Google IT Support Professional Certification
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Information Technology (IT)
Is the use of digital technology, like computers and the internet, to store and process data into useful information
What does an I.T specialist do day-to-day?
Confirms that an organization technological equipment is running
Data
Computer data is information processed or stored by a computer.
What is a computer?
A device that stores and processes data by performing calculations
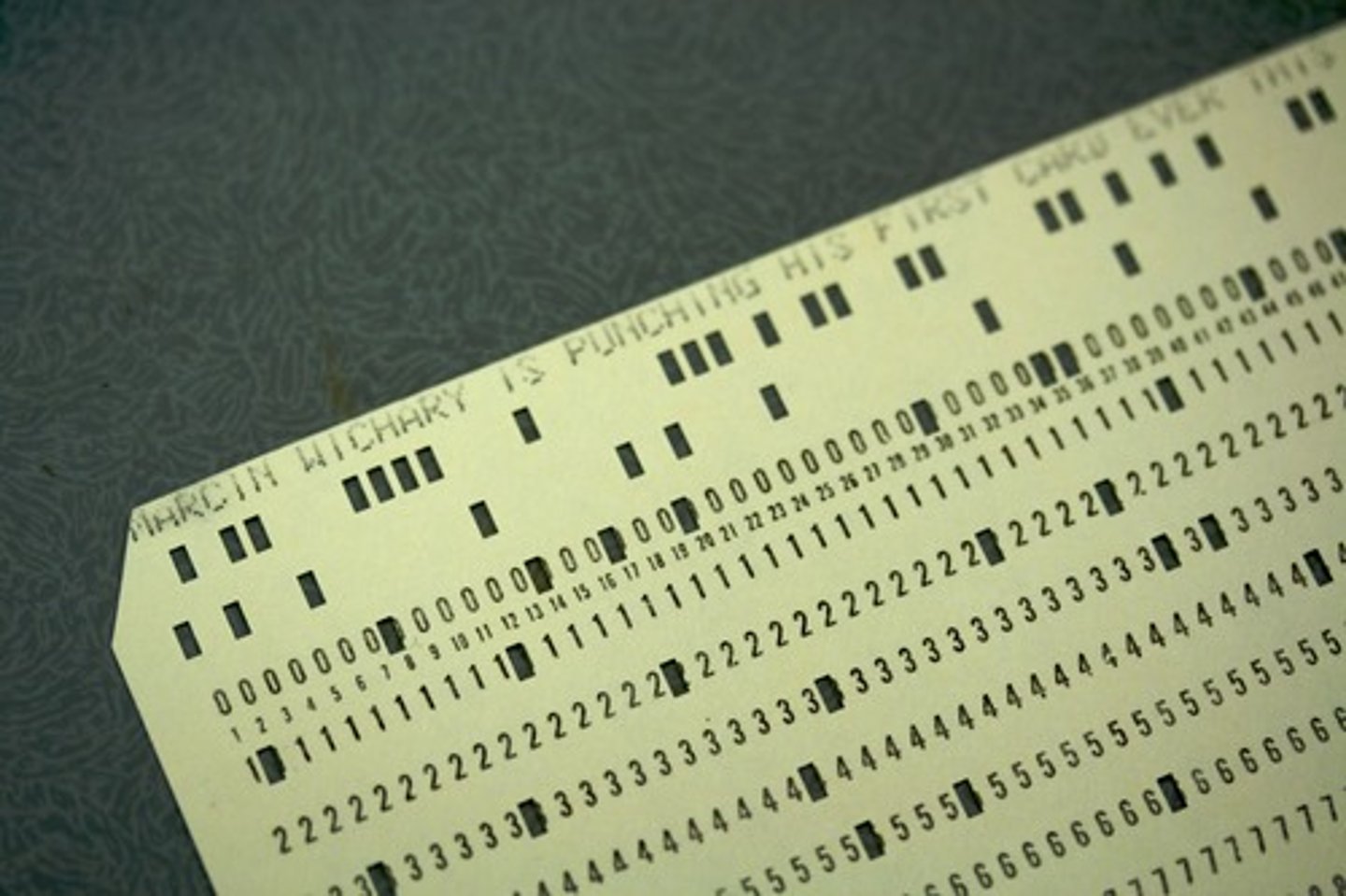
What cards had holes in them that were historically used to store data?
Punch Cards
What is cryptography
The art of writing and solving code
What is magnetic tape?
An older secondary storage medium that uses a strip of thin plastic coated with a magnetically sensitive recording medium
What is software called when it can be freely distributed, modified, and shared?
Open source
Binary System
A system in which numbers and values are represented using only the digits 0 and 1.

Bits
The smallest unit of data the computer can process
Bytes
8 bits
Character Encoding
Assigns our binary values to characters, so that we as humans can read them
Abstraction
A simplified representation of something more complex.
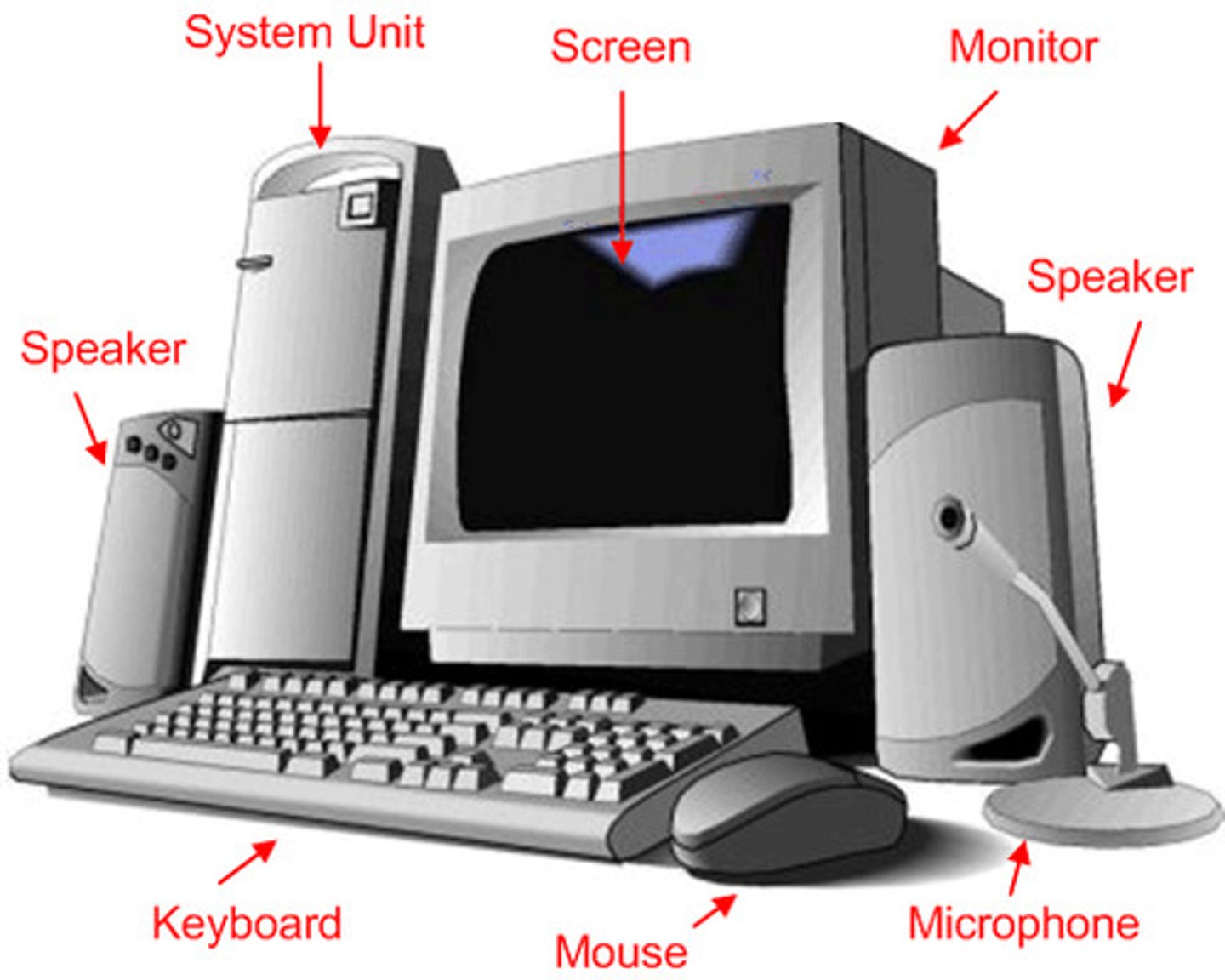
Hardware
The physical components of a computer.
- Motherboard
- CPU
- RAM/ROM
- Power Drive.
- HDD/SSD
Software
The programs and other operating information are used by a computer.

