fundamentals of algorithm
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms

what does this denote
Denotes a set of elements

what does this symbol denote
empty set

what does this symbol denote
variable or value is an element of a given set

what does this symbol denote
variable or value is not a element of a given set
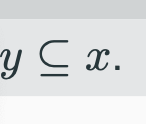
what does this subset symbol denote
variable is a subset of a given set

what does this subset symbol denote
variable is a proper subset of a given set
what does (x,y) denote
a pair of values
what does this symbol denote |x|
size of a given set or list x
what does this symbol denote y[I]
ith element of a given list where I = 0,1, |y|-1

what does this symbol denote
floor value of a given value or variable
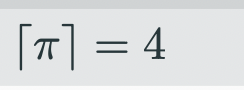
what does the ceiling symbol denote
ceiling value of a given variable or value
what does mod or % denote
modulo
what is the definition of alphabet Σ
finite non empty set whose elements are called letters
when is string y a factor of string x
when two strings exist
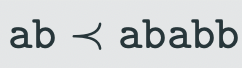
what is the Lexicographic order
strings induced by an order of letters and denoted by the same symbol
log(a) + log(b)
log(ab)
log(a) - log(b)
log(a/b)
log(n^k)
k log(n)
log(2^n)
n
2^log(n)
n
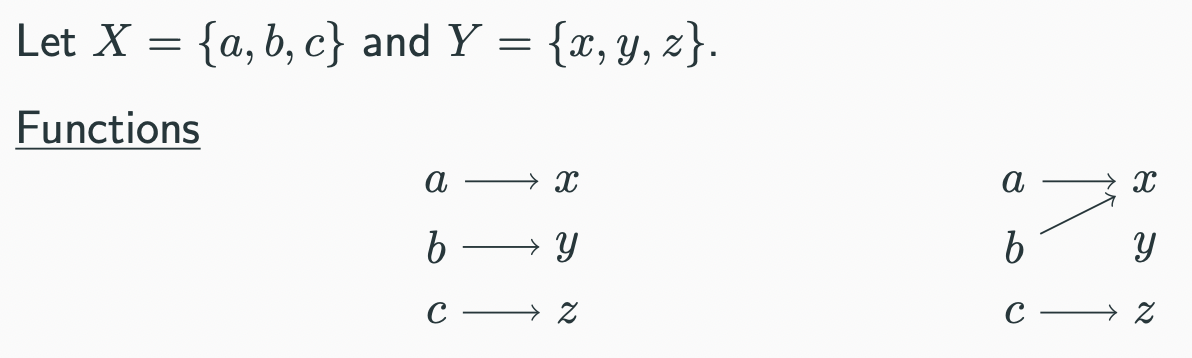
what does the function rule do
assigns each element of x to one element of y
what does space complexity change depend on
input and data structures used and size of output
what does pseudocode provide
general description of the algorithm
input and output algorithm
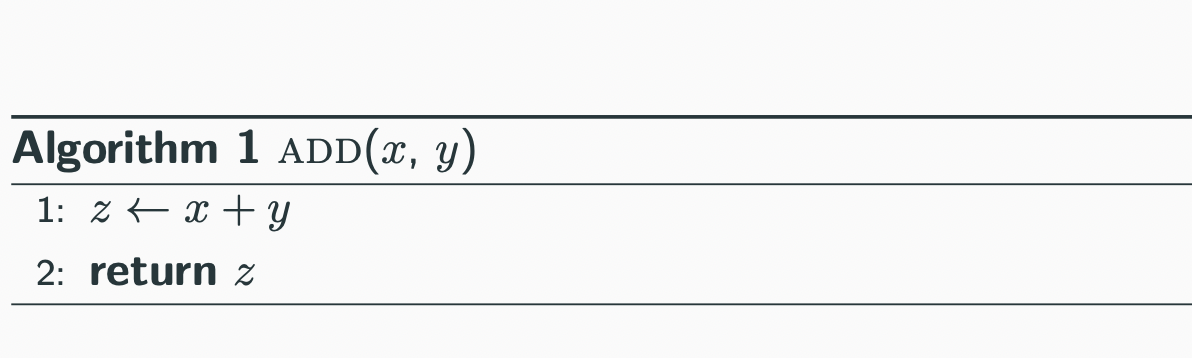
Assignment algorithm

