Carbon Cycle, Great Oxidation Event, Snowball Earth
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
what did the concepts look like 200 million years ago?
Pangea
how does the asthenosphere change the Earth?
permits plate-tectonic processes, leading to contiental drift, volcanism, and orogenies
how does solar heat change the Earth?
kepps streams, glaciers, waves, wind in motion, causing erosion and deposition
gradual change
millions to billions years
catastrophic change
seconds to milennia
undirectional change
changes that do not repeat
cyclic change
repeats same stems
biogeochemical cycle
exchange of chemicals among living and nonliving reservoirs
describd differentiation
the planet began to melt, allowing liquid iron alloy to sink to the center
what are some unidirectional changes?
differentiation, evolution of atmosphere and oceans
describe Archaean continental crust formation
partial melting from subduction or upwelling of mantle plums produces low-density rocks like granite. these rocks could not be subducted and sutured to form continents.
what did the first atmosphere consist of
gases of the protoplanetary disk
what did the second atmosphere consist of
carbon dioxide, water, nitrogen
what did the third atmosphere consist of
mostly nitrogen
when did oxygen become a major constituent of the atmosphere
2.5-2.0 Ga
list the cyclic changes
supercontinent cycle, sea-level change cycle, rock cycle, biogeochemical cycles
supercontiennt cycle
convergence, collision, supercontinent, rifting, divergence
sedimentary sequence
grouping of sedimentary units bounded on top and bottom by regional unconformities
what do sedimentary sequence suggest
advances adn retreats of seal level
steady-state condition
proportions of a chemical remain constant despite constant flux of chemical
hydrologic cycle
movement of water from reservoir to reservoir
describe where carbon is transported in the carbon cycle
dissolves to form bicarbonate, absorbed by photosynthetic organisms, reacts with rock
what were the climate conditions in the Cretaceous?
warm with no polar ice caps
what are the most important greenhouse gases?
carbon dioxide and methane
paleoclimate
past climate
how can stratigraphic record reflect climate change?
nature of sedimentary strata
what is an example of stratigraphic record reflecting climate change?
an outcrop of sandstone with cross beds overlain successively by coal and glacial till indicates desert, tropical, and glacial climates
how does paleontological evidence reflect climate change?
succession of assemblages
how do oxygen-isotope ratios reflect climate change?
the ratio of 18O to 16O is higher in cooler climates
from where are oxygen isotopes measured
calcite or silica molecules in shells or water molecules in glacial ice
describe the behavior of oxygen isotopes during evaporation
lighter isotope evaporates easier
describe the behavior of oxygen isotopes during condensation
heavier molecules prefer to condense and freeze
how do oxygen isotopes change during climate cooling and growth of glaciers?
more 16O evaporates, 18O increases in oceans and more 16O is in ice on land
how do bubbles in ice reflect climate change?
the trap the air present at the tieme ice forms; the concentration of carbon dioxide can be measured to reflect temperature
how do growth rings reflect climate change?
trees grow more in warmer years and slower in colder years
list ways how geologists study paleoclimate?
stratigraphic record, paleontological evidence, oxygen-isotope ratios, bubbles in ice, growth rings, human history
what causes long-term global climate changes?
positions of continents, volcanic activity, uplift of land surfaces, formation of fossil fuels, life evolution
how do the position of continents cause climate change?
they control the pattern of ocean currents, which redistribute heat around the planet’s surface. also, drift determines whether land lies at high or low latitudes (influences level of solar radiation), whether large continental interior regions exists (where cold temperatures develop), and whether there is lots of rainfall (which cause weathering reactions that absorb carbon dioxide)
how does volcanic activity affect global climate?
an increase of carbon dioxide may cause greehouse conditions
how does the uplift of land surfaces affect global climate change?
they expose the land to chemical weathering that absorbs carbon dioxide
how does the formation of fossil fuels affect global climate?
burial of organic material removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
how does live evolution affect global climate?
extinctions or appearance of life forms may cause changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide
what are factors that control short-term climate change?
