Pregnancy + Lactation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
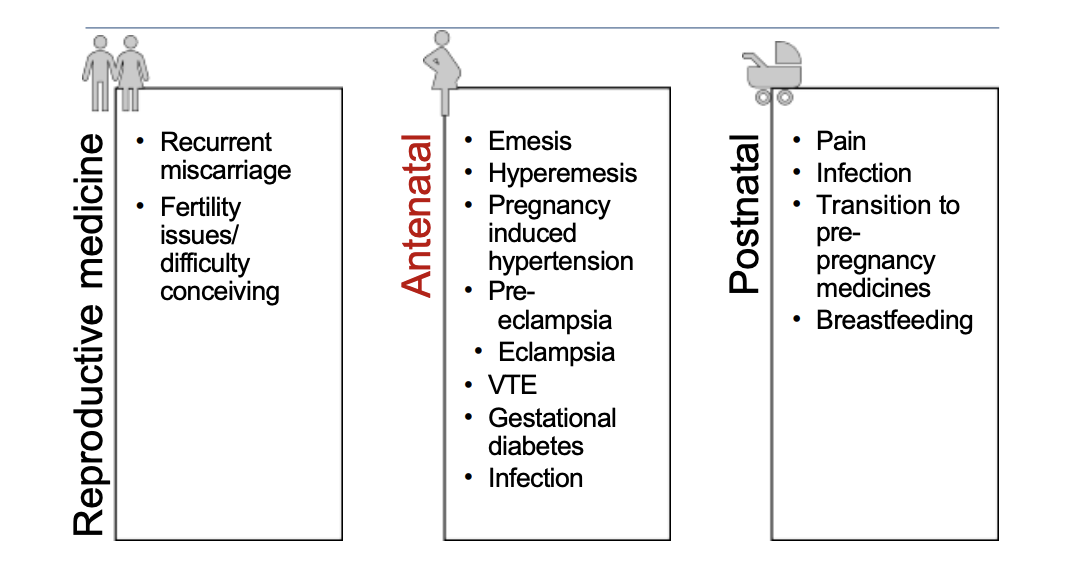
What are the three areas of medicines in pregnancy?
Emesis - aka morning sickness - can happen any time of day/24 hours a day
Hyperemesis - uncontrollable N+V - may be admitted to hospital for IV fluids
If extreme - TPN potentially
Pregnancy induced HTN - didn't have before pregnancy
Can progress to pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia - rare - but serious - stage before eclampsia
Eclampsia - can have seizures during pregnancy - dangerous for foetus
Expectant mother may have to undergo emergency C-section
VTE - risk of developing blood clot e.g., DVT - higher risk in pregnancy
Gestational diabetes - e.g., due to hormones in placenta
Insulin resistance as pregnancy progresses
Usually tested with oral glucose tolerance test
Usually resolves post pregnancy - as hormonal
Increased risk of developing T2DM later in life/post-pregnancy
Important to manage - e.g., diet + exercise and/or medication
Infection - amnionitis (infection in the amniotic fluid)
Monitor infection markers
Postnatal:
Pain - e.g., tear, stitches, C-section etc.
When is term?
37 weeks
What are commonly used medicines in pregnancy?
Folate/folic acid - reduces risk of neural tube defects in developing foetus
Advised in first trimester (esp. first 12 weeks)
Vitamins - esp. vitamin D.
Also multivitamins (iron can be in these)
Iron - may have dilutional anaemia during pregnancy
Aspirin - if have risk of pre-eclampsia or other conditions e.g., migraines (since other meds may not be safe)
Metformin and/or insulin
Labetalol + nifedipine - for HTN in pregnancy
Anti-sickness, antacids, PPIs - for GI symptoms during pregnancy
Vaccinations - may be seasonal e.g., flu and COVID
Whooping cough + RSV vaccine recommended - antibodies pass onto the baby - baby protected - when gets to about 8, 12, 16 weeks - start receiving own vaccinations after this point
What is teratogenicity?
