Unit 1 Muscle' Action/ rule/Knee ROM
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
2
Joint
Rule 1
muscles must have at least ___ attachments must cross @ least one _____
pull
Rule 2
muscles always ______ and get shorter
insertion
origin
Rule 3
the attachment that moves is known as the _______ and the attachment that remains stationary is known as the _______
Flexors
Extensors
Rule 4
muscles that decrease the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as _____; muscles that increase the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as _________
pairs
Rule 5
muscles work in opposing _______
striations
Rule 6
muscles _______ point to the attachments and show the direction of pull
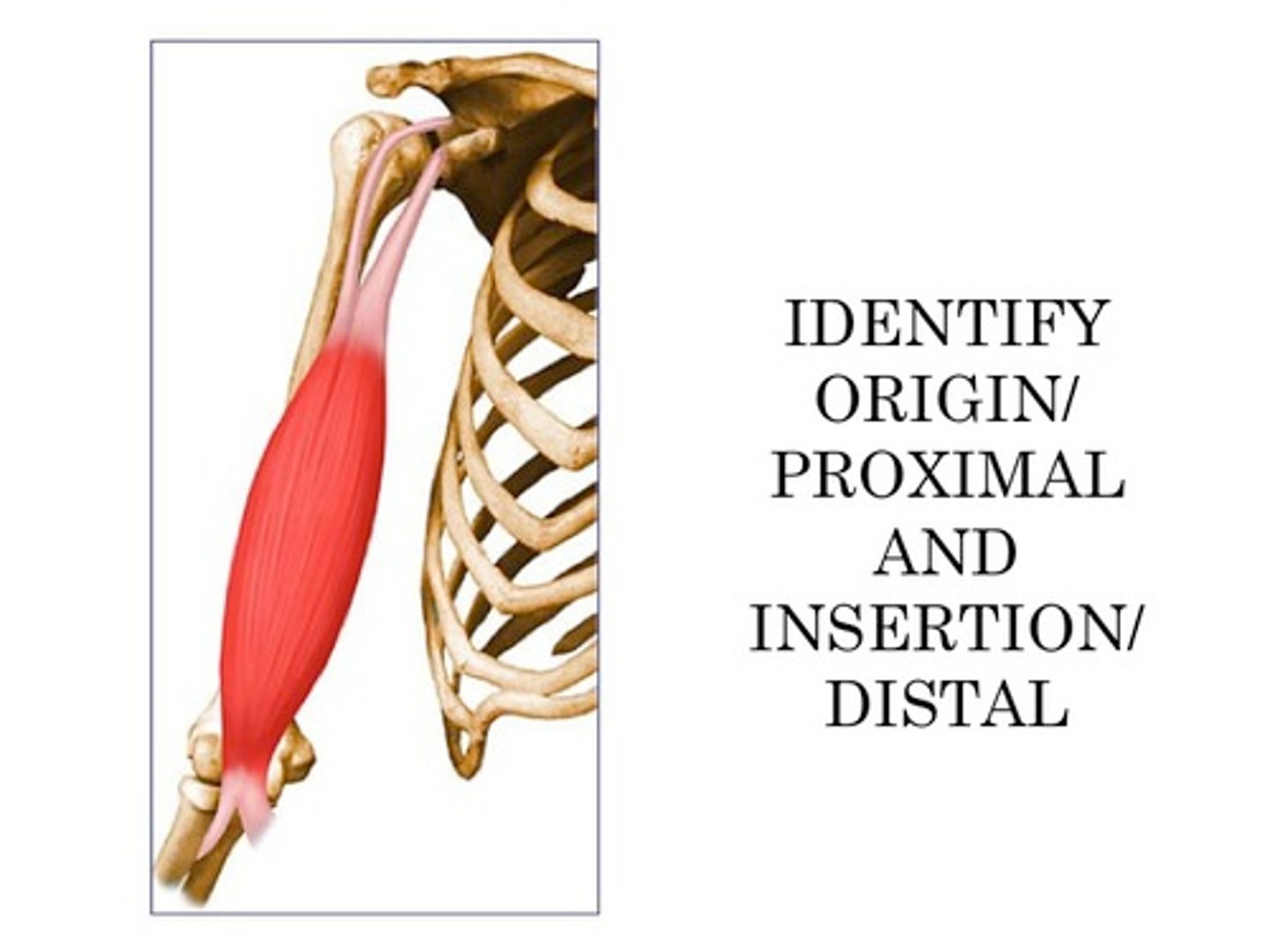
Brachialis
flexes elbow (halfway down the humerus)
triceps medial head
extends the elbow (proximal half of the dorsal humerus
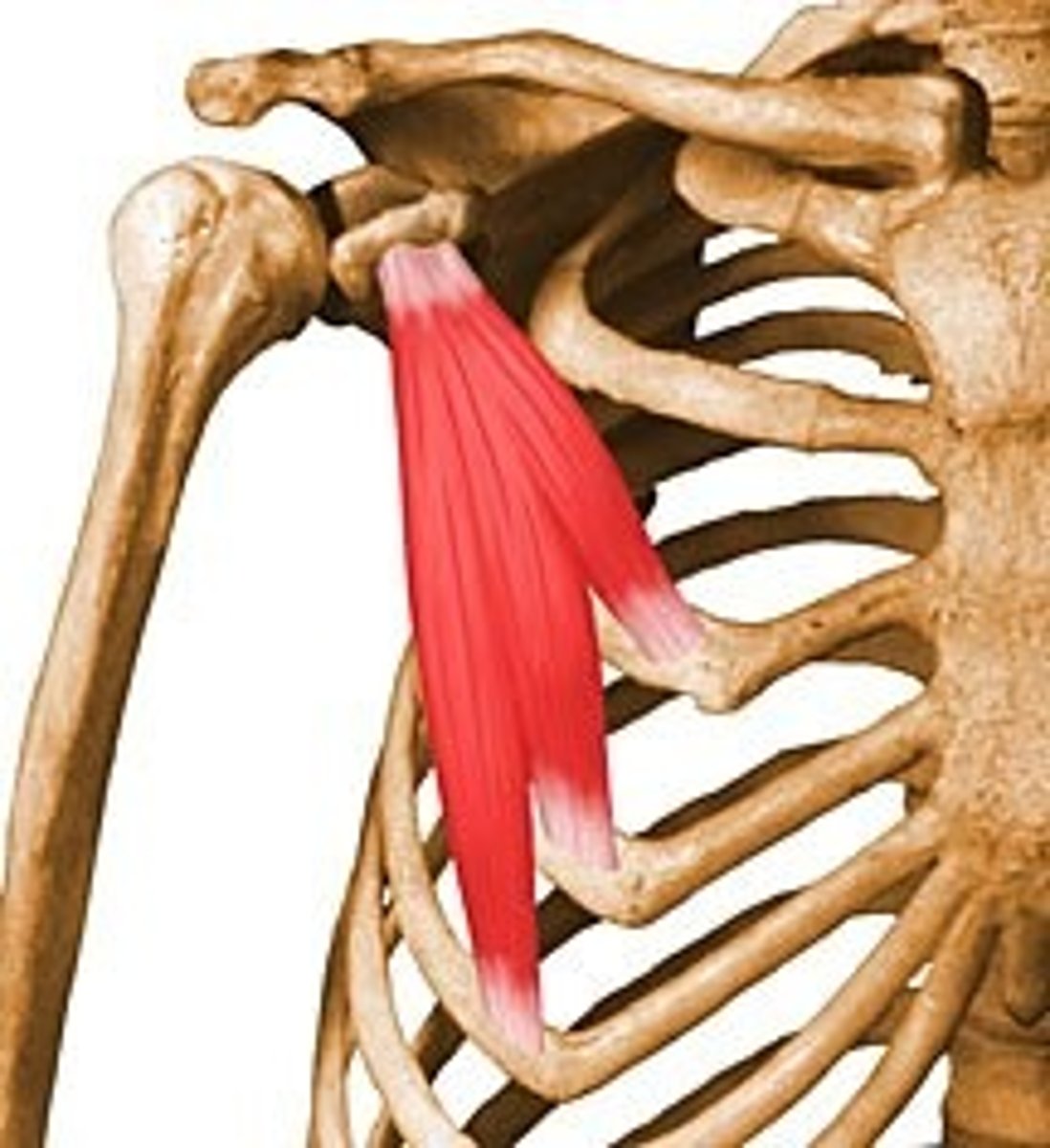
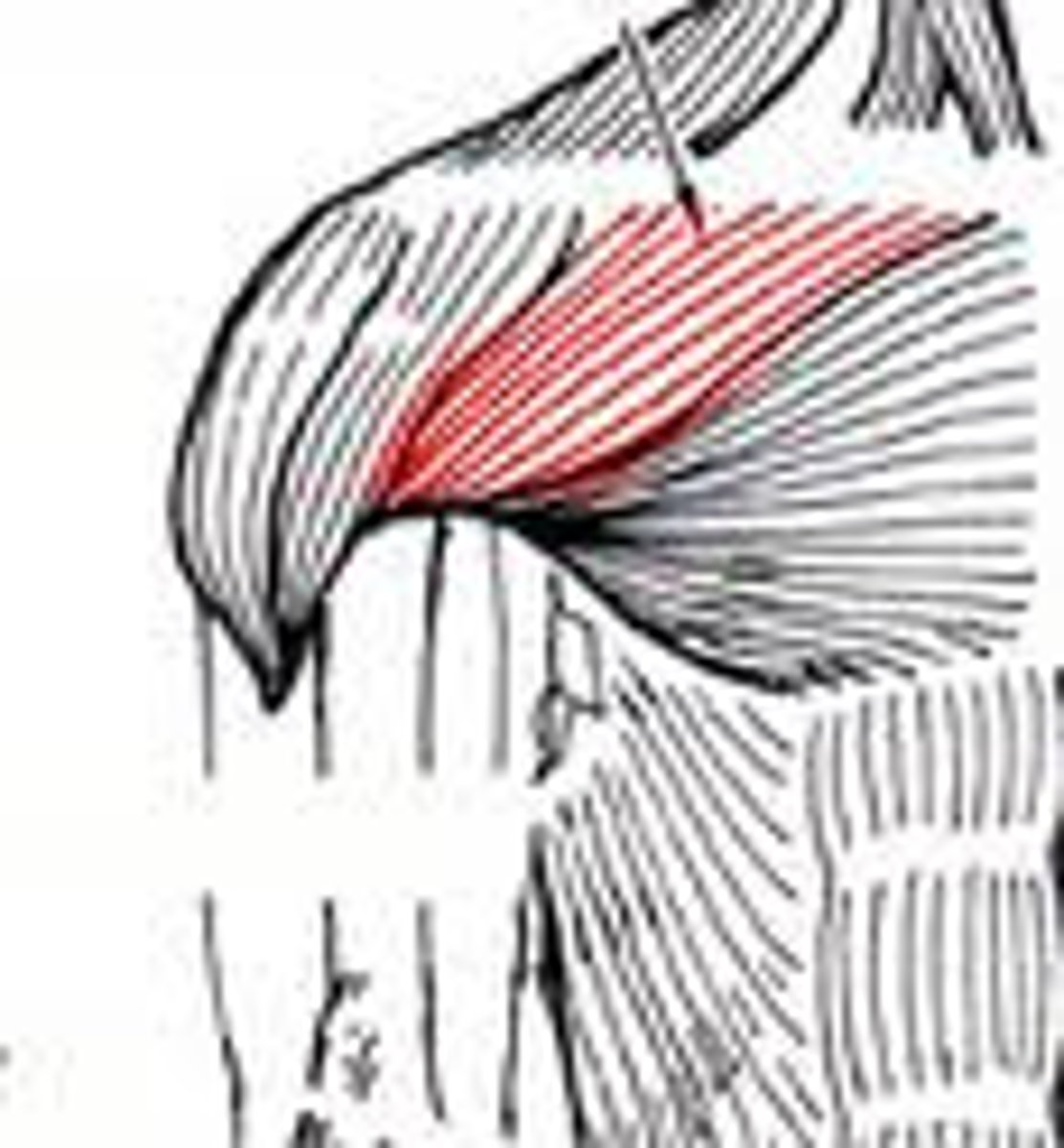
Pectoralis minor
rotate the shoulder forward (Anterior surface of ribs 3-5)
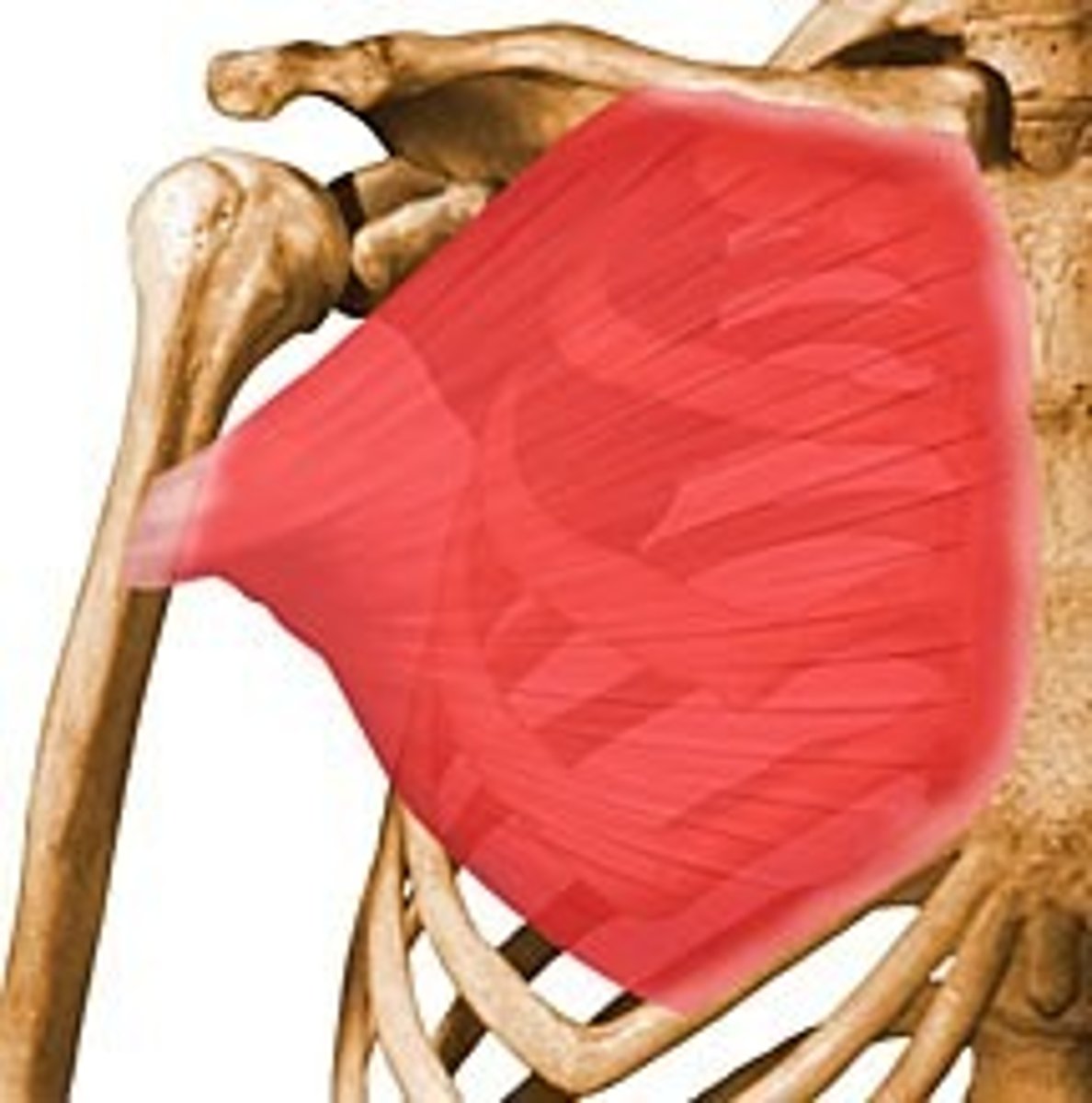
pectoralis major abdominal head
Pull arm down *serve/volleyball spike
