Adaptive Immunity and Antibody Structure in Biosci107
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Adaptive immunity
Immune response evolving over time for efficiency.
Immune memory
Long-lasting protection against previously encountered pathogens.
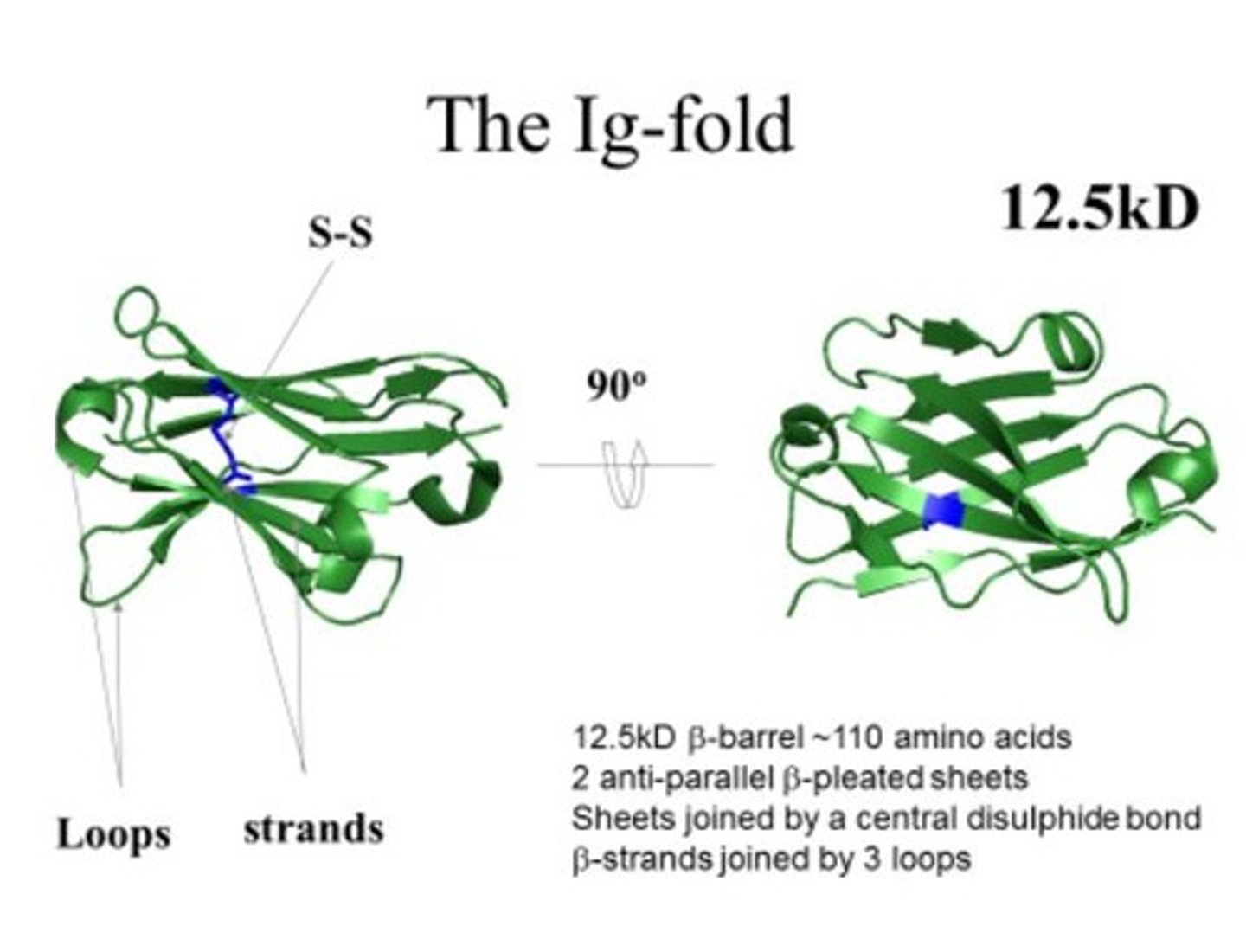
Ig domain
Basic structural unit of antibodies, shaped like β-barrel.