if statement algorithm

for loop algorithm

while loop algorithm


what does Big O denote
the upper bound of the algorithm

what does big Ω (omega) denote
lower bound of the algorithm
what does big Θ denote
tight bound of an algorithm

O(1) Constant time
operation takes the same amount of time regardless of input size
O(log(n)) Logarithmic time
time grows with logarithmically with input size
O(n) Linear time
Time grows proportionately to input size
O(n log(n)) Quasilinear time
Time grows slightly faster than linear
O(n2) Quadratic time
time grows quadratically with input size
O(n3) Cubic time
time grows cubically with input size
O(2n) Exponential time
Time grows exponentially with input size
what is a P (Polynomial) problem
time complexity can be expressed as O(n^k)
what is the NP (Non-deterministic Polynomial) problem
if a solution exist its correctness can be verified in polynomial time
when is a problem considered NP-Hard
NP problems can be reduced to its polynomial time
NP-Complete
both NP and NP hard
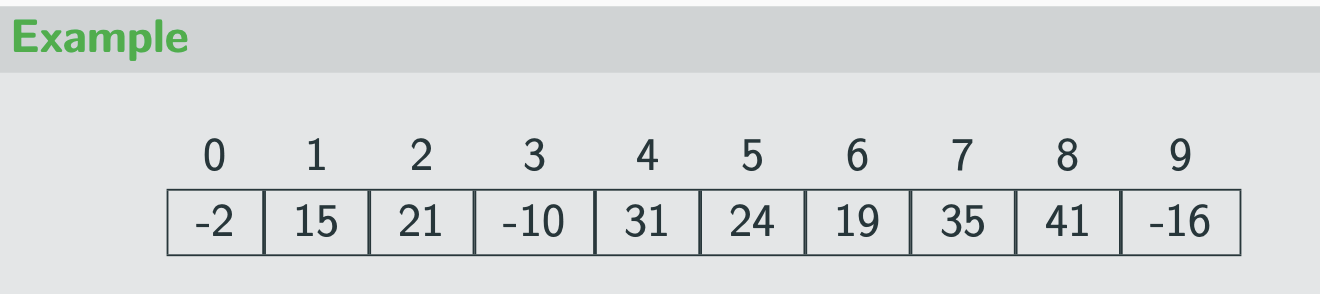
Array
sequenced collection of variable of the same type
equals(A,B)
Return true if the array A and B are equal
fill(A, x)
stores the value x in every cell of array x
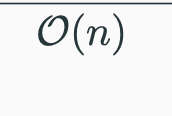
copyOf(A, n)
returns array size of n such that the first k element of this array are copied from A
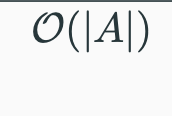
toString(A)
Returns string representation of the Array A
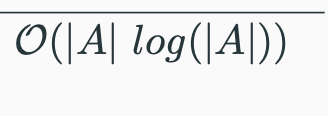
sort(A)
Sorts array based on natural ordering of its elements

binarySearch(A, x)
search the sorted array for value x returning index where its found
Stack
collection of objects of the same type which are inserted and removed