The ability of a drug/ agent to cause foetal abnormalities or deformities.
teratogens cross placenta
directly or indirectly cause structural abnormalities in foetus or child after birth
may not be apparent until later in life
Foetal response to a teratogen depends on dose, route, timing of exposure, genetic and environmental factors, number of concomitant drugs.
dose dependent teratogen = carbamazepine (higher dose = high risk to foetus)
E.g. thalidomide, alcohol, chemicals, some infections
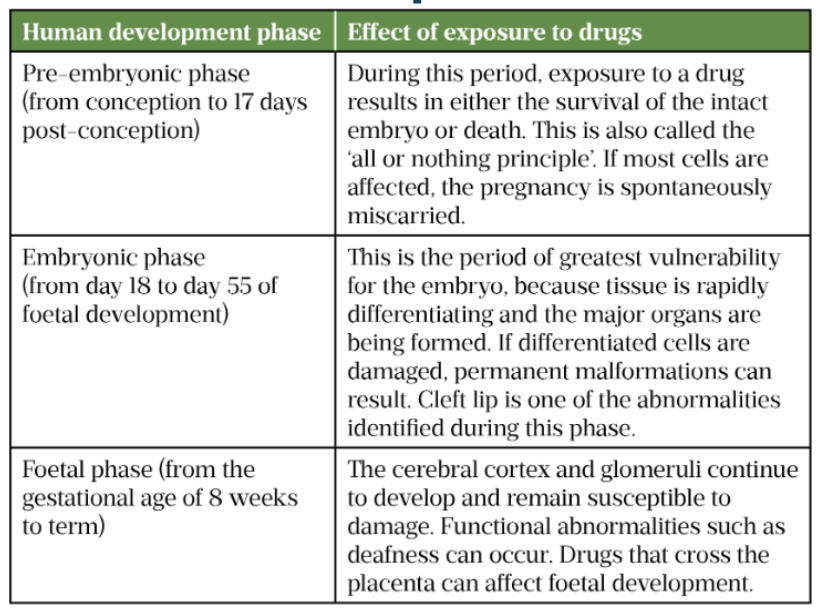
What are the phases in human development?
Pre-embryonic:
First few weeks
Harmful exposures of teratogenic medications - interfere with embryo ability to attach to uterus - greatest risk of miscarriage (all or nothing period)
Embryonic phase
Up to ~8 weeks of foetal development
Greatest vulnerability
Foetal phase:
8 weeks to rest of term
When are medicines generally avoided in pregnancy?
Generally advise AVOID using medicines in first trimester where possible.
Structural defect risk.
2nd + 3rd trimester - growth + functional defects risk.
Meds even during labour/end of pregnancy
Can affect neonate after delivery.
E.g., withdrawal effects with opioids.
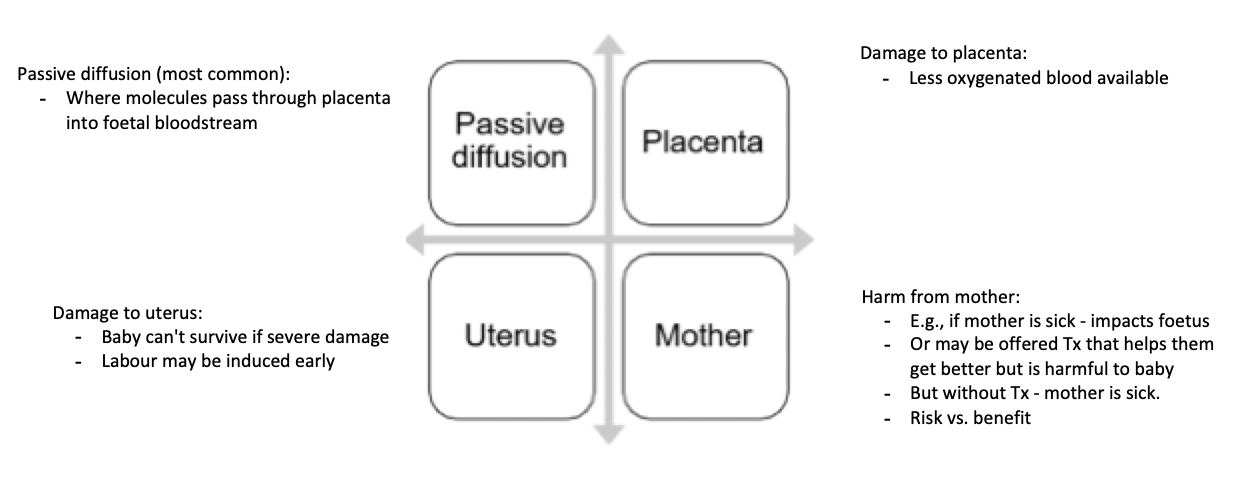
What properties of drugs allows them to cross the placenta?
