Kinesiology Exam 1, Kine sample questions exam 1, KIN 3304 Exam 2 Review: Upper Thorax and Extremity, Kinesiology Exam 3 Review
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Reference positions and Anatomical directions
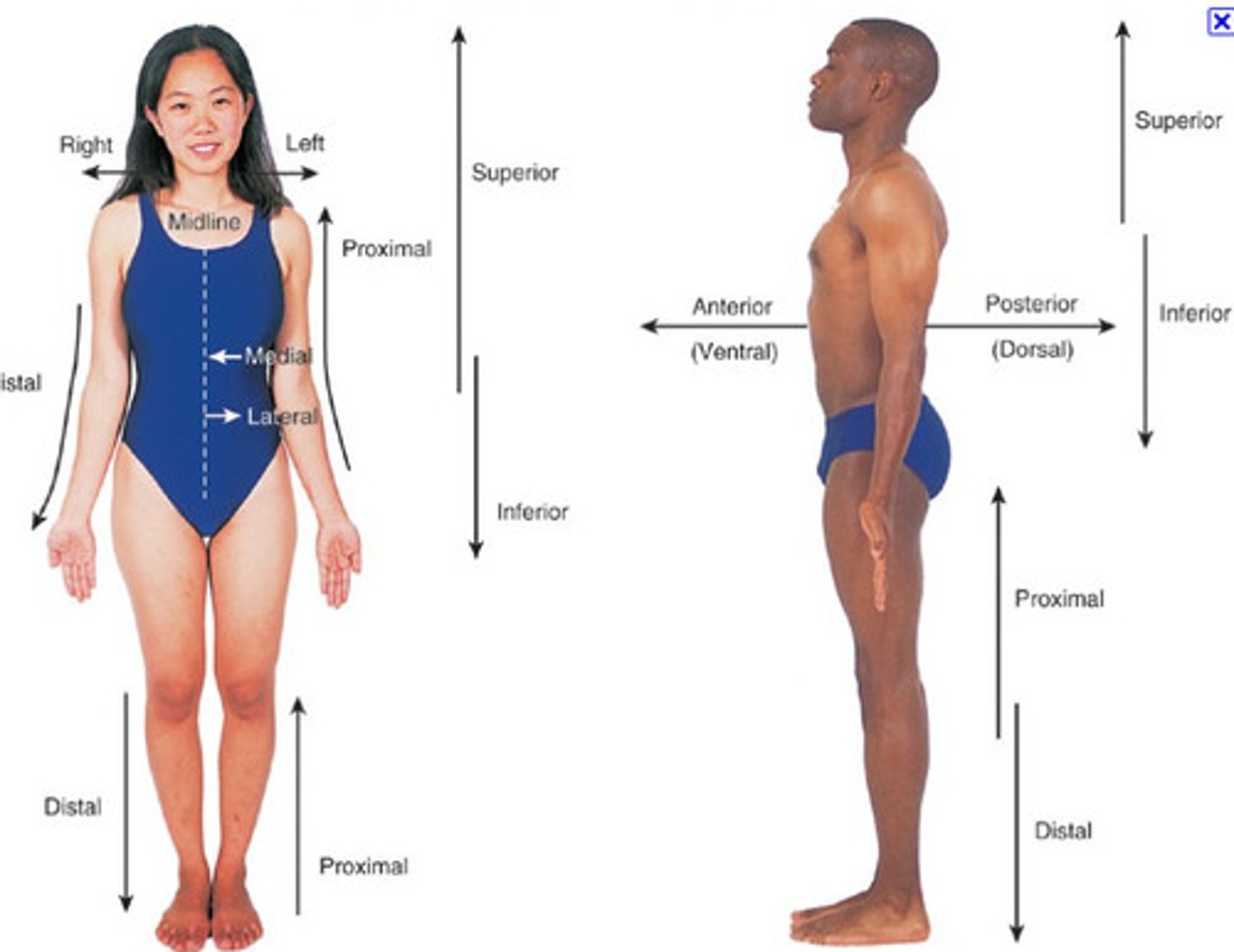
Anatomical directions
deep
superficial
prone
supine
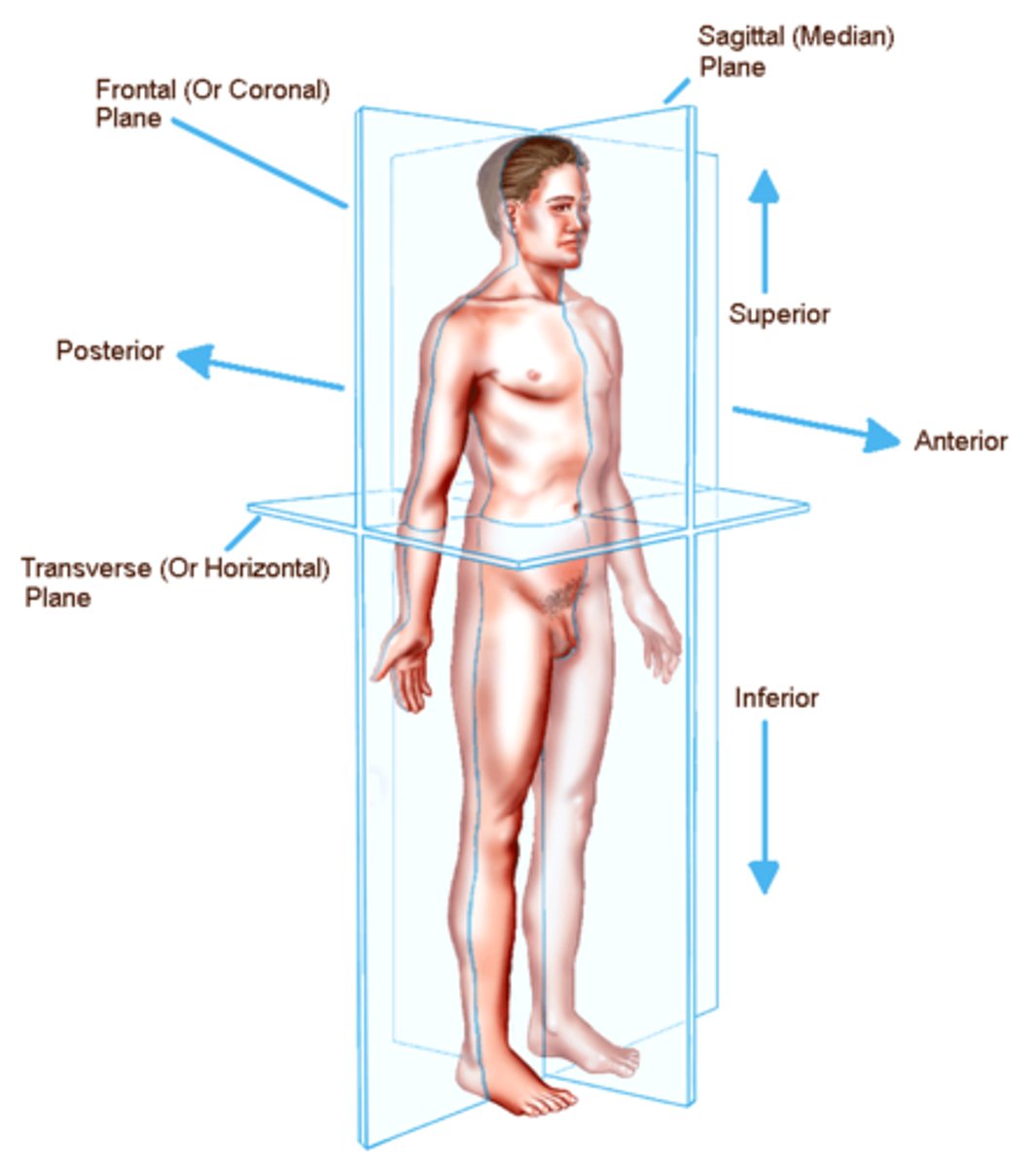
Planes of motion
-cardinal
-sagittal(anteroposterior)
-frontal(lateral)
-transverse(horizontal)
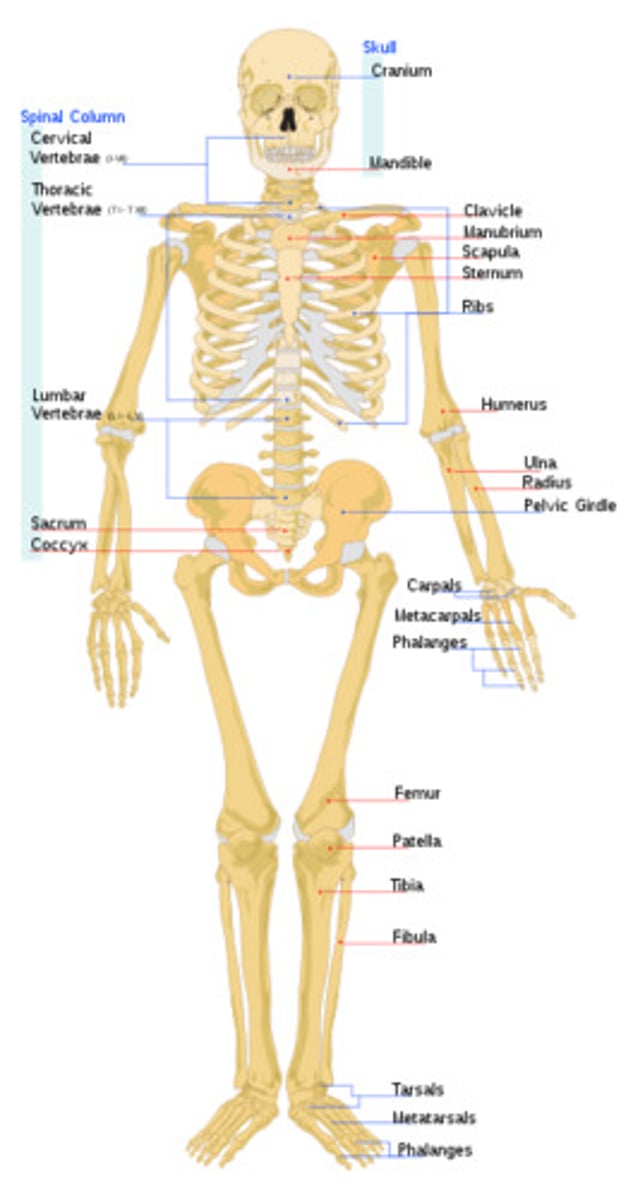
Skeletal system
-axial
-appendicular
Bone markings: Processes
condyle
epicondyle
head
line
trochanter
tuberosity
tubercle
spine or spinous
process

Bone markings: Cavities
facet
foramen
fossa
sulcus or groove
Types of joints
-synarthrodial
-amphiarthrodial
-diarthrodial
Diarthrodial joints
synovial joints (structural)
-joint capsule
six types: each has different type of bone arrangement
-arthrodial(plane)
-hinge(ginglymus)
-pivot(trochoidal)
-condyloid
-saddle(sellar)