push(e)
adds element e to the top of the stack

pop()
removes and returns the top element of the stack

top()
returns top element of stack without removing it

size()
returns number of elements in the stack

isEmpty()
returns a boolean indicating weather a stack is empty

queue
collection of objects that are inserted and removed

enqueue(e)
add element e to back of the queue

dequeue()
removes and returns the first element in the queue

first()
returns the first element of the queue without removing it

size()
return the number of elements in the queue

isEmpty()
returns a boolean indicating wether the queue is empty
list
linear sequence of elements where it can be added or removed
size() (Array lists)
Returns the number of elements in their list
isEmpty() (Array List)
Returns a boolean indicating weather a list is empty
get(i) (Array List)
Returns the element of the list having index I
set(i, e) (Array List)
Replaces element at index I with e returns old element which was replaced
add(i, e) (Array List)
inserting element e into list moving all elements one index later
remove(i) (Array List)
Removes and returns all the elements at index I
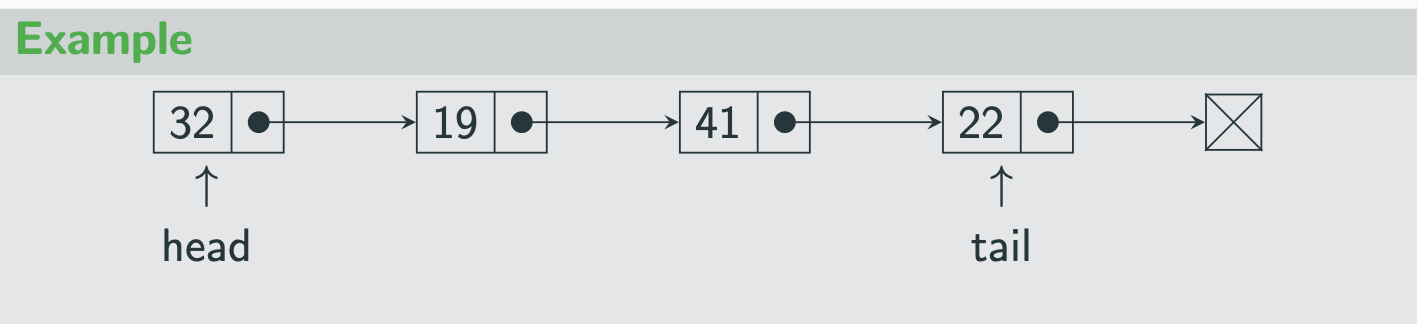
Singly linked list
collection of nodes which form a linear sequence
doubly linked list
node stores a reference the next and previous node
addFirst(e) (LinkedList Method)
insert the specified element at the beginning of the list
addLast(e) (LinkedList Method)
insert the specified element at the end of the list
getFirst() (LinkedList Method)
Returns the first element in the list
getLast() (LinkedList Method)
Returns the last element in the list
removeFirst() (LinkedList Method)
Removes and returns the first element from the list
removeLast() (LinkedList Method)
Removes and returns the last element from the list
set(I,e) (LinkedList Method)
replaces the element I with index e and replaced element
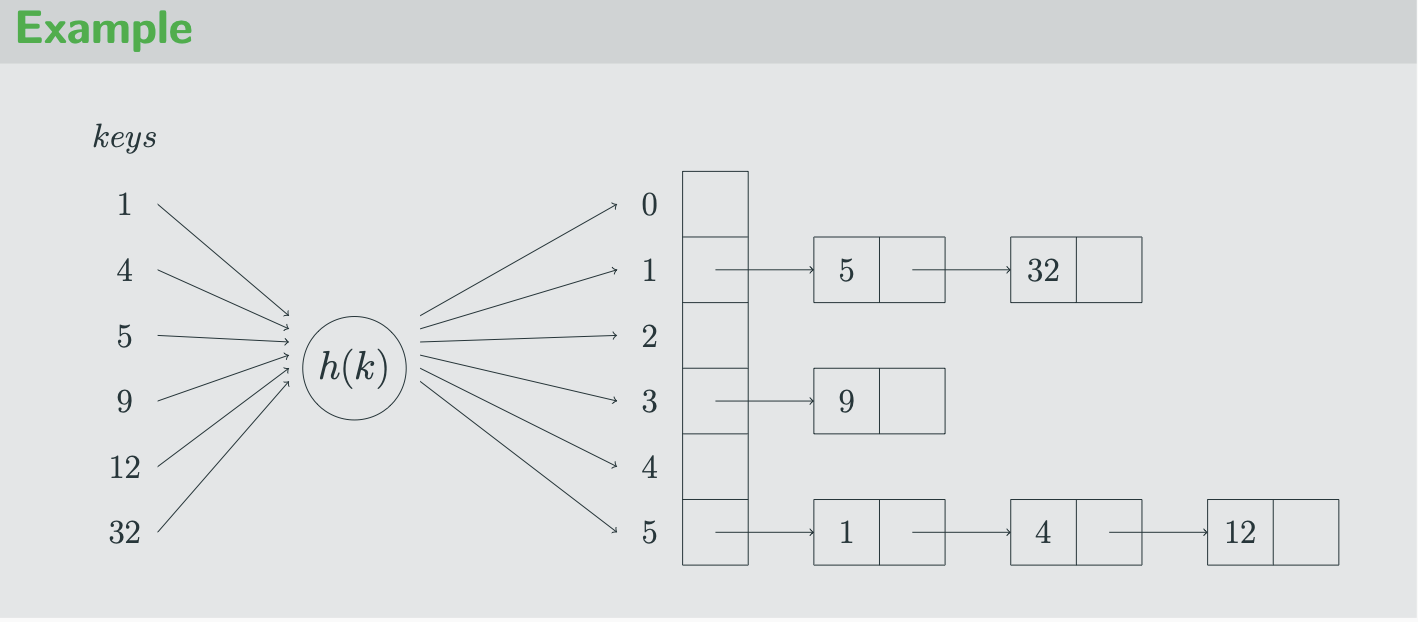
hash map
stores data in the form of keys where value pair are denoted as k and v
hash function h(k)
take key k and compute an integer
when will a collision happen
k1 = k2
what does the collision affect
insertions , deletions and searches
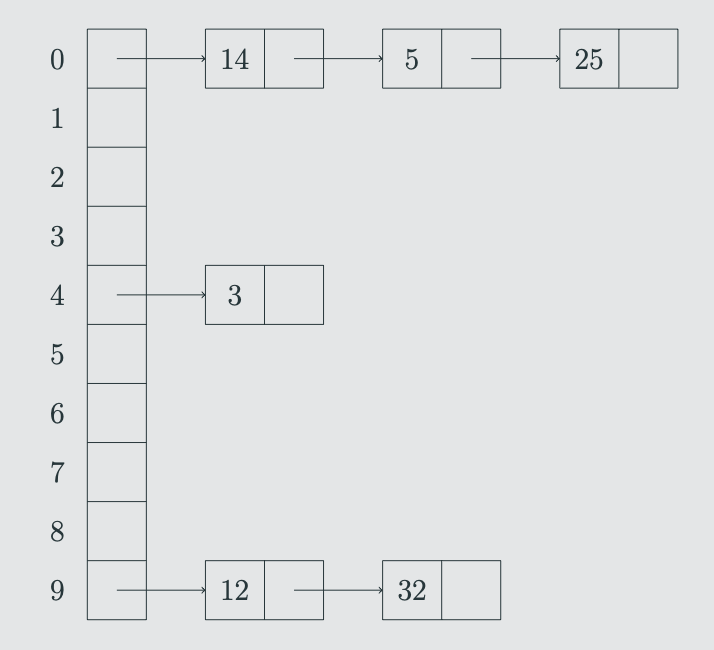
how does separate chaining solve collision issues
storing a single linked list in each index A[j]

