Psychology LO4-6
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
YEEEE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Habitation
A decrease in behavioral response after lengthy or repeated exposure to a stimulus.
Sensitization
An increase in behavioral response after lengthy or repeated exposure to a stimulus
Classical Conditioning
A type of learned response in which a neutral object comes to elicit a response when it is associated with a stimulus that already produces a response.
Associative
Learning the relationship between two pieces of information
Unconditioned stimulus & Response
Stimulus that is not learned and response that is not learned
Conditioned stimulus & Response
Stimulus that is learned and response that is learned (like McDonalds arch means fries)
Acquisation
The gradual formation of an association between conditioned and unconditioned stimuli.
Extinction
A process in which the conditioned response is weakened when the conditioned stimulus is repeated without the unconditioned stimulus.
Spontaneous Recovery
A process in which a previously extinguished response reemerges after the conditioned stimulus is presented again.
Stimulus generalization
Learning that occurs when stimuli that are similar but not identical to the conditioned stimulus produce the conditioned response.
Stimulus discrimination
Learning that differentiates between two similar stimuli when only one of them is consistently associated with the unconditioned stimulus.
Operant Conditioning
A learning process in which an action’s consequences determine how likely an action is to be performed in the future.
Reinforcers (Primary and Secondary)
A consequence of an action that affects the likelihood of the action being repeated in the future
1. Primary Reinforcer: An innately reinforcing stimulus, food or dink
2. Conditioned (Secondary) Reinforcer: A learned reinforcer that gets its power through association with the primary reinforcer
Positive Reinforcement vs Negative Reinforcement
P: The addition of a stimulus to increase the probability that a behavior will be repeated.
N: The removal of a stimulus to increase the probability that a behavior will be repeated.
Positive Punishment vs Negative Punishment
P: The addition of a stimulus to decrease the probability that a behavior will recur.
N: The removal of a stimulus to decrease the probability that a behavior will recur.
Observational Learning
The acquisition or modification of a behavior after exposure to at least one performance of that behavior
Modeling
Demonstrating a behavior to imitate a behavior that was previously observed.
Vicarious Conditioning
Learning the consequences of an action by watching others being reinforced or punished for performing the action
Mirror Neurons
When you watch someone performing an action, mirror neurons in your brain become activated. Mirror neurons are especially likely to become activated when you observe someone making a movement that has some goal
Encoding
The processing of information into a neural code that can be stored in the brain.
Storage
The retention of information in the brain over time.
Retrieval
The act of accessing stored information when it is needed.
Selective attention
The ability to direct mental resources to relevant information in order to process that information further while ignoring irrelevant information
Filter Theory
In which we selectively attend to the most important information in a message. In this model, attention is like a filter. Important information is allowed through the filter, but irrelevant information is prevented from getting through the filter.
Sensory Storage
A memory store that very briefly holds information from the five senses
Short term storage
A memory store that briefly holds a limited amount of information in awareness.
Working memory and chunking
Generally seven items. An active processing system that allows manipulation of different types of information to keep it available for current use Using working memory to organize information into meaningful units to make it easier to remember.
Long term storage
A memory store that allows relatively permanent retention for probably an unlimited amount of information.
Maintenance storage
Using working memory processes to repeat information based on how it sounds (auditory information); provides only shallow encoding of information and less successful long-term storage.
Elaborate Rehearsal
Using working memory processes to think about how new information relates to yourself or your prior knowledge (semantic information); provides deeper encoding of information for more successful long-term storage
Schemas
Cognitive structures that aid in the perception, organization, processing, and use of information.
Network of Associations
Each unit of information in the network is a node, and each node is connected to many other nodes. The resulting network is like the linked neurons in your brain, but the nodes are simply bits of information, not physical objects
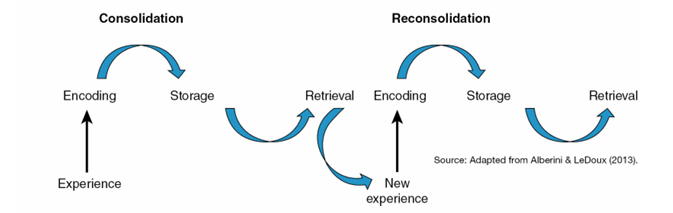
Consolidation and reconsolidation
Process whereby immediate memories become lasting memories when new neural connections are created and prior neural connections get stronger.
