Foundations of Learning and Behaviorism
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Learning
Enduring change in behavior from experience.
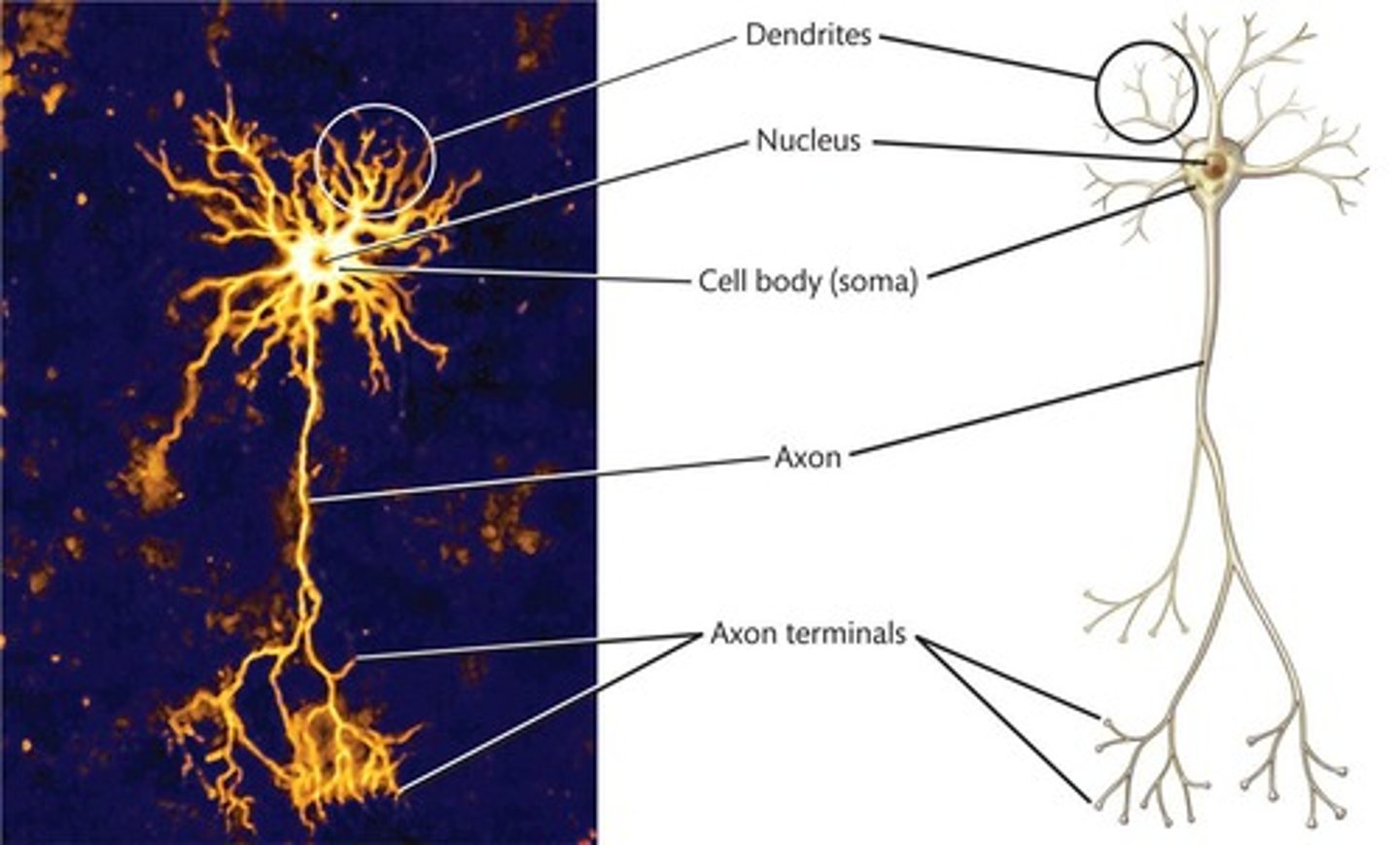
Neurons
Basic units of the nervous system transmitting signals.
Associationists
Theorists focusing on learning through associations.
Primary rules
Basic principles governing associations in learning.
Secondary rules
Factors influencing strength of associations.
British associationists
Philosophers emphasizing knowledge from experience.
Tabula rasa
John Locke's concept of the mind as a blank slate.