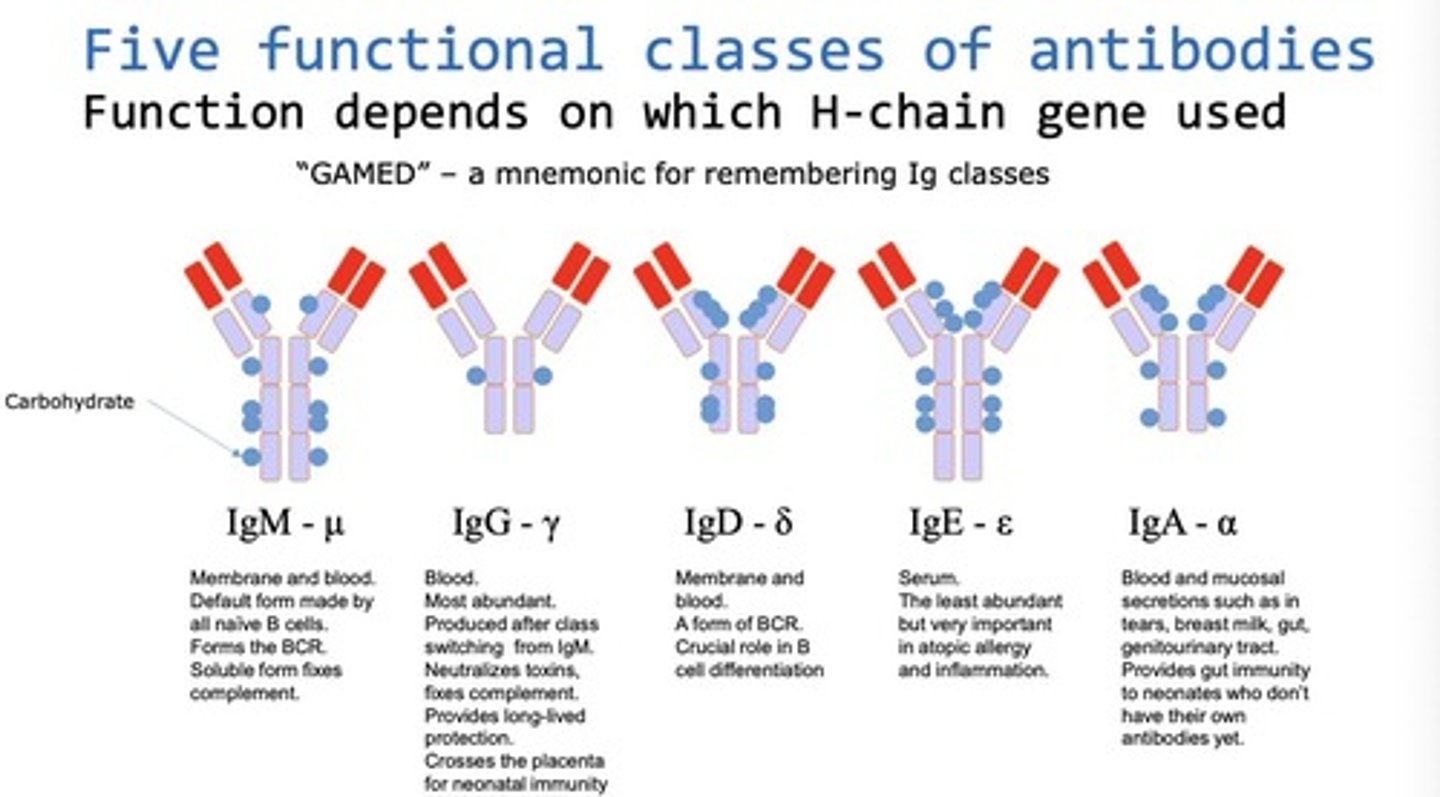
Antibody classes
Five types, each with distinct functions in immunity.
Affinity
Strength of binding between antigen and receptor.
