Brain Cross Sectional Anatomy
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
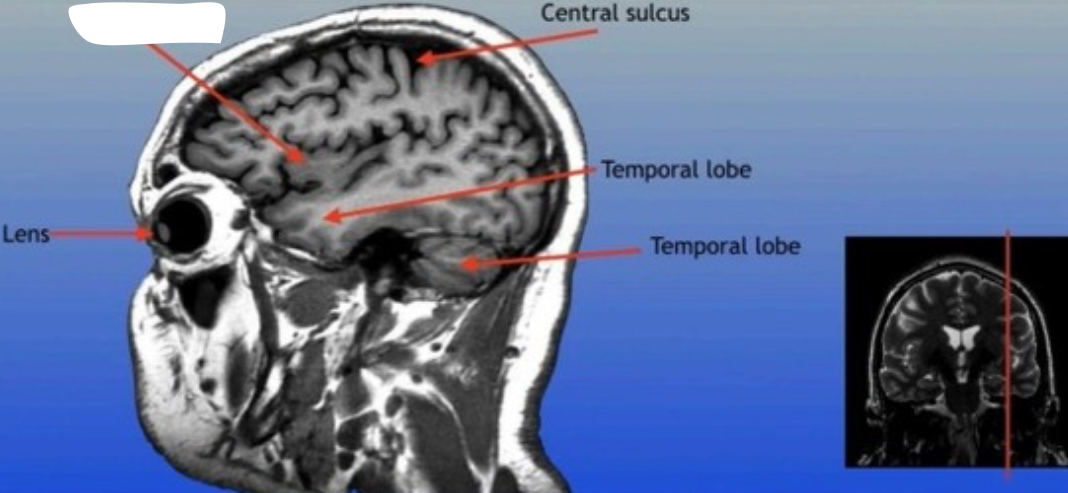
Central Sulcus
A prominent groove in the brain that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe, important for distinguishing motor and sensory functions.
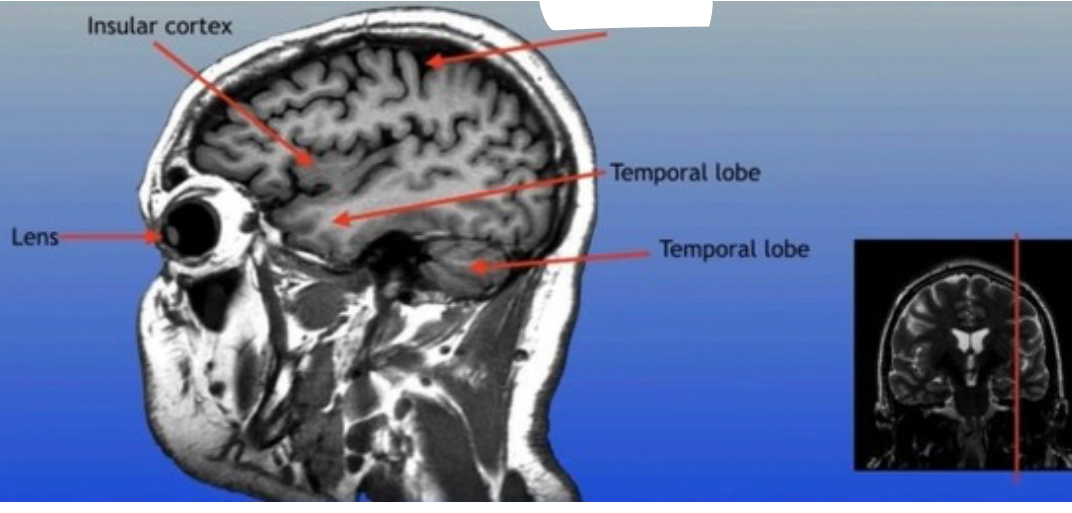
Insular Cortex
Region of the brain located deep within the lateral sulcus, involved in functions such as emotion processing and self-awareness.
Caudate Nucleus
A C-shaped structure within the brain's basal ganglia, involved in various functions including motor control and learning.