Action potential
Electrical impulse traveling along a neuron.
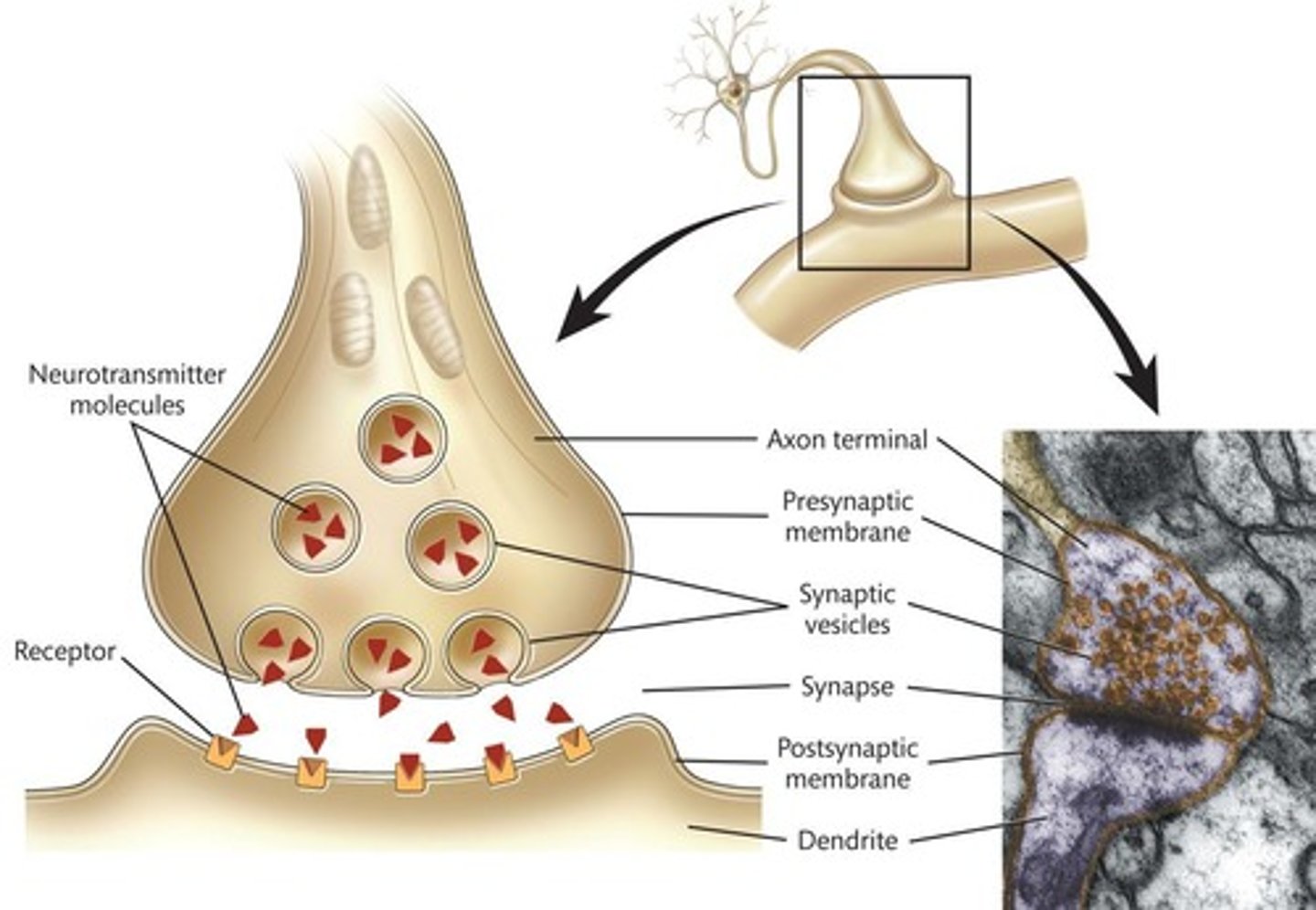
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals transmitting signals across synapses.
Classical conditioning
Learning through association of stimuli.
Operant conditioning
Learning through consequences of behavior.
Complex learning
Acquiring skills requiring multiple cognitive processes.
Concept learning
Understanding and categorizing objects or ideas.
Observational learning
Learning by watching others' behaviors.
Motor skills
Physical abilities involving coordinated movements.
