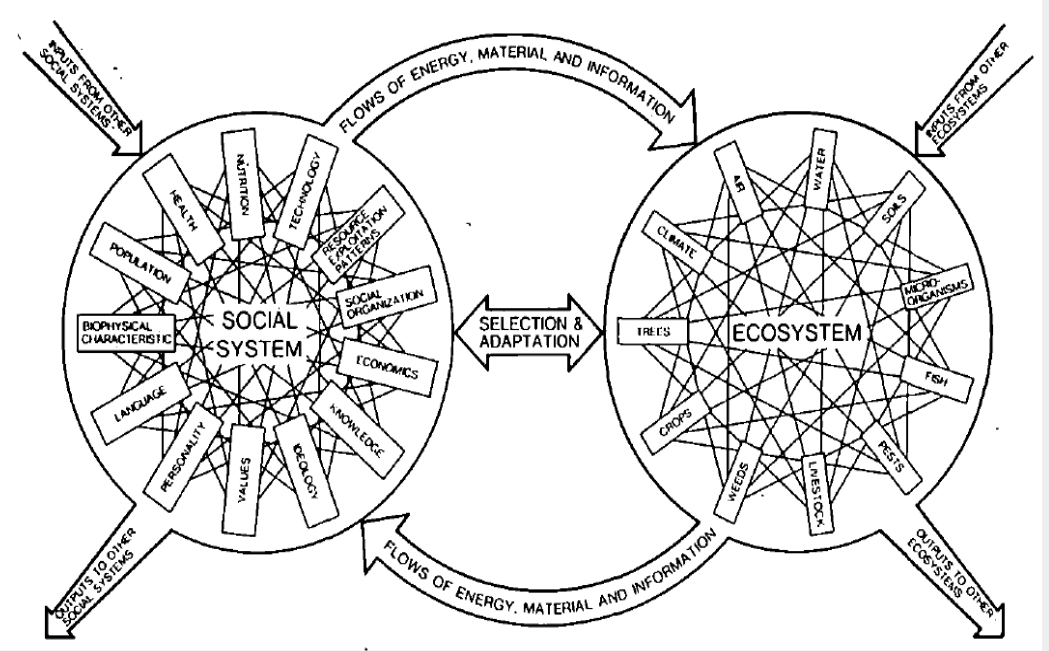
Social system with the ecosystems model
What human ecological framework is this?
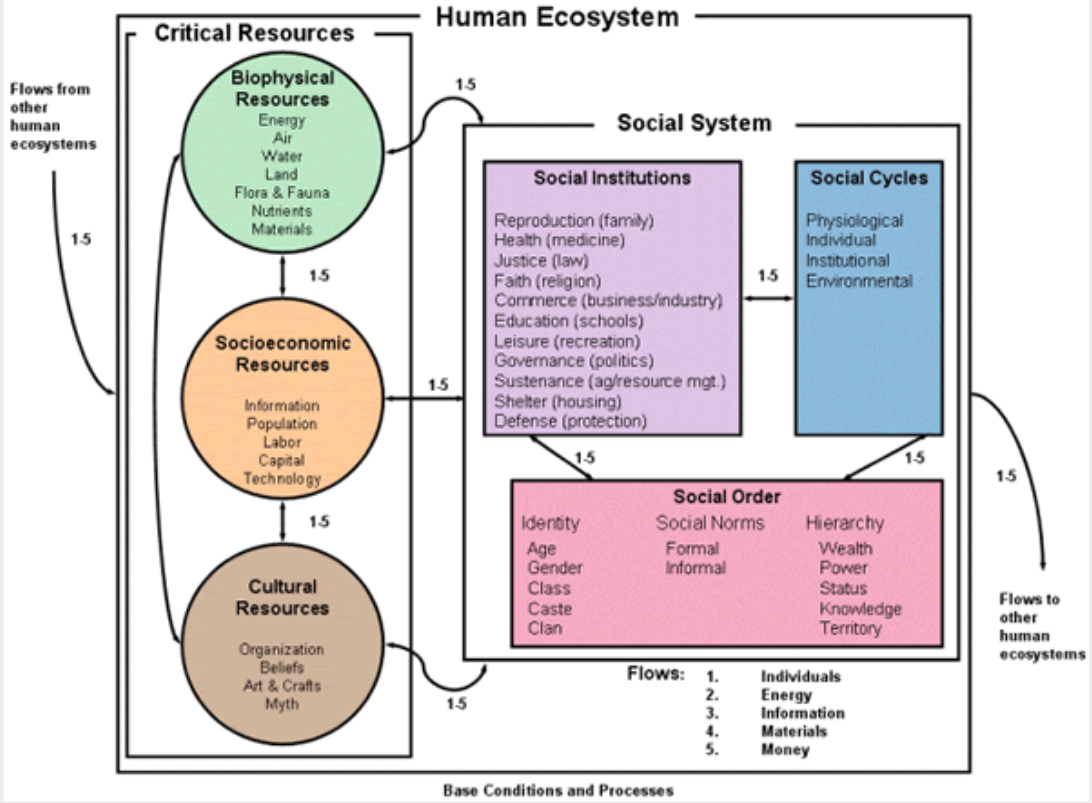
Human ecosystems model
What human ecological framework is this?
