computer science 💀
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
The Associative Law means
Numbers will equal the same, no matter which way round they are.
Data + Meaning = ?
Information
ASCII stands for
American standard code for information interchange
How many cores is a dec core
10
What is lossless compression
Is not permanent and temporary
In ASCII, how many bits is 1 character
8 bits
How do you work out the compression file size with only the original size and compression ratio
E.g 200MB 10:1 ?
Divide 200 by 10, then multiply by 1
What are the main components inside a CPU
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Register
Control Unit
What is overflow
Overflow is where a value exceeds the maximum value a register can hold. If you had the value 10000000 stored in an 8 bit register, the result would be 00000000, as it’s lost the leading one, destroying the value.
How many bits in a nibble
4
What is lossy compression
Permanent
What types of Meta Data are included in all files
File name
File type
File size
How to convert binary to Denary
Add headings above numbers, circle the values with 1 underneath then add them together
How many cores in a hex core
6
To go from bits to bytes you…
Divide by 8
What is cache
The fastest way to process data, type of RAM.
More the better, but is expensive
Has 3 levels, each having a high/low clock speed of memory and a high/low amount of memory
What are the key components of a computer
CPU
Motherboard
RAM
What is the Idempotent Law
A.A = A
A +A = A
Level 1 cache is allocated to
1 single core
The fastest memory, but the smallest amount
To up from bytes to bits you…
Multiply by 8
How many calculations per second is 1GHz
1000MHz, which is 1,000,000,000 calculations per second
Binary shifting
Shifting is where all the numbers shift one place left or right.
PC
Program Counter
CIR
Current Instruction Register
ACC
Accumulator
MAR
Memory Address Register
MDR
Memory Data Register
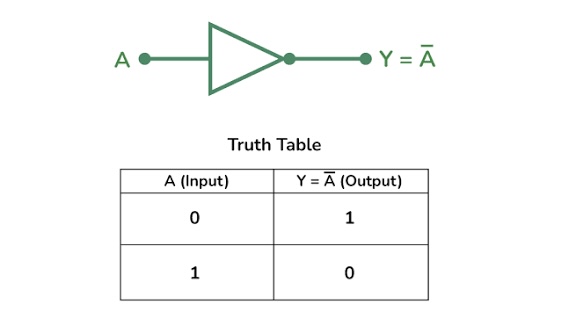
What is this
NOT
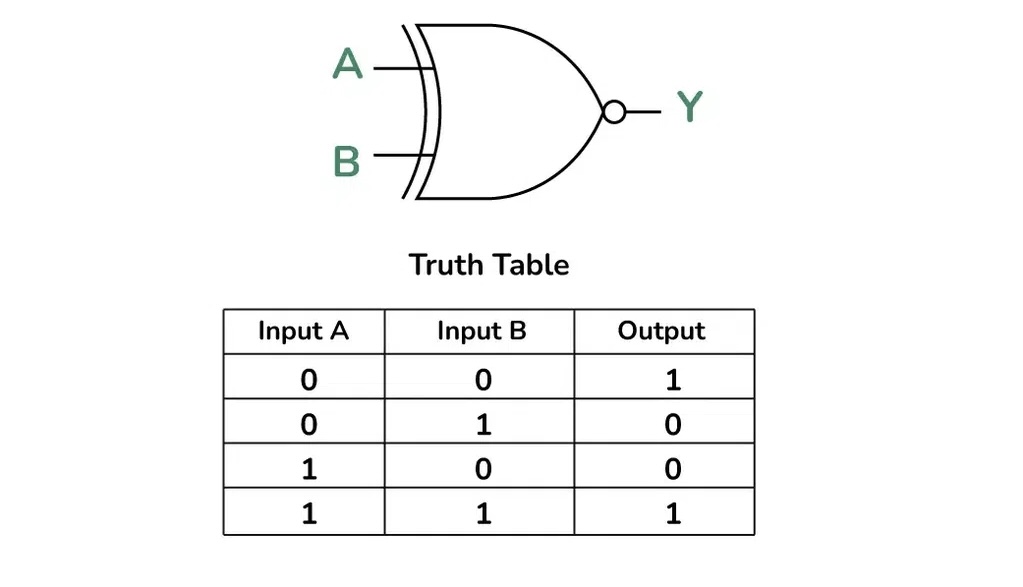
What is this?