Contiguity
Association formed by proximity in time or space.
Recency
Effect of recent experiences on learning.
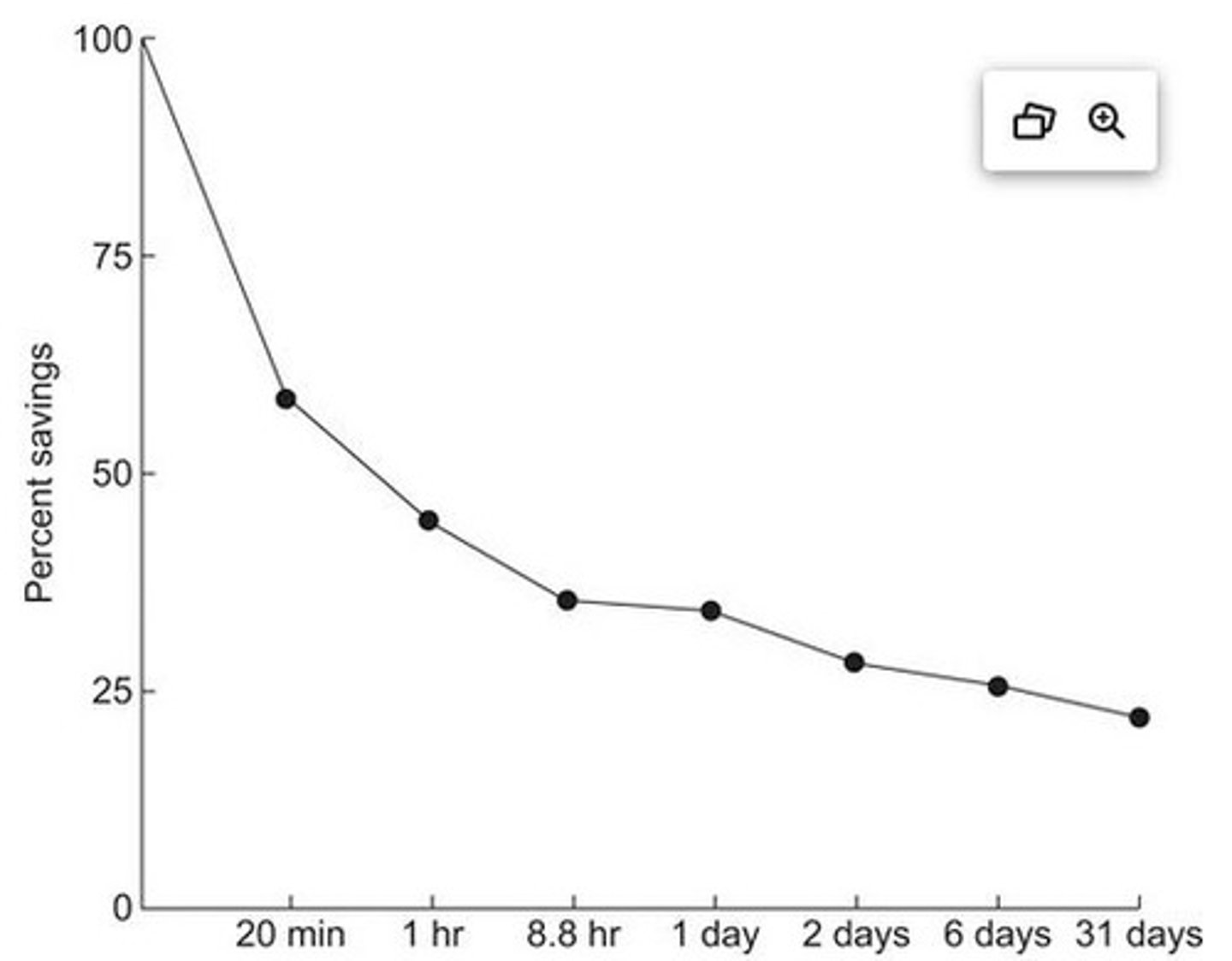
Forgetting curve
Graph showing retention decline over time.
Fixed action pattern
Innate sequence of behaviors triggered by stimuli.
Sensitization
Increased response to a stimulus after exposure.
Habituation
Decreased response to repeated, non-significant stimuli.
Innate behavior patterns
Behaviors present at birth, not learned.
Tropism
Directional movement in response to stimuli.
Kinesis
Random movement in response to stimuli.