Linear probing
is another way of dealing with collision
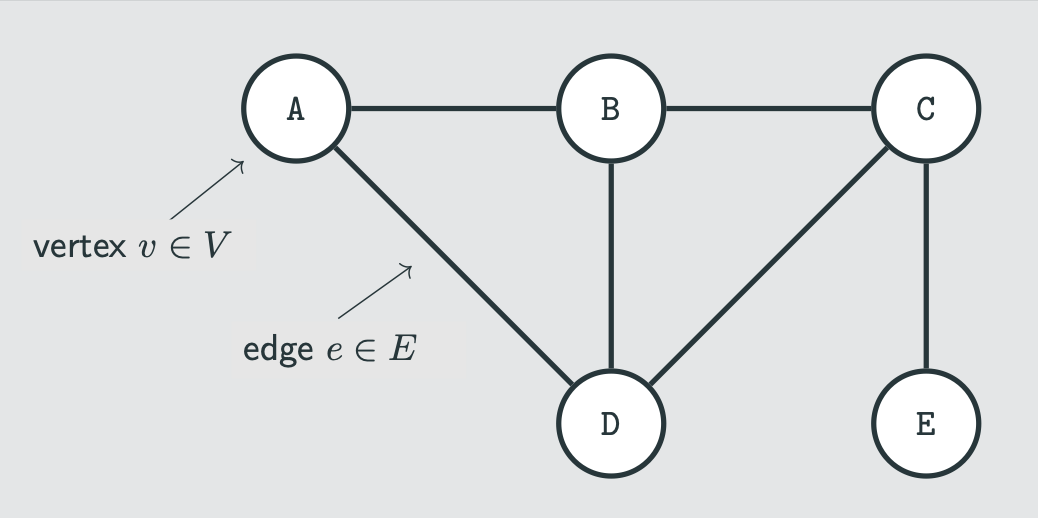
graph
finite non empty sets of points and lines
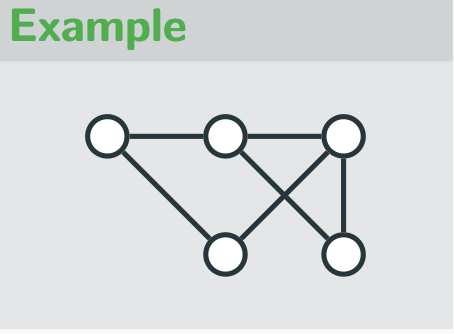
Undirected graph
edge between each vertex pair is not directed
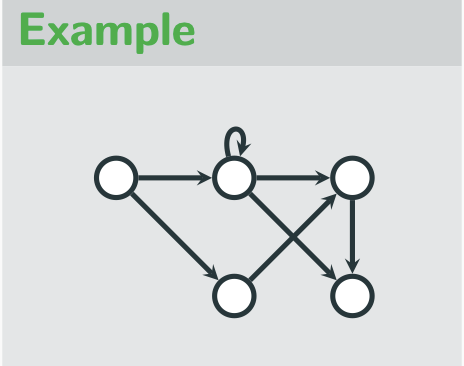
Directed graph
edge between each vertex has a direction
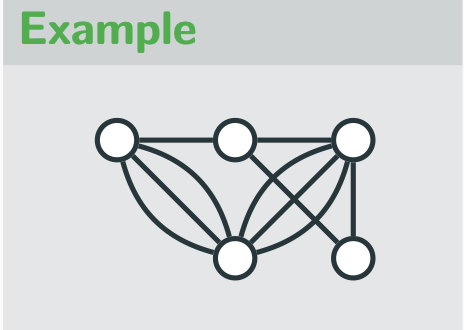
Multigraph
there is more or one edge between a pair of vertices