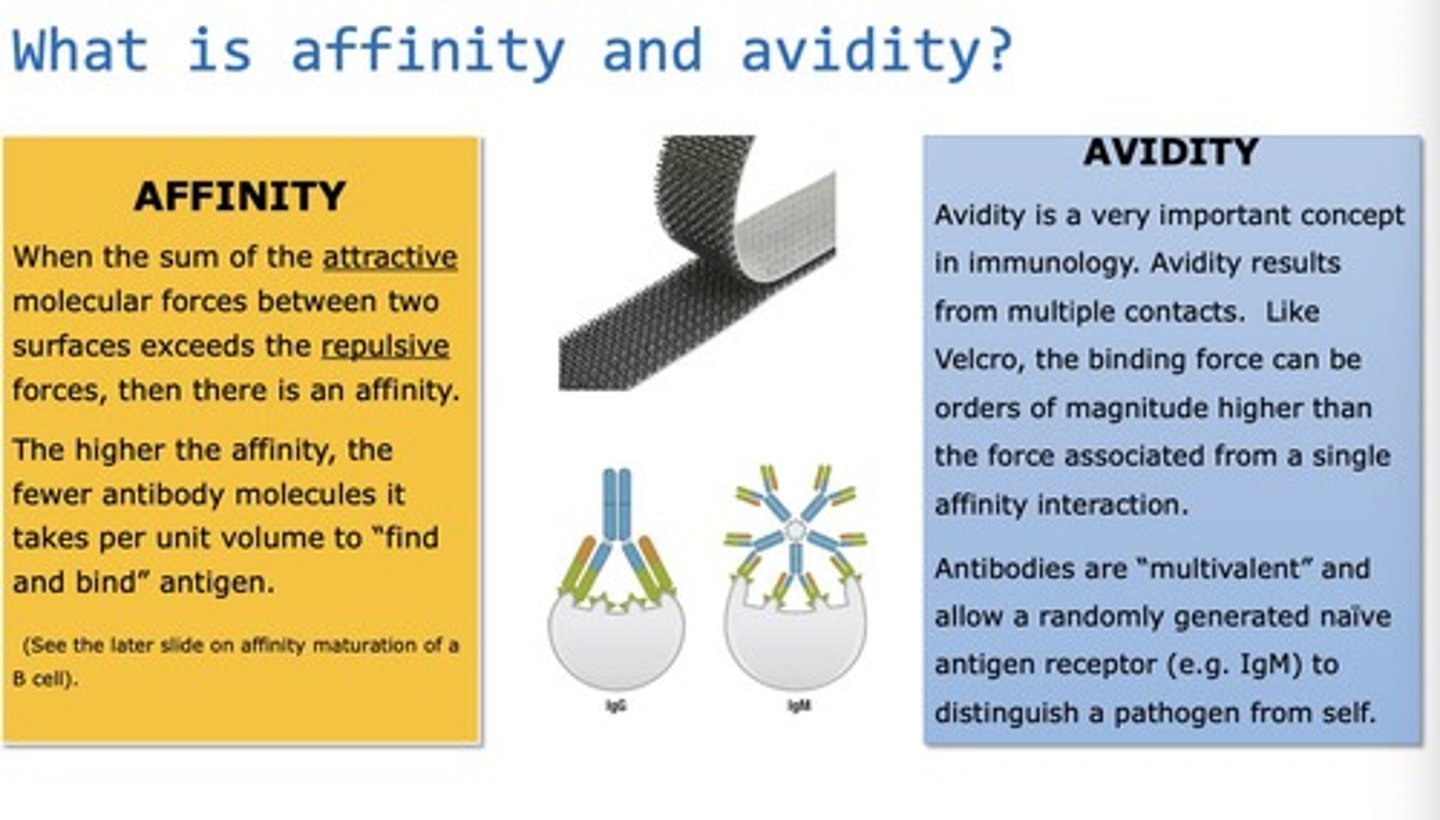
Avidity
Overall strength of binding from multiple interactions.
Genetic recombination
Process generating diversity in antibody genes.
Clonal selection
Process where specific B cells expand upon antigen exposure.