Operating system
The software that supports a computer's basic functions, such as scheduling tasks, executing applications, and controlling peripherals.
- MS Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Software Layer
How we, as users, directly interact with our computers
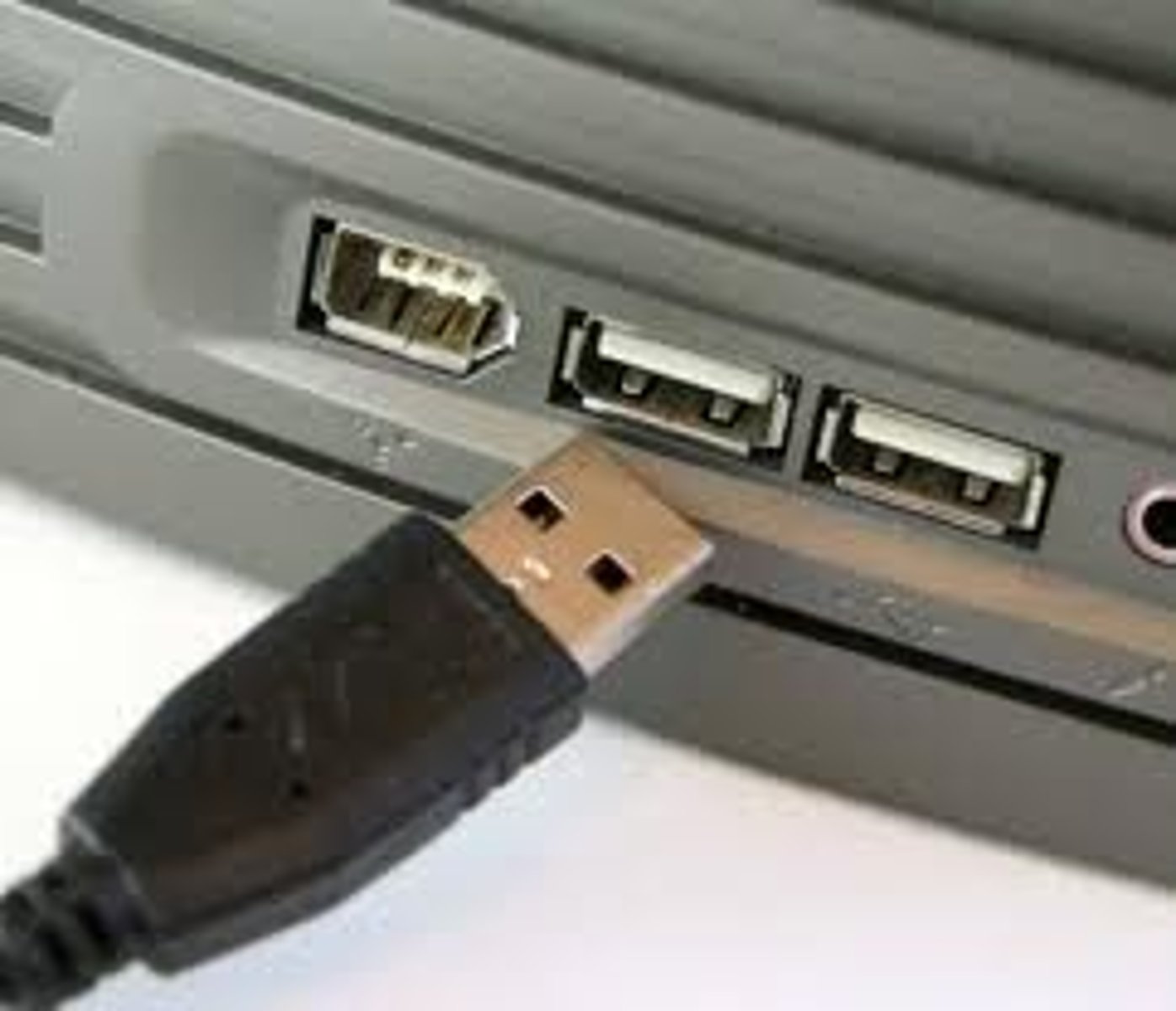
Ports
Plug sockets that enable you to connect an external device.

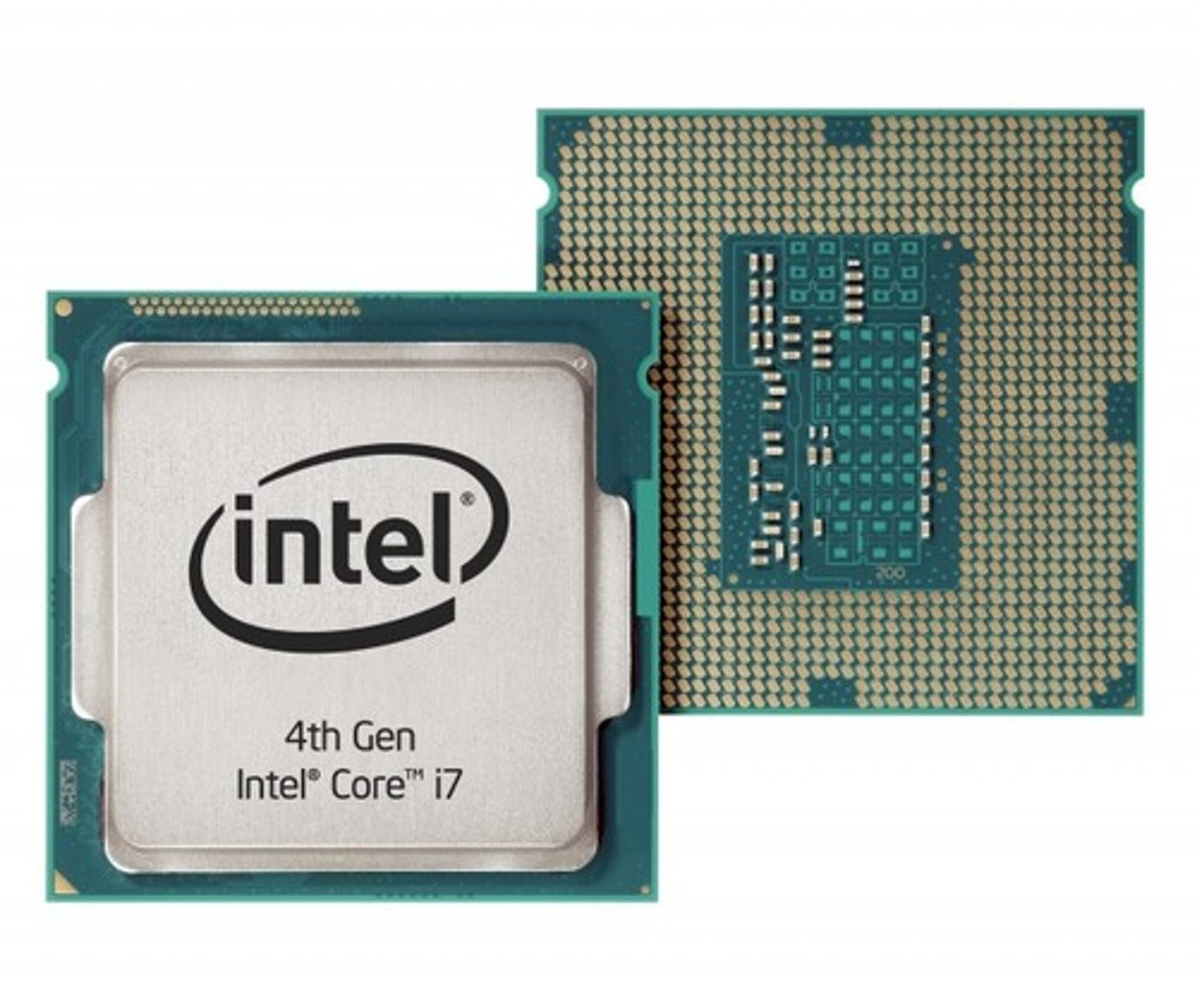
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The brain of the computer that performs instructions defined by software; processing all of your commands and actions. As more tasks are completed by the CPU, more heat will be produced by it, so this means that your CPU needs to be cooled appropriately.

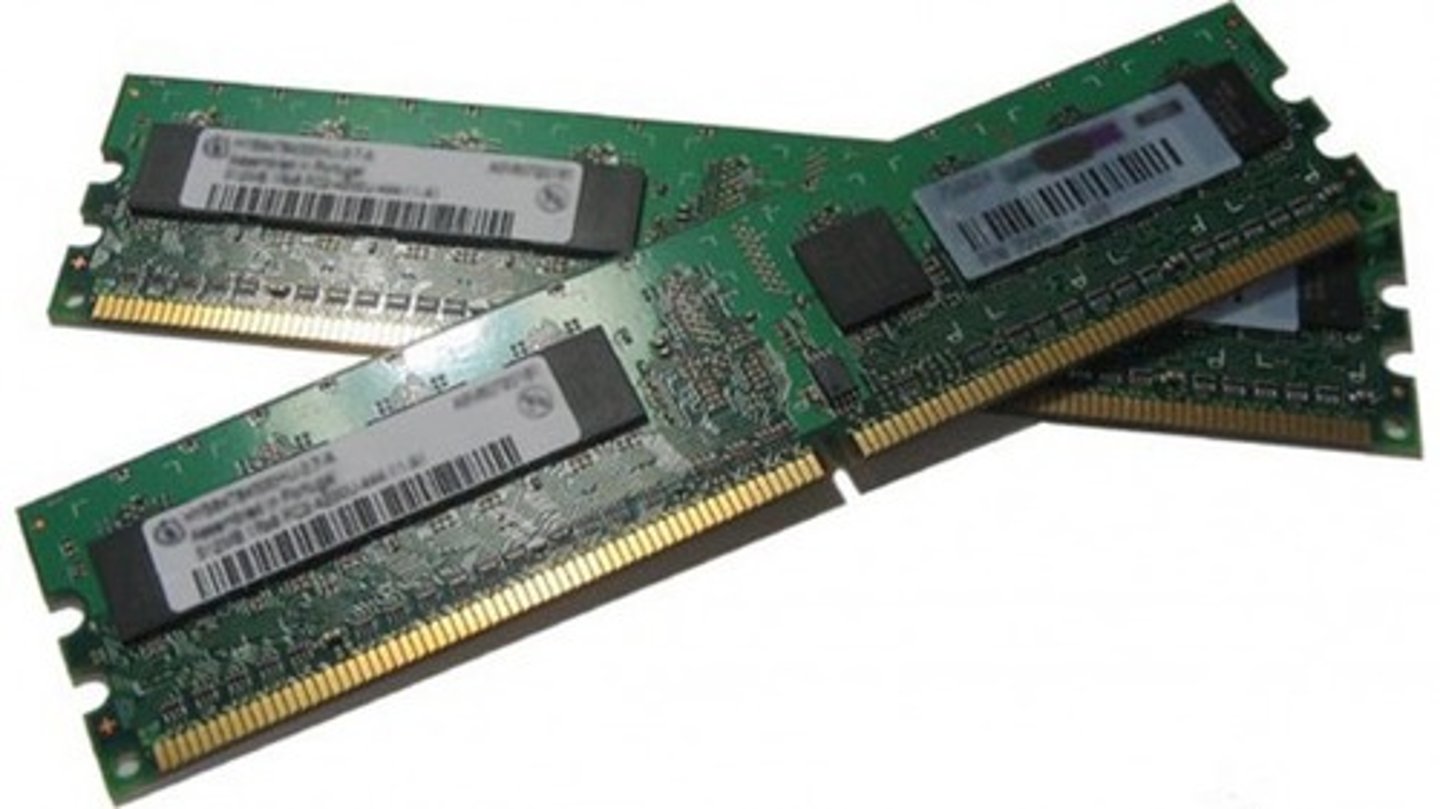
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Computer location where instructions and data are stored on a temporary basis. Responsible for storing the data from the apps and programs you open. This memory is volatile.

