(DONE) Agents - Compression
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
primary clinical applications for compression
-prevent DVT
-facilitate healing of venous ulcers
-residual limb shaping
-scar control
-control of peripheral edema
fluid travels thru 3 major pathways
1. circulatory system
2. lymphatic system
3. interstitial spaces between cells
T/F: compression can be static or intermittent
true
T/F: compression can be applied uniformly or sequentially to a limb
true
fluid exchange at capillary occurs via __ & __ pressure
hydrostatic & osmotic
We (do/do not) treat systemic diseases with compression!
DO NOT!!!
fluid travels through what 3 major pathways
circulatory system
lymphatic system
interstitial spaces b/w cells
indications for intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC)
edema
prevention of DVT
venous stasis ulcers
lymphedema
in (normal//abnormal) edema, fluid leaks into interstitial space but is reabsorbed in venous or lymph system
normal
what things may cause abnormal edema?
-Venous/lymphatic obstruction or insufficiency
-Increased capillary permeability
-Immobility (airline travel)
-Pregnancy
-Increased plasma volume
-trauma, surgery, burns
-inflammation
do we do compression with congestive heart failure?
NO!
edema can lead to..
-delayed healing
-decr ROM
-decr function
-pain
-skin pigment and collagen changes
-contractures/deformities
-ulceration
-cellulitis
-incr risk of infection
T/F: edema causes permanent changes to collagen
TRUE
what is the brown pigment on legs common with venous insufficiency?
hemosiderin staining
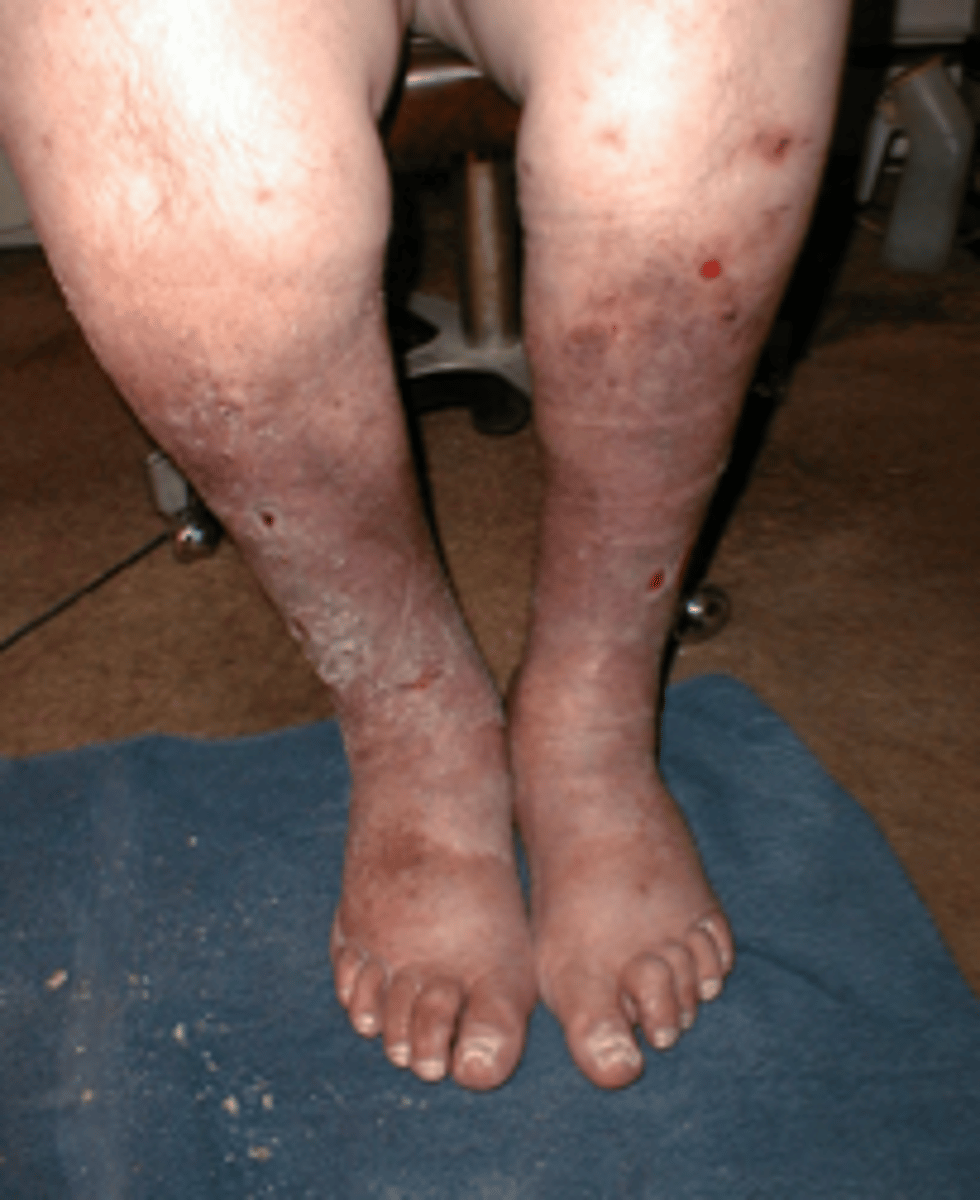
3 ways to measure edema
-anthropometric measurements (REPRODUCIBLE landmarks)
-volumeter
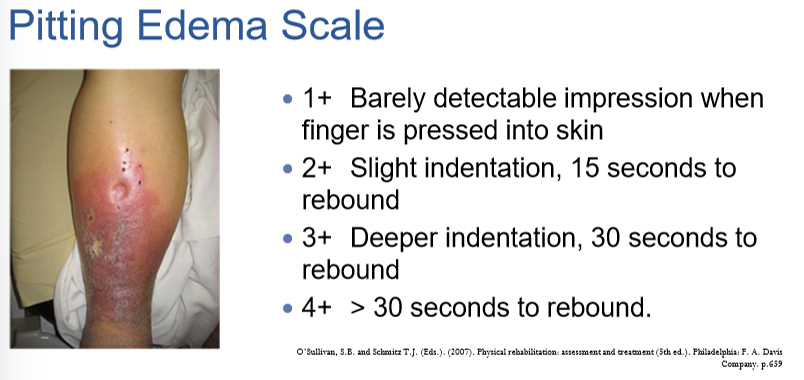
-pitting edema scale
pitting edema is a ___ issue
venous
pitting edema scale
__% of patients undergoing orthopedic surgery will develop a venous thromboembolism without prophylactic (intended to prevent disease) interventions
80%
who's most at risk for DVT?
bedridden pt, paralysis, post-op, obesity, pregnancy
_________ increases blood flow, decreases venous stasis, and therefore decreases opportunity for clot to form
intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC)
best way to resolve venous insufficiency?
exercise!
____ therapy is the cornerstone of venous ulcer treatment!
COMPRESSION!!!
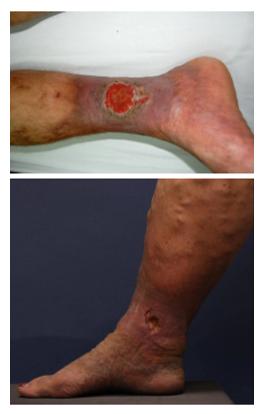
T/F: compression can improve venous circulation and rate of healing of venous stasis ulcers
TRUE!
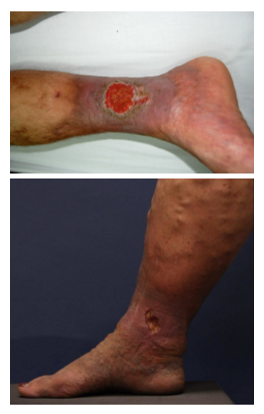
risks for venous stasis ulcers
prolonged immobility
obesity
calf muscle pump dysfunction
pregnancy
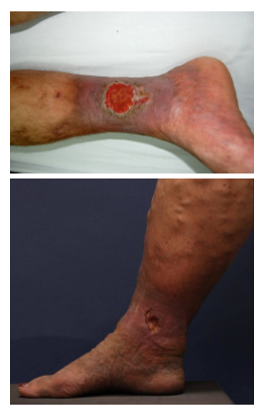
valve incompetence and/or obstruction of vein →______
venous HTN, a condition associated with venous stasis ulcers