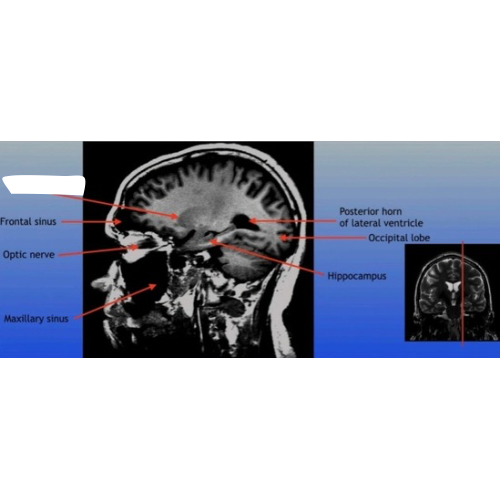
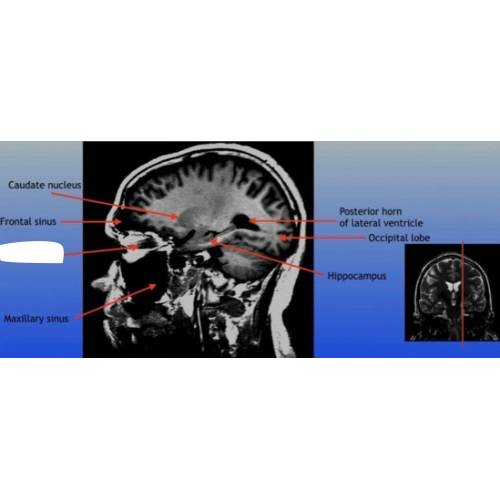
Frontal Sinus
A paired cavity located within the frontal bone, above the eyes, that plays a role in sinus drainage and resonance of the voice.
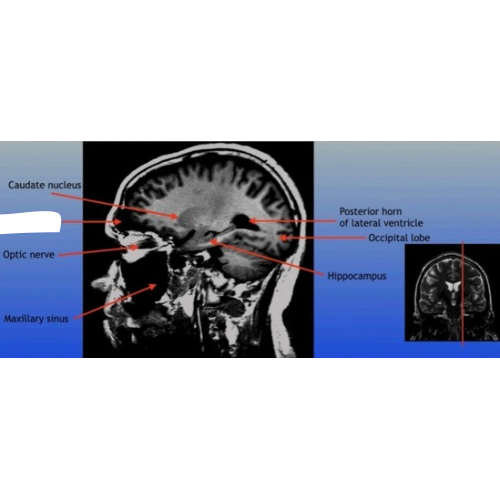
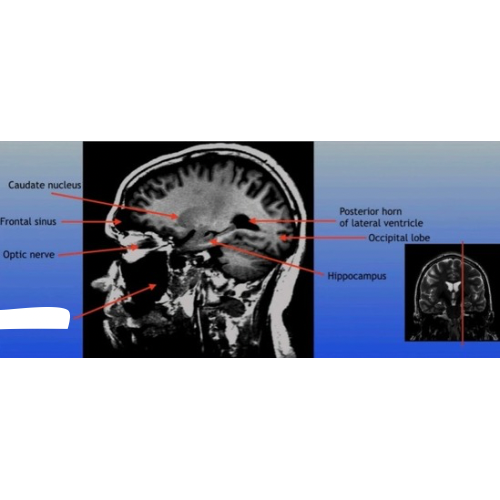
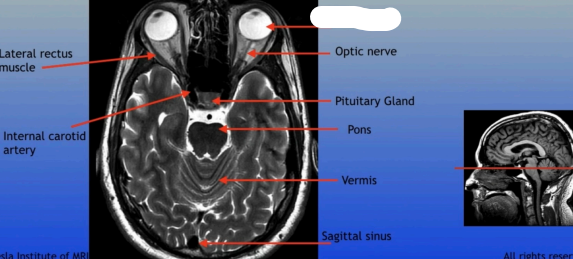
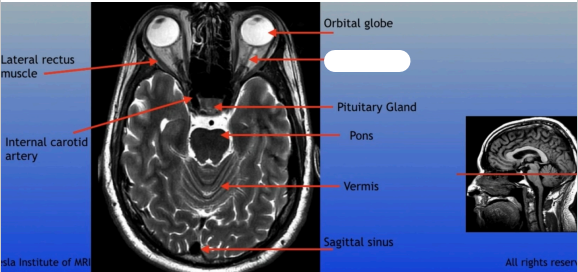
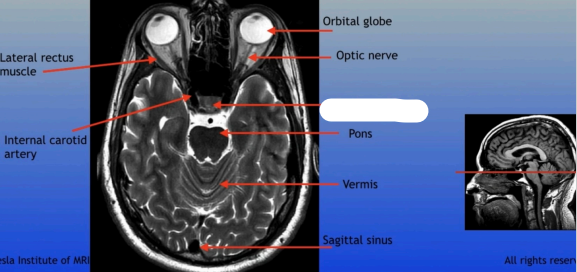
Optic Nerve
The bundle of nerve fibers that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. It plays a crucial role in the sense of sight.
