Understanding Adolescent Brain Development
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
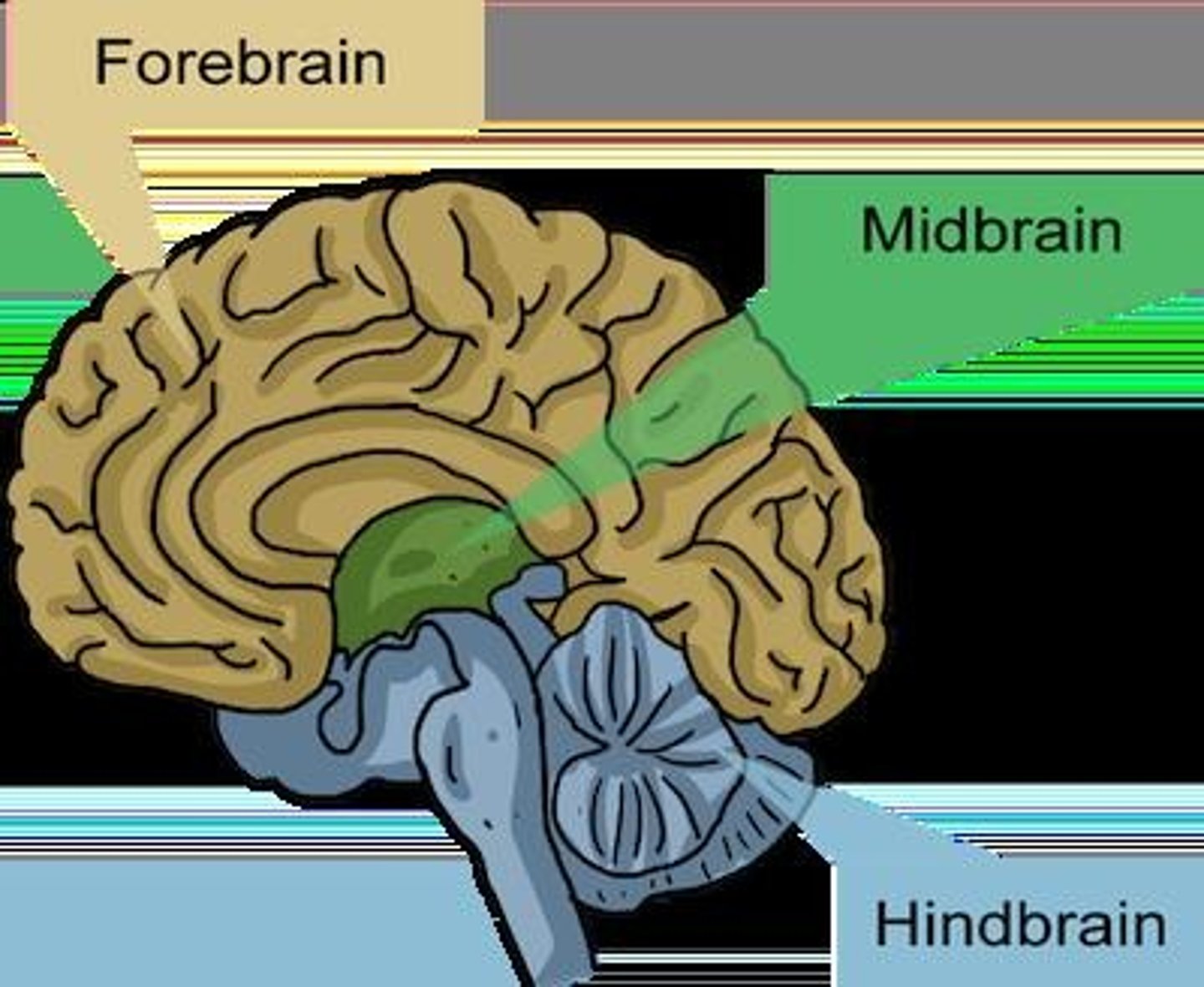
Forebrain
Largest brain region; includes cerebrum and cortex.
Cerebrum
Responsible for thinking, planning, and sensory processing.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of cerebrum; contains four lobes.
Four Lobes
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal lobes of brain.