for venous stasis ulcer compression therapy, is it best to use a single layer of compression or multiple
multiple
static compression can also be used for.... (2)
-limb shaping
-hypertrophic scarring (compression reduces scar formation by increasing collagenase activity)
T/F: static compression decreases contractures in hypertrophic scarring
TRUE
precautions for IPC
-recent skin graft
-acute local dermatologic infection
-impaired sensation
-impaired mentation
contraindications for IPC
-arterial insufficiency
-uncontrolled HTN
-DVT or PE
-obstructed venous return
-CHF
-acute pulmonary edema
-malignancy
-acute trauma/fx
-arterial revascularization
can we do IPC on a patient with ABI less than .6?
NO!!!! CONTRAINDICATED

can we do IPC on a patient with ABI greater than .8?
YES!! FULL COMPRESSION

potential adverse effects
-incr edema
-impaired circulation
-ischemia
-peripheral n injury
-incr cardiac load
why might ted hose INCREASE edema???
pts doing activities and moving around, they bunch up in areas and cut off circulation and make edema WORSE
(sequential/uniform) compression device is thought to provide more effective "milking" than single chamber compression sleeves
SEQUENTIAL
bandages apply ____ OR ____ pressure
resting // working
___ pressure is exerted by elastic when it is put on stretch
resting (ace bandage)
___ pressure is produced by active muscles pushing against inelastic bandages
working (only works if patient can move!)
for resting pressure, use (high/low) stretch bandage
HIGH!!
for working pressure, use (high/low) stretch bandage
LOW!!!
why do high stretch bandages provide little to no working pressure?
they have some give when muscle expands
(high//low) stretch bandages are most effective on immobile patients
high
tubigrip and ace wraps are examples of (high//low) stretch bandages and will be used for (resting//working) pressure
HIGH // RESTING
durelast is an examples of (high//low) stretch bandage and will be used for (resting//working) pressure
LOW // WORKING
(high//low) stretch bandages do not work in flaccid or inactive limbs
LOW!!!
TED hose (thrombo-embolic stockings) provide what pressure?
moderate resting AND working
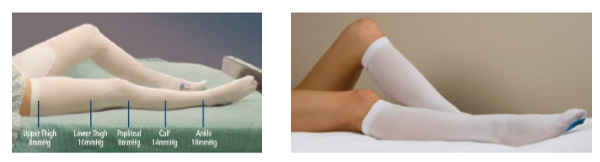
how long to wear TED hose?
24 hrs a day