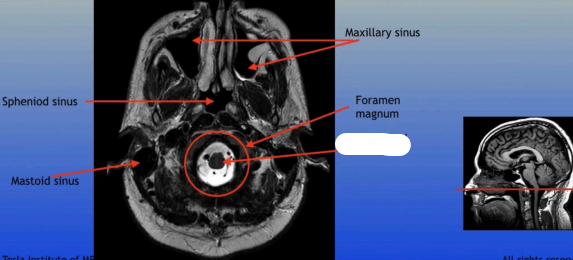
Maxillary Sinus
A paired cavity located within the maxilla, situated below the eyes, that contributes to sinus drainage and helps lighten the weight of the skull.
Posterior Horn of Lateral Ventricle
The posterior part of the lateral ventricle, involved in the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain.
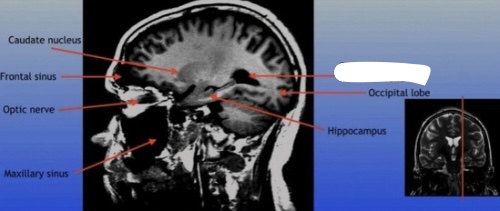
Hippocampus
A critical region in the brain associated with memory formation and spatial navigation, located in the medial temporal lobe.
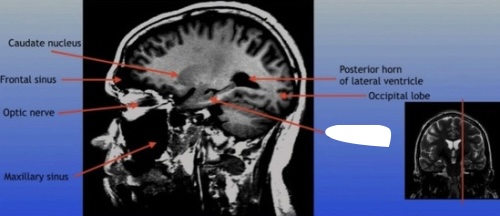
Caudate Nucleus
A C-shaped structure within the brain's basal ganglia, involved in various functions including motor control and learning.
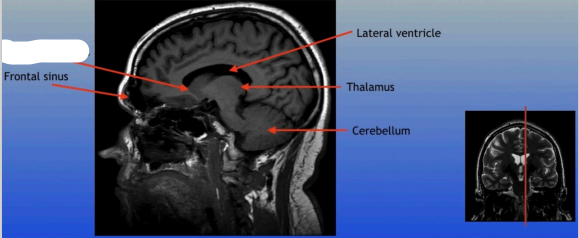
Frontal Sinus
A paired cavity located within the frontal bone, above the eyes, that plays a role in sinus drainage and resonance of the voice.
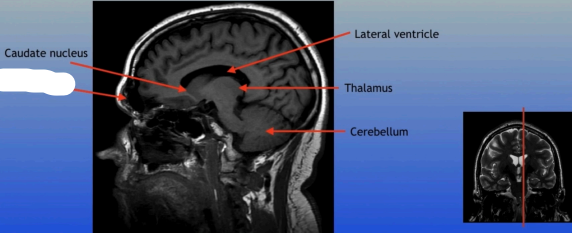
Lateral Ventricle
A fluid-filled cavity located within each hemisphere of the brain, part of the ventricular system, that helps cushion the brain and circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
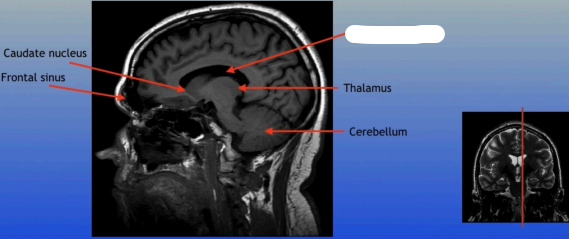
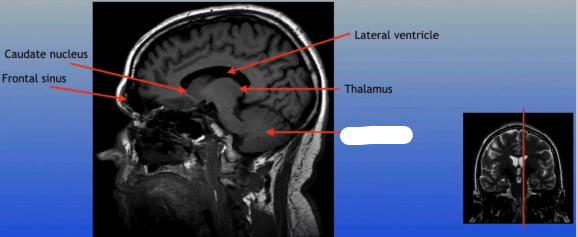
Thalamus
A large mass of gray matter located in the diencephalon, acting as a relay station for sensory information and playing a key role in regulating consciousness and sleep.