Hard Drive
The primary storage component of a computer holds all software and data. Can be used to store lower amounts of data than other digital storage media such as flash drive

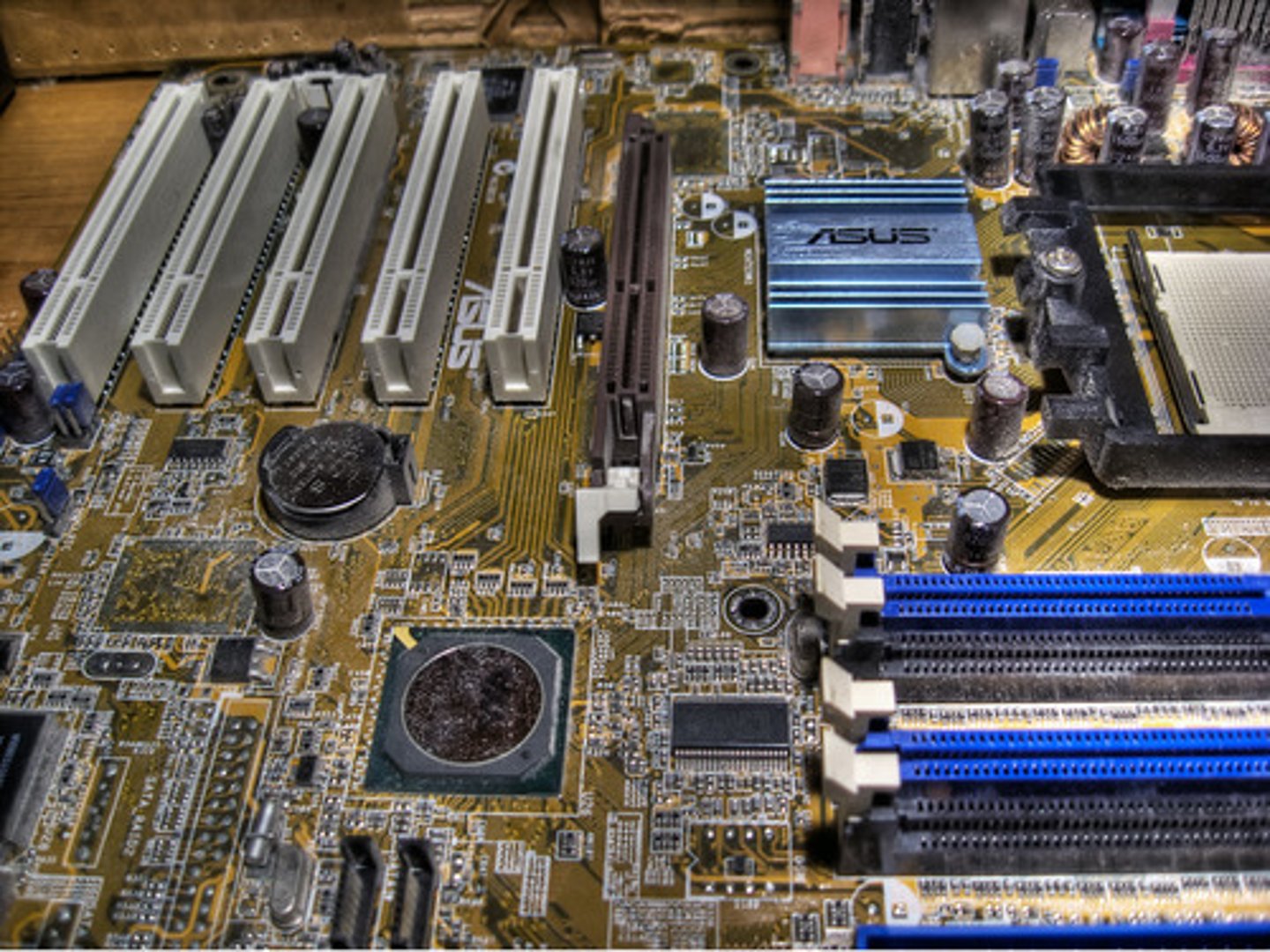
Motherboard
A motherboard is the central part of a computer. All of the computer components are connected to the motherboard. The motherboard has many jobs, including controlling power to all the parts, managing data flow between parts, and organizing communication between the CPU and other parts of the machine.
Power Supply
Converts AC power from the wall outlet into the lower voltages of DC power required to power all components of the computer such as the CPU, RAM, and motherboard.

Programs
Sets of instructions that carry out the tasks of the user.
Land Grid Array (LGA)
A feature of a CPU socket whereby pads, called lands, are used to make contact in uniform rows over the socket.
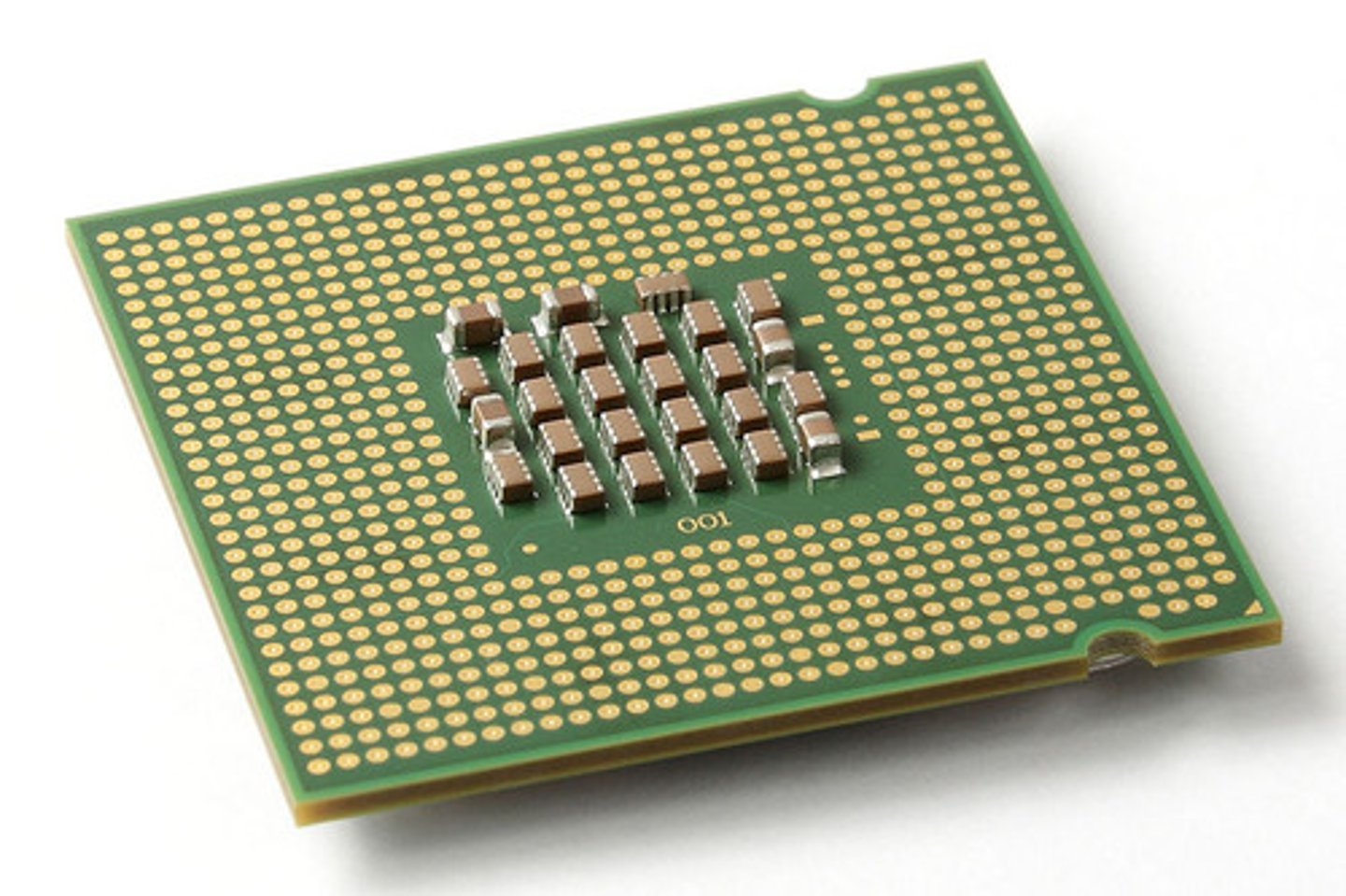
Pin grid array (PGA)
A feature of a CPU socket whereby the pins are aligned in uniform rows around the socket.
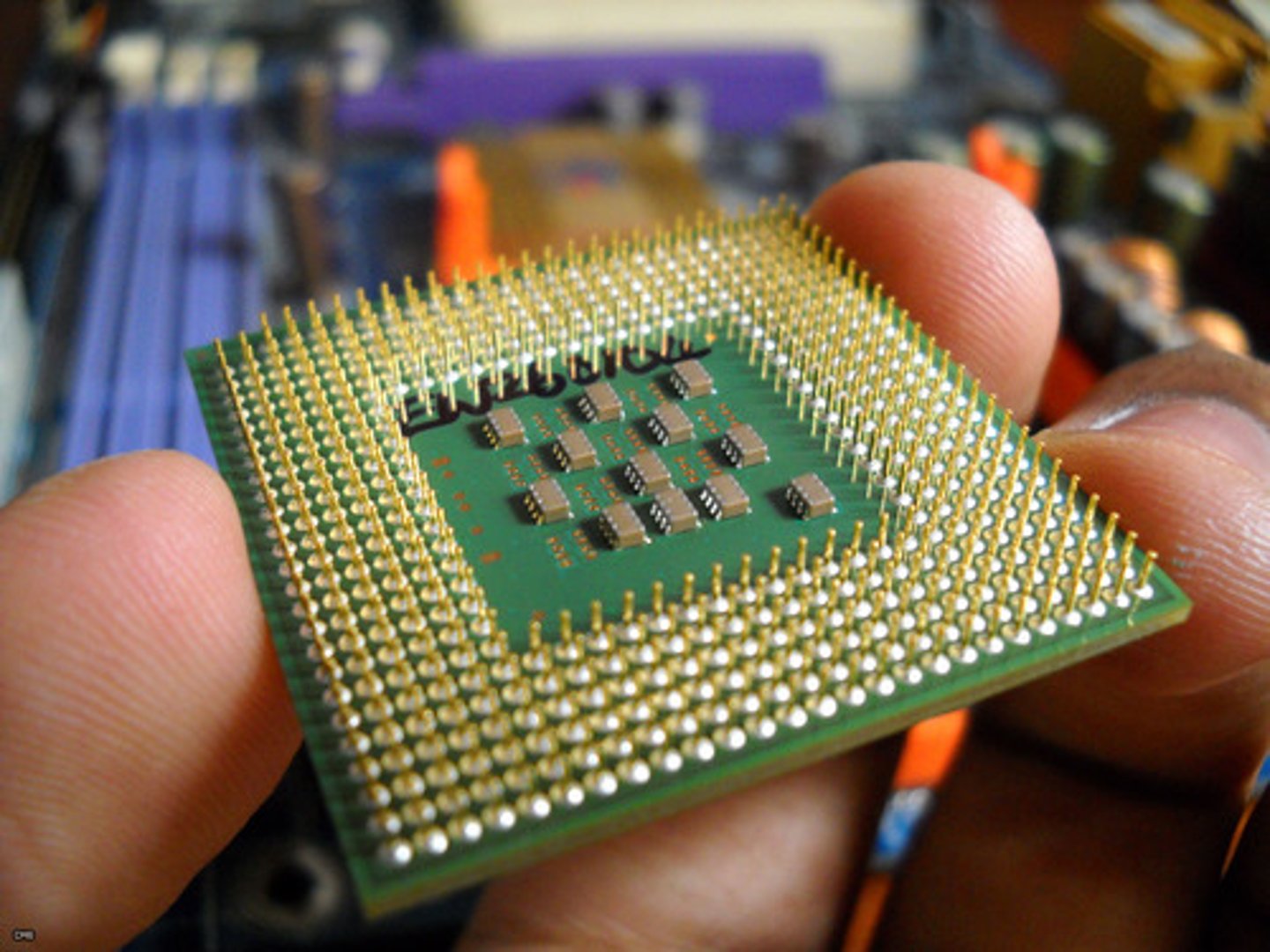
Heat Sink
A device or substance for absorbing excessive or unwanted heat.