changes in Earth’s orbit and tilt, changes in ocean currents, large eruptions of volcanic aerosols, fluctuations in solar radiation, fluctuations in cosmic rays, changes in surface albedo, changes in concentrations of greenhouse gases
how do Milankovic cycles cause short term climate change?
change amount of summer insolation
how do changes in ocean currents cause short term climate cahnge?
changes in currents can affect climate (for example inhibiting the thermohaline circulation)
how do large eruptions of volcanic aersols cause short term climate cahnge?
increases albedo
how do changes in solar radiation affect the climate?
more sunspots release more solar energy
how do changes in cosmic rays affect the climate?
cosmic rays that strike the atmosphere produce condensation nuclei
discuss the causes of the permian/triassic extinction
either a superplume or a large asteroid
discuss the causes of the K-Pg boundary event
an asteroid that caused the Chicxulub crater
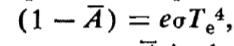
interpret the equation
equilibrium equation for Earth for emission and absorption of heat; S is the solar constant, A is the Russel-Bond spherical albedo Earth, e is the mean emissivity of the surface, ¼ is the ratio of intercepting sunlight to area emitting infrared sunlight
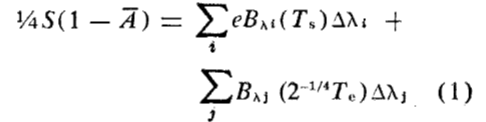
interpret the equation
this equation accounts for greenhouse gases
faint young sun paradox
Earth should have been below the freezing point of seawater because of lower sun luminosity
what are some evidence of liquid water during the Archean?
pillow lavas, mud cracks, ripple rocks, microfassils of algae and stromatolites
what do Sagan and Mullens say explains the faint young sun paradox?
high concentrations of ammonia
why did they concentration of ammonia likely decrease according to sagan and mullens?
an increase of oxygen
waht is some proof that ammonia is the solution for the faint young sun paradox?
ammonia is a key intermediary in nitrogen fixation
what is another solution to the faint young sun paradox?
the carbon cycle
what are the steps of the geologic carbon cycle?
inorganic carbon species, chemical weathering of silicate materials, precepitation and burial of carbonate
how is volcanic outgassing related to the carbon cycle?
it accounts for some carbon dioxide
what is the effect of chemical weathering in the context of the global carbon cycle?
dissolves unstable and soluble minerals
what is the effect of physical weathering in the context of the global carbon cycle?
increases the surface area of the planet
describe waht happens after the weathering of calciate rock
calcium carbonate from shells and coral skeletons form bicarbonate ions
describe what happens after atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves
it mixes with water to for carbonic acid, which forms bicarbonate and hydrogen ions
what is the effect of chemical weathering of silicate minerals?
different minerals are released into the atmosphere
describe the chemical weathering of silicate minerals
outgassing of carbon dioxide causes the formation of carbonic acid, which precipitates into clay
describe the chemical weathering of carbonate minerals
outgassing of carbon dioxide causes the formation of carbonic acid, which precipitates into clay and limestone
how is continental weathering estimated?
river chemistry
how do calcium ions get into the ocean?
clay is weathered into calcium ions
how does calcium carbonate form?
calcium from clay mixes with with carbonate ions from marine organisms
summarize the inputs and outputs of the global carbon cycle
volcanoes and weather input carbon, calcium carbonate is buried
describe the burial products of calcium carbonate
calcium sediments, clay
when does silicate weathering increase?
at higher temperatures
how does the carbon dioxide thermostat work
increased carbon dioxide gassing leads to increased silicate weathering which means carbonate burial
what is calcium carbonate a proxy of and why?
heat, because more calcium carbonate is buried at higher temperatures
what is the equation for stable isotope abundance variations?
for most elments
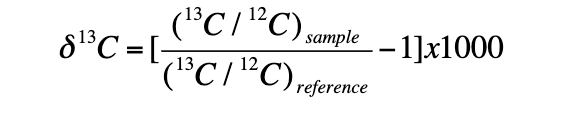
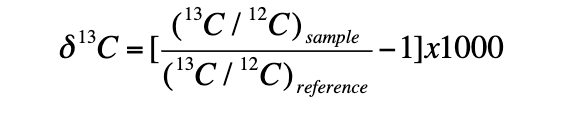
what is delta 13 C?