pectoralis major sternal (sternocostalis) head
Pulls arm down across chest *butterfly machine( ribs 1-5)
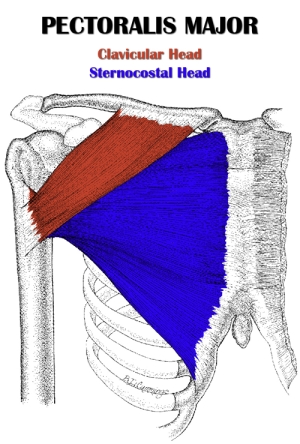
pectoralis major clavicular head
arm underhand motions *bowling (medial half of inferior edge of clavicle)
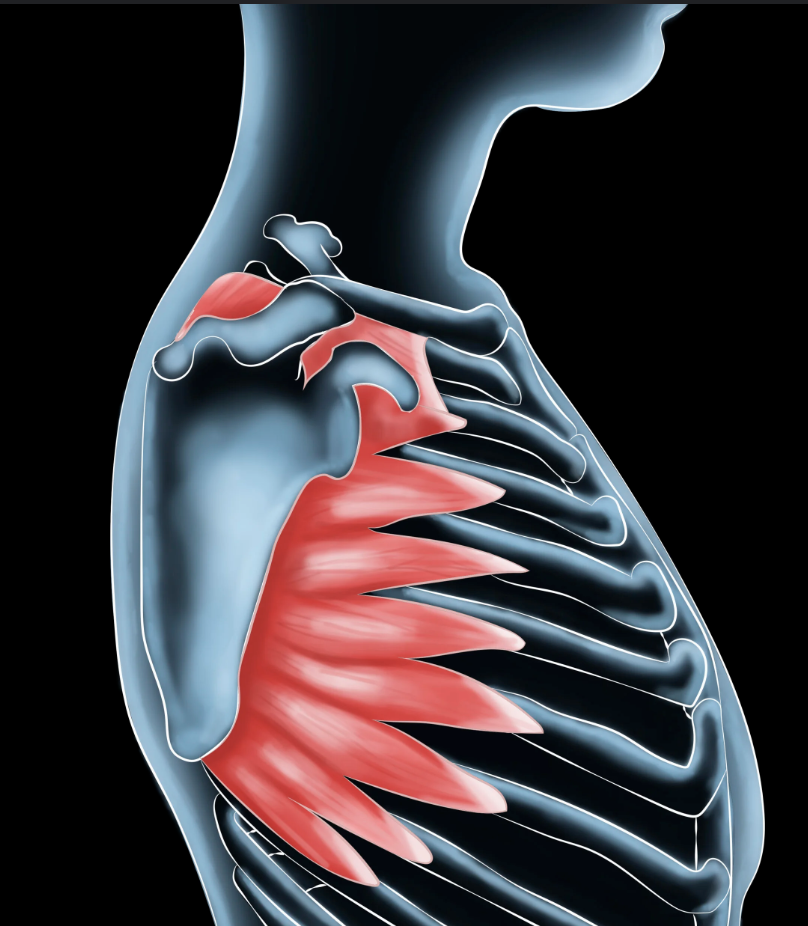
serratus anterior
to help move the scapula and push in at the big movement *swimming ( lateral surface of 1-8)
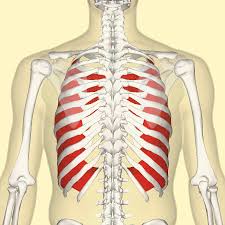
intercostals
muscle between the ribs
ligaments
tendons
_______-connective tissues that connect bones to bones
________-connective tissues that attach muscle to bone
Sprain
injury to a ligament that occurs when overstretched
Strain
injury to a muscle or tendon that occurs when overstretched
tear
injury to a variety of different soft tissues such as tendons, muscle, or ligaments
Anterior Cruciate ligament (ACL)
connects the anteromedial tibia to the lateral femur and provides rotational stability to the knee
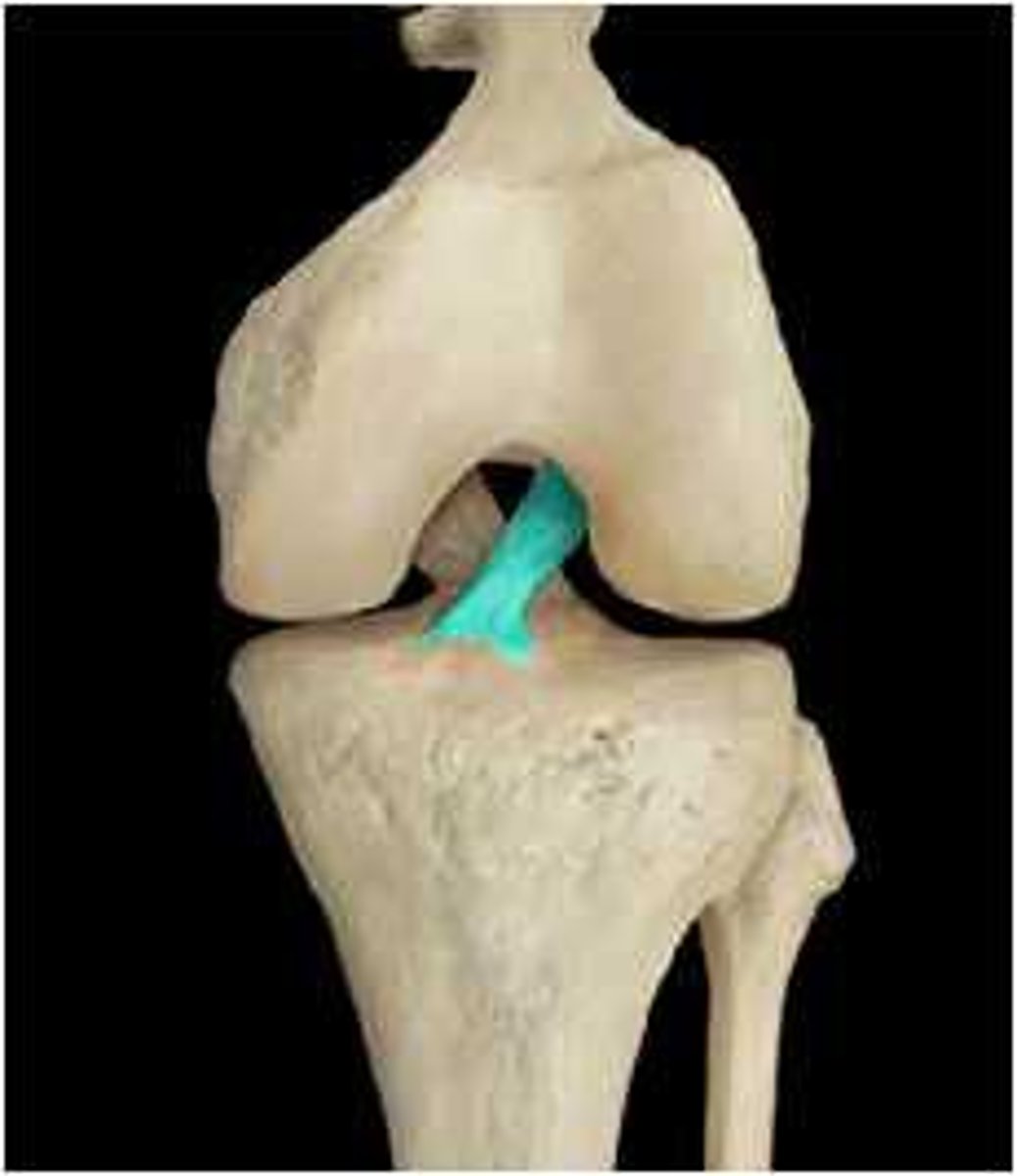
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
connects the anterolateral femur to the posterior tibia and keeps the shin bone from moving back to far