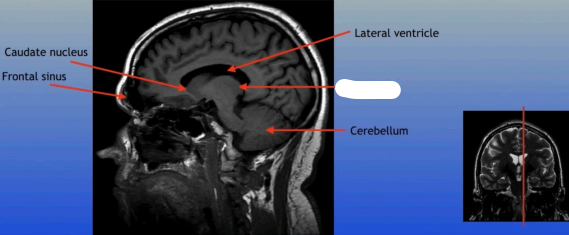
Cerebellum
A large structure located at the back of the brain responsible for coordination, balance, and fine motor control.
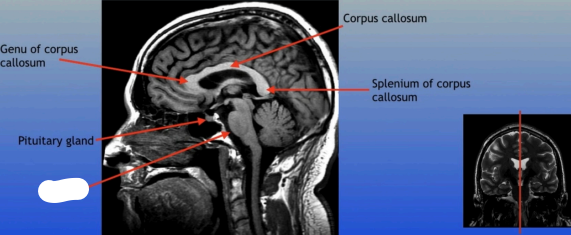
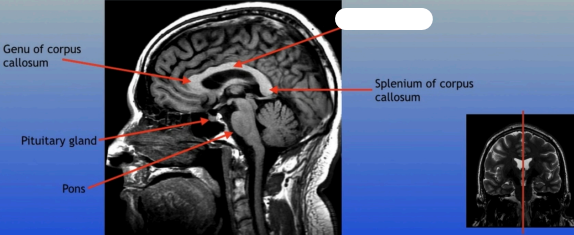
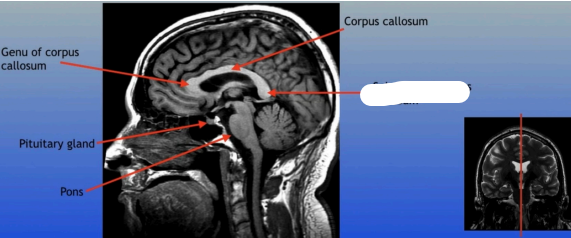
Genu of Corpus Callosum
The anterior part of the corpus callosum that connects the frontal lobes of the left and right hemispheres, playing a role in interhemispheric communication.
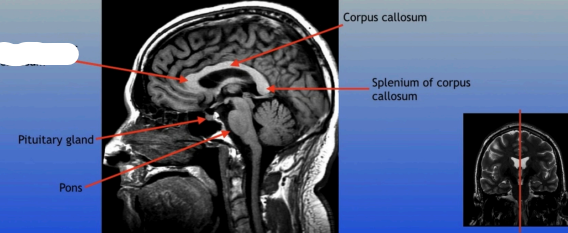
Pituitary Gland
A small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, often referred to as the "master gland" because it regulates many bodily functions through hormone secretion.
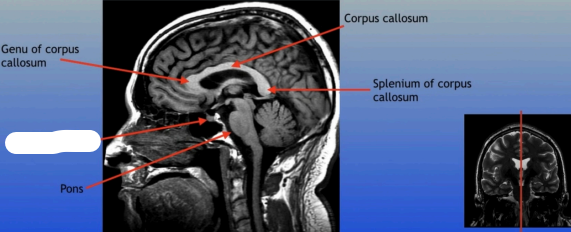
Pons
A round structure located above the medulla oblongata and below the midbrain, it acts as a relay station for signals between the cerebellum and cerebrum, and plays a role in regulating sleep and arousal.
