Biological Molecules
1/97
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
what are hydrogen bonds
Force of attraction between oppositely charged regions of neighbouring water molecules
define cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
define adhesion
attraction between molecules of different substances
properties of water
Good solvent
Can transport dissolved substances into and out of cells
Cohesive properties
Adhesive properties
high specific latent heat
high specific heat capacity
Why is water a good habitat (3)

\
In beta glucose OH above C1
Condensation reaction
when 2 molecules join together releasing H2O
advantages of glucose being soluble
glucose can dissolve in cytosol of cells
can be transported in blood
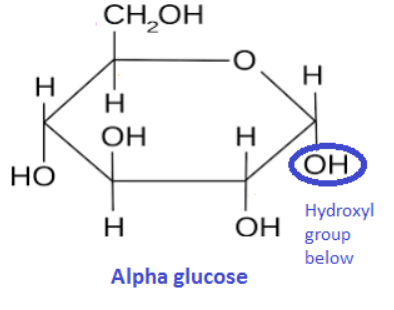
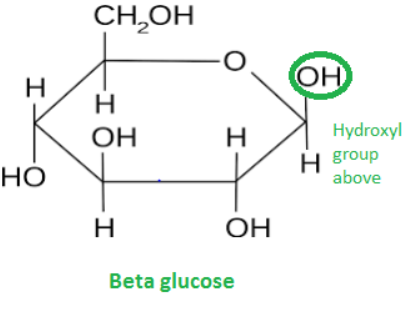
Which monosaccharides make lactose
beta glucose + galactose
How to use colorimeter?
(6 steps)
precipitate is filtered so only the blue benedicts solution remains
red light is shined through the solution because red is complimentary to blue light
a photoelectric cell measures the amount of red light transmitted through the blue benedicts solution
more red light is transmitted, higher the concentration of glucose
this is repeated with a range of known concentrations of glucose and the amount of red light transmitted is noted down
a calibration curve can be drawn, which can be used to work out unknown concentrations based on amount of red light transmitted
Each alternate monomer is flipped
Bonded with 1,4 -beta glycosidic bonds
Properties of cellulose (5)