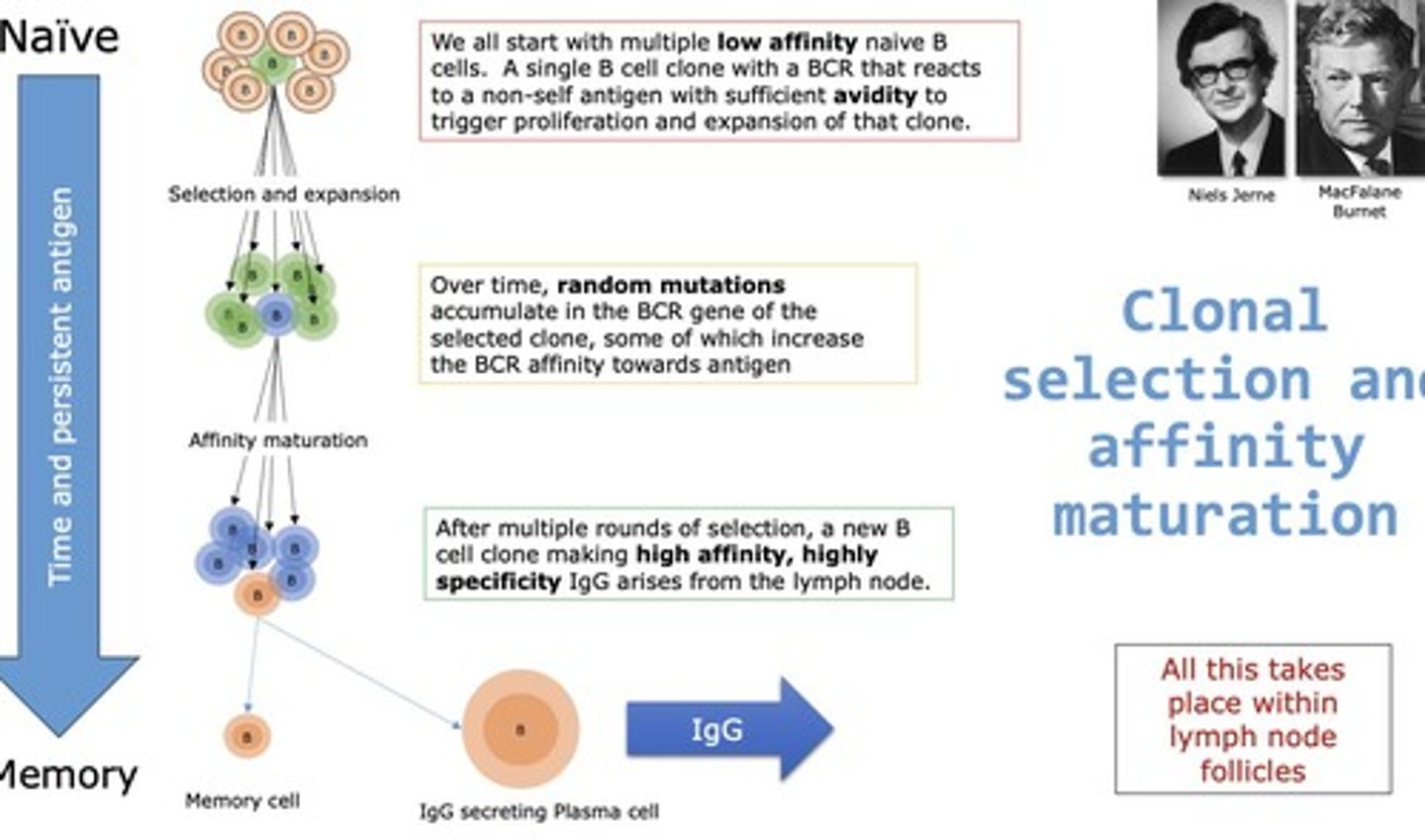
Affinity maturation
Improvement of B cell receptor affinity over time.
Lymph node
Organ where immune responses and B cell activation occur.