RAM Information
When the machine is powered off the RAM is usually wiped and to run a program it needs to be stored in RAM for computers to process it
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM)
RAM that does need to be periodically refreshed. This is because every bit of information stored in DRAM is stored in a separate capacitor
- Slower than SRAM
- Volatile
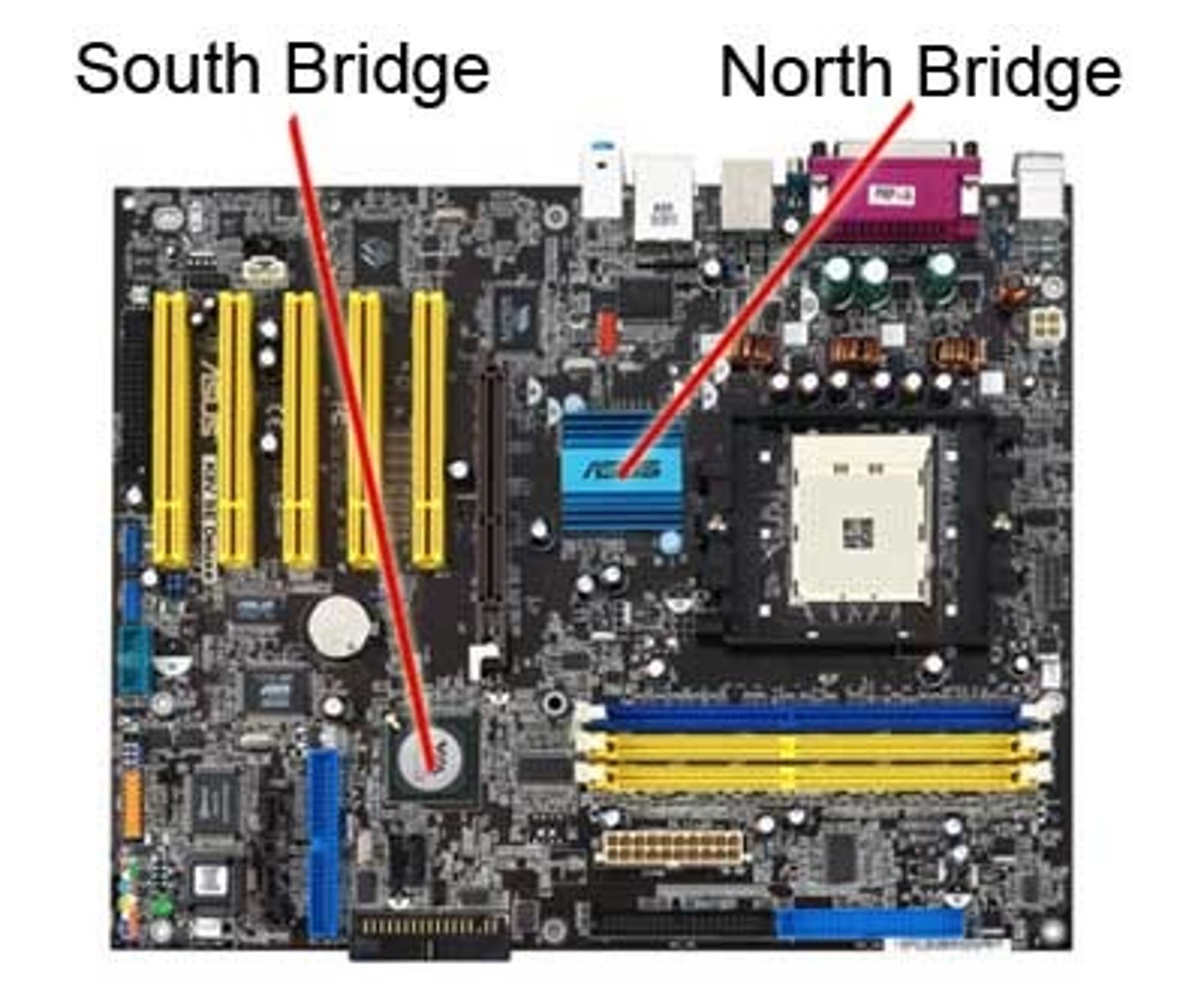
Northbridge
One or more chips in a computer's chipset that controls communications between the CPU and RAM on the motherboard.
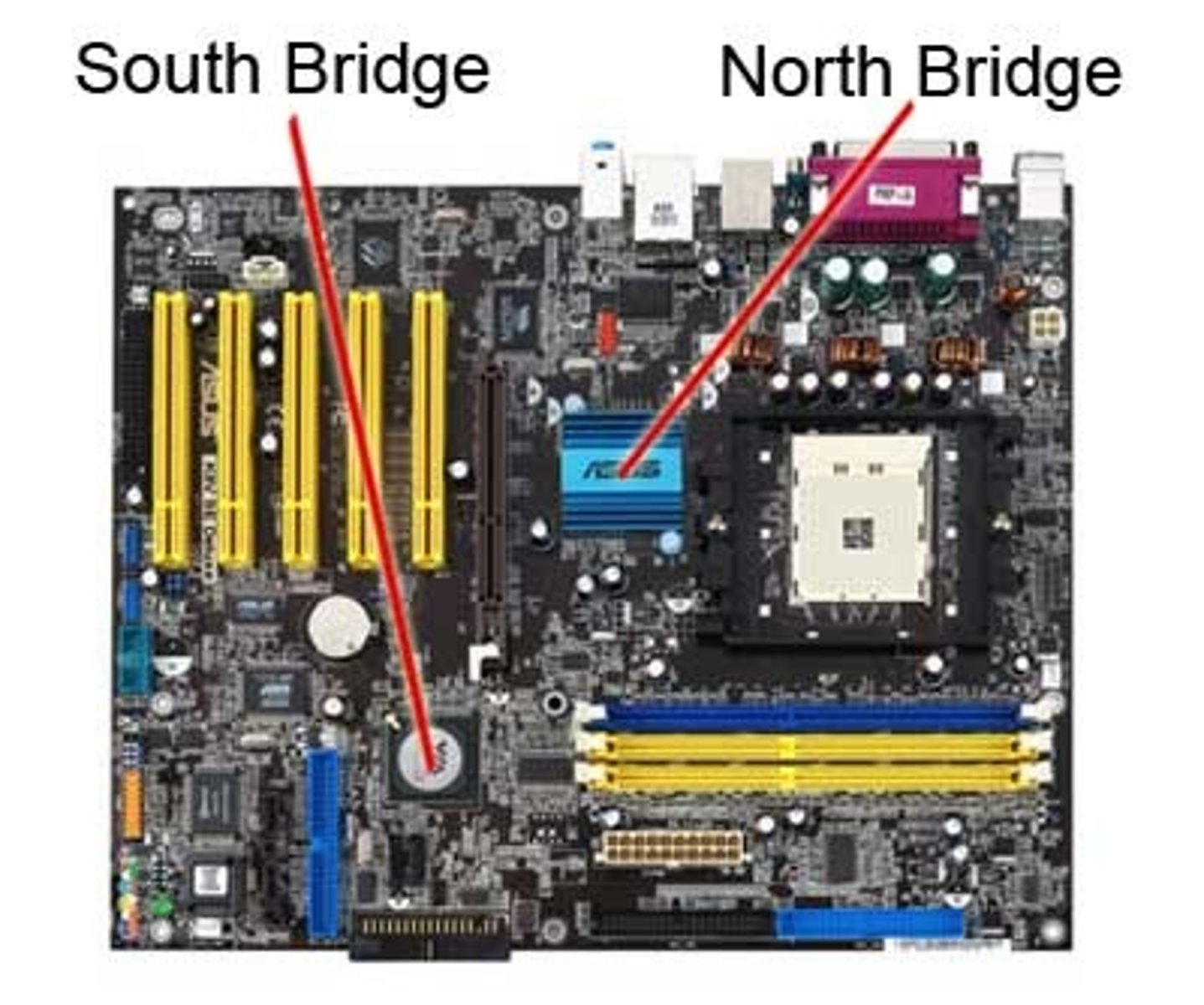
Southbridge
Part of a motherboard chipset; handles all the inputs and outputs to the many devices in the PC.