the difference in the ratio of 13C to 12 C to the reference standard
what are the two modes of stable isotope fractionation?
kinetic processes (biological processes, evaporation cooking), and bonds of light isotopes are more easily broken and react faster
equilibrium istope fractionation
heavier isotopes form stronger bonds, and different compounds in equilibrium compete for the heavier isotopes
isotope exchange reaction
a chemical reaction in which the isotopologues change but the chemical composition of reactants and products are the same
fractionation factor (α)
isotope ratio in compound B that is formed from compound A divided by the isotope in compound A
ε
fractionation factor expressed in a way that is easily compared to δ units
how is the oxidation state of Earth’s layers controlled?
reactions between carbon, iron, sulfur, and other elements as they occupy multiple oxidation states
describe how oxidation reactions reactions reflect the history of Earth.
free oxygen from photosynthesis is recycled in carbon dioxide and oxygen. free oxygen also reacts with metals.
is Earth’s interior reduced or oxidized?
reduced
why is it important that most of Earth is reduced?
magmas and gases expelled to the surface can react with oxygen
describe weathering in terms of oxidation reducation reactions
reduced species are oxidized
what would happen if oxygen concentration increased today?
fires would be rampant and organic carbon would be overconsumed
how is oxygen concentration balanced today?
production is balanced by aerobic respiration, sulphide mineral oxidation, oxidation of iron, and oxidation of reduced volcanic gases
describe the mass balance of oxygen?
organic matter burial should equal the oxygen incorporated in oxidized species
why does Earth’s surface have a high oxidation state?
reduced carbon in black shales, soils, coal, oiil, and natural gas
why does life prefer 12C?
because biological processes that make organic carbon preferentially incorporate 12C.
what does δ13C mean?
it is the difference in the ratio of 13/12C of carbon to that of an arbitrary standard
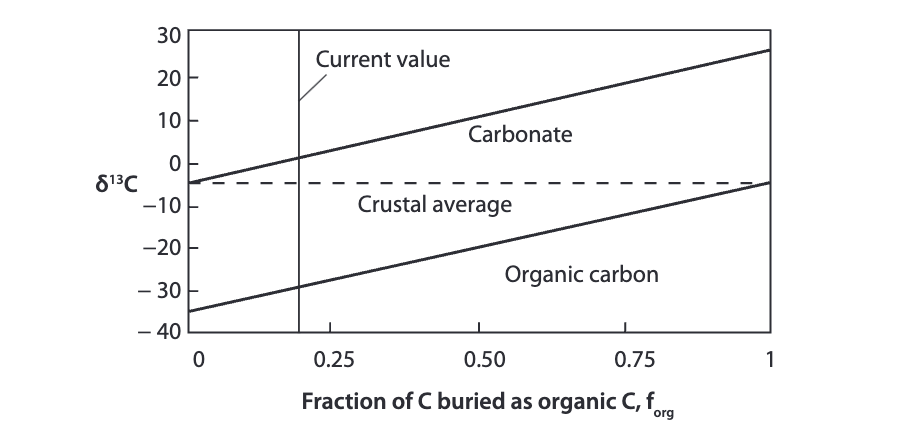
interpret the graph
the total value del C 13 of carbon in the system always has to be negative 5. The del 13 of organic carbon is always 30 per mil lower than mantle carbon
does inorganic carbon have a higher or lower del 13 than the mantle?
higher
what elements track oxygen consumption?
oxidizied iron and sulfur
what do sulfur and iron suggest about oxygen?
most oxygen that has produced in the formation of organic matter in stored in iron and sulfur molecules
describe the solubilities of iron and sulfur
ferric iron is insoluble, ferrous iron is soluble, reduced sulfur is insoluble, oxidizied sulfur forms sulfate
what does the solubility of iron and sulfur suggest about the Earth
a reduced Earth has soils with low iron and high sulfur and oceans with high iron and sulfur
what do light carbon isotopes mean?
an increse in methane