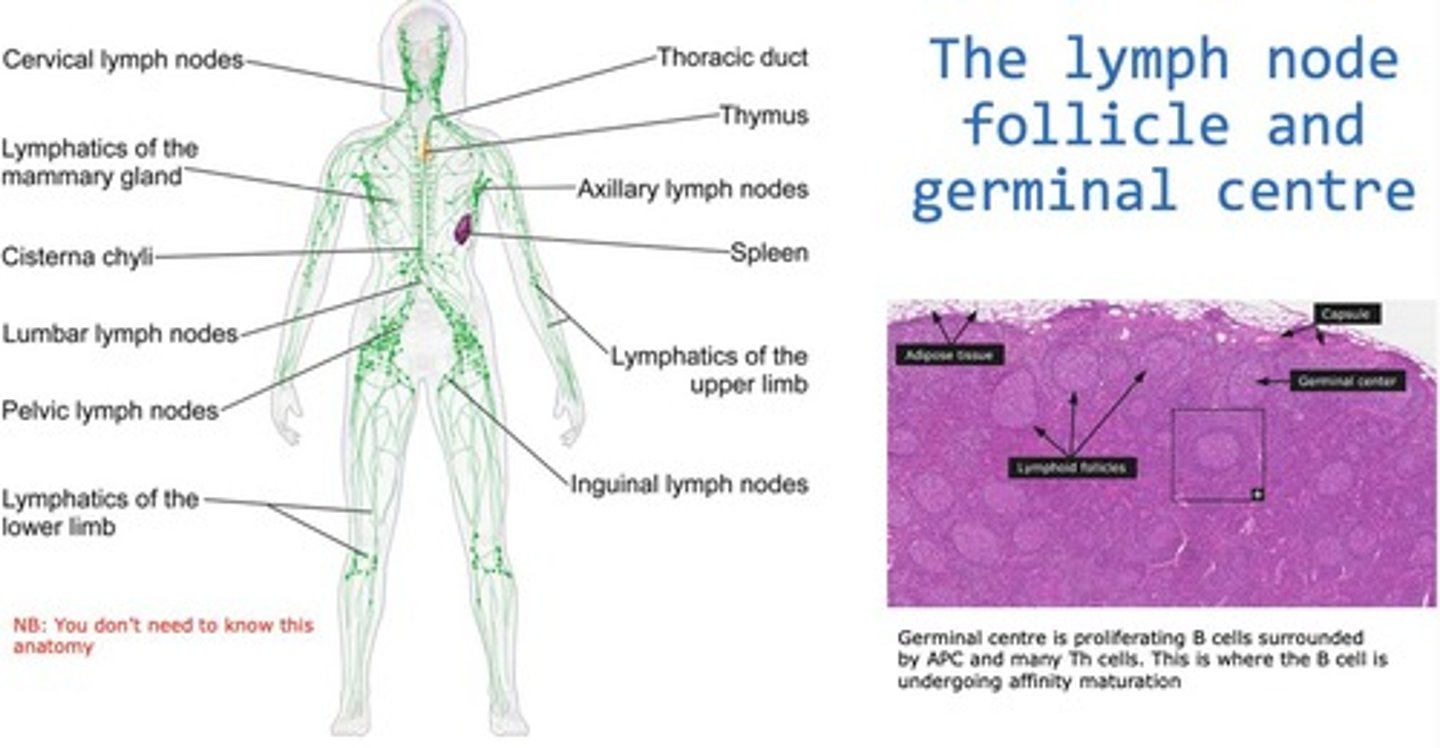
Germinal centre
Site in lymph nodes for B cell proliferation and maturation.
Vaccination
Inducing immunity through exposure to harmless antigens.