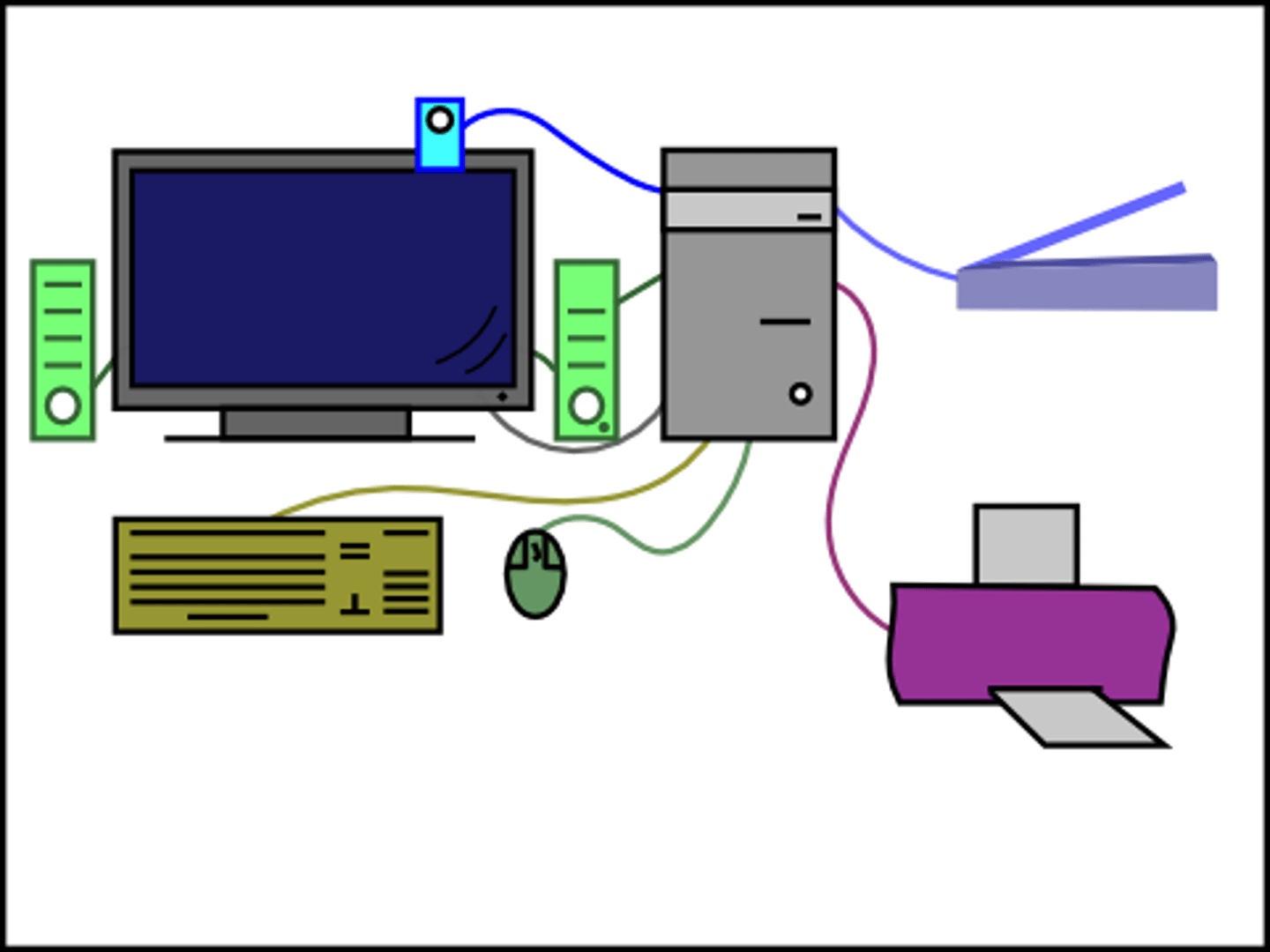
Peripheral
External devices we connect to our computer
- Computer Mouse
- Keyboard
- Loudspeakers
- Webcams
- Microphone
Expansion slots
A narrow slot on the motherboard where an expansion card can be inserted. Expansion slots connect to a bus on the motherboard.
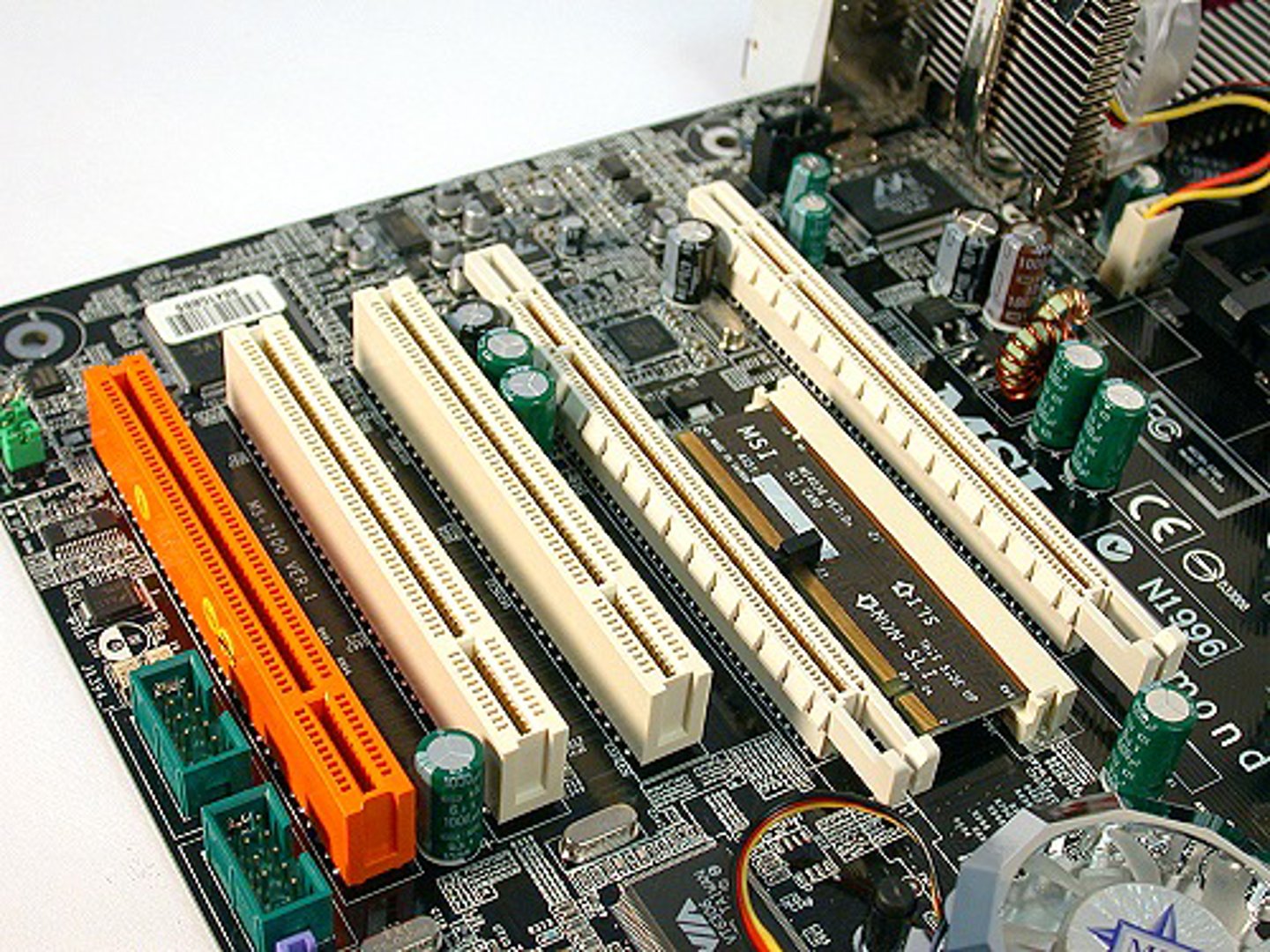
Form Factor
Refers to the size, shape, and physical specifications of hardware or hardware components
A kilobyte is made up of
1,024 bytes
A megabyte is made up of
1,024 kilobytes
A gigabyte is made of
1,024 megabytes
A terabyte is made up
1,024 gigabytes
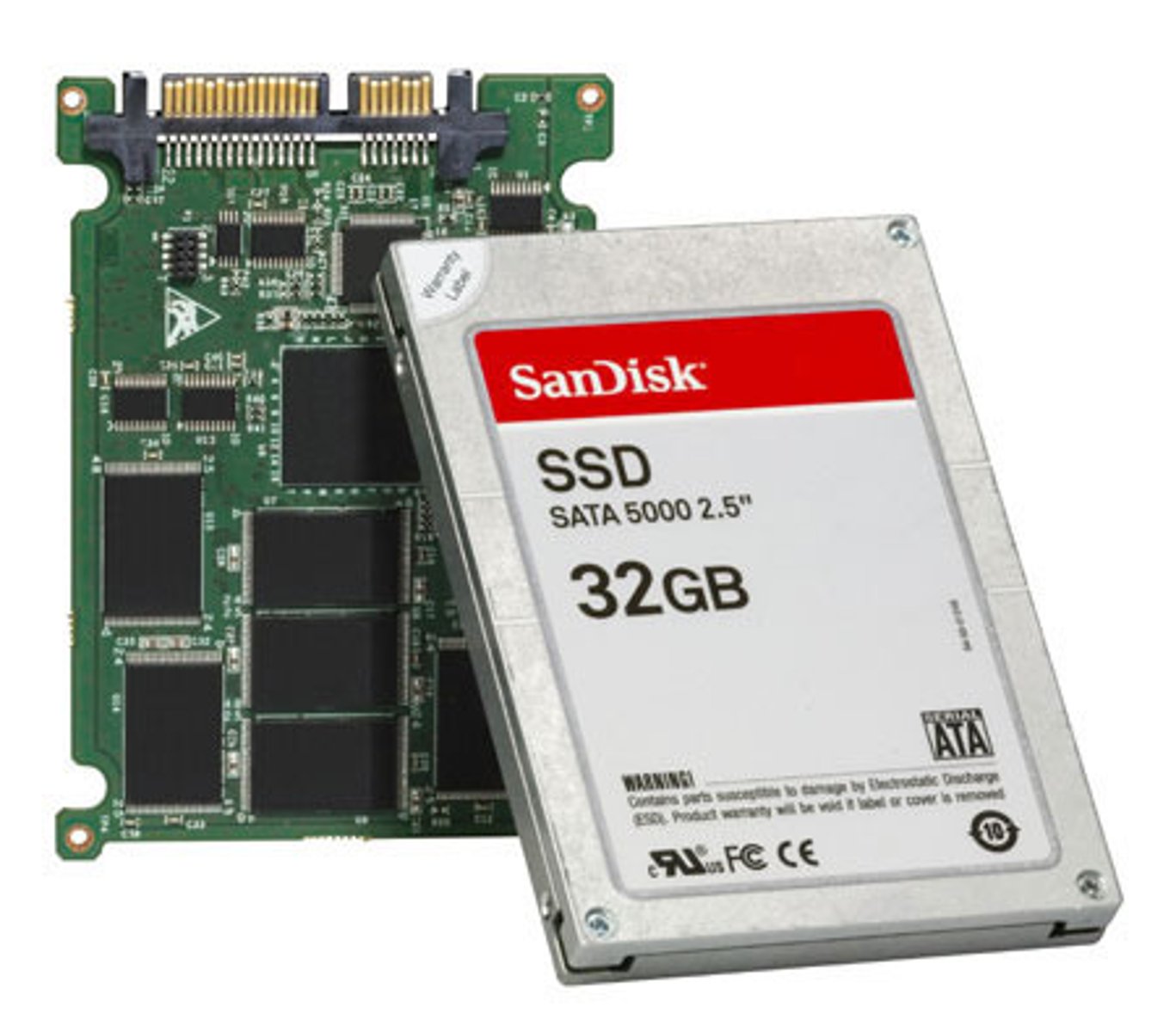
Hard Disk Drive
Use a spinning platter and a mechanical arm to read and write information

