HYPOTHESIS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:11 AM on 4/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
frequencies
basic measurements
basic measurements
2
New cards
normal distribution
* probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, that the data is centered around the mean, less frequent occurence of observations happen outside mean
* bell shaped curve, symmetric and mesokurtic
* bell shaped curve, symmetric and mesokurtic
3
New cards
gaussian curve
bell shaped curve of normal distribution
4
New cards
following characteristics shall be met
1. mean should always be at the center of curve.
2. must be unimodal (1 mode)
3. must have a predictable strandard deviation
4. symmetric
5
New cards
positive skewed
right skewed
6
New cards
negative skewed
left skewed
7
New cards
kurtosis
4th movement in statistics
* measures peakedness (+leptokurtic) or flatness(-platykurtic) of the data set
* normally distributed data shoulf be mesokurtic having a value of 3.
* measures peakedness (+leptokurtic) or flatness(-platykurtic) of the data set
* normally distributed data shoulf be mesokurtic having a value of 3.
8
New cards
leptokurtic curve
positive kurtosis, higer pic longer tail
9
New cards
platykurtic curve
negative kurtosis, low peak, shorter tails
10
New cards
hypothesis
predition of relationship between one or more vriables and the problem under study
* to measure relationship among variables need to be identifies
* represents what the researchers think will hapepen in the experiment
* provide the framework of reporting the inferences of the study
* to measure relationship among variables need to be identifies
* represents what the researchers think will hapepen in the experiment
* provide the framework of reporting the inferences of the study
11
New cards
null and alternative hypothesis
types of hypothesis
12
New cards
null hypothesis
* egenerally denoted as Ho
* the researchers try to disprove, reject, nullify
* defines the statement which states that there is non exact/actual relationship between variables
* the researchers try to disprove, reject, nullify
* defines the statement which states that there is non exact/actual relationship between variables
13
New cards
alternative hypothesis
* H1
* there is a difference - things are different from each other
* suggests that the experimental/independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable
* there is a difference - things are different from each other
* suggests that the experimental/independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable
14
New cards
independent variable
cause
15
New cards
dependent variable
effect
16
New cards
steps to follow statistical hypothesis testing
1. analyze the problem
2. formulate null and alternative hypothesis
3. determine the tails of the test
4. determine the test to be used (statistical test)
5. compute
6. conclude
17
New cards
one tailed hypothesis
* drug a si better/worse than drug b
* there is a bad/good effect of mount pinatuo’s eruption on the landscape of angeles, pampanga
* outcome is expected in a signle direction
* we are interested in the direction of any difference
* there is a bad/good effect of mount pinatuo’s eruption on the landscape of angeles, pampanga
* outcome is expected in a signle direction
* we are interested in the direction of any difference
18
New cards
two tailed hypothesis
* the direction of the effect is unknown
* difference between treatments, but we do not state which way it will go
* drug a has significant difference than drug b
* there is an effect of the mt pinatubo’s eruption on the landsape of angeles pampange
* difference between treatments, but we do not state which way it will go
* drug a has significant difference than drug b
* there is an effect of the mt pinatubo’s eruption on the landsape of angeles pampange
19
New cards
level of significance
* maximum probability of committing error
* greek letter alpha
* can have 2 tails or 1 tail depending on problem and hypothesis
* 0.10, 0.05, 0.01
* greek letter alpha
* can have 2 tails or 1 tail depending on problem and hypothesis
* 0.10, 0.05, 0.01
20
New cards
parametric test
rely on assumptions about the shape of the distribution normal distribution in the underlying population and about the form of parameters (man, SD) of assumed distribution
* based on distribution
* infromation of puplation is known
* uses mean
* tests:
* 1 sample t test
* 2 sample t test
* one way ANOVA
* based on distribution
* infromation of puplation is known
* uses mean
* tests:
* 1 sample t test
* 2 sample t test
* one way ANOVA
21
New cards
non parametric tests
* rely on no or few assumptions about the shape or parameters of the population distribution from which the sample was drawn
* refer to a statistical method in which the data is not required to fit a normal distribution.
* • uses data that is often ordinal, meaning it does not rely on numbers, but rather on a ranking or order of sorts.
* refer to a statistical method in which the data is not required to fit a normal distribution.
* • uses data that is often ordinal, meaning it does not rely on numbers, but rather on a ranking or order of sorts.