what is a complete graph (Kn)
simple graph with n vertices where there is an edge between every pair of distance vertices
when is a graph connected
there is a path between every pair of vertices
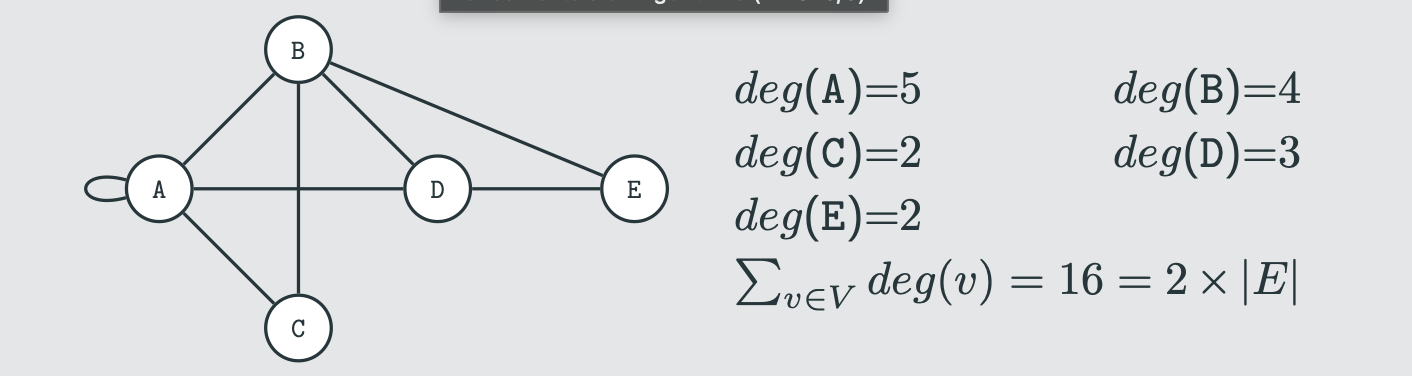
total degree
sum of degrees of all vertices
in a directed graph what is an in degree in-deg(v)
number of edges that are incoming in v
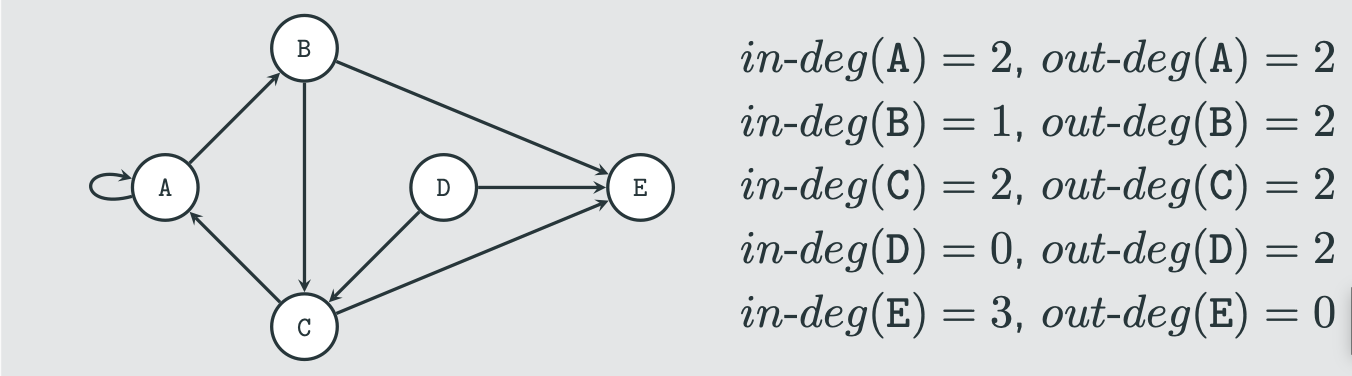