Three degrees of freedom:
-ball-and-socket(enarthrodial)
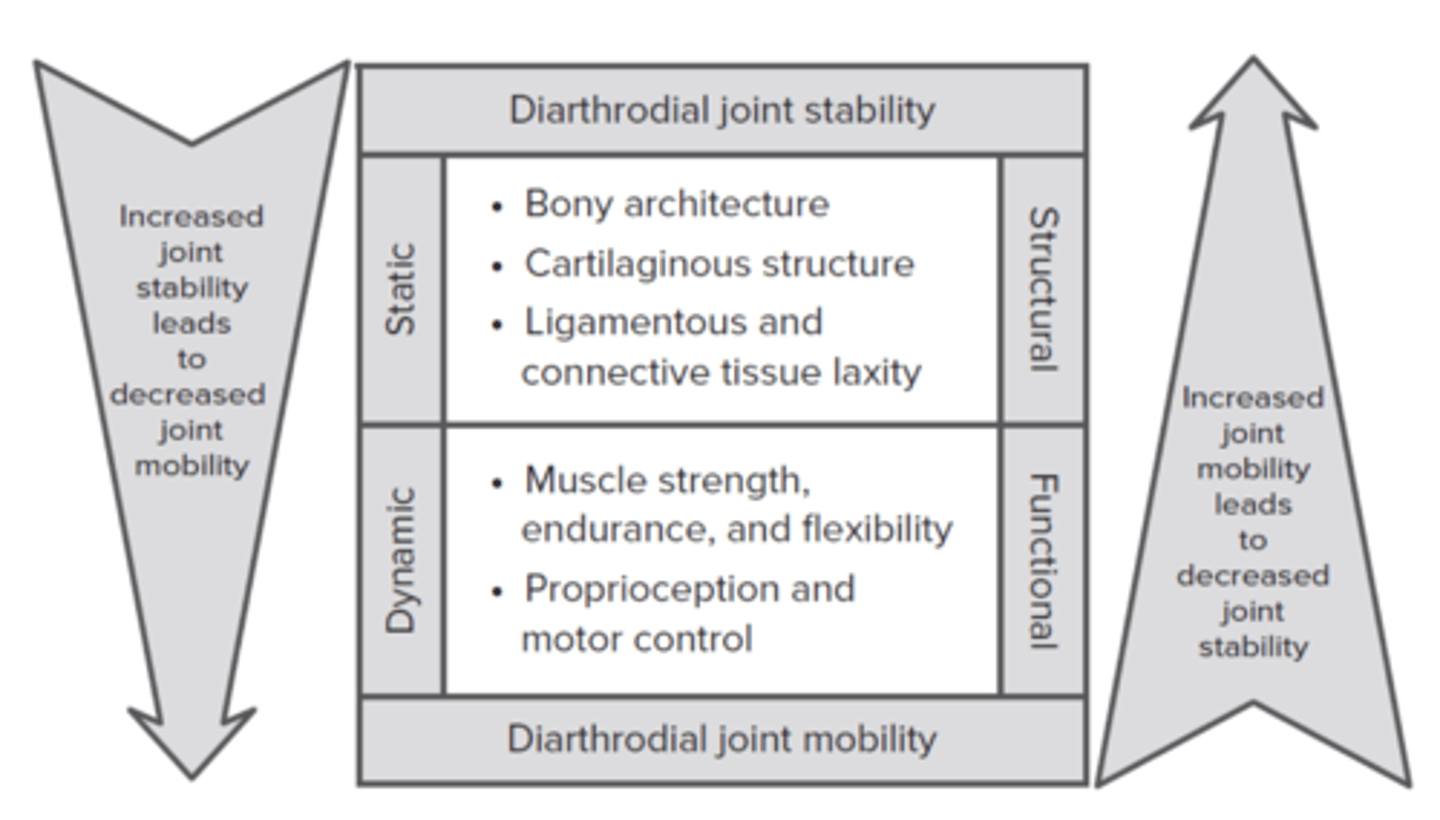
Diarthrodial joint stability and mobility
five major factors affect the total stability and mobility of a joint
Movement in joints
-range of motion:
abduction
adduction
flexion
extension
rotation
diagonal abduction
diagonal adduction
circumduction
Neuromuscular Fundamentals-Ch. 2
skeletal muscle
-aggregate muscle action:
-function:
Muscle Nomenclature
muscles are usually names based on:
-visual appearance
-anatomical location
-points of attachment
muscle nomenclature
-function:
flexor:
extensor:
adductor:
Abductor:
Muscle fiber arrangement: 2 major types of fiber arrangements
1. Parallel
2. Pennate
Tying muscles to joints
-insertion
-origin
muscle contraction:
-contraction
-isometric contraction
-isotonic contraction
-concentric
-eccentric
You are attempting to extend your knee maximally. What strategy do your knee extensors (quadriceps) use to increase the amount of muscle tension?
Activate motor units with a greater number of muscle fibers AND increase the number of motor units activated
Tension development is minimized in muscle fibers that are ______ of their resting length
shortened to around 60% OR increased beyond 130%
Which of the following statements best describes the fulcrum?
It may occur in any orientation relative to the force application and the resistance
Which of the following levers would be best to use to move a specific object if your objective was to increase speed of the object's movement?
a third-class lever
In the scenario where the radius of the wheel is greater than the radius of the axle, then the _____ has the mechanical advantage
wheel
When determining possible muscle action, which of the following is NOT one of the main considerations to bear in mind?
Consider the movement resulting from moving tendon of origin towards tendon of insertion
The length of the muscle during its contraction is a factor in
the amount of active tension the muscle may develop
Which of the following is a characteristic for which skeletal muscles are typically named?
size
How much muscle tension is required to balance a 5 newton resistance, given that the distance between the weight and the joint is 20 centimeters and the distance between the joint and the muscle tendon of insertion is 10 centimeters?
10 newtons
Which of the following is a function of stabilizer muscles?
Maintain a stable position for efficient movement
A muscle that assists the agonist in performing a movement is called a:
synergist
When a muscle contracts but does not change in length, this is known as:
Isometric contraction
Which of the following structures provides static stability to a diarthrodial joint?
Ligaments and cartilage
Which of the following best describes a second-class lever?
The load is between the fulcrum and the effort
In a third-class lever system, what is the mechanical disadvantage?