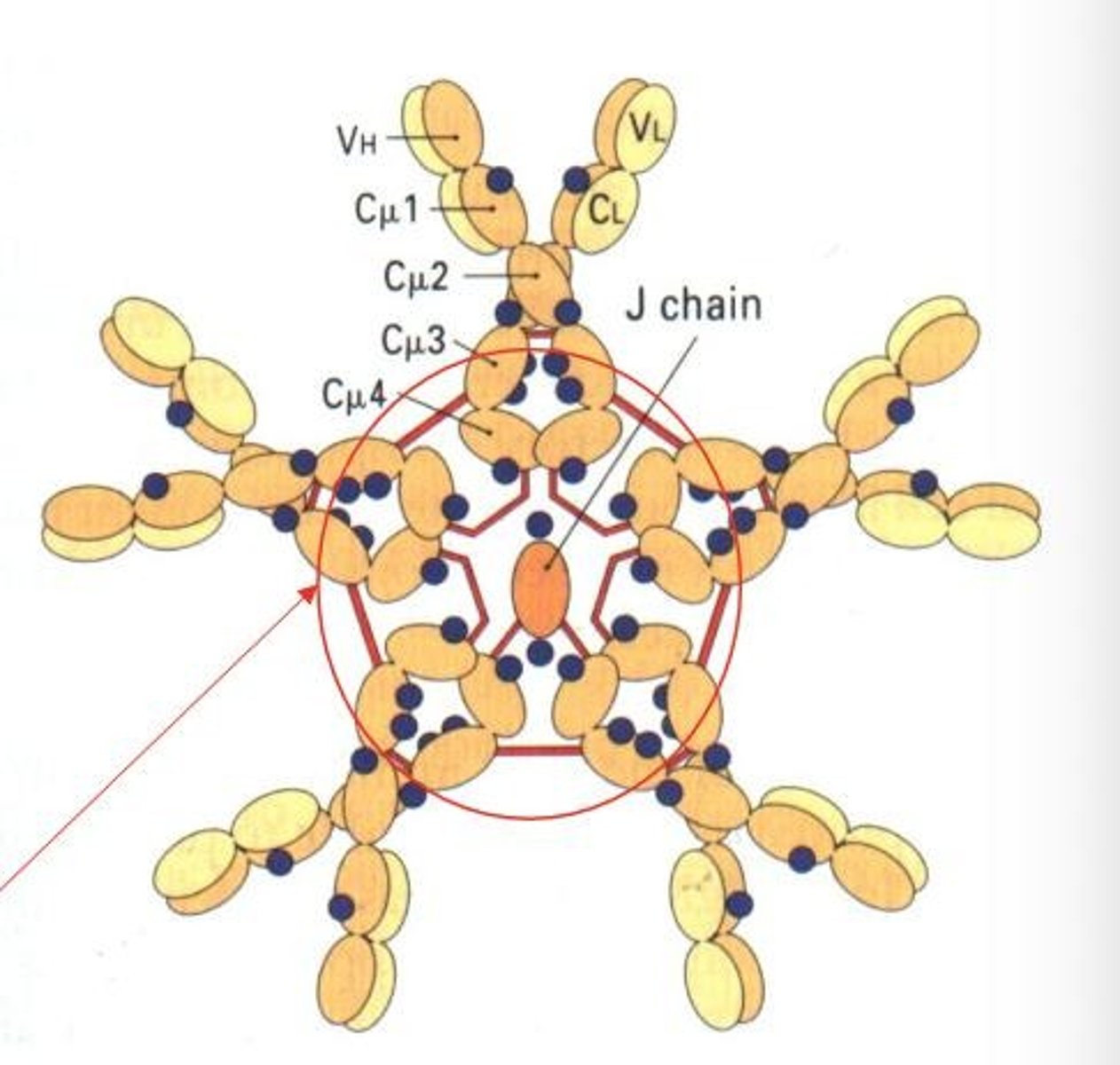
IgM
First antibody produced by naive B cells.
Transposition
Movement of genetic material within a genome.
Transposase
Enzyme facilitating gene repositioning during transposition.
Recognition sequences
Conserved DNA sequences recognized by transposase.
BCR
B cell receptor, specific for antigens.
TCR
T cell receptor, recognizes antigens presented by MHC.
Somatic hypermutation
Random mutations in B cell genes for affinity improvement.
Plasma cell
B cell that secretes antibodies after activation.
Memory B cell
Long-lived B cell ready to respond to future infections.
Complement component C1
Protein that binds to antibodies, initiating complement cascade.
Herd immunity
Community protection when a significant population is vaccinated.
DTaP vaccine
Vaccine for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
Bordetella pertussis
Bacteria causing whooping cough, spread via respiratory droplets.