22
New cards
drawing conclusion
the calculated value is compared to the critical value to determine if the difference is significant enough to reject Ho at the predetermined level of significance
* if critical value > calculated value then do not reject Ho (accept Ho)
* if critical value > calculated value then do not reject Ho (accept Ho)
23
New cards
t test
parametric test used to test significant difference
24
New cards
paired t test
determine whether the mean of the differences between two paired samples differs from 0 (or target value)
* calcualtes
* calcualtes
25
New cards
ANOVA
* aparametric test used to test the significant difference of 3+ groups
* method of testing the quality of 3+ population means by analyzing sample variations
* equal no of respondents in ech group
* unequal no of respondents in each group
* method of testing the quality of 3+ population means by analyzing sample variations
* equal no of respondents in ech group
* unequal no of respondents in each group
26
New cards
pearson r
* continuos (noral distribution, relationship,correlation)
* ex.
* parametric used in determining relationship between 2 sets of data
* qualitative description of coefficient relation
* Positive: increase in one variable will result to an increase of another, and vice versa
* Ex: as age increases, the weight increases •
* Negative correlation: negative r value. Increase of one will result in decrease of another •
* Ex: The more people are vaccinated, the less that illness occurs
* ex.
* parametric used in determining relationship between 2 sets of data
* qualitative description of coefficient relation
* Positive: increase in one variable will result to an increase of another, and vice versa
* Ex: as age increases, the weight increases •
* Negative correlation: negative r value. Increase of one will result in decrease of another •
* Ex: The more people are vaccinated, the less that illness occurs
27
New cards
spearman rank correlation
nonparametric used to find out if there is a significant relationship between 2 variables
28
New cards
DEMOGRAPHY
* statistical study of human population
* encompasses the study of size, structure, and distribution of populations
* spatial/temporal changes in response to birth, migration, aging and death
* encompasses the study of size, structure, and distribution of populations
* spatial/temporal changes in response to birth, migration, aging and death
29
New cards
demographics
characteristic of a population
30
New cards
population
study of character, no and distribution of living organisms
31
New cards
* social science
* biological science
* size of breeding groupd
* biological science
* size of breeding groupd
factors in population
32
New cards
social science
* relationships, politics, sa isang lugar
33
New cards
biological science
* birth death
34
New cards
size of breeding group
dami ng babae sa lugar
35
New cards
* computation of vital and health statistics rates and ratios
* setting up coverage of activities
* setting up norms for assignment of health facilities, staff, and funds
* setting up coverage of activities
* setting up norms for assignment of health facilities, staff, and funds
principal uses of population data in health administration
36
New cards
description of population
variables and observation
37
New cards
variable
* chaacteristics that can change values from case to case (gender, income, age, political party affilication)
* 2 types
* dependent variable
* independent
* 2 types
* dependent variable
* independent
38
New cards
dependent variable
variable whose variation depends on other variable
39
New cards
observation/cases
entity from which data are collected; also known as unit of analysis (individuals, households, states, countries)
40
New cards
formal demography
* development and application of new methods for the analyses of demographic data
* comprises a set of techniques by which data collected in censuses, surveys and vital registration systems about age, sex, birthds, deaths, migration, marriages
* analyzing components of population change
* comprises a set of techniques by which data collected in censuses, surveys and vital registration systems about age, sex, birthds, deaths, migration, marriages
* analyzing components of population change
41
New cards
social demography
* encompasses the study of feritility mortality, politics, migration
* study of reasons for changes in population and its structures and their results