XNOR
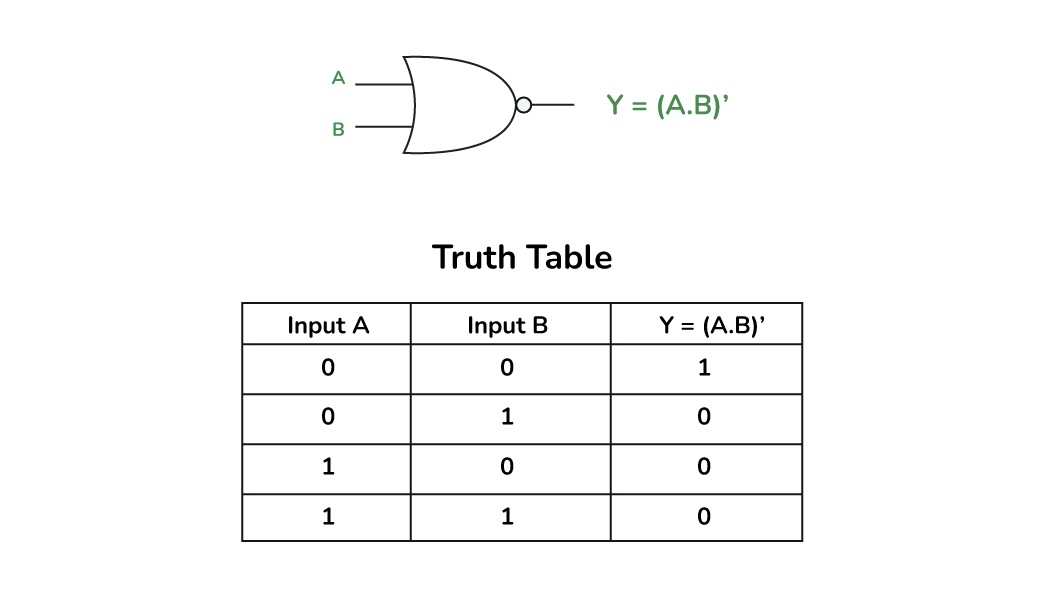
What is this?
NOR
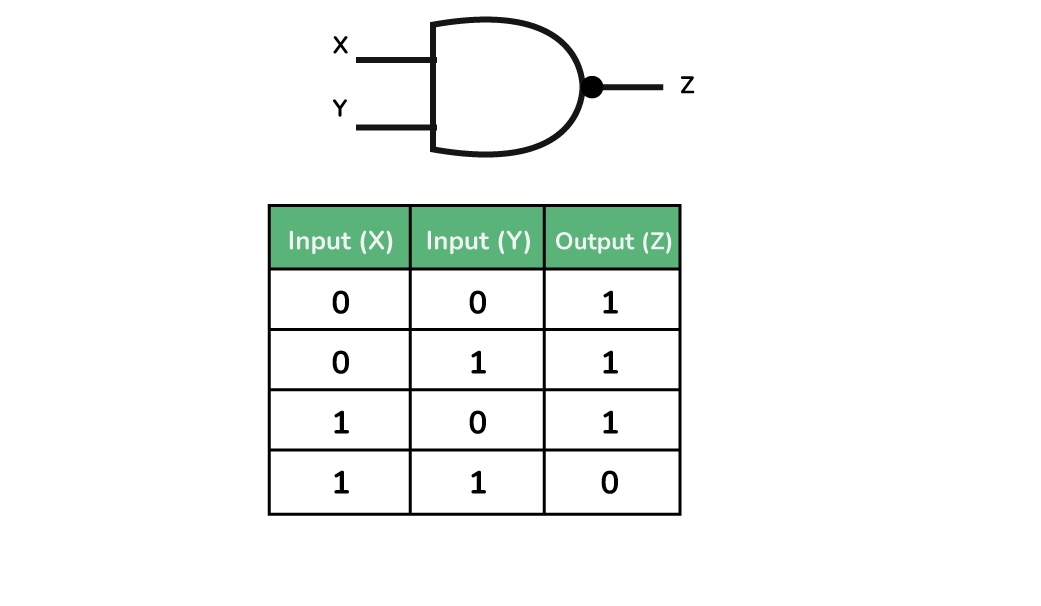
What is this?
NAND
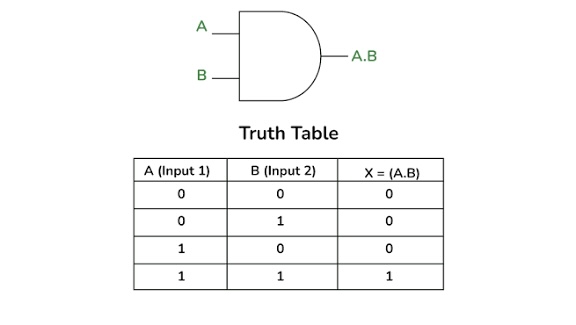
What is this?
AND
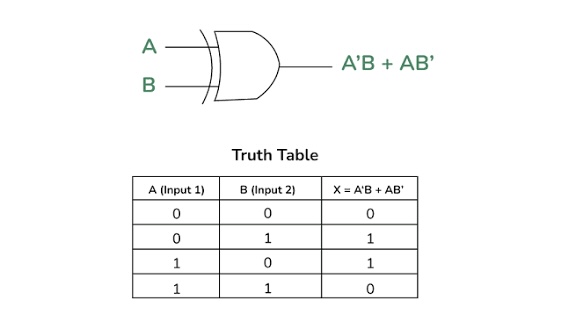
What is this?
XOR
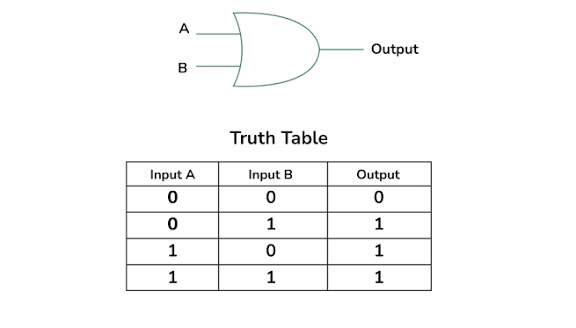
What is this
OR
The distributive law
the wave thing, expanding
A + (B . C) = (A + B) . (A + C)
DeMorgan’s Law
Break the not symbol and change the sign
How are samples stored in computers
Record analogue sound
Convert to binary (analogue to digital conversion)
Can be stored to create digital version
Benefit to ASCII set
It is simple and all American computers can easily and quickly communicate using 8 bits
Limitation to ASCII
It only supports American English, meaning other languages such as Japanese aren’t supported.
Describe the relationship between a kilobit and kilobyte
1 KB = 8 Kb, Kb is used as a measurement for transfer speed, kilobytes is used to measure storage, there are 1024 B in 1KB, there are 1024b in 1Kb
State the effect of arithmetic shifts on 0011000 shift 2 places left/right
Left is multiplied by 4, right is divide by 4
IMAGE
Height x width x bit depth
SOUND
Bit rate x sample rate x length (s)
VIDEO
(Height x width x bit depth x frames per s) + (Sample Rate x Bit depth) X length of video in seconds
Possible amount of colours with 24 bits
2^24
The Complement Law
A AND NOT A is false, A OR NOT A is true
Presence Check
Checks data has been entered
Type check
Checks data is the correct data type
Length check
Checks the correct number of characters has been entered
Range check
Checks data is within a valid range
Format check
Checks the format of data