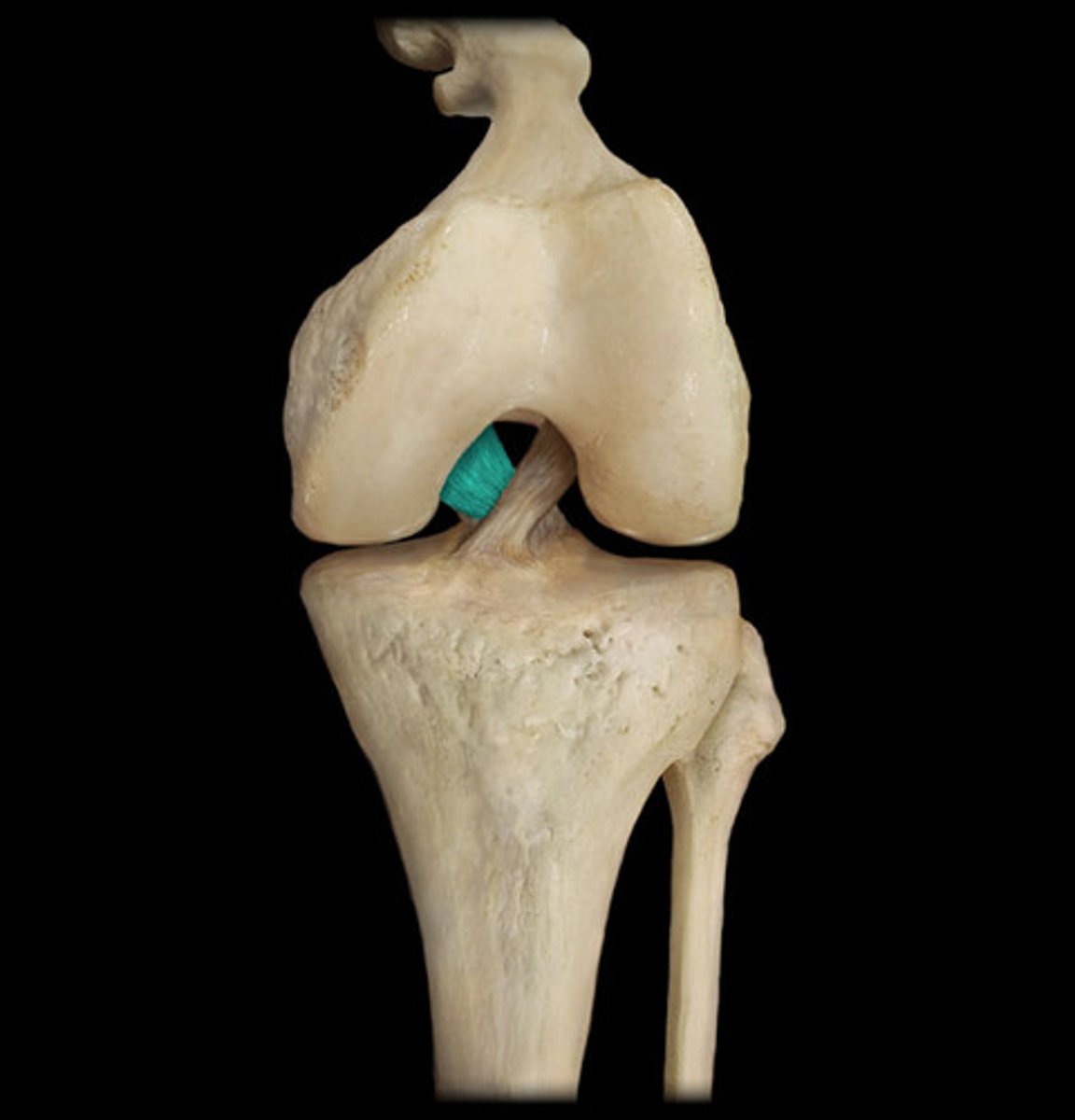
Medial Collateral ligament (MCL)
The inferior femur to the superior tibia and prevents the leg from extending too far inward
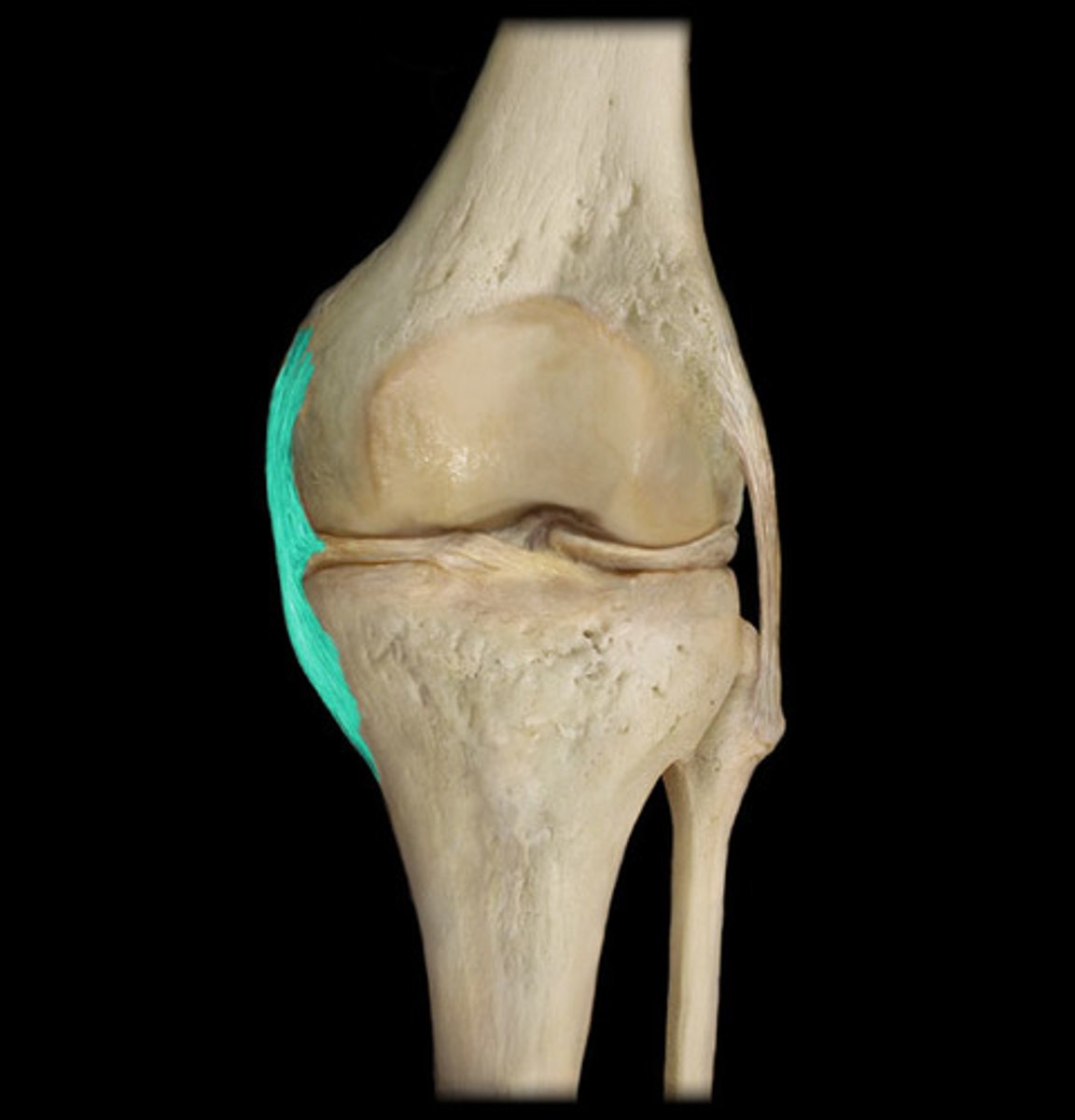
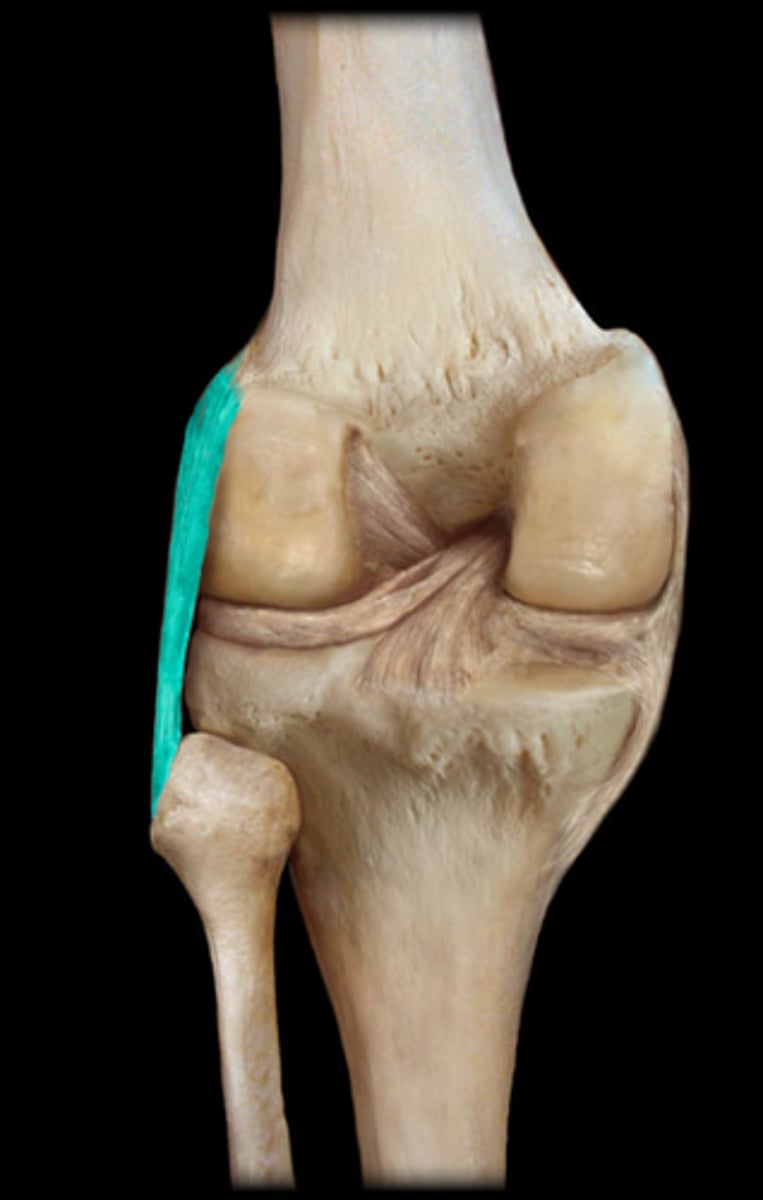
Lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
connects the lateral femur to the proximal fibula and helps keep the other knee joint stable
anterior
posterior
__________ drawer test- knee flexed at 90 degrees, the proximal tibia is pulled anteriorly relative to the femur. Positive if femur slides