* study of reasons for changes in population and its structures and their results
42
New cards
population studies
study of fertility mortality and migration
43
New cards
continuous population registration (CPR)
* consist of registering births, deaths. emigration and immigration, making necessary additions and - to the existing population
* mathematical estimates
* arithmetic increase method
* geometric increase method
* mathematical estimates
* arithmetic increase method
* geometric increase method
44
New cards
arithmetic increases method
assumed that the population increases at a constant amount per year
* +100 000 people per year
* +100 000 people per year
45
New cards
geometric increase method
assume that population increases at a constant rate per year
* +10% per year
* +10% per year
46
New cards
natural increase
difference between the number of births and the number of death occuring in a population in a specified period of time
* number of births- no of deaths
* number of births- no of deaths
47
New cards
rate of natural increase
* difference between crude birth rate and crude death rate on a population in a specific amount of time
* CBR-CDR
* CBR-CDR
48
New cards
CEnsus
* official and periodic enumeration of population
* common direct method of collecting demographic data conducted by a national govt and attempts to enumerate every person in a country
* 5 yrs
* not the best source of data on births and deaths
* common direct method of collecting demographic data conducted by a national govt and attempts to enumerate every person in a country
* 5 yrs
* not the best source of data on births and deaths
49
New cards
* de jure method
* de facto method
* de facto method
census
50
New cards
de jure method
* done when people are assigned to the place where they usually live regardless of wher they are at the time of the census
51
New cards
de facto method
done when the people are assigned to the place where they ar physically present at the time of census regardless of their usual place of residence
52
New cards
sample survey
* specific data are gathered
* may happen anytime a needed
* use in policy analysis and election
* on a small population
* may happen anytime a needed
* use in policy analysis and election
* on a small population
53
New cards
direct method
* comes from vital statistics registries that track all births and deaths
* changes in legal status (marriage divorce)
* migration (registration of pace of residence)
* administered throu the use of an interviewer or self-enumerated
* changes in legal status (marriage divorce)
* migration (registration of pace of residence)
* administered throu the use of an interviewer or self-enumerated
54
New cards
indirect method
* required in countries where full data are not available
* sister method techqnieuq - where survey researchers ask women how many of their sisters have died or children and at what age
* other indirect methods include asking people abt sibling parents children
* data are not collecter initially for statistical purposes but can be orgnized to produce statistics
* sister method techqnieuq - where survey researchers ask women how many of their sisters have died or children and at what age
* other indirect methods include asking people abt sibling parents children
* data are not collecter initially for statistical purposes but can be orgnized to produce statistics
55
New cards
\
key measures in demography
56
New cards
chi square
• A non parametric that test the comparison between 2 variables. •Normality distribution is not required.\`
57
New cards
58
New cards
kruskal wallis (h test)
* Non parametric test that uses ranks of sample data from three or more independent populations.
* • It is the counterpart of ANOVA
* • Assumptions
* 1. We have 3 different independent samples, all of which are randomly selected
* 2. Each sample has at least 5 observation each
* 3. No requirement of having a normal distribution or any particular distribution.
* • It is the counterpart of ANOVA
* • Assumptions
* 1. We have 3 different independent samples, all of which are randomly selected
* 2. Each sample has at least 5 observation each
* 3. No requirement of having a normal distribution or any particular distribution.
59
New cards
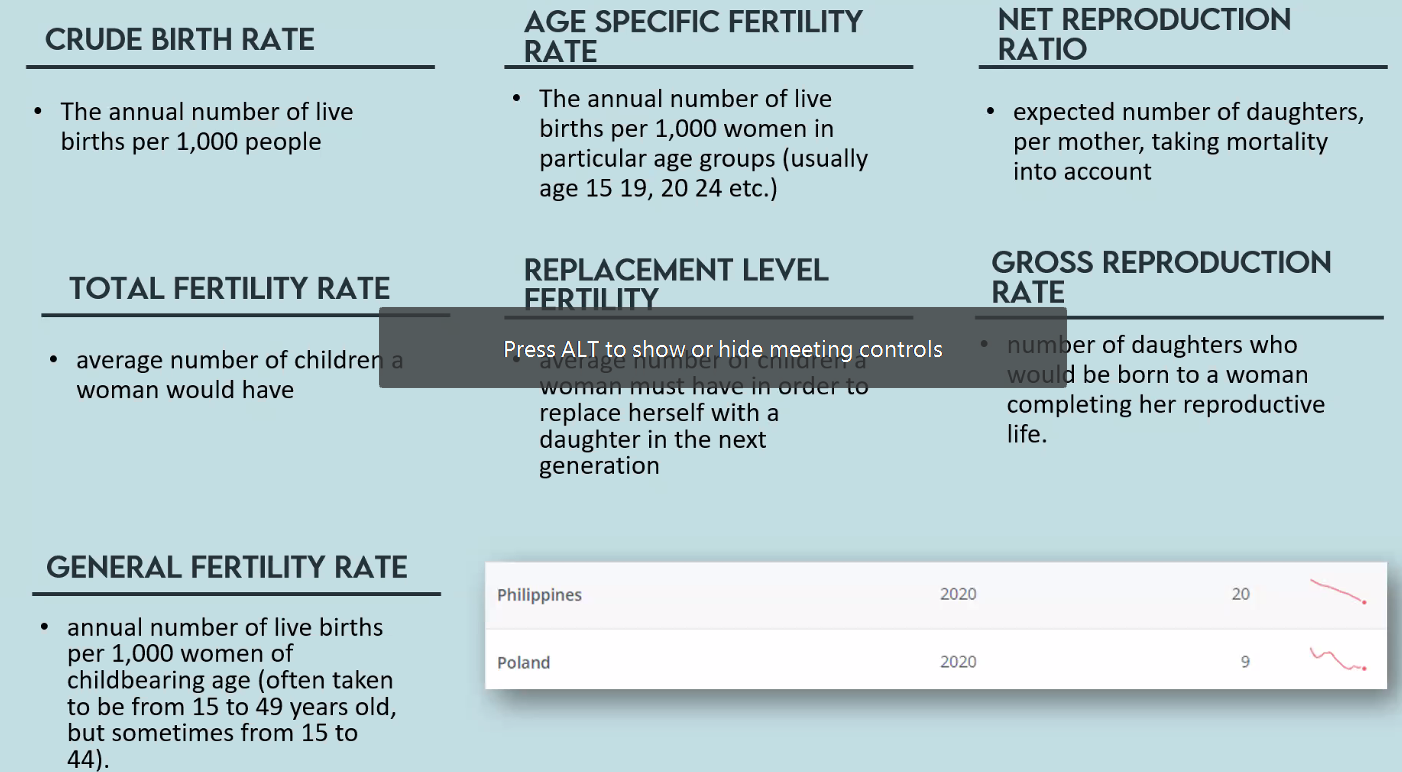
crude birth rate
The annual number of live births per 1,000 people
60
New cards
age specific fertility ate
The annual number of live births per 1,000 women in particular age groups (usually age 15 19, 20 24 etc.)