Corpus Callosum
Splenium of Corpus Callosum
Ethmoid Sinuses
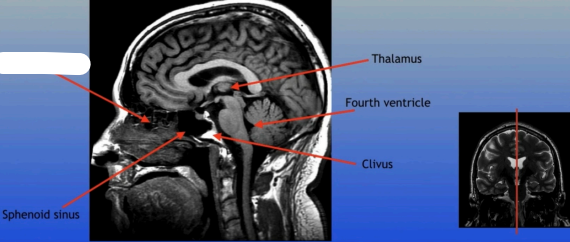
Sphenoid Sinus
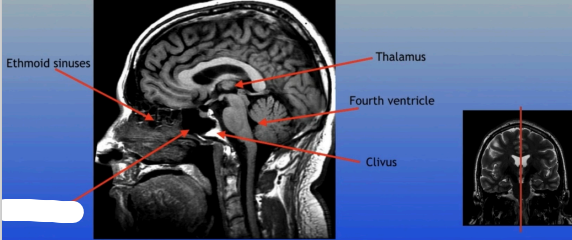
Thalamus
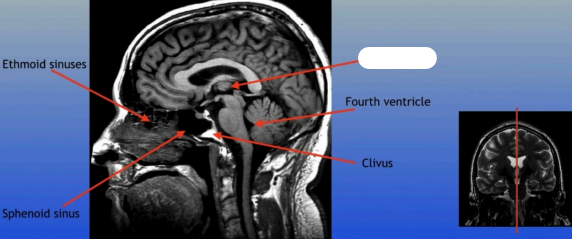
Fourth Ventricle
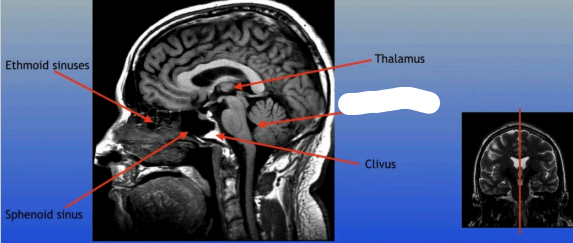
Clivus
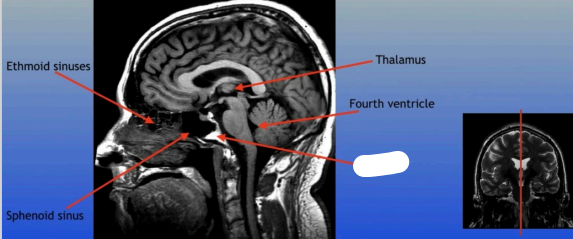
Sphenoid Sinus
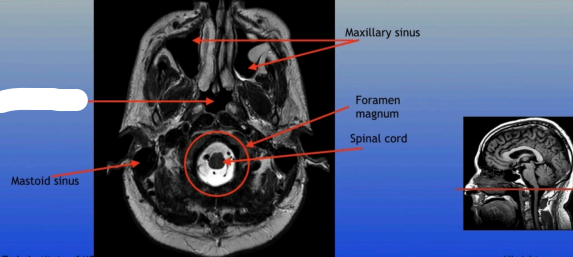
Mastoid Sinus
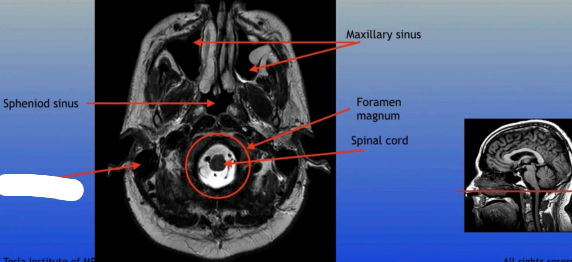
Maxillary Sinus
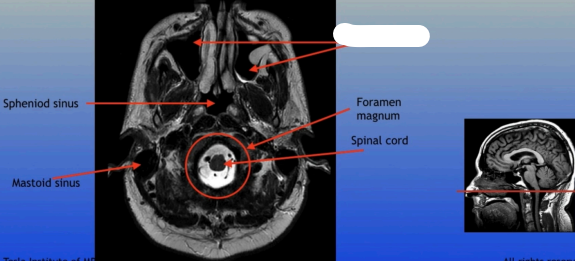
Foramen Magnum