Non-ionised, lipid-soluble drugs (e.g. labetalol) will cross into the placenta, in preference to more polar, ionised, hydrophilic compounds (e.g. atenolol)
High MW drugs tend not to cross placenta (e.g. insulin, heparin), but there are exceptions (e.g. infliximab)
N.b. some drugs do not cross placenta but can still cause harm e.g. by causing vasoconstriction of placental vasculature
constricts blood supply - needed for foetal growth for nutrients + oxygen for the baby
What is some potential harm in pregnancy (e.g., conditions)?

What are the mechanisms of harm?
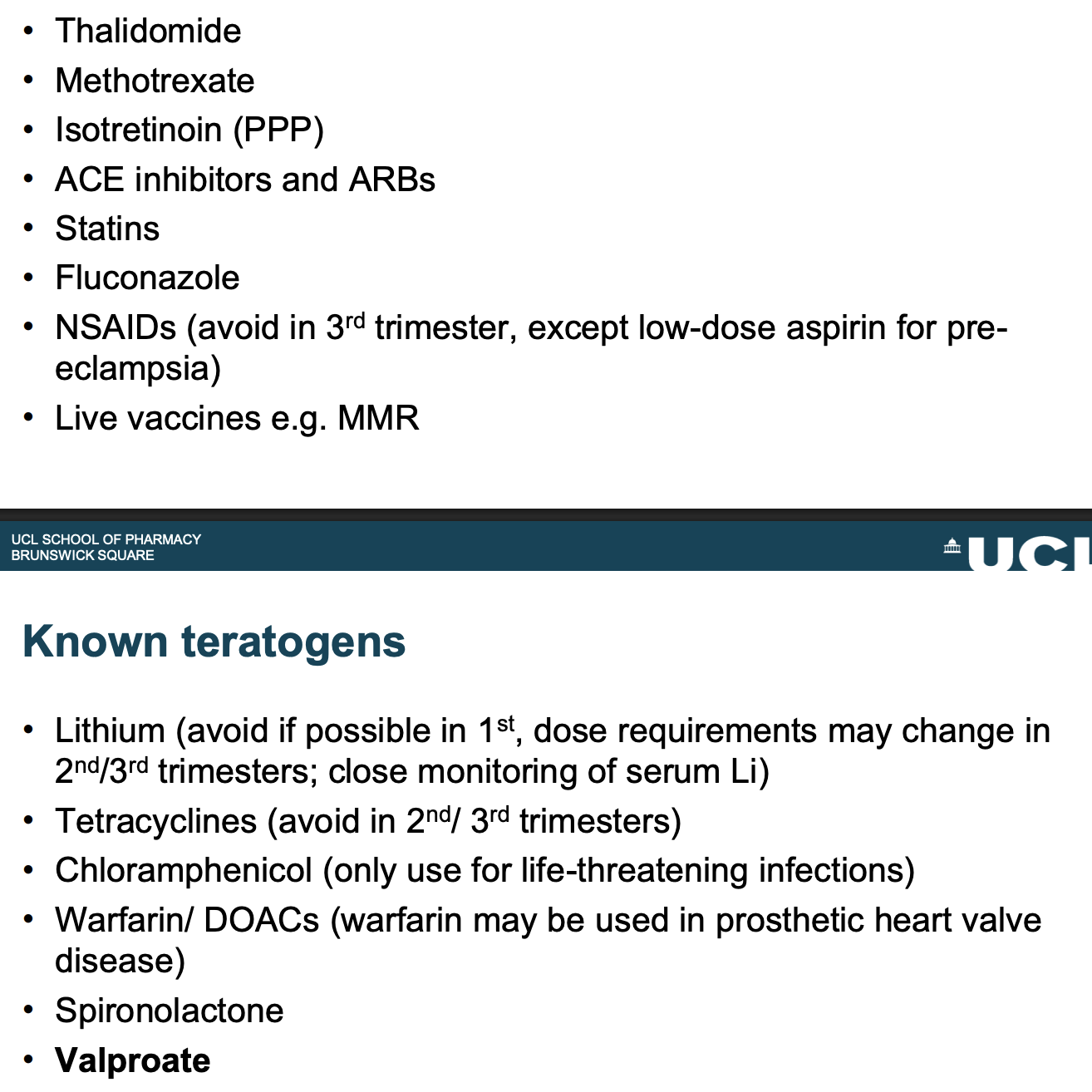
Give examples of known teratogens?
Tetracyclines - can affect teeth and foetal bones
Some teratogens - benefit may outweigh risk
What update has there been on valproate (i.e., requirements)?
Negative pregnancy test - monthly basis