Corpus Callosum
Connects left and right brain hemispheres.
Midbrain
Relay center for visual and auditory information.
Hindbrain
Controls vital functions; includes pons, medulla, cerebellum.
Cerebellum
Coordinates movement and balance.
Child Brain Development
Rapid growth; significant synaptic growth in infancy.
Synaptogenesis
Formation of new synapses for learning and memory.
Myelination
Axons covered in myelin; increases transmission speed.
Synaptic Pruning
Removal of unused neurons for efficiency.
Developmental Plasticity
Brain's ability to change during childhood and adolescence.
Prefrontal Cortex
Responsible for planning, impulse control, decision-making.
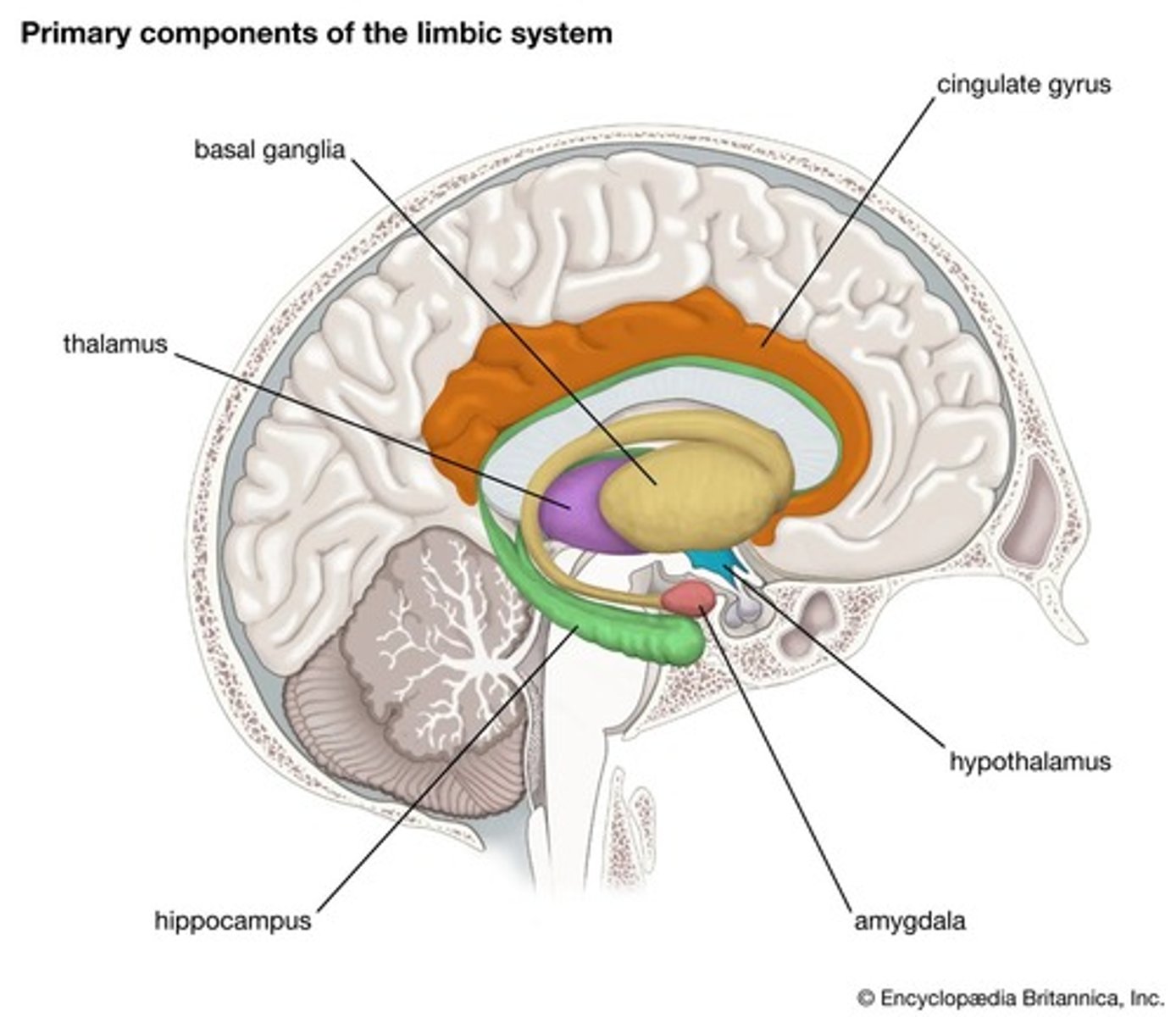
Limbic System
Processes emotions, memories, and learning.