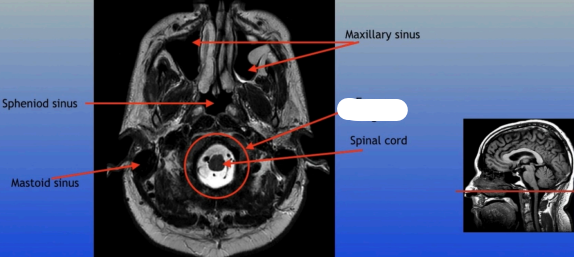
Spinal Cord
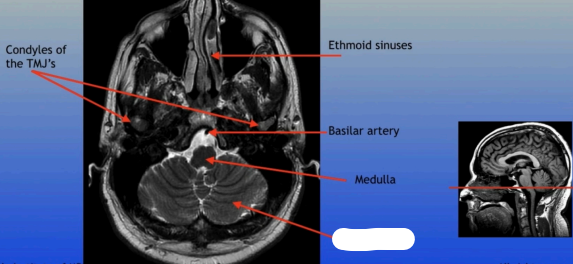
Condyles of the TMJ
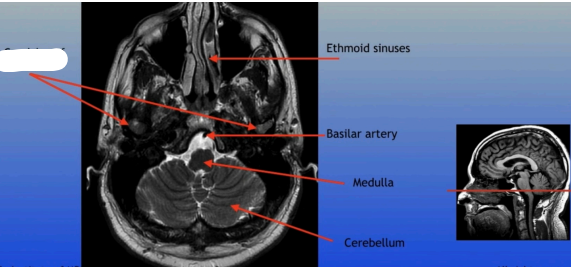
Ethmoid Sinuses
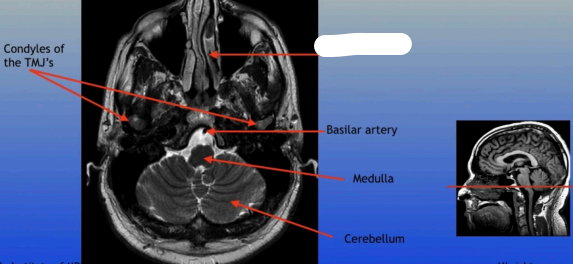
Basilar Artery
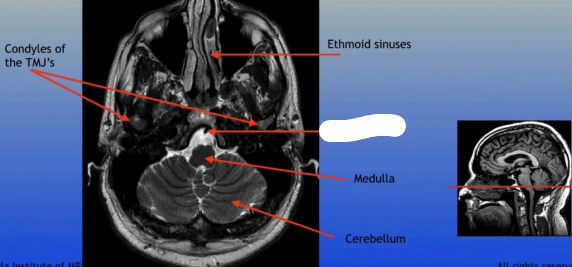
Medulla
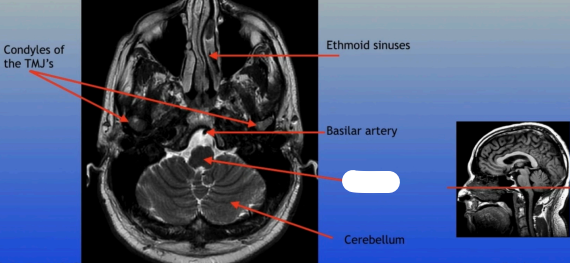
Cerebellum
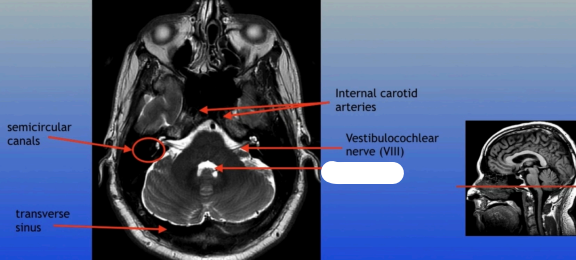
Semicircular Canals
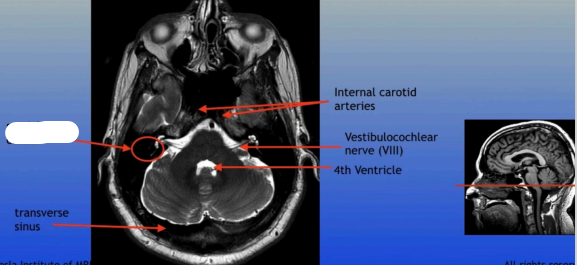
Transverse Sinus
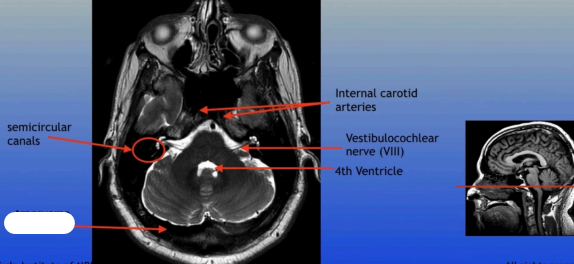
Internal Carotid Arteries
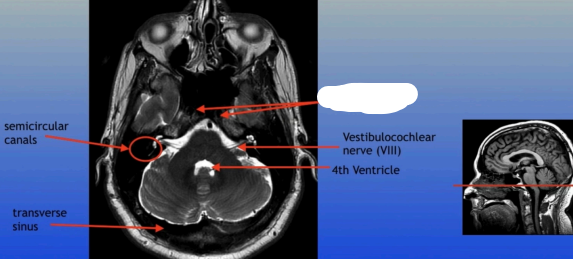