Must meet PPP requirements
Annual review - to explain risks
Packs have warning sticker
Annual risk acknowledgement form - must sign this
Advised potential infertility risk in men
Two specialists required to initiate valproate in male or female pts that are younger than 55 years old
Risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in babies where father was on valproate - effective contraception recommended during and for 3 months after Tx has stopped
Inform pts to not stop taking without specialist advise - risk of epilepsy or bipolar disorder if suddenly stop
How does absorption change in pregnancy? Effect?
Think about effect on prodrugs - form of ionisation may need to change for them to turn into the active drug wanted.
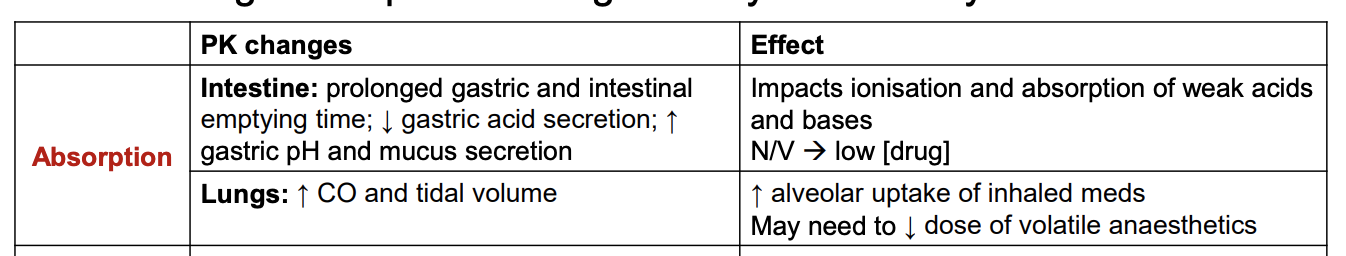
How does distribution change in pregnancy? Effect?