When you retrieve memories for past events, those memories can be affected by new circumstances, so reconsolidated memories may differ from their original versions
Dual Coding
A combination of both visual and semantic encoding
Primacy effect
Refers to the better memory people have for items presented at the beginning of the list
Recency effect
Refers to the better memory people have for the most recent items, those at the end of the list
Retrograde Amnesia
A condition in which people lose the ability to access memories they had before a brain injury.
Anterograde Amnesia
A condition in which people lose the ability to form new memories after experiencing a brain injury
Explicit Memory
The long-term storage of conscious memories that can be verbally described.
Episodic Memory
A type of explicit memory that includes a person’s personal experiences
Semantic Memory
A type of explicit memory that includes a person’s knowledge about the world, independent of personal experiences
Henry Molaison
As a young man, Molaison suffered from severe epilepsy, which caused seizures that made it impossible for him to lead a normal life. Molaison’s seizures originated in the temporal lobes of his brain and then spread to other parts of his brain. So in September 1953, Molaison’s doctors removed parts of his medial temporal lobes, the area in the middle of the temporal lobes, including the hippocampus The surgery quieted Molaison’s seizures, but it had an unexpected and very unfortunate side effect: He lost the ability to store most types of new information in long-term storage, a condition called amnesia.
Implicit Memory
The long-term storage of unconscious memories that cannot be verbally described.
Implicit Memories
The long-term storage of unconscious memories that cannot be verbally described.
Procedural Memory
A type of implicit memory that involves learning motor skills and behavioral habits and knowing how to do things.
PFC
The prefrontal cortex is particularly important for working memory
Amygdala
The amygdala is very important for another type of implicit memory. Recall that in classical conditioning, we may unconsciously learn to be afraid of something. But those with damage to the amygdala cannot learn to fear objects that signal danger.
Temporal Lobe (including hippocampus)
The temporal lobes are less important for implicit memories, such as classical conditioning and procedural memory. This area is important for the ability to form new explicit memories
Hippocampus
This area is important for the ability to form new explicit memories, CONSOLIDATION OF EXPLICIT MEMORIES
Cerebellum
The cerebellum plays a role in implicit memory. It is especially involved in procedural memory for learning motor actions.
Retrieval cues: Context-dependent memory
Anything that helps a person access information in long-term storage. The context of an event includes details such as the physical location, odors, and background music. That context is encoded along with the memory. The change in context interfered with your memory
State-dependent memory
When your internal states are the same during both encoding and retrieval, the situation can provide a retrieval cue that enhances your access to a memory.
Mnemonics
Learning aids or strategies that use retrieval cues to improve access to memory. People commonly memorize phrases to help them remember particular details.
Forgetting: Interference
retroactive interference A type of interference in recalling memories that occurs when access to older memories is impaired by newer memories.
proactive interference A type of interference in recalling memories that occurs when access to newer memories is impaired by older memories.
Blocking
This type of forgetting occurs when we are temporarily unable to remember something. The tip-of-the tongue phenomenon.
Absentmindness
The inattentive or shallow encoding of events. The major cause of absentmindedness is failing to use selective attention to pay attention to relevant information and ignore irrelevant information (Figure 7.31). For instance, you absentmindedly forget where you left your keys because when you put them down, you were also reaching to answer your phone.
Memory bias
Memory bias is the changing of your memories over time so that they become consistent with your current beliefs or attitudes.
Flashbulb moments
Detailed and vivid memories about the circumstances in which we heard about surprising and emotionally arousing events.
Misattribution
Misattribution occurs when you misremember the time, place, person, or circumstances involved with a memory. Source amnesia is a form of misattribution that occurs when you have a memory for an event but cannot remember where you encountered the information
Suggestibility
When people are given misleading information, this information affects their memory for an event.