Taxis
Directed movement toward or away from stimuli.
Intervening variables
Unobservable factors influencing behavior outcomes.
Behaviorism
Study of observable behaviors, excluding mental processes.
Ebbinghaus
Pioneer in memory research and association tests.
IACUC
Committee ensuring ethical treatment of animal research.
Neurogenesis
Growth of new neurons in the brain.
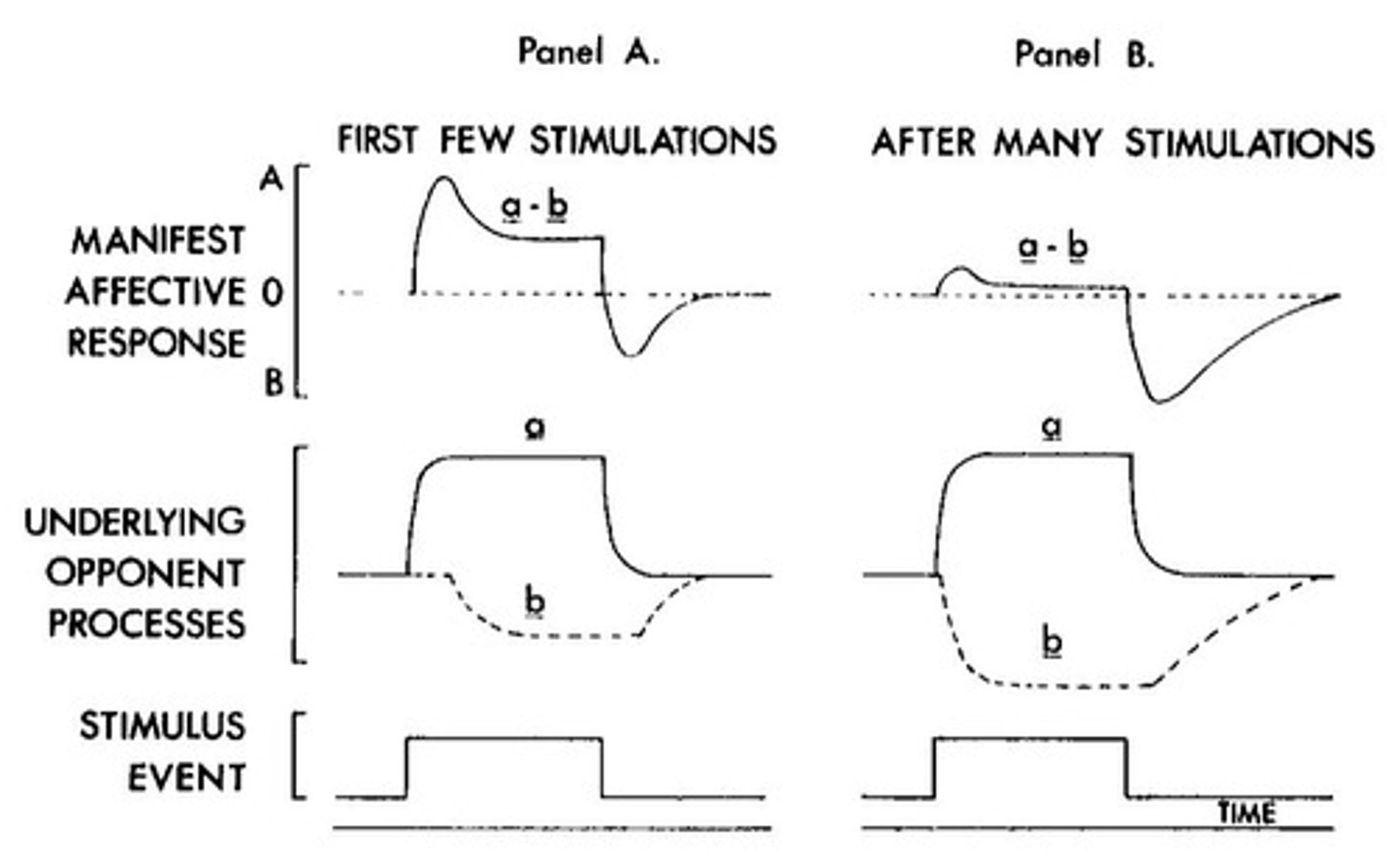
Opponent process theory
Theory explaining biphasic emotional responses.