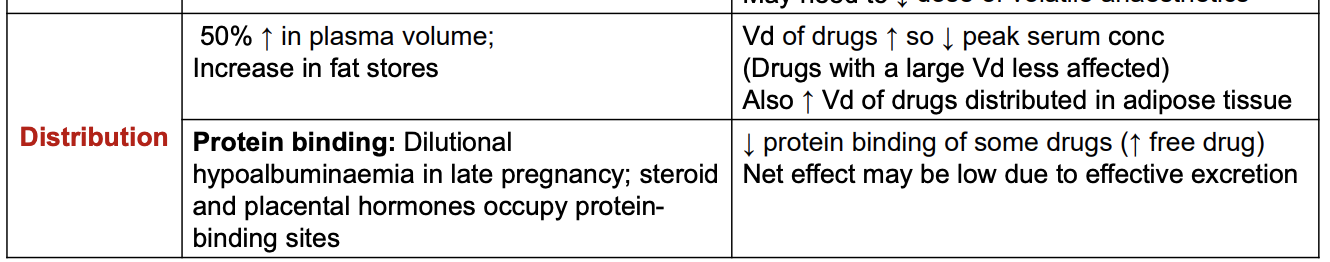
How does hepatic metabolism and elimination change in pregnancy? Effect?
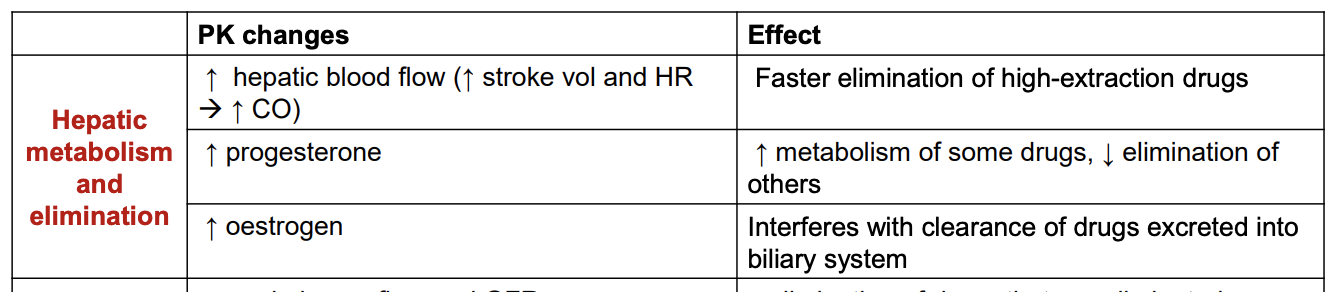
How does renal elimination change in pregnancy? Effect?

What should be done to doses changed post-delivery?
Adjust doses back post-delivery.
How long does effective contraception (± barrier methods) need to be used for cytotoxic agents before planning?
During exposure until treatment is finished
For cytotoxic agents, usually wait 2 spermatogenic cycles (6 months)
Cyclophosphamide (3 months), rituximab (12 months)
What questions should be asked to a pregnant/planning pregnancy patient when information gathering?

What are the key principles for medication use in pregnancy?

How should risk vs. benefit be weighed in pregnancy?

What should be mentioned when counselling on medication in pregnancy?
Potential consequences of using a medicine during pregnancy?
Likely benefits of treating the maternal condition and risks if not treated?
How likely the woman and her child are to be affected?
What can be done to manage any risks?
What are the benefits of breastfeeding?
WHO recommends exclusive BF for first 6 months
With supplemental BF continuing for 2 years and beyond
Formula can be hard to obtain at times/expensive
Composition of breastmilk changes based on babies needs
If mother or baby exposed to infection - milk produced during BF will have more antibodies
Or e.g., composition incl. melatonin in BF - helps babies during sleep during night feed.
Reduces risks of allergies developing

What are the issues with breastfeeding?
Can make it more difficult for babies to breastfeed.
What is the composition of breastmilk?
“ a suspension of fat droplets in an aqueous phase containing proteins, lactose and electrolytes”
Medicines can be present in:
Lipid phase
Aqueous phase
Bound to milk proteins
Composition of milk changes with:
Duration of feed
Time of day
Needs of baby
Why do we need to look at medicines in lactation?