Solid State Drivers
Have no moving parts; the data is stored in microchips; they're faster, more reliable, and much less vulnerable to physical damage than traditional spinning disks but SSD is expensive.

Direct current
An electric current that flows in one direction steadily
Alternating current
A flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction.
Wattage
The amount of volts and amps that a device needs.
System on a Chip (SoC)
All the necessary hardware components contained on a single microprocessor chip
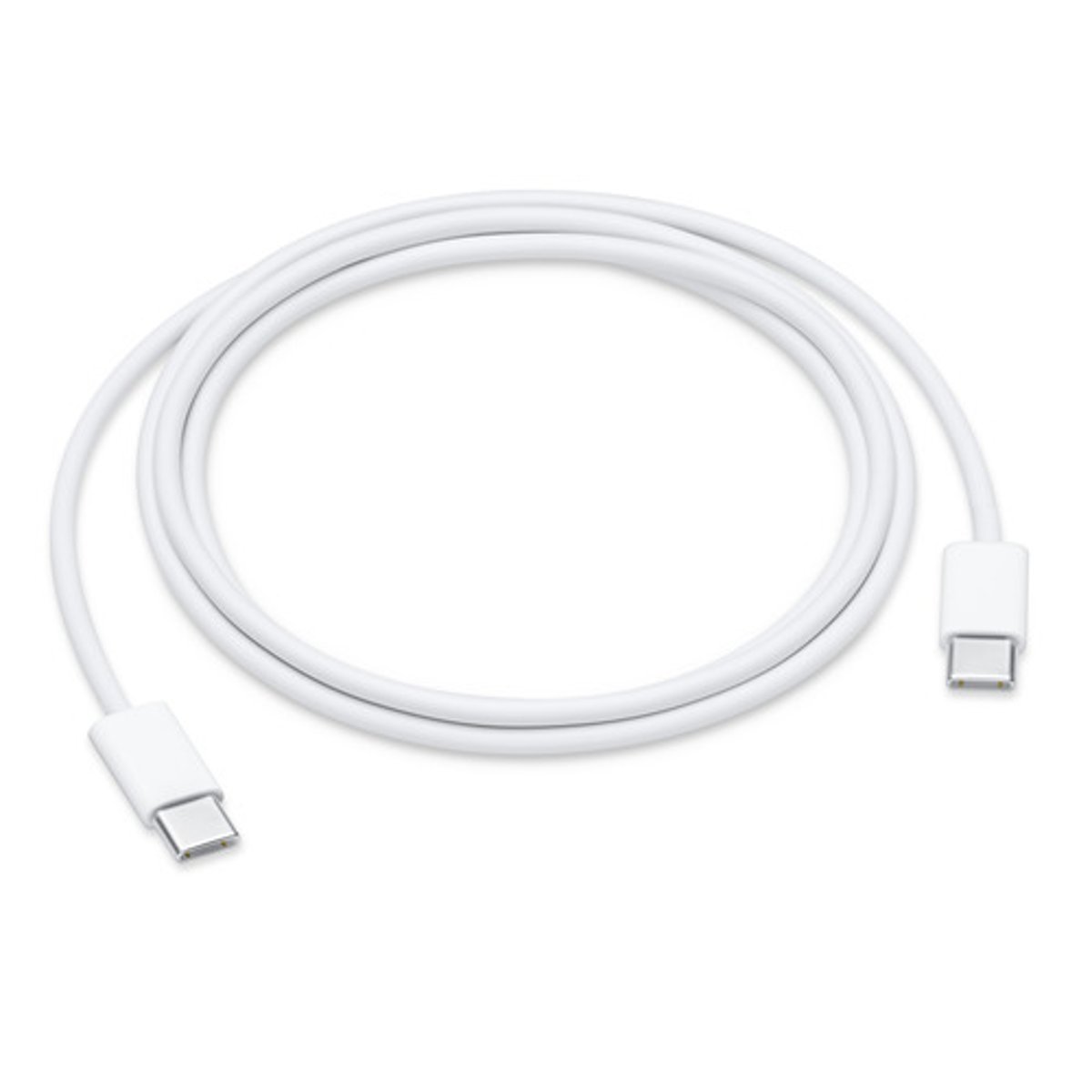
USB-C
The newest, and most versatile, type of USB connector.

Lightning Adapter
Power connector created and designed by Apple Inc.

Mini-USB
Smaller USB connector often found on digital cameras.

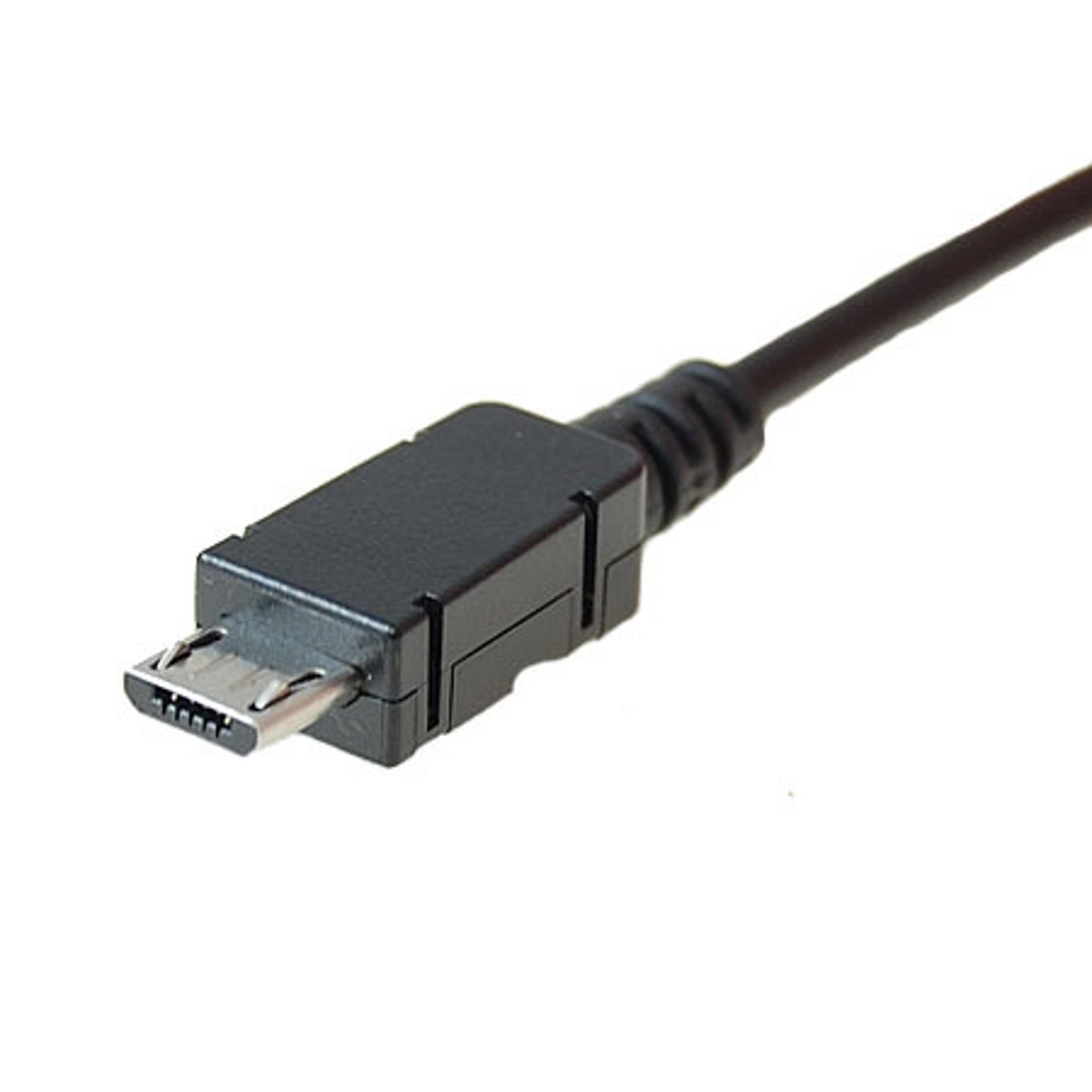
Micro USB
Smallest type of USB, commonly used for mobile Phones and tablets.

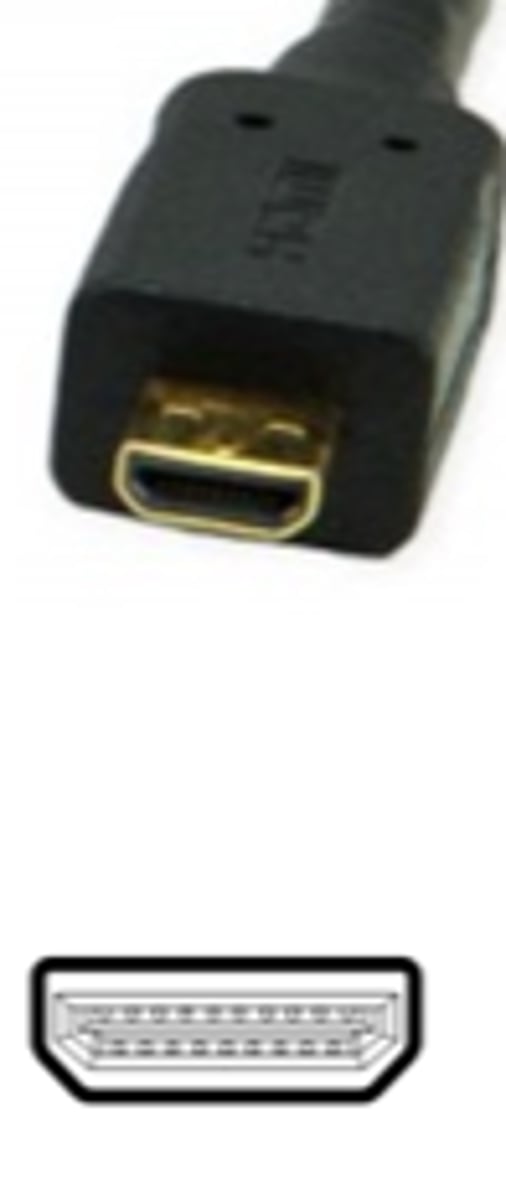
Micro HDMI
This cable provides HD viewing and allows for the connection of small portable equipment and devices including GoPro action cameras, SmartPhones, small video recording devices and portable media players.