significantly in the posterior direction
__________ drawer test- knee flexed at 90 degrees, the tibia is pushed posteriorly relative to the femur. Positive if femur slides significantly in the anterior direction
valgus
varus
______ stress test- knee flexed at 30 degrees and femur held fixed, the tibia is rotated medially. Positive if the femur slides significantly in the medial direction
________ stress test- knee flexed at 30 degrees and femur held fixed, the tibia is rotated laterally. Positive if the femur slides significantly in the lateral direction
valgus
varus
_______ movement- distal end of bone or joint moves inward or medially
_______ movement- distal end of a bone or joint moves outward or laterally
posterior drawer
valgus stress
varus stress
anterior drawer
______- diagnoses MCL injury
______-diagnoses LCL injury
_______-diagnoses ACL injury
_________-diagnoses PCL injury
Kinesiology tape
improves circulation, support muscles through stimulation, drain excess fluid and promote healing
mechanoreceptor
located within synovial joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and skin that respond to mechanical pressure or distortion and convert the mechanical pressure into electrical signals that travel through neurons to the brain. Give your sensation of touch, stimulate your reflexes, monitor strength of organs and provide propricoception
proprioception
The body's ability to sense movement, action, and location
ex. being able to walk without looking @ your feet
drainage
ligament correction
_______ taping helps mostly with swelling post initial injury, while ______ _______ taping is used for mechanical correction later on in the recovery/treatment process or post-op