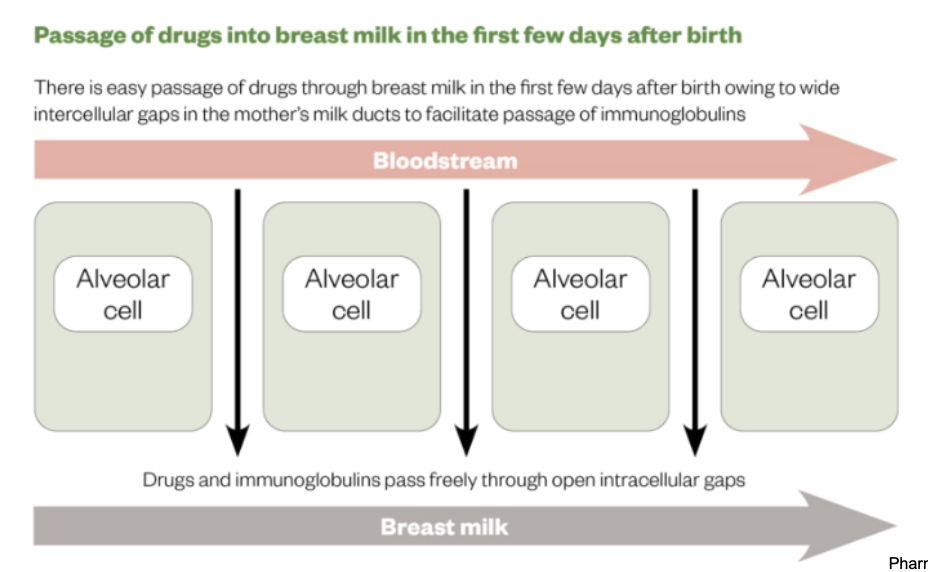
Explain the pharmacokinetics in lactation in the first few days after birth?
Reason - to protect baby from infection - it is a way of passing on immunity
Also means medications enter from bloodstream into breastmilk more easily.
Explain the pharmacokinetics in lactation after the first few days after birth?
After few days
Gaps start to close
Harder for meds to pass membrane + enter breast milk
Explain how other pharmacokinetics are affected in lactation?
Try choose shorter acting medicines - to reduce toxic effect - as neonate kidneys not well functioning yet right after birth
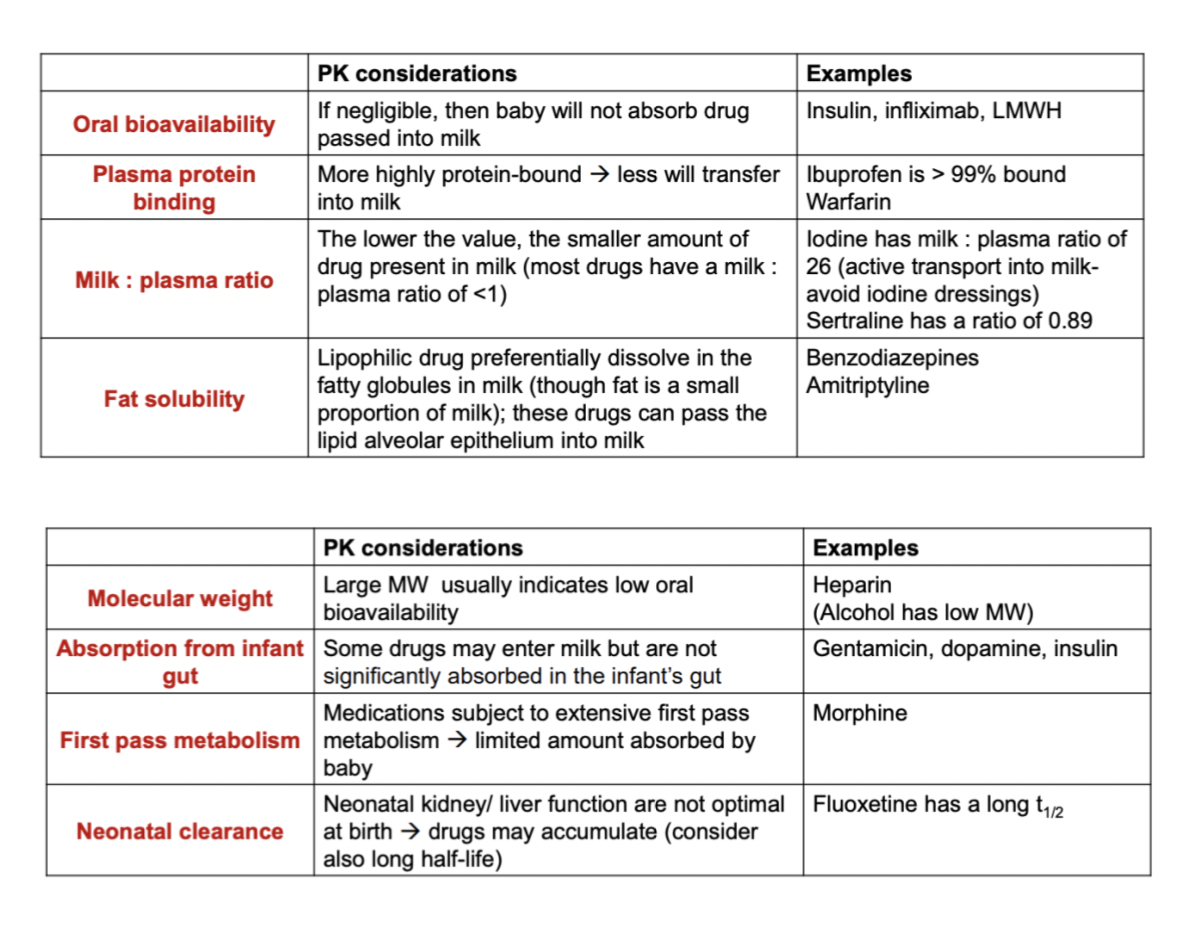
How is toxicity of the drug affected by lactation?

What is the relative infant dose?

How can we information gather in a breastfeeding mother?
Corrected age - e.g., age if they went through to full term if born prematurely.
Feed much more when newborn rather than couple months old.

How can we manage the risk in a breastfeeding mother?
Is it essential? Are there non-pharmacological options?
Avoid if not essential
Disease might be worse than medicine – more important to treat.
Consider alternative drugs
Choice primarily depends on suitability for patient and their condition, then assess compatibility with breastfeeding
Can BF be interrupted temporarily?
only for very short courses, otherwise can be difficult to resume
avoid this option if possible – may not have any other option
Timing – unhelpful if course exceeds 5 half-lives and reaches steady state