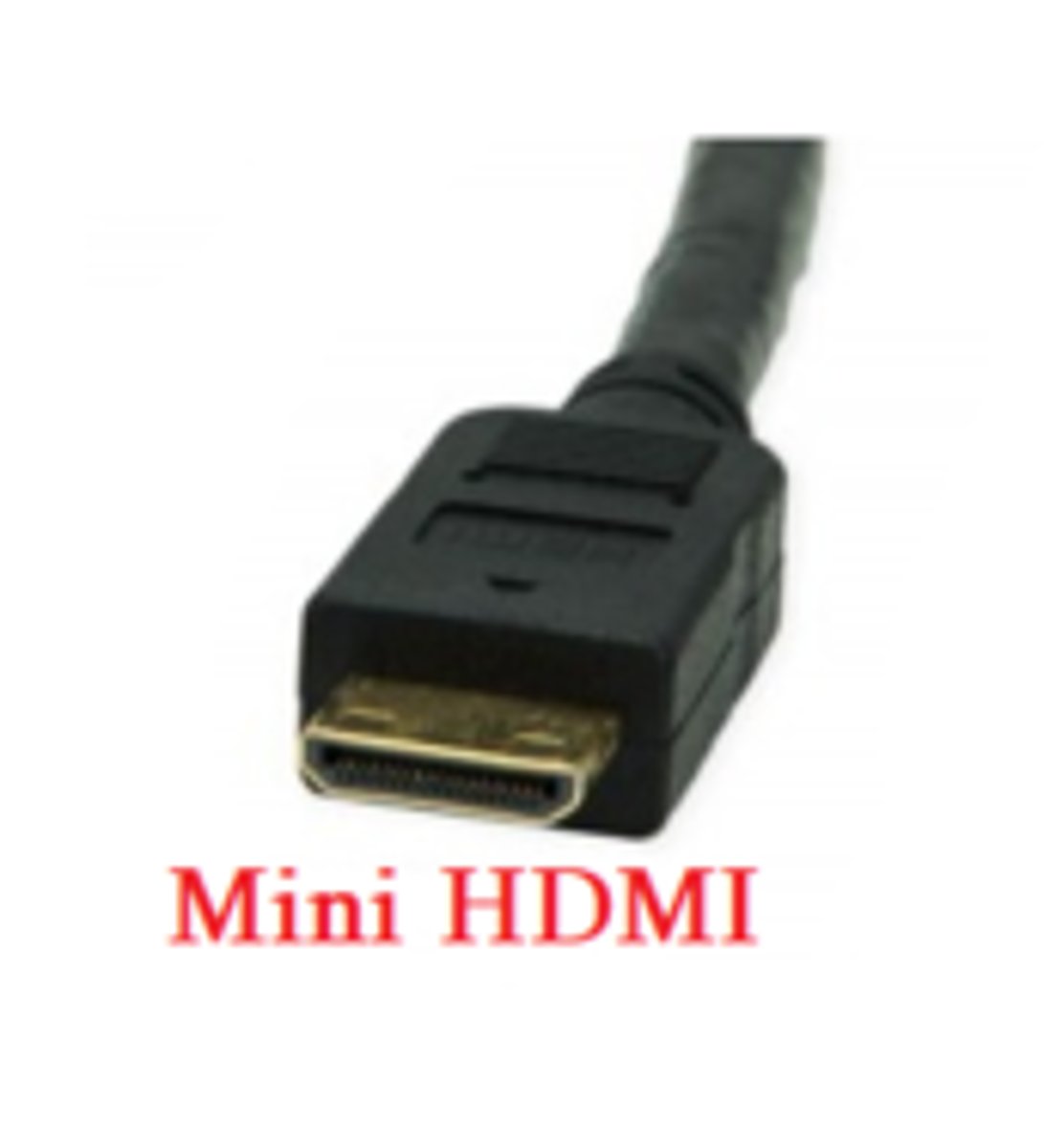
Mini-HDMI
Used to transfer high-quality video/audio from smaller devices to larger screens

Charging Cycle
One full charge and discharge of battery
USB
Universal Serial Bus
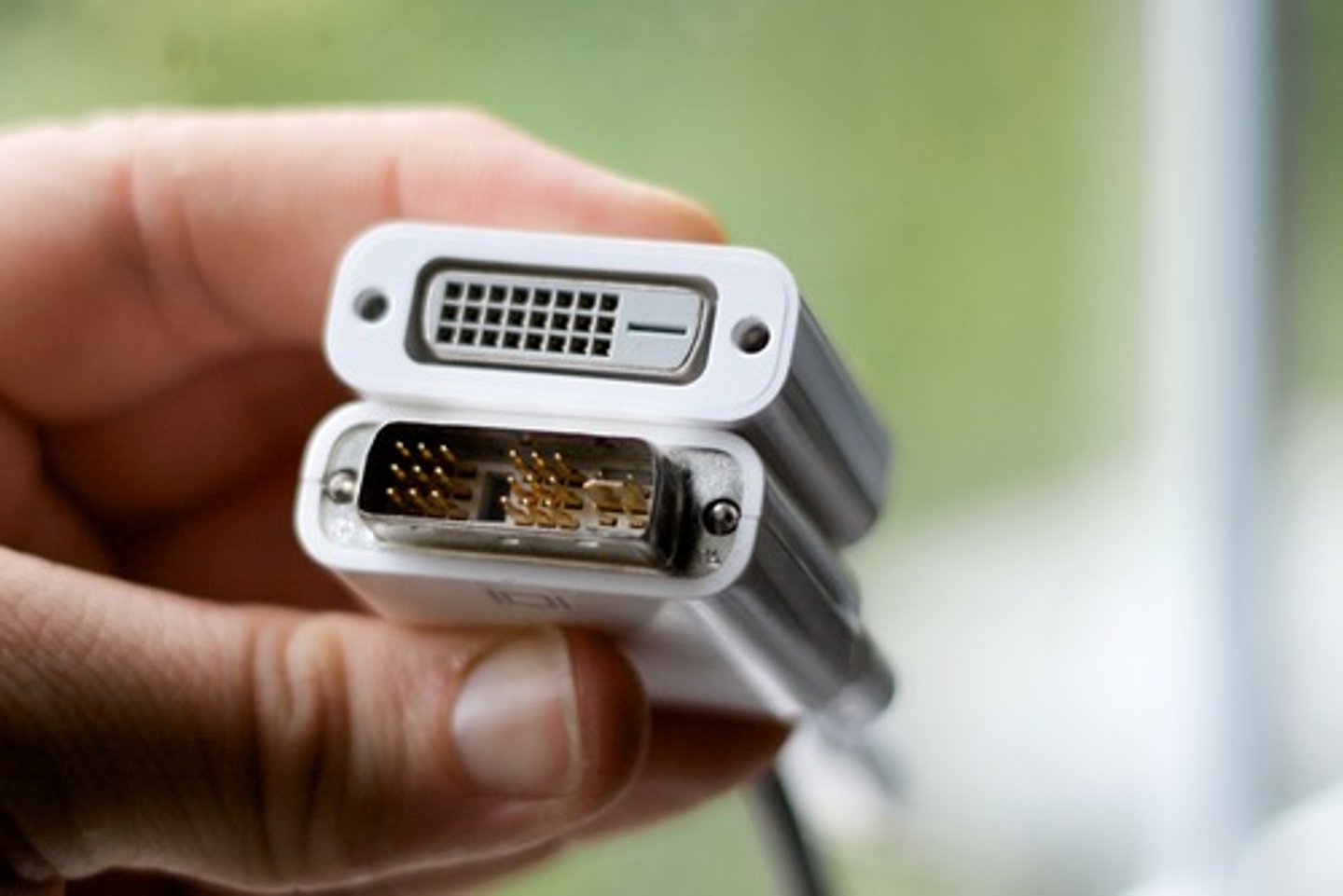
Digital Visual Interface (DVI)
Transmitting digital video content to display devices

HDMI outputs
A standard for simultaneously transmitting digital video and audio from a source, such as a computer or TV cable box, to a computer monitor, TV or projector.
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
Software that helps initialize the hardware in our computer and gets our operating system up and running
Read-only memory (ROM)
Computer memory chips containing permanent or semi-permanent data. Unlike RAM, ROM is non-volatile; even after you turn off your computer, the contents of ROM will remain.
Power-on self-test (POST)
A group of tests, stored in the BIOS and performed as a PC boots up, to check for the presence and function of system components.
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) Chip
Stores basic data about booting the computer. The CMOS battery powers the BIOS firmware in your laptop. BIOS needs to remain operational even when your computer isn’t plugged into a power source. That’s where the battery comes in. When your computer gets unplugged, BIOS relies on the CMOS battery for power.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
The rapid flow of electric current between two objects of different electrical potential. Because it can carry a large charge, ESD can cause serious damage to electronic equipment.
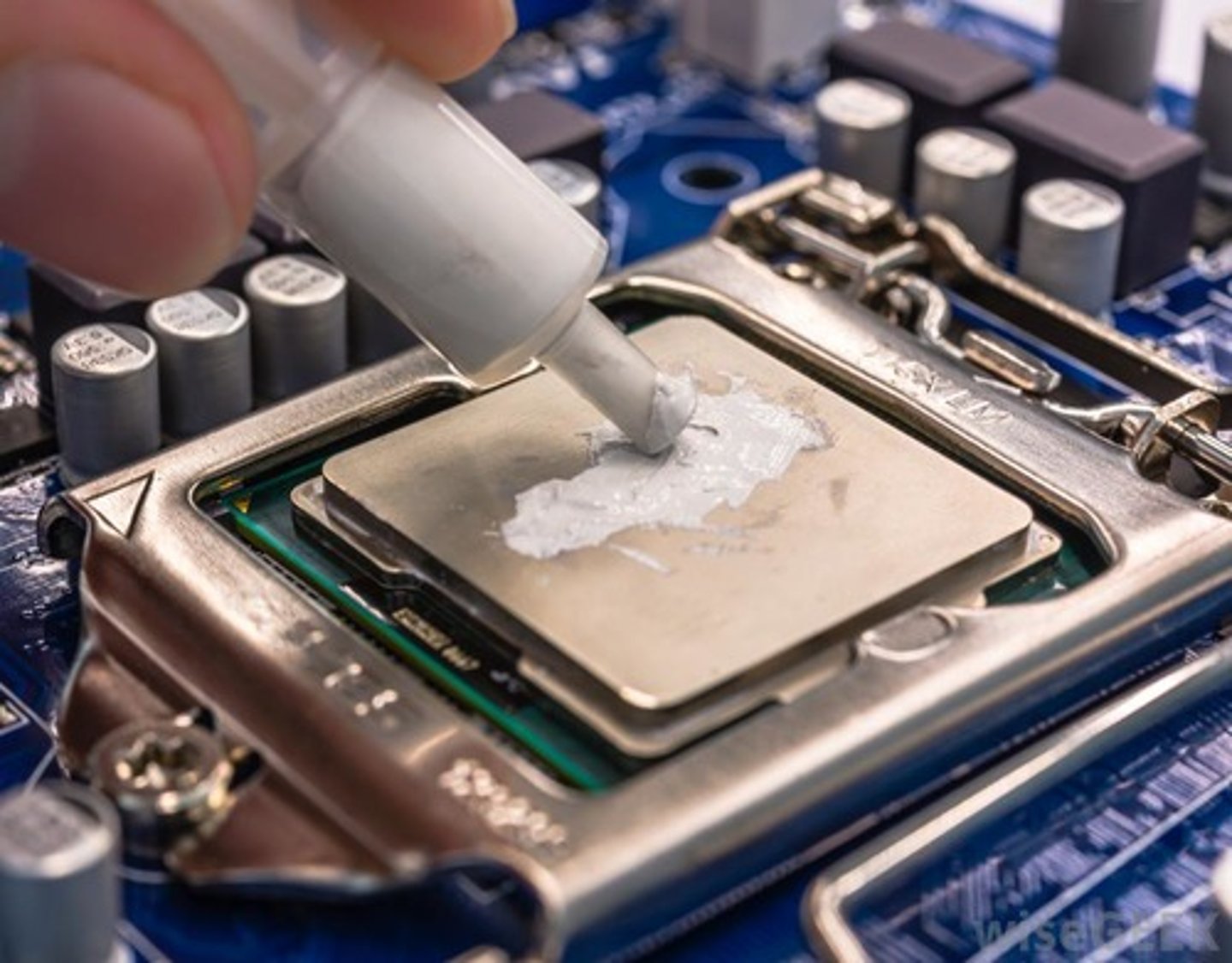
Thermal Paste
A special compound used between CPUs and heat sinks. It fills in microscopic gaps and helps draw heat from the CPU into the heat sink where it is dissipated.

