NUTR 400 3.4 Disordered Eating and Eating Disorders
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
The college transition
new dining environment
demanding schedule
increased independence
eating behavior spectrum
normal eating: choices made based on hunger/preference, flexibility, eating a variety
disordered: choices made on how they will affect the body
eating disorders: restricting, coping, isolation
disordered eating
eating behaviors that do not fit within the DSM-5 criteria (that would make it an ED)
unhealthy eating behaviors
hard to detect, can become an ED
physiologically and physically harmful
eating disorders
very serious but treatable
extreme disturbance in eating behaviors
physiologically and physically harmful
EDs facts and statistics
among the deadliest phycological illnesses
ages 18-21 most common
9% of the US pop will have an ED
Rates in males are inc at a faster rate than in females
10-15% of peeps w/ anorexia/bulimia are male
over 70% with ED’s don’t seek treatment
ED’s in college
“freshman 15” = not real
10-20% of college woman have one
4-10% of college men have one
pre pandemic, 15%
post pandemic, 28%
trans students 4x more likely
91% of girls have tried to control their weight via diets
35% of “normal” dieters progress to pathological dieting. 20-25% of these turn to at least partial ED’s
Risk factors
Biological-
genetic
fam history
co-existing metal health issues
dieting history
alch/drug use
negative energy balance
type 1 diabetes
phycological-
perfectionism, body image dissatisfaction, personal history if mental health condition, trauma
environment-
bullys
weight stigma
fam dynamic
media
idolize thin
INC likely hood of development in…
females
adolescence
pre-existing conditions,
family history
“type A”
unhealthy environment
body focused career/dieting
chronic dieting
Types of eating disorders
Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
Bulimia Nervosa (BN)
Binge Eating Disorder (BED)
Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID)
Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder (OSFED)
Unspecified Feeding or Eating Disorder (UFED)
Pica (eating rocks and shit)
Rumination Disorder (RD) (bringing food up from the stomach the second it enters)
Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
distorted body image
excessive dietary restrictions
low weight
fear of weight gain
restriction of energy intake relative to body weight
There are two types of AN- what is the difference?
one does not have a purge/binge, one does
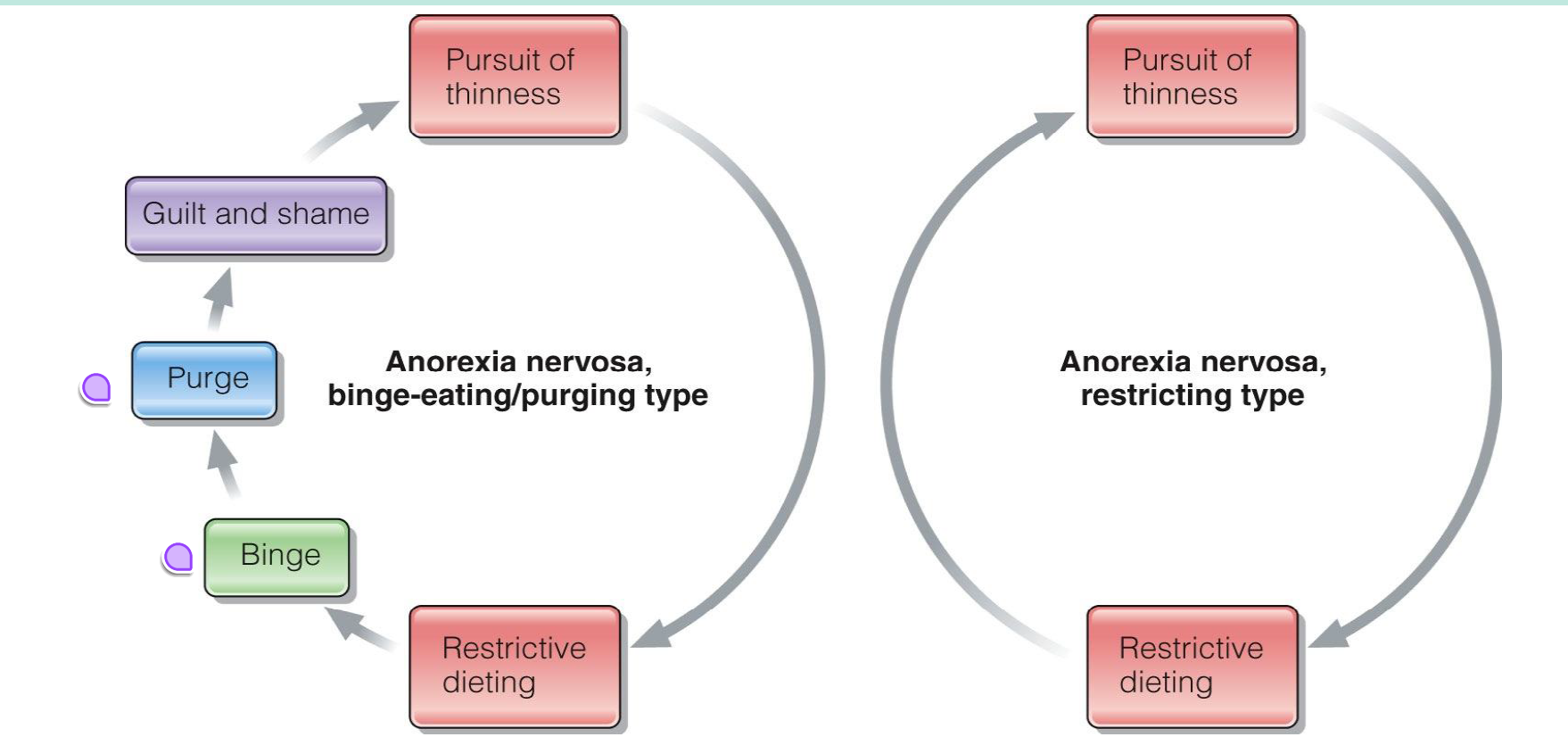
risks of AN
brain- fatigue/dizzy, bad mental health
heart- low BP, low heart rate, cardiac arrest
endocrine- impact hormonal function (no period w/ woman)
skin- dry, thin hair/hair loss, lanago (small hairs trying to keep your body warm
GI- stomach pain, bloating constipation dehydration
THE SOONER CAUGHT, THE MORE WE CAN REVERSE
Bulimia Nervosa
Eating a lot in a short amount of time
recurrent episodes of binging and then a purge
the binge/purge must occur at least once a week for 3 months
self evaluation is influenced by body shape/weight, fear of weight gain
purging methods- vomit, fasting, excessive exercise, meds, laxatives
The binge/purge cycle
strict diet
diet “slips”
binge triggered
purge to avoid gain
guilt shame
Bulimia Nervosa health risks
mouth- tooth decay, erosion of dental enamel (from puke)
heart- low BPm cardiac arrhythmias
brain- dizzy/faint, bad mental health
throat- sore, heart burnm damaged esophagus swollen salivary glands
skin- callus/scars/dry hands/knuckles
kidneys- dehydration
GI- stomach ulcers
Warning Signs of Bulimia Nervosa
Evidence of binge eating:
Consuming large amounts of food in short periods of time, lots of empty food wrappers of packages..
Evidence of purging behaviors:Frequent trips to the bathroom after meals
Creation of complex lifestyle schedules
Swelling of the cheeks or jaw area
Discoloration or staining of the teeth
Calluses on the back of hands and knuckle
Frequent dieting
May see fluctuations in weight - up or down
Binge eating disorder (BED)
not associated with recurrent use of inappropriate coping behaviors (unlike AN/BN)
occurs at least one a week for three months
Associated with 3 or more of the following: Eating more rapidly than normal
Eating until uncomfortably full
Eating large amounts when not hungry
Eating alone out of embarrassment
in peeps of al sizes
eating till uncomfortably full
feelings of shame and guilt
The binge/restrict cycle
Restrict → Struggle → Binge → Struggle
when you are not eating enough, you are more likely to binge

Health risks of Binge eating
Brain- bad mental health
heart- high BP, stroke, high cholesterol
weight gain
type 2 diabetes
osteoarthritis
gallbladder disease
Other specified feeding or eating disorder (OSFED)
Recognize and categorize ED’s that don’t meet criteria for AN, BN, or BED
examples:
Atypical Anorexia Nervosa (meets all the criteria besides low weight)
Bulimia Nervosa of low frequency/limited duration
Binge Eating Disorder of low frequency/limited duration
purging disorder (no binge)
Night Eating Syndrome (all/most energy intake is at late hours)
Orthorexia
not formally recognized in the DSM-5
fixation on healthy eating
ridget eating styles/exercise patterns
cutting out all of some food groups
checking nutrition labels
obsessed with food health
anxiety when there is no “healthy” option
think of food for hours
Treatment
Appropriate, multidisciplinary, compassionate intervention
Team approach: RD, physician, and counselor
Individual/group/family therapy
Typical treatment goals:Restore adequate nutrition
Restore and maintain body weight
Reduce excessive exercising
Improve food-related behavior
Nutrition counseling is important
Barriers to Care
Denial – unwilling to seek care
Fear of weight gain
Stigma
Cost/Insurance coverage
Lack of awareness/knowledge
Weight bias
Access to care