If a drug with potential neonatal side effects is still used while breastfeeding:
Monitor the baby carefully
Avoid multiple drugs with similar potential adverse effects
Use minimum doses needed
Use dosage forms that limit systemic exposure if possible
Avoid new drugs with limited information if possible
Avoid medicines with long half-lives if possible
What should be considered about codeine for BF mothers?
Avoid in breastfeeding.
Codeine - can be metabolised (ultra-rapid metabolisers) into morphine
Can happen in a breastfed infant
Try avoid codeine
Dihydrocodeine preferred
What should be considered about drowsy medicines and antibiotics for BF mothers?
Medicines that may cause drowsiness (e.g. chlorpheniramine) can pass through the BBB → sedative effect (avoid)
Antibiotics:
may cause temporary lactose intolerance but not a reason to interrupt bf
antibiotics that are licensed to give in children can be given to breastfeeding mother (level reaching baby through milk will be lower than licensed dose)
What should be considered about SSRIs for BF mothers?
SSRIs:
sertraline and citalopram are well-studied - little passes into breast milk
lithium is contraindicated
stopping breastfeeding may exacerbate symptoms of depression due to loss of oxytocin
What should be considered about methadone and herbal remedies for BF mothers?
Methadone – highly plasma protein-bound
RID 1.9-6.5%
Can be used if prescribed by a specialist service
Herbal remedies – limited data (avoid)