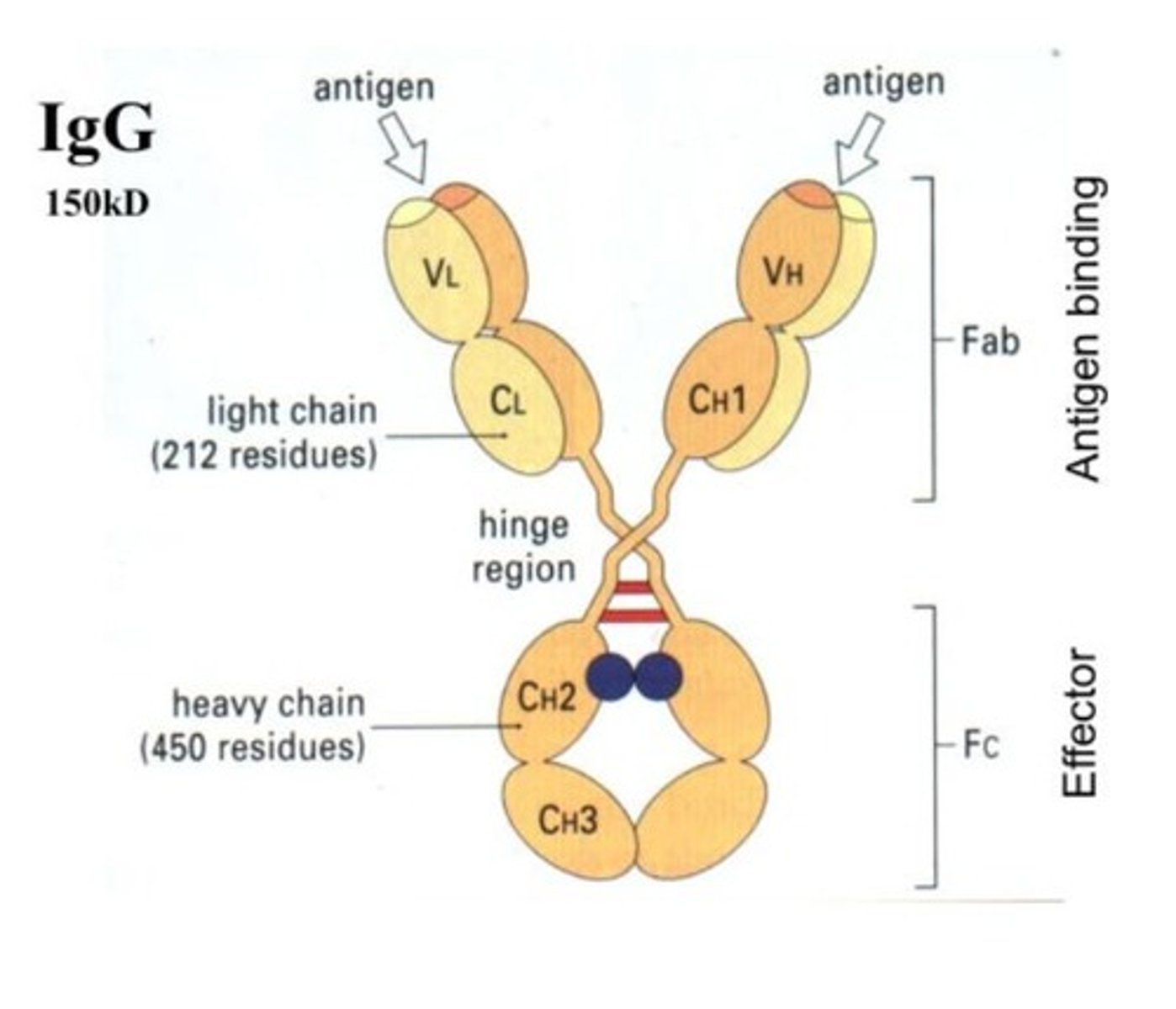
Antigen binding site
Region on antibody that specifically binds to antigens.

Variable domain
N-terminal region of antibodies containing antigen binding site.
