kine 300 - post-midterm content
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
social and behavioral sciences in health final exam preparation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
health belief model (background)
one of the most widely used and broadest of health behavior theories
has roots in behaviorist and and an emphasis on cognitive psychology — decision making process
individual-level health behavior theory
developed in the 50’s by the us public health service
social psychologists were asked to explain why people do not participate in health behaviors
health belief model (framework)
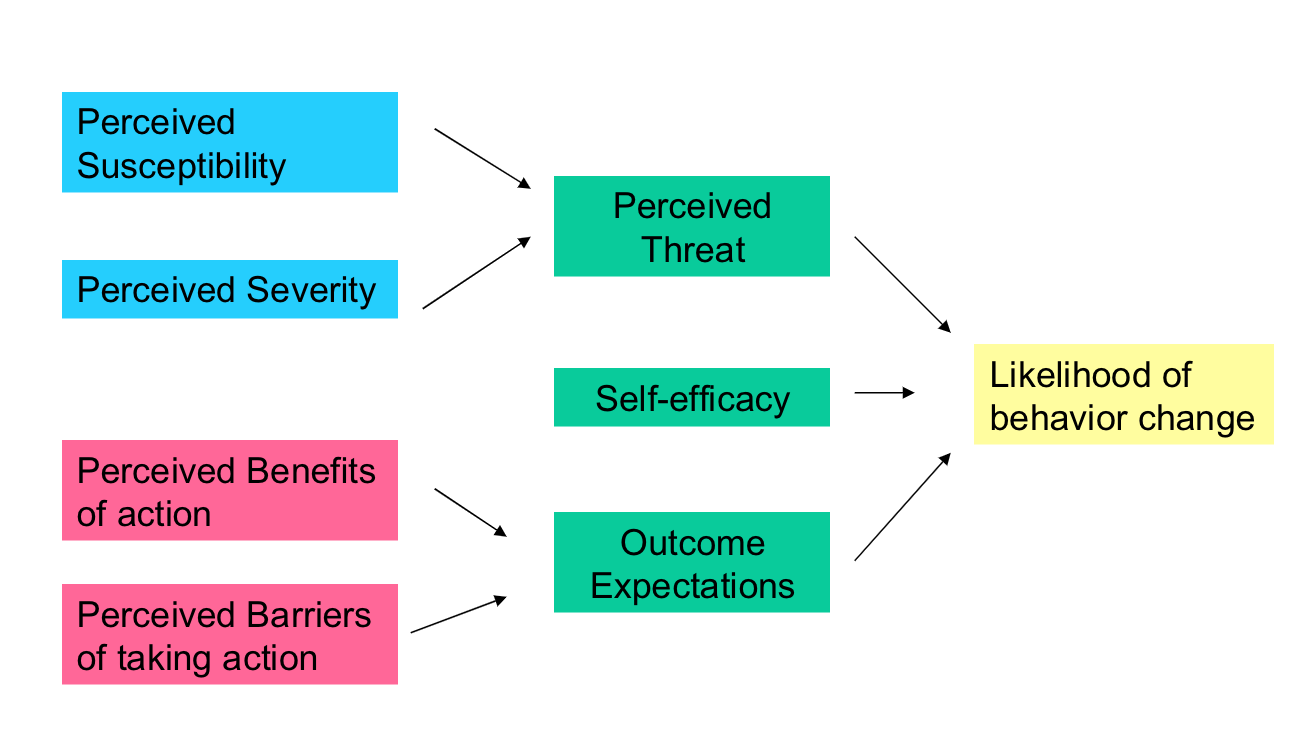
perceived susceptibility + perceived severity
= perceived threat
perceived barriers of action + perceived barriers of taking action
outcome expecations
perceived threat + self-efficacy + outcome expectations
= likelihood of behavior change
cues to action
a reminder or stimulus to do the health behavior
examples:
mass media cue
public health campaign
social support-based
a note about “susceptibility,” severity, and fear tactics
notions to turn people away by scaring someone away from a behavior change
ex: “do this or else…”
critiques of the health belief model
focus is on individual decisions
it is not always clear how all six HBM constructs operate (or are supposed to operate) in changing behavior
a lot of programs use HBM constructs, but not necessarily all of them together
some research says not all constructs are necessary
example: health belief model applied to adolescents and condom use
perceived susceptibility: youth believe they can get STIs or pregnant (or partner can get pregnant)
perceived severity: youth believe that the consequences of getting STIs or HIV or creating a pregnancy are significant enough to try to avoid
perceived benefits: youth believe that the recommended action of using condoms would protect them from getting STIs or HIV or creating a pregnancy
perceived barriers: youth identify their personal barriers to using condoms (i.e., condoms limit the feeling or they are too embarrassed to talk to their partner about it) and explore way sto eliminate or reduce these barriers (i.e. teach them to put lubricant inside the condom to increase sensation for the male and have them practice condom communication skills to decrease their embarrassment level)
self-efficacy: youth confident in using a condom correctly in all circumstances