made of 2 polysaccharide chains - amylose and amylopectin
Structure and properties of amylose
Structure
Unbranched
1,4 -alpha glycosidic bonds
twists to form helical structure and stabilised by hydrogen bonds
Properties
compact
insoluble
Why is amylose being insoluble an advantage
It does not affect osmotic balance of cells
Structure and property of amylopectin
Structure
branched
made of alpha glucose monomers
1-4 and 1-6 alpha glycosidic bonds
Properties
compact
glucose quickly hydrolysed
more insoluble than amylose
why is starch a good storage molecule of energy in plants (3)
insoluble so doesn’t affect osmotic balance of cell
large so cannot diffuse out of cell
compact so can store lots of glucose in small space
structure of glycogen (3)
more branched than amylopectin
made of alpha glucose monomers
1-4 and 1-6 alpha glycosidic bonds
why is glycogen a good store of glucose in animals (3)
compact
lots of free ends so glucose can be rapidly added or removed
useful as animals move around alot - high metabolic rate
add equal volume benedicts reagent
heat gently in waterbath
observe colour change
add NaHCO3 to make solution alkaline
add benedicts reagent and heat in water bath
observe colour change
colour change from orange to black if positive
why is boiling point of unsaturated triglycerides lower (3)
double bond causes kinks in structure of fatty acid tails
molecules cannot pack closely together
weaker Van der Waals forces
function of triglycerides (6)
energy store
respiratory substrate
thermal insulator (blubber in seals)
protection of internal organs
aids in buoyancy (whales)
waterproofs fur (otters)
Why are triglycerides a good energy store (3)
2x more energy dense compared to same mass of glucose
due to large number of C-H bonds
insoluble so does not affect osmotic balance of cells
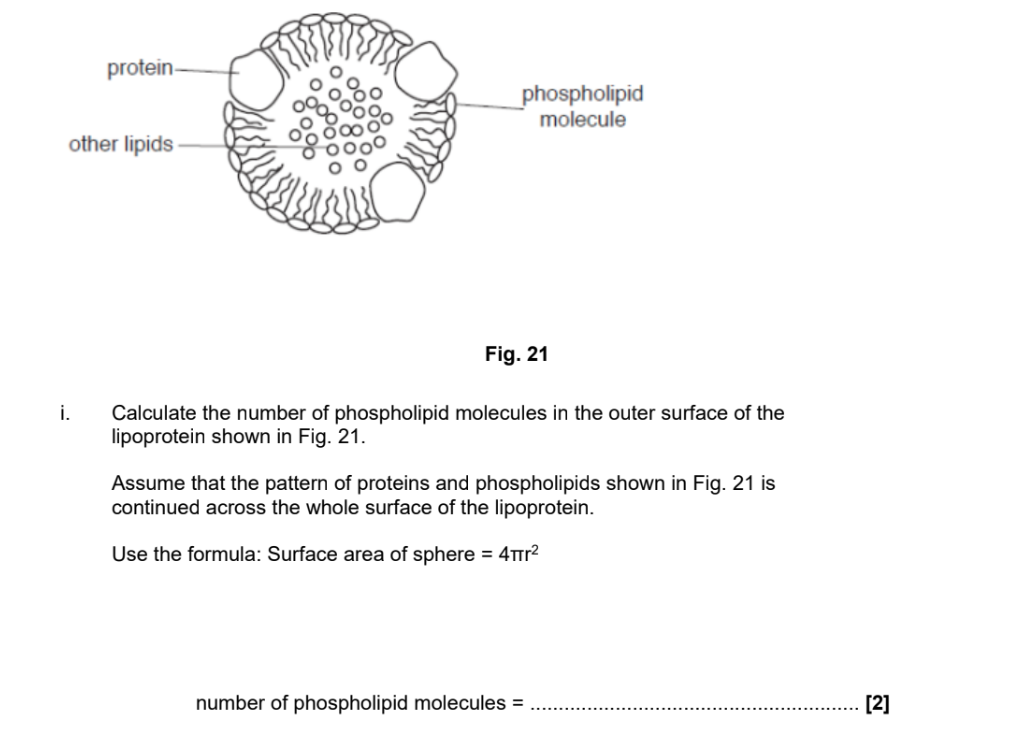
function of phospholipids (3)
cell membrane
act as emulsifiers in food
regulate cellular activities such as cell migration
used in liver to produce bile
used to make vitamin D
used as starting point for many hormones
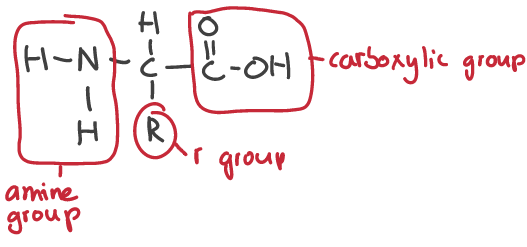
how is a peptide bond formed
when amino group and carboxyl group react in a condensation reaction
determines final shape of polypeptide chain
what are the interactions that occur in tertiary structure of proteins
hydrophillic and hydrophobic - weak interactions between polar and non-polar R groups
hydrogen bonds - formed formed between OH groups of R groups
ionic bonds - bonds between oppositely charged R groups
disulfide bridges - covalent bonds between sulfur atoms in R groups
roughly spherical in shape
play a metabolic role in body
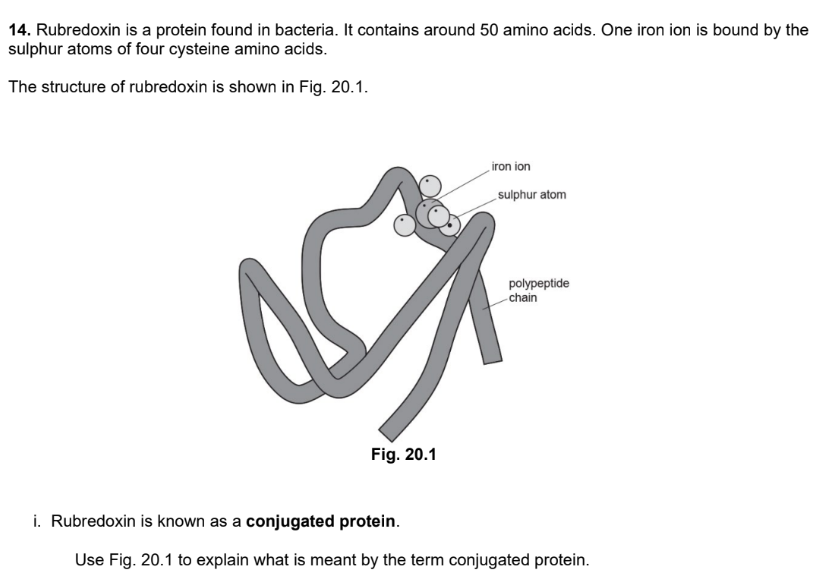
Structure of haemoglobin (2)
conjugated protein made of 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits
each subunit has prosthetic haem group
structure of lyzozyme
single polypeptide chain
folds to form groove on surface which is the active site
function of lyzosyme emzyme
catalyse breakdown of a molecule in bacterial cell wall
where is lyzosyme enzyme found
tears and saliva
structure of catalase
conjugated protein with 4 haem groups
function of catalase (2)
breaks down hydrogen peroxide into hydrogen and oxygen
prevents build up of hydrogen peroxide in cells
play a structural role in body
long rope-like molecules
organised structure
what is collagen (2)
connective tissue found in skin, tendons, ligaments and nervous system
used for shock absorbtion
properties of keratin
very strong due to large number of disulfide bridges
what is elastin
protein found in elastic fibers in skin, walls of blood vessels, alveoli
mix ethanol-sample solution with water and shake
look for white emulsion
helical shape
3 marks

describe how structure of llama haemoglobin is likely to be different from that of camel haemoglobin with reference to the four levels of protein structure (6 marks)
difference in primary structure
different amino acid sequence
one amino acid changed
amino acid change could cause change in secondary structure
initial coiling of polypeptide change different
different number of hydrogen bonds formed
different arrangement of alpha helices, beta pleated sheets
amino acid change could cause change in tertiary structure
different 3d shapes of polypeptide chains
ionic bonds, disulfide bridges
amino acid change has not changed quaternary structure
alpha and beta subunits still able to form haemoglobin in both camel and llama

2 marks

3 marