Unit 4 - Humanistic, Social Cognitive & Trait Theories
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Social-Cognitive Theory of Personality
states that our traits and social environments interact with one another, and those traits are learned through observation or imitation
Social Exchange Theory
our social behavior is an exchange process, the aim of which is to maximize benefits and minimize cost
Reciprocity Norm
If we infer “social debt” from another we’re more likely to help them (ex: inviting someone to your get together party because they invited you to their cookout)
Reciprocal Determinism
Behavior, personal factors, and environment influence each other.
Humanistic Theories
Focus: Positive aspects of personality, free will, and self-actualization.
Key Theorists: Carl Rogers & Abraham Maslow.
Carl Rogers (Humanist)
People are inherently good and have self-actualizing tendencies.
Growth requires Acceptance (unconditional positive regard), Genuineness, and Empathy.
Person-Centered Perspective: Complete acceptance and love.
Ideal vs. Real Self
Ideal Self: Who you want to be.
Real Self: Who you actually are.
Congruence vs. Incongruence
Congruence: When these align → higher self-worth.
Incongruence: Mismatch → maladjustment.
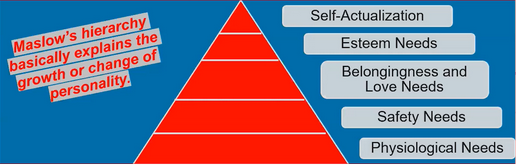
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Self-Actualization is the ultimate goal but only pursued after basic needs are met.
Social-Cognitive Theory (Albert Bandura)
Personality develops through interactions with the social environment.
Self-Esteem
How you value yourself.
Self-Efficacy
Confidence in abilities.
Self-Concept
Overall perception of oneself.
Trait
a characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act, as assessed by self-report inventories and peer reports
Trait Theories
Personality traits are stable and predictable across situations.
Factor Analysis
Statistical method to identify personality dimensions.
Raymond Cattell’s 16 Personality Factors
Used factor analysis to identify bipolar personality dimensions (e.g., shy vs. bold).
Gordon Allport’s Personality Theory
Cardinal Traits: Dominant personality traits (e.g., altruism in Mother Teresa).
Central Traits: General characteristics (e.g., honesty, shyness).
Secondary Traits: Situation-specific traits (e.g., public speaking anxiety).
Hans Eysenck’s Two-Factor Model
Emotional Stability vs. Neuroticism
Extraversion vs. Introversion
Proposed biological basis for personality differences.
Personality Inventory
a questionnaire on which people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors; used to assess selected personality traits
The Big Five Personality Factors
model of personality traits that describes five basic trait dimensions
OCEAN (Openness, Consciousness, Agreeableness, Extroversion, and Neuroticism)
Openness
do you like change? Can you adapt to it?
Creativity, curiosity
Low score: practical, prefers routine, comforting
High score: imaginative, prefers variety, independent
Consciousness
are you organized and careful?
Organization, discipline
Low score: disorganized, careless, impulsive
High score: organized, careful, disciplined
Agreeableness
how well do you get along with others?
Compassion, trustworthiness
Low score: ruthless, suspicious, uncooperative
High score: soft-hearted, trusting, helpful
Extroversion
Are you shy or outgoing?
Sociability, assertiveness
Low score: retiring, sober, reserved
High score: sociable, affectionate, fun-loving
Neuroticism
Are you anxious often?
Emotional instability, anxiety
Low score: calm, secure, self-satisfied
High score: anxious, insecure, self-pitying
Emotional Stability
The opposite end of the spectrum from neuroticism; characterized by consistency in moods and emotions