in a directed graph what is an out degree out-deg(v)
number of edges that are out coming in v
what is a circuit
path which starts and ends at the same vertex
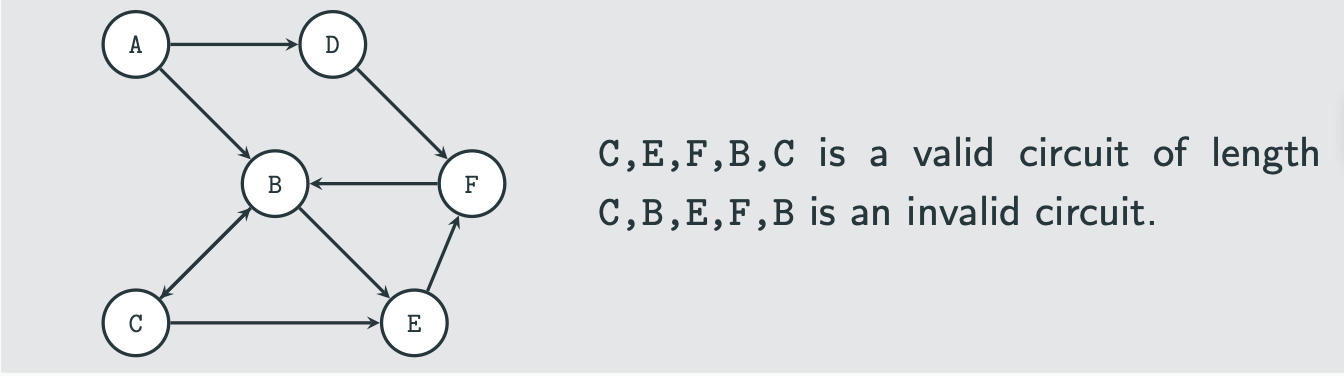
what is a cycle
circuit that contains no repeated vertices
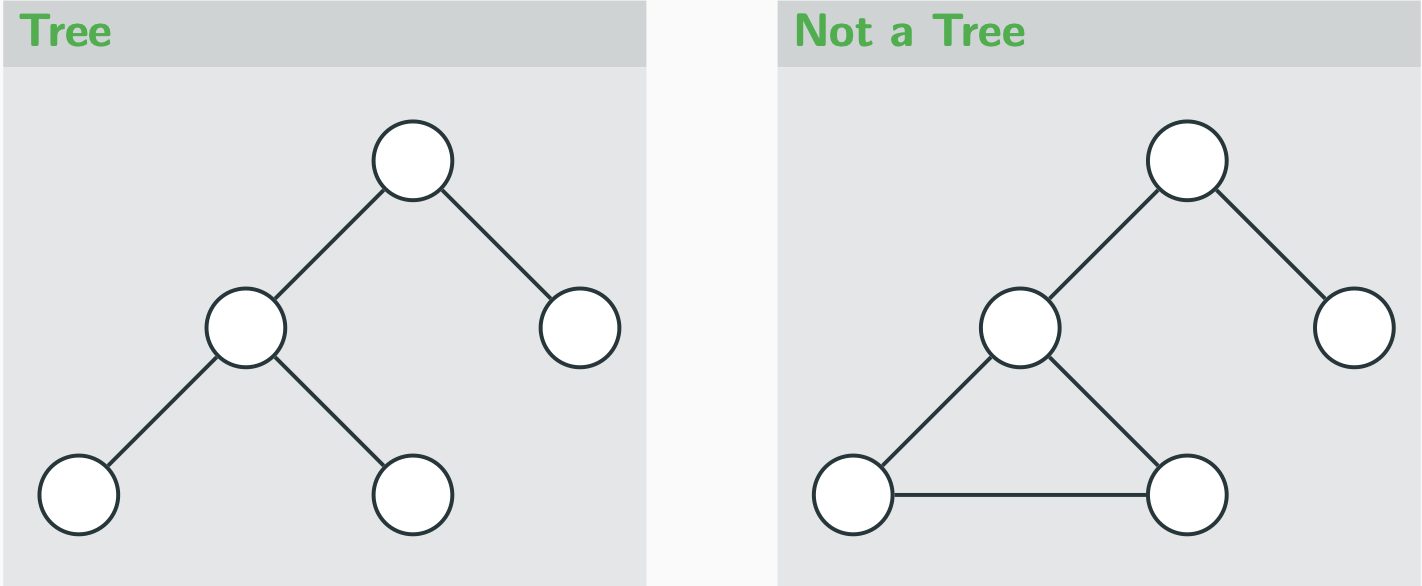
what is a tree
undirected graph that contains no cycle and is connected
Rooted trees
one vertex is specified as root