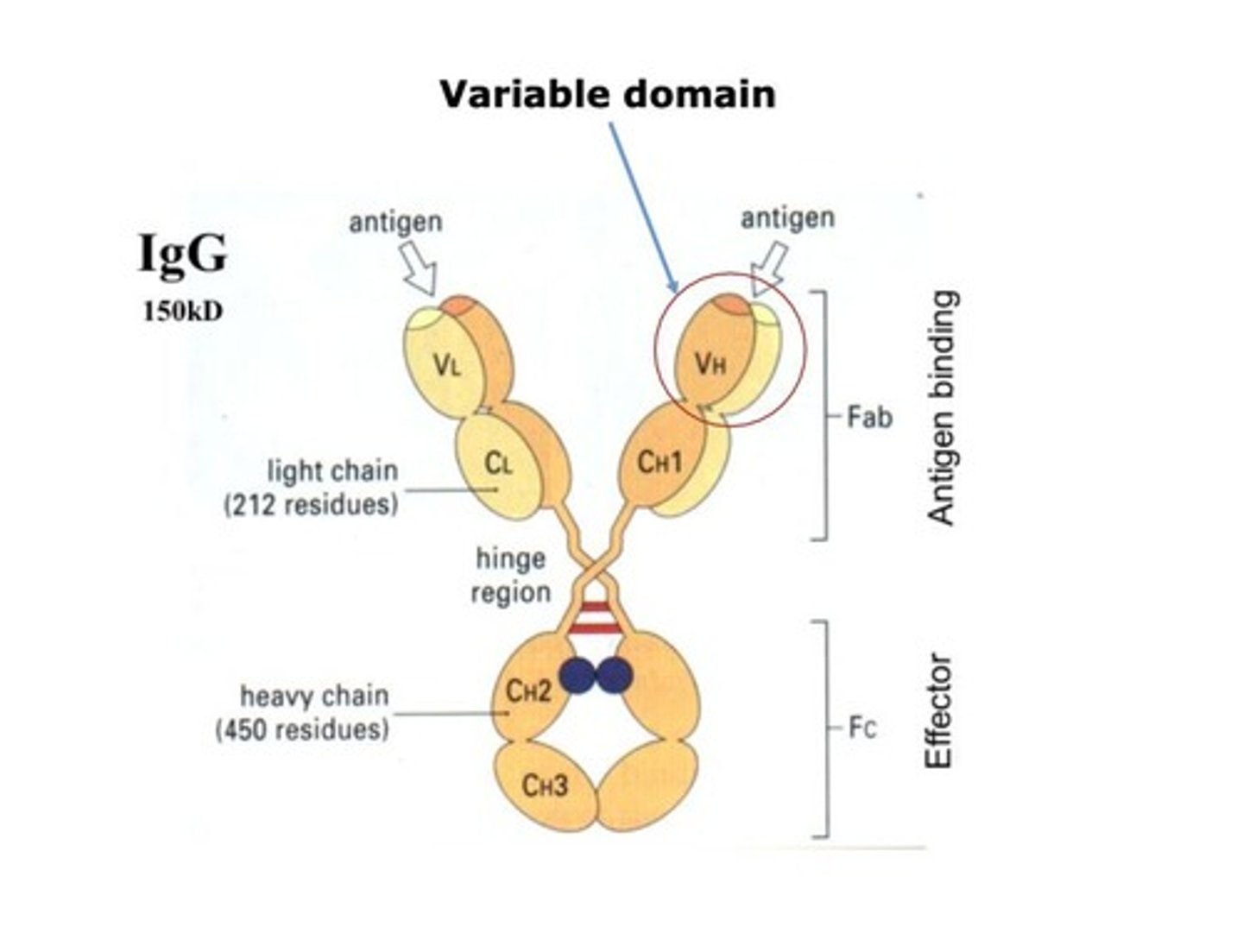
Hypervariable loops
Regions contributing to variability in antigen binding sites.
Naïve B cell
Unactivated B cell with unique antigen specificity.
Inactivated toxin
Modified toxin used in vaccines to stimulate immunity.