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
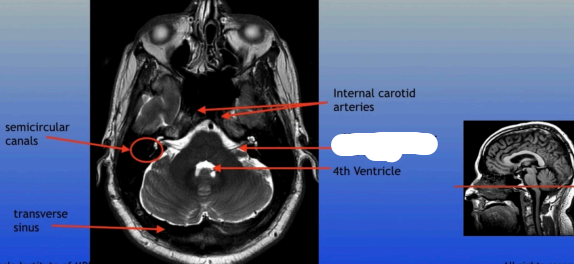
4th Ventricle
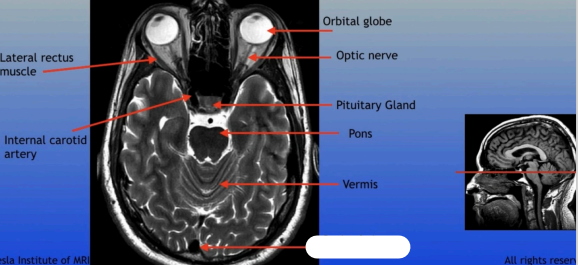
Lateral Rectus Muscle
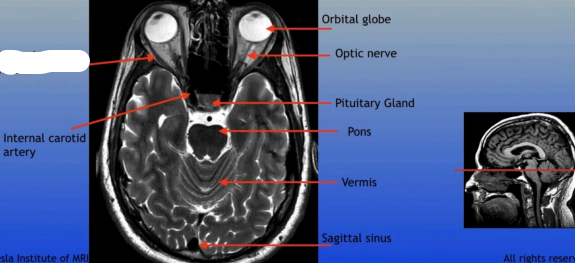
Internal Carotid Artery
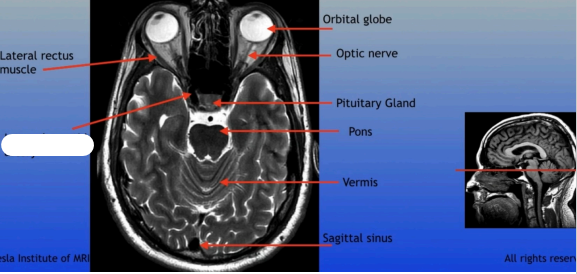
Orbital Globe
Optic Nerve
Pituitary Gland
Pons
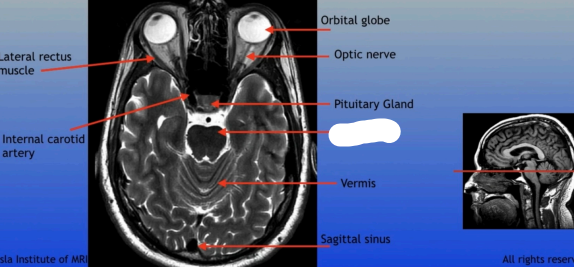
Vermis
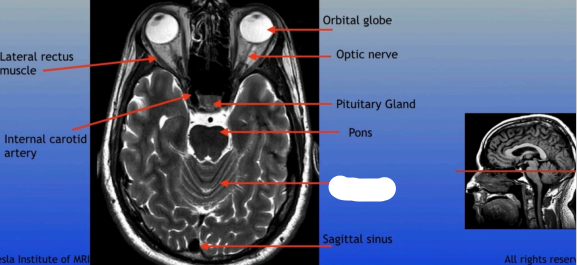
Sagittal Sinus
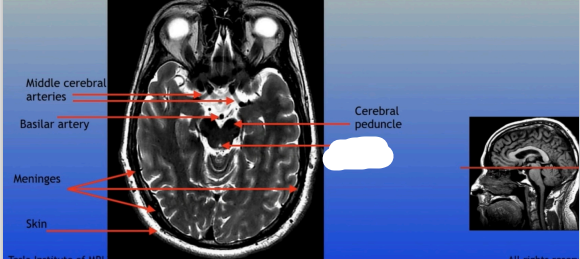
Middle Cerebral Arteries