61
New cards
net reproduction ratio
expected number of daughters, per mother, taking mortality into account
62
New cards
total fertility rate
• average number of children a woman would have
63
New cards
replacement level fertility
• average number of children a woman must have in order to replace herself with a daughter in the next generation
64
New cards
gross reproduction rate
• number of daughters who would be born to a woman completing her reproductive life.
65
New cards
general fertility rate
annual number of live births per 1,000 women of childbearing age (often taken to be from 15 to 49 years old, but sometimes from 15 to 44).
66
New cards
crude death rate
• annual number of deaths per 1,000 people
67
New cards
infant mortality rate
annual number of deaths of children less than 1 year old per 1,000 live births
68
New cards
expectation of life/life expectancy
number of years which an individual at a given age could expect to live at present mortality levels.
69
New cards
fertility
number of years which an individual at a given age could expect to live at present mortality levels.
70
New cards
mortality
• is the study of the causes, consequences, and measurement of processes affecting death to members of the population.
71
New cards
migration
• is the study of the causes, consequences, and measurement of processes affecting death to members of the population.
72
New cards
sex composition
• To describe the sex composition of the population, the nurse computes for the sex ratio.
• The sex ratio compares the number of males to the number of females in the population using the formula below
• The sex ratio represents the number of males for every 100 females in the population
• The sex ratio compares the number of males to the number of females in the population using the formula below
• The sex ratio represents the number of males for every 100 females in the population
73
New cards
* median age
* dependency ratio
* dependency ratio
age composition
74
New cards
median age
divides the population into two equal parts.
• if the median age is 19 years old, it means half of the population belongs to 19 years and above, while the other half belongs to ages below 19 years old.
• if the median age is 19 years old, it means half of the population belongs to 19 years and above, while the other half belongs to ages below 19 years old.
75
New cards
dependency ratio
compares the number of economically dependent with the economically productive group in the population.
* -• The dependency ratio represents the number of economically dependent for every 100 economically productive.
* -• The dependency ratio represents the number of economically dependent for every 100 economically productive.
76
New cards
economically dependent
0-14 and 65 above age groups.
77
New cards
economically productive
those within the 15-64 age group.
78
New cards
AGE AND SEX COMPOSITION
• described at the same time using a population pyramid. - It is a graphical presentation of the age and sex composition of the population.
79
New cards
population distribution
* can be described in terms of urban rural distribution, population density and crowding index.
* • The measures help how resources can be justifiably allocated based on concentration of population in a certain place.
* • The measures help how resources can be justifiably allocated based on concentration of population in a certain place.
80
New cards
urban rural distribution
• simply illustrates the proportion of the people living in urban compared to rural areas.
81
New cards
crowding index
• described by number of persons in a household divided by the number of rooms used by the family for sleeping.