More force is required than the resistance force
If the resistance arm is twice as long as the force arm, what is the mechanical advantage (MA)?
2
Which of the following statements correctly defines reciprocal inhibition?
The inhibition of the antagonist when the agonist contracts
What is the primary proprioceptor involved in the stretch reflex?
Muscle spindles
Which of the following terms refers to the point at which an action potential will always generate a muscle contraction?
Threshold stimulus
A basketball player is performing a jump shot.
Question: During the upward phase of the jump, what type of contraction is occurring in the quadriceps?
concentric
You are performing a squat.
Question: What type of muscle contraction occurs in the quadriceps as you lower into the squat position?
eccentric
A baseball pitcher is throwing a fastball.
Question: Which type of lever system is primarily at work at the elbow joint during the throwing motion?
third class
A person is doing a bicep curl with a dumbbell.
Question: As they slowly lower the weight back to the starting position, which type of muscle contraction occurs in the biceps brachii?
Eccentric
A football player is tackled while running forward.
Question: If their hamstring muscles are unable to control the rapid stretching of the muscle, what type of reflex might be triggered?
stretch reflex
A gymnast is holding a handstand.
Question: What type of contraction is occurring in the shoulder muscles to maintain stability?
Isometric
A cyclist is pedaling uphill and must use more force to push the pedals down.
Question: What strategy does the body use to increase the force of contraction in the quadriceps?
Both a and b
A person is pushing a heavy box across the floor.
Question: Which type of lever system is primarily at work in the ankle joint as they push off the ground?
second class
A rock climber is gripping onto a ledge and holding their body weight.
Question: Which type of contraction is occurring in the finger flexor muscles?
isometric
A soccer player is kicking a ball.
Question: What is the main function of the antagonist muscles in the kicking leg during the follow-through phase of the kick?
decelerate the movement
A sprinter is pushing off the starting blocks at the beginning of a race.
Question: What type of contraction is occurring in the gastrocnemius during the push-off phase?
concentric
A gymnast lands from a vault and bends their knees to absorb the impact.
Question: What type of contraction occurs in the quadriceps as they control the landing?
eccentric
A weightlifter is holding a barbell overhead in a locked-out position.
Question: What type of contraction is occurring in the deltoids?
Isometric
A person is performing a sit-up.
Question: What type of contraction occurs in the abdominal muscles during the upward phase?
concentric
A soccer goalie jumps sideways to block a shot.
Question: Which type of movement primarily occurs at the hip joint during the jump?
abduction
A person is using a shovel to lift dirt.
Question: What type of lever is at work at the elbow joint during the lifting motion?
third class
A dancer is standing on their toes in a ballet pose.
Question: What type of lever system is at work in the ankle joint?
second class
A construction worker is using a crowbar to pry open a wooden crate.
Question: What type of lever is being used?
first-class
A rower is pulling the oar through the water.
Question: Which of the following best describes the mechanical advantage of this movement?
It sacrifices force for speed
A person is turning a screwdriver by holding the handle.
Question: What provides the mechanical advantage in this scenario?
the length of the handle
Question: If the person applies force 30 cm from the bolt and the resistance arm (distance from the bolt to the force applied) is 10 cm, what is the mechanical advantage (MA) of this lever system?
3
Question: If the force arm (distance from the wheel to where the person applies force) is 50 cm and the resistance arm (distance from the wheel to the load) is 25 cm, what is the MA of the wheelbarrow?
2
Question: If the distance from the elbow (fulcrum) to the biceps insertion (force arm) is 5 cm, and the distance from the elbow to the dumbbell (resistance arm) is 30 cm, what is the MA of the arm in this movement?
0.17
Question: If the child is sitting 2 meters from the fulcrum and the adult applies force 1 meter from the fulcrum on the opposite side, which type of lever is this?
first class
Question: Which type of lever is being used at the ankle joint during the upward phase of the movement?
second class
Question: Which type of lever system is created by the fingers when using chopsticks?
third class
Scapula
Shoulder blade, connects upper limb to torso.
Clavicle
Collarbone, connects arm to body.
Humerus
Upper arm bone, connects shoulder to elbow.
Ulna
Forearm bone, located on the inner side.
Radius
Forearm bone, located on the outer side.
Sternoclavicular Joint
Movement: slight movement in all three planes.
Saddle joint connecting sternum and clavicle.
Acromioclavicular Joint
Joint between acromion and clavicle.