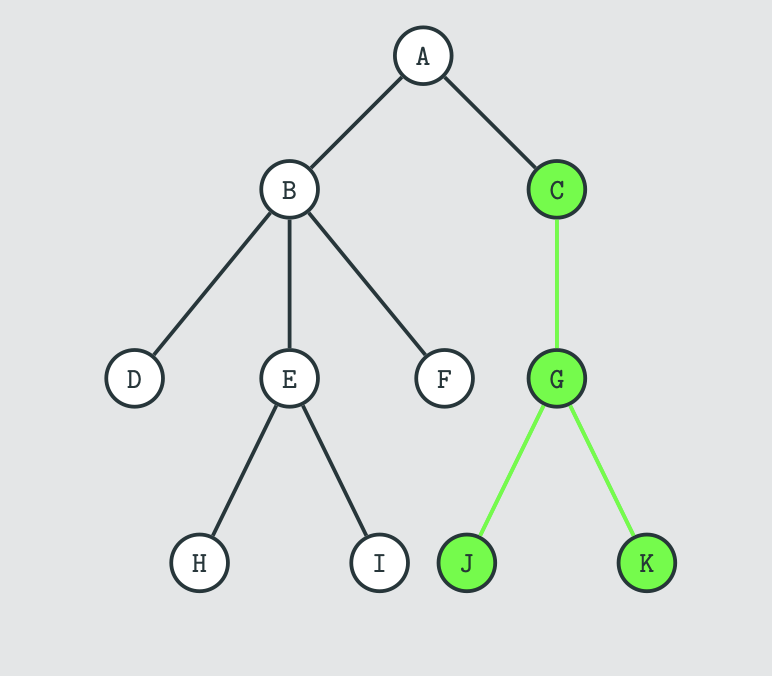
what is a subtree of tree t
tree consisting of a vertex in t and all its descendants
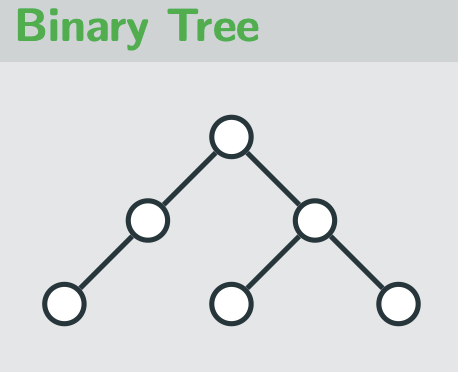
binary tree
rooted tree in which each parent has at most two children
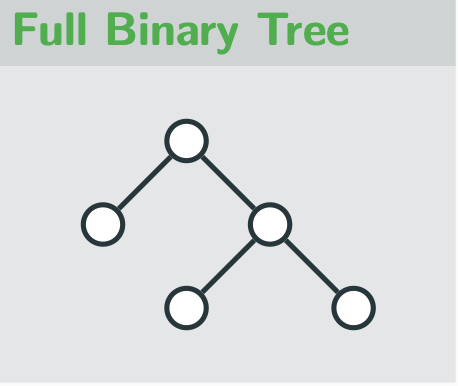
full binary tree
each parent has exactly two children
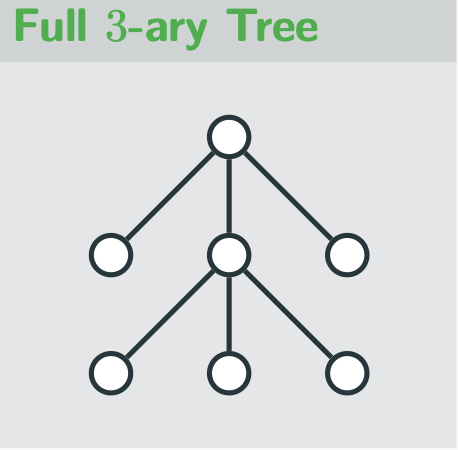
full m-ary tree
each parent has exactly m children