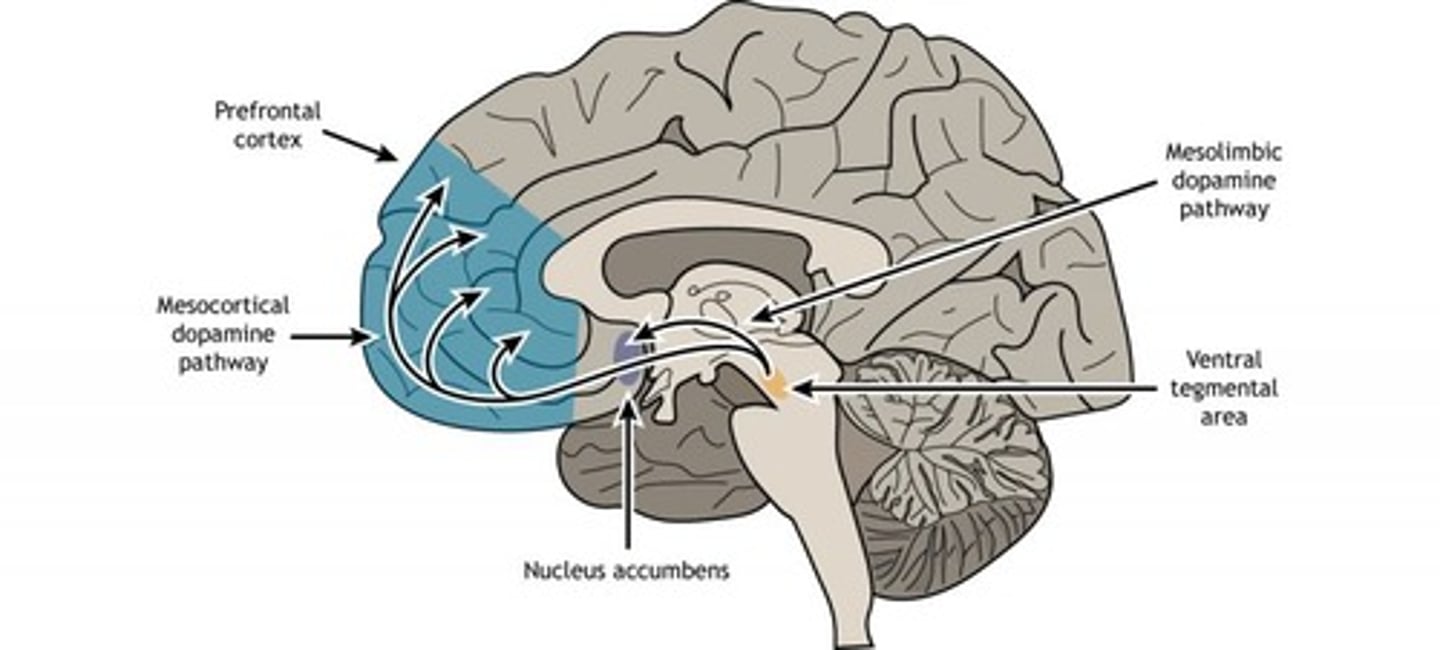
Mesolimbic System
Detects rewards; influences memory and behavior.