Scapulothoracic Joint
Movement in 3 planes: moves with the AC and SC joints.
Functional joint between scapula and thorax.
Glenohumeral Joint
Ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder (shoulder join and shoulder girdle work together)
Humeroulnar Joint
Movement: flexion and extension of the form. Hinge joint between humerus and ulna.
Radioulnar Joint
Movement: pronation and supination of the forearm. Pivot joint between radius and ulna.
What is the relationship between movements at the shoulder joint and the shoulder girdle?
The shoulder joint and girdle coordinate to increase arm movement range and stability by adjusting scapular position during motion.
Could you identify a movement of the scapulothoracic, shoulder, elbow, and radioulnar joint from an image?
Shoulder Girdle: Levator Scapulae
Origin: Upper vertebrae
Insertion: Scapula
Action: elevation of shoulder girdle
Shoulder Girdle: Concentric Contraction
Muscle shortens while generating force.
Shoulder Girdle: Elbow Flexion
Bending of the elbow, decreasing angle.
Shoulder Girdle: Elbow Extension
Straightening of the elbow, increasing angle.
Shoulder Girdle: Shoulder Abduction
Movement away from the body in the frontal plane.
Shoulder Girdle: Shoulder Adduction
Movement towards the body in the frontal plane.
Shoulder Flexion
Raising arm forward in the sagittal plane.
Shoulder Extension
Moving arm backward in the sagittal plane.
Trapezius Muscle
Muscle responsible for shoulder girdle movements.
Diagonal Abduction
Movement of arm away from body at an angle.
Coracobrachialis Muscle
Assists in flexion and adduction of the shoulder.
Bony Landmarks of Humerus
Includes medial/lateral epicondyles and trochlea.
Identify the type of joint (e.g., hinge, ball and socket, etc.) of each of the following, aswell as the bony landmarks involved in the articulation of each joint
Atlanto-occipital joint
Type of Joint: Condyloid joint
Bony landmarks: occipital condyles of the occipital bone and the superior articular facets of the atlas (C1 vertebra)
Hip Joint
Type of Joint: Ball and socket joint
Bony Landmarks: head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis (ilium, ishium and pubis)
Intervertebral joints
Two types:
1) Between vertebral bodies
Type of joint: Cartilaginous joint
Bony landmarks: adjacent vertebral bodies with the intervertebral discs in between
2) between articular processes (facet joints)
Type of joint: Plane joint
Bony landmarks: inferior articular process of one vertebra and superior articular process of the vertebra below
Metatarso-phalangeal joints (MTP)
Type of joint: condyloid joint
Bony landmarks: heads of the metatarsals and bases of the proximal phalanges
patellofemoral joint
Type: Plane joint
Bony landmarks: patellar surface (trochlear groove) of the femur and the posterior surface of the patella
Talocrural joint (ankle joint)
Type of joint: Hinge joint
Bony Landmarks: distal ends of the tibia and fibula (forming the mortise) and the trochlea of the talus
Tibiofibular Joints
There are two:
1) Proximal tibiofibular joint
Type of joint: Plane joint
Bony landmarks: head of the fibula and lateral condyle of the tibia
2) Distal tibiofibular joint
Type of joint: plane joint
Bony landmarks: distal ends of tibia and fibula
Tibiofemoral joint (knee joint)
Type of joint: Modified hinge joint (allows some rotation in addition to flexion/extension)
Bony landmarks: condyles of the femur and the condyle of the tibia
Place the following bones in order of the transfer of body weight from the midsection tothe ground when standing up right (some bones may not be named): Calcaneus, Femur,Fibula, Patella, Pelvic Girdle, Talus, Tibia
1) Pelvic Girdle- receives weight from the vertebral column and transmits it to the lower limbs
2) Femur- the thigh bone; connects the pelvis to the lower leg bones
3) Tibia- the main weight-bearing bone of the lower leg (not the fibula)
4) Talus- the topmost bone of the foot that receives weight from the tibia
5) Calcaneus- the heel bone; receives weight from the talus and transmits it to the ground
Not in this: Patella (kneecap)- not involved in weight transfer-it protects the knee joint and improves leverage for the quads muscle
Fibula- provides muscle attachment and lateral stability but carries very little weight
The _____________________________forms the 'ball' and the _______________ forms the 'socket' of the hip joint
head of the femur; acetabulum of the pelvis
The three boney segments that form the pelvic girdle are
ilium, ishium and pubis