82
New cards
population density
Population density is defined as #of People divided by Land area
83
New cards
epidemiology
Study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states among specified populations and the application of that study to the control of health problems
84
New cards
• Disease was due to evil spirits
• Recovery was attributed to good spirits
• Disease as a form of punishment
• Control measures include offering sacrifices and “casting- out demons”
• Recovery was attributed to good spirits
• Disease as a form of punishment
• Control measures include offering sacrifices and “casting- out demons”
theories of disease causation
85
New cards
germ/bacteriological theory
• Koch confirmed Pasteur’s previous claims
• Disease is due to microscopic forms of life
• Opened the concepts of isolation and quarantine
• Measures to destroy and remove the bacteriological cause such as disinfection , fumigation and general cleanliness
• Bacteriology – explained the origins and spread of communicable disease
• Disease is due to microscopic forms of life
• Opened the concepts of isolation and quarantine
• Measures to destroy and remove the bacteriological cause such as disinfection , fumigation and general cleanliness
• Bacteriology – explained the origins and spread of communicable disease
86
New cards
filth theory
• Associates disease with the physical environment
• Disease change with seasons, climate, temperature, overcrowding and filth
• Diseases were due to poisonous substances and gases from the earth
• “Bad air”
• Disease change with seasons, climate, temperature, overcrowding and filth
• Diseases were due to poisonous substances and gases from the earth
• “Bad air”
87
New cards
concept of multiple causation
Disease results from the interaction of multiple ecologic factors within a dynamic system made up of an agent of disease, host and the environments
88
New cards
the web
States that effects never depend on single isolated causes but rather develop as the result of chains of causation result of complex genealogy and antecedents
89
New cards
epidemiologic lever
* The host and agent are at the opposite ends of a hypothetical lever while the environment serves as the fulcrum
* Based on biologic laws:
* Disease results from an imbalance between disease agent and man
* The nature and extent of the imbalance depends on the nature and characteristics of the host and the agent
* The characteristic of the two are influenced considerably by the conditions of their environment
* Based on biologic laws:
* Disease results from an imbalance between disease agent and man
* The nature and extent of the imbalance depends on the nature and characteristics of the host and the agent
* The characteristic of the two are influenced considerably by the conditions of their environment
90
New cards
environment
* external to the host and in which the agent may exist, survive, or originate
* Can be physical, climatologic, biologic, social and economic
* It may enhance or diminish survival of agent. It may also serve to bring agent and host into contact.
* Can be physical, climatologic, biologic, social and economic
* It may enhance or diminish survival of agent. It may also serve to bring agent and host into contact.
91
New cards
reservoirs
\- medium that fosters the survival of infectious disease agent.
* o An individual or animal infected with a pathogenic microbe is called a Reservoir host.
* o Human reservoir hosts can be patients, personnel, or visitors and include those with an active disease, those incubating a disease, and chronic carriers of a disease.
\
* o An individual or animal infected with a pathogenic microbe is called a Reservoir host.
* o Human reservoir hosts can be patients, personnel, or visitors and include those with an active disease, those incubating a disease, and chronic carriers of a disease.
\
92
New cards
* human reservoir
* animal reservoir
* animal reservoir
reservoirs
93
New cards
animal reservoir
• Zoonotic diseases •
infectious diseases of animals that can cause disease when transmitted to humans.
- rabies
\- plague
infectious diseases of animals that can cause disease when transmitted to humans.
- rabies
\- plague
94
New cards
agent of disease
•any element, substance, or force whether living or non-living, the presence or absence of which can initiate or perpetuate a disease process
•2 types: Living and Non-living
•Characteristics:
* o Inherent Characteristics
* o Characteristics directly related to man
* o Characteristics related to the environment
•2 types: Living and Non-living
•Characteristics:
* o Inherent Characteristics
* o Characteristics directly related to man
* o Characteristics related to the environment
95
New cards
physical features
biologic requirements
biologic requirements
inherent characteristics (2)
96
New cards
physical feature
• include morphology, motility, presence or absence of capsule, spore or cyst forms
97
New cards
biologic requirements
• refers to the things needed by agent to survive
• Ex. some are aerobic, anaerobic, capnophilic
• Ex. some are aerobic, anaerobic, capnophilic
98
New cards
infectivity
o the ability of an agent to invade and multiply in a host.
o Example:
* o infection of high infectivity: measles
* Infection of low infectivity: leprosy
* dependent on a number of factors including viability, portal of entry, susceptibility of the host, susceptible tissues and body defenses of the host.
o Example:
* o infection of high infectivity: measles
* Infection of low infectivity: leprosy
* dependent on a number of factors including viability, portal of entry, susceptibility of the host, susceptible tissues and body defenses of the host.
99
New cards
pathogenicity
* ability to produce clinically apparent illness.
* dependent on factors such as dosage, presence or absence of capsule, degree of toxigenicity, condition of the host
* dependent on factors such as dosage, presence or absence of capsule, degree of toxigenicity, condition of the host
100
New cards
virulence
severity of the reaction produced and measured in terms of fatality