False memories
Memories that you didn’t happen but you connected dots when given information by others
Activating
Stimulates you to do something
Directive
Guides your behavior towards specific goals or needs
Sustains
Sustain your behavior until you achieve your goals or satisfy your need
Relative Strength
Motives differ in strength, depending on the person and on the situation.
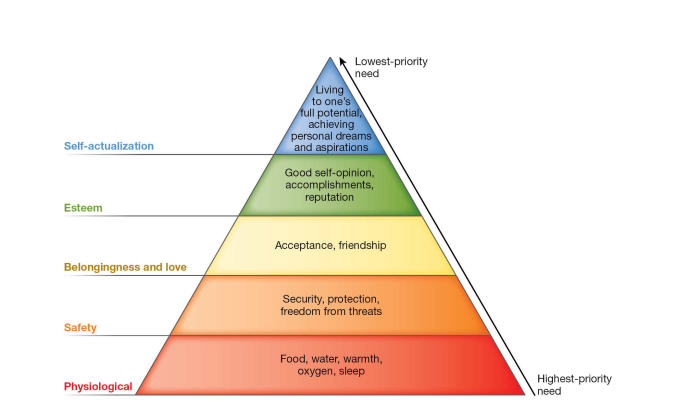
Abraham Maslow & Need Heierarchy
Survival needs (such as food and water) are the foundation of the hierarchy, based on the idea that they are most critical. Less urgent needs such as personal growth are at the top of the hierarchy. To experience personal growth, Maslow believed, people must first focus on their biological needs. They also have to address their needs to feel safe and secure, to feel loved, and to have a good opinion of themselves.
Humanistic psychology
Views people as striving toward personal fulfillment
Self-actualizaiton
Occurs when people achieve their personal dreams and aspirations
Homeostatic and Set Point
Tendency for bodily functions to remain in equilibrium. You set the thermostat to some desired temperature called a set point. This set point indicates homeostasis for the system
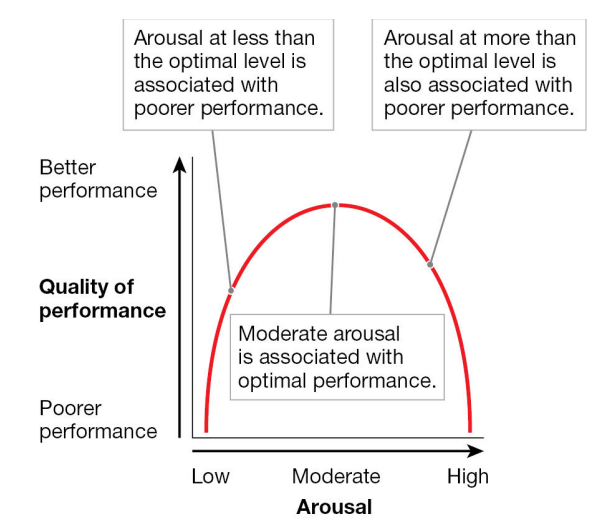
Yerkes-Dodson law
Describes the relationship between arousal, motivation, and performance.
Pleasure Principle
People do things that feel good. If something feels good, they do it again, they avoid pain
Incentives
External objects or external goals, rather than internal factors, that motivate behaviors
Intrinsic vs extrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation, the desire to get the value or pleasure from the activity rather than to achieve an external goal.
Extrinsic motivation is the desire to perform an activity to achieve an external goal, such as receiving a reward.
Self-determination theory
People are motivated by a desire to feel good about themselves, which inspires them to do their most creative work (Deci & Ryan, 1987). They are motivated to engage in certain behaviors because they need to feel successful at something, have personal control, or develop personal relationships with others.
Self-perception theory
According to this theory, people are seldom aware of their specific motives. Instead, they make inferences about their motives according to what seems to make the most sense..