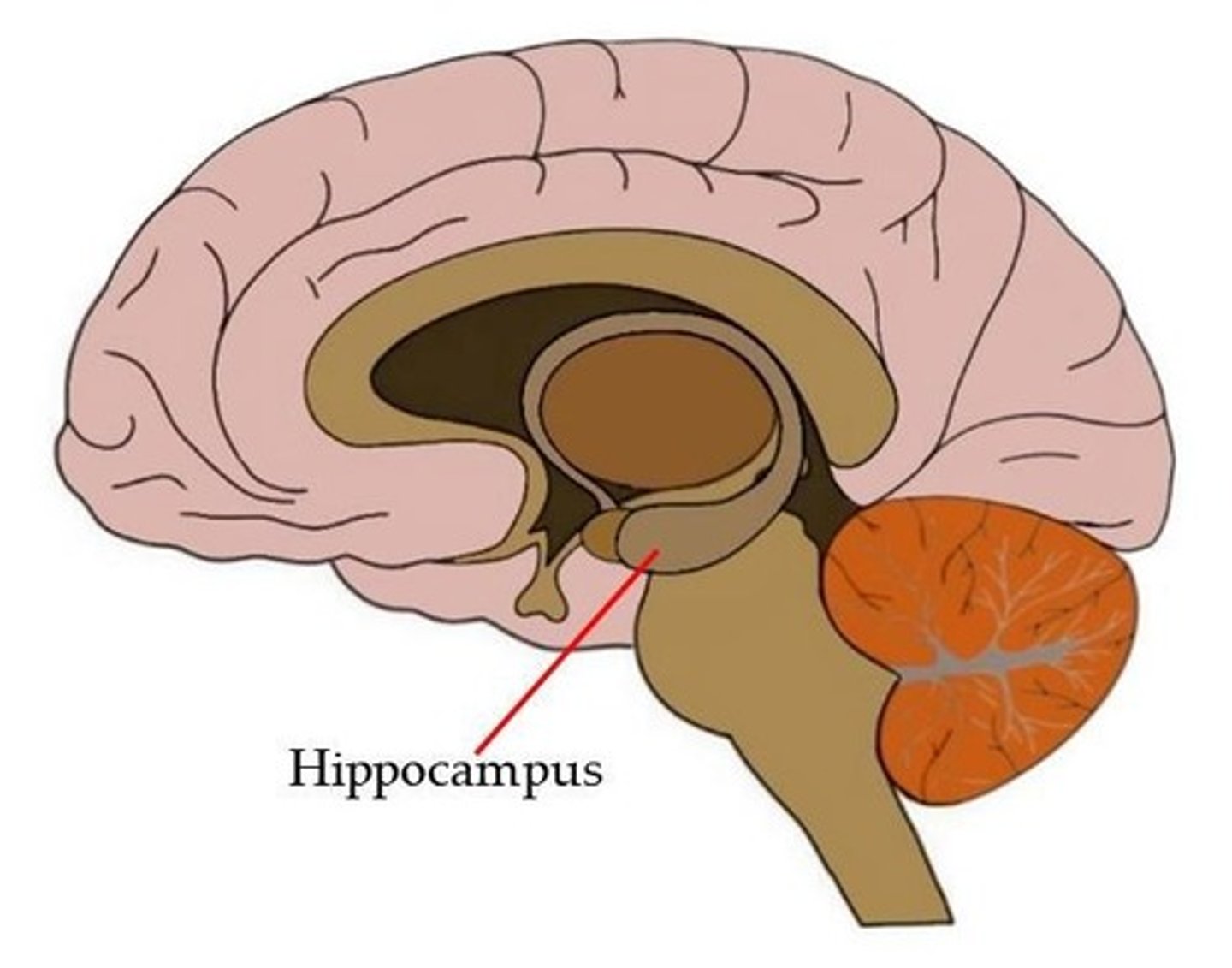
Hippocampus
Key structure for learning and memory formation.
Serotonin Levels
Lowest during teenage years; affects mood.
Brain Growth Stages
Over-produces connections, then eliminates based on use.
Adolescent Brain Development
Continues until mid-20s; not fully mature at 18.
Neural Networks Analogy
Brain compared to telephone networks for understanding.
Teen Mood Swings
Result from increased myelination and serotonin changes.
Nervous System
Body system controlling functions through neural pathways.
Brainstem
Includes midbrain and hindbrain; vital functions.
Cerebral Cortex Lobes
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal; each with functions.
Visual and Auditory Processing
Main functions of the midbrain.
Autonomic Functions
Controlled by the hindbrain; includes heart rate.
Neural Efficiency
Improved through synaptic pruning in adolescence.
Adolescent Learning
Increased hippocampal cell generation during puberty.