Ecology
The entire science of the relations of the organism to the surrounding exterior world, to which relations we can count in the broader sense all the conditions of existence. These are partly of organic, partly of inorganic nature. (Haeckel, 1870)
Ecosystem
A model for the cycles of matter and energy that include organic entities and their linkages to the inorganic.
Ecosystem
All organisms depend on energy and on matter. Such relationships, taken together, constitute a vast network of individuals exchanging the energy, nutrients, and chemicals necessary to life; humans and bacteria alike are involved in the same process.
Carrying capacity
Amount of organisms within a region that the environment can support sustainably.
Overshoot
This occurs when the population growth exceeds the carrying capacity, leading to a die off for the individuals in the population.
Unstable equilibrium
The fluctuation of the population above and below the carrying capacity, changing based on the relationship between natality and mortality.
Degraded carrying capacity
May be due to resource destruction during an overshoot, carrying capacity is not static.
Natural
Type of ecosystem wherein:
The actual and historical role of humans in the functioning of the ecosystem is nil or almost nil.
Species composition and species numbers are uninfluenced. Geomorphic, ecological, and biological processes are almost undisturbed by humans.
2% to 3%
How much of the Earth’s land remains ecologically intact?
Semi-natural
Type of ecosystem wherein:
Altered by human actions, but retains significant native elements.
May range from unaltered species composition to just using the natural background soil and or water by man.
Examples: Almost all ecosystems resulting from “traditional” forms of agricultural land use, such as steppes, puszta, and wooded meadow, fall in this category.
Human Systems
Interconnected networks where individuals interact and influence each other.
These systems are not isolated; they are embedded within larger societal structures and shaped by various factors.
Understanding these systems is crucial for addressing individual and collective well-being.
Environmental Determinism
Environmental Possibilism
Cultural Ecology
Ecosystem-based Model
Actor-based Model
Systems Model
What are the 6 parts of the development of conceptual approaches to human ecology?
Environmental Determinism
Part of the development of conceptual approaches to human ecology, where in:
Humans are complete products of their environments and must adapt to its conditions.
All aspects of human culture and behavior are caused directly by environmental influences.
Environmental Possibilism
Part of the development of conceptual approaches to human ecology, where in:
Presence or absence of environmental factors placed limits on developments
Development of civilizations can be explained by their responses to environmental challenges
Cultural Ecology
Part of the development of conceptual approaches to human ecology, where in:
cultural differences and similarities are a result of environmental and technological adaptations
Ecosystem-based Model
Part of the development of conceptual approaches to human ecology, where in:
Human beings constitute simply another population among the many populations of plants and animal species that interact with each other and with the nonliving components (climate, soil, water) local ecosystem.
Actor-based Model
Part of the development of conceptual approaches to human ecology, where in:
Adaptation occurs at the level of individuals rather than of cultures or populations.
From this perspective, any higher levels of organization (communities, ecosystems, or human social systems) exist only as the outcome of interactions.
Systems Model
Based on General Systems Theory (von Bertalanffy, 1968). Concerned with the general properties of the structures and functions of systems, rather than with their specific contents.
Inputs and Outputs
Feedback Loops
Open Systems
What are the characteristics of the Systems Model of HE?
Inputs and Outputs
Characteristic of the Systems Model of HE that pertains to the exchange of energy, matter, and information?
Feedback Loops
Characteristic of the Systems Model of HE that pertains to changes in one system affect another.
Open Systems
Characteristic of the Systems Model of HE that pertains to it being influenced by neighboring systems.
individual, family, community, larger ecosystem
What are the 4 levels of the locus of concern in HE?
Human Health and Nutrition
Human/Family Development
Community Governance
Environmental Planning and Sustainability
What are the 4 human-environment interactions?
The inner environment
Family and home (immediate environment)
The Community and the Bigger Human society
Ecosystem (Socio-cultural, Biological, Physical)
What are the 4 levels of the domains of HE?