Regions that influence eating
Hypothalamus: Processes signals about nutrient levels to regulate eating
Blood: Low glucose (blood sugar) levels provide a hunger signal
Stomach: When empty, secretes the hormone Ghrelin, which provides a hunger signal
Pancreas: The pancreas is a part of the body that produces the hormone insulin
Fat cell: Secrete the hormone leptin, which discourages eating
Hormones that influence eating
Glucose: Provides the main source of energy needed to keep our bodies alive. We get glucose from the carbohydrates we eat.
Insulin: A hormone produced by the pancreas that controls glucose levels in the blood
Ghrelin: A hormone, secreted by an empty stomach, that is associated with increased eating behavior.
Leptin: A hormone, secreted by fat cells, that is associated with decreased eating behavior.
Need to belong theory
The need for social relations is a fundamental motive that evolved for adaptive reasons
Achievement motivation
The need or desire to attain a certain standard of excellence.
Self-efficacy
The expectation that your efforts will lead to success
Delaying gratification
One common challenge in meeting our long-term goals is postponing an immediate reward
Grit
People with grit have a deep passion for their goals and a willingness to keep working toward them, even in spite of hardships and pitfalls
Emotion vs Mood
Emotion: An immediate, specific, negative or positive response to environmental events or internal thoughts
Mood: Long-lasting emotional states that do not have an identifiable object or trigger.
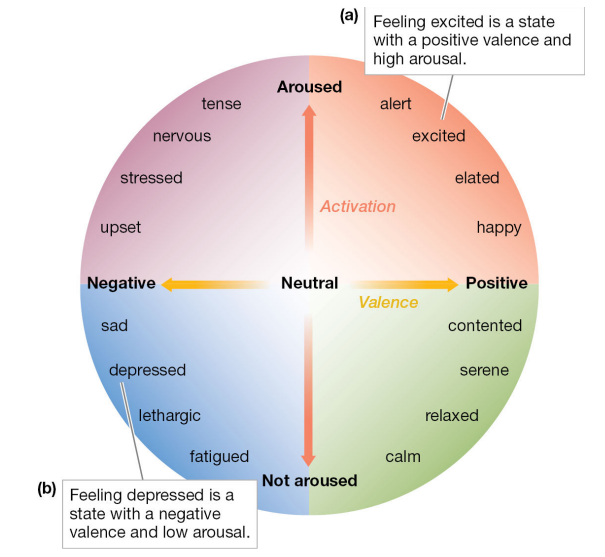
Circumplex Model (Valence and Arousal)
Emotions are plotted along two dimensions that lie along a continuum: valence and arousal
Valence refers to how negative or positive the emotion is.
Arousal describes the extent to which the emotion causes increased brain activity or autonomic responses
James-Lange theory of emotion (Facial feedback hypothesis)
Theory stating that emotions result from physiological reactions in the body. “We feel sorry because we cry, afraid because we tremble”
Moving your muscles to create facial expressions triggers your emotions, not the other way around
Cannon-Bard theory
Theory stating that information about emotional stimuli is sent to the cortex (emotional experience) and the body (physical reactions) at roughly the same time.
Two-factor theory (misattribution of arousal)
Theory stating that how we experience an emotion is influenced by the cognitive label we apply to explain the physiological changes we experience.
You can attribute physical states caused by a situation to the wrong emotion. That is, you use the wrong emotion label. This mistaken identification of the source of your arousal is called misattribution of arousal.
Fast & slow paths to amygdala
A fast path sends information straight from the thalamus to the amygdala for immediate action.
A slow path first sends information to the visual cortex for additional processing before it reaches the amygdala.
Rumination
Rumination involves thinking about, elaborating, and focusing on undesired thoughts or emotions
Positive Reappraisal
In positive reappraisal, you directly alter your emotional reactions to an event by thinking about the events in more neutral or even positive terms.
Humor
When you find something humorous, you smile, laugh, and enter a state of pleasurable, relaxed excitation.
Distraction
Distraction involves doing or thinking about something other than the troubling activity or thought.
Social & cultural norms: display rules
Rules that are learned through socialization and that indicate what emotions should be shown in certain situations.