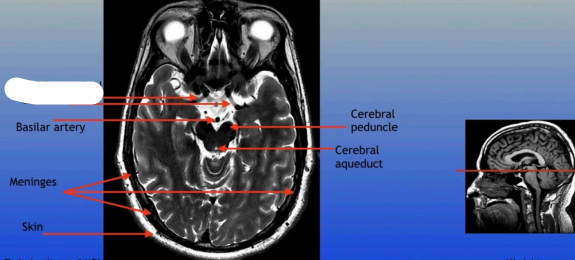
Basilar Artery
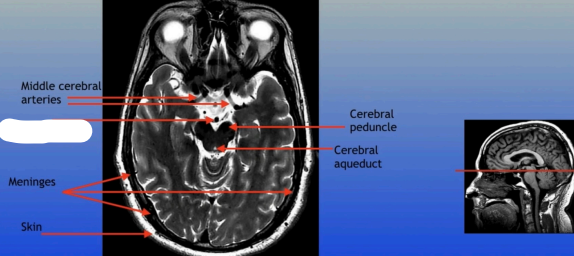
Meninges
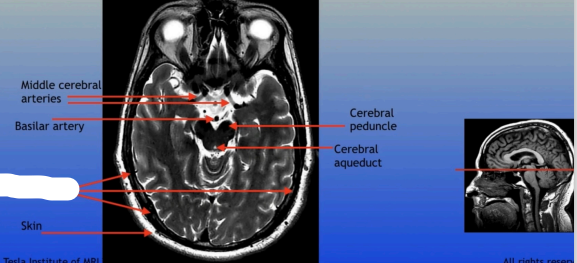
Skin
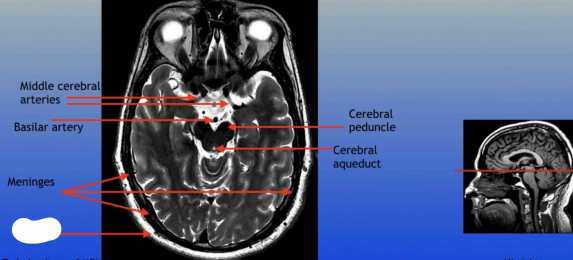
Cerebral Peduncle
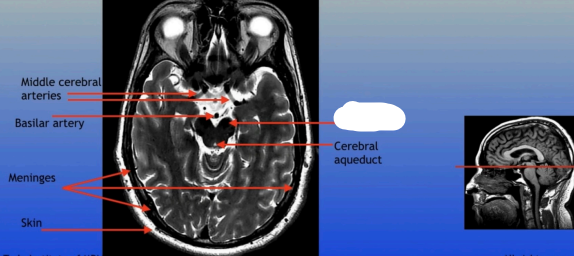
Cerebral Aqueduct
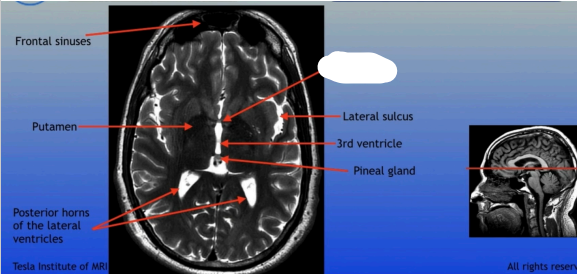
Frontal Sinuses
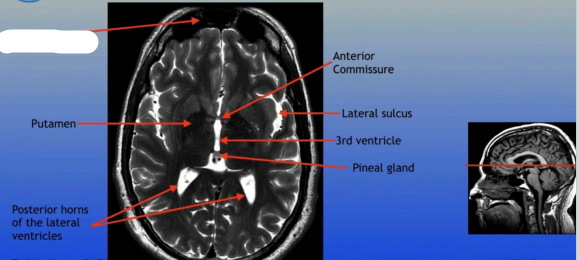
Putamen
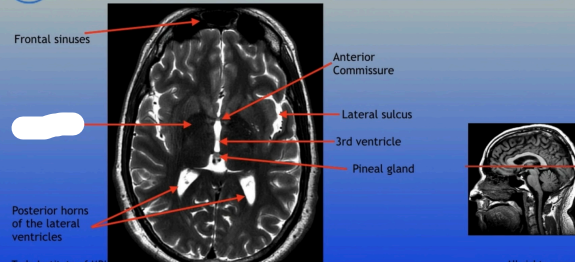
Posterior Horns of the Lateral Ventricles
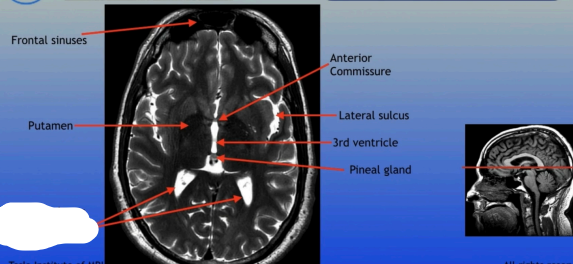
Anterior Commissure