DIMM Slots (Dual In-Line Memory Module)
Places on a motherboard where RAM slots go
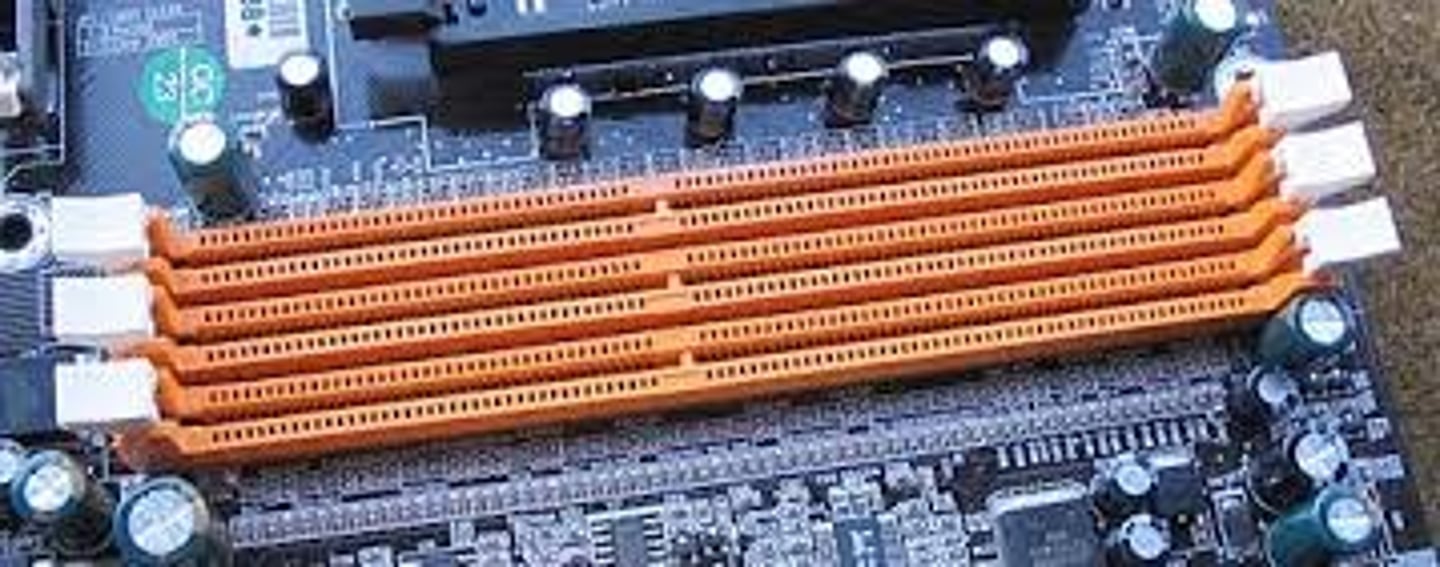
Remote Connection
The ability to access one computer on a network from another computer on the same network
Secure Shell (SSH)
A protocol implemented by other programs to securely access one computer from another
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Allows a secure private connection over a public network, using an encrypted 'tunnel'. For example, a remote computer can securely connect to a LAN, as though it were physically connected.
PuTTY
A free, open source software that you can use to make remote connections through several network protocols, including SSH
NTFS (New Technology File System)
A file system developed by Microsoft to be used with all Windows Operating Systems
Data Blocks
Where directories and files are stored
Block Storage
Improves faster handling of data, because the data isn't stored as one long piece and can be accessed quicker.
File Metadata
Information about a file that can include the creation, modified and last access dates, and also the user who created the file
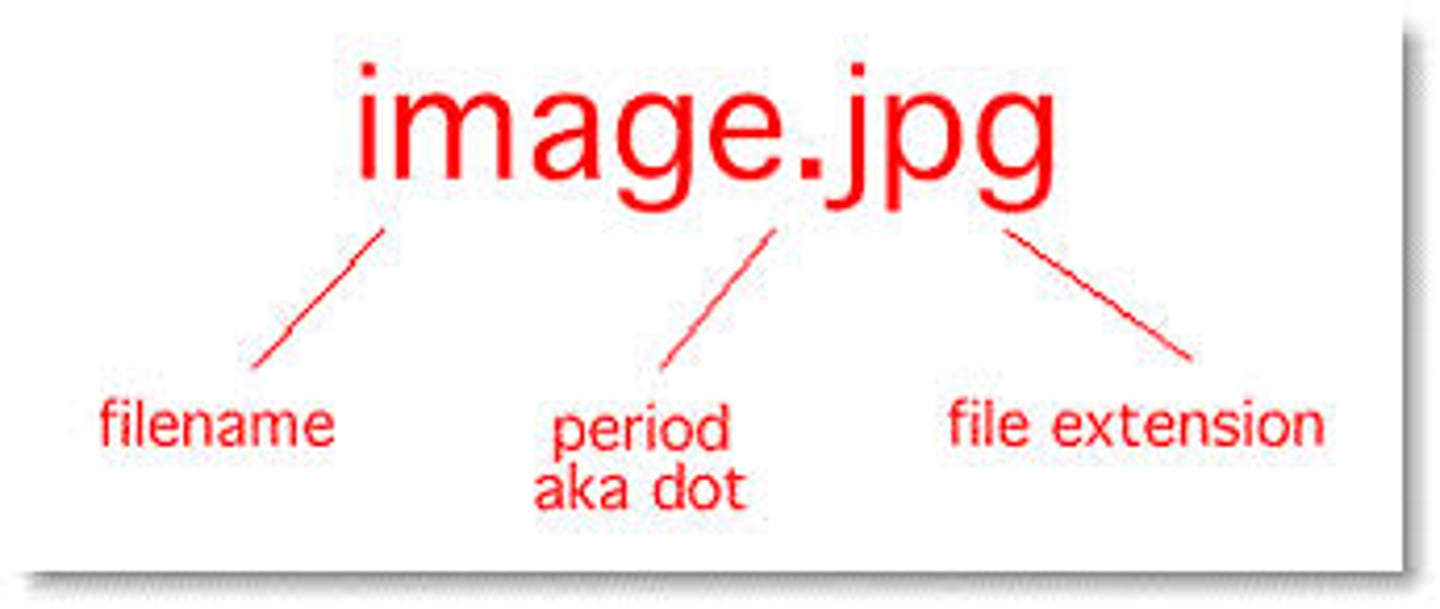
File Extension
A tag of three or four letters, preceded by a period, which identifies a data file's format or the application used to create the file.
Process
A program that is executing, like our internet browser or text editor (We can have many processes of the same program running at the same time)
Program
An application that we can run, for example, Chrome
Kernel
Creates processes, efficiently schedules them, and manages how processes are terminated.
Time Slice
A very short interval of time that gets allocated to a process for CPU execution. A CPU processes each process in time slices, one-by-one.
Virtual Memory
Space on a hard disk or other storage device that simulates random access memory.
I/O
Devices that perform input and output
Shell
A program that interprets text commands and sends them to the OS to execute.
Graphic User Interface (GUI)
A user interface in which icons represent applications, files, and commands

Logs
Files that record system events on our computer, just like a system's diary.
Boot Up Process
A list of detailed procedures that the system undergoes to perform all system checks and load all necessary files to bring the computer to an operable state.

Bootloader
A small program that loads the operating system up.
Virtual Machine
Just a copy of a real machine and stimulates software using software
Qwiklabs
An online learning environment that takes you through live, real-world scenarios you may encounter as an IT Support Specialist.
Cloud
Gives users access to storage, files, software, and servers through their internet-connected devices
Network
The interconnections of computers
The Internet
The physical connection of computers and wires around the world
The Web
The information on the internet
Internet Service Provider (ISP)
A company that connects computers to the internet for a fee.

IP Address (Internet Protocol Address)
A unique number identifying every computer on the Internet (like 197.123.22.240)
MAC Adresse (Media Access Control)
A unique cereal number
Packets
Small chunks of information that have been carefully formed from larger chunks of information.
WiFi
A facility allowing computers, smartphones, or other devices to connect to the Internet or communicate with one another wirelessly within a particular area.
Ethernet
Is the standard way to connect computers on a network over a wired connection.
Router
Is the piece of network hardware that allows communication between your local home network—like your personal computers and other connected devices—and the internet.
Network Stack
A set of hardware or software that provides the infrastructure for a computer.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Delivers information from one network to another
Internet Protocol (IP)
The network protocol that deals with the routing of packets through interconnected networks to the final destination
Hyper Markup Language (HTML)
The standard markup language used to create web pages.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
The address used for locating a document on the Web.
Domain Name
The part of a network address that identifies it as belonging to a particular domain.
- google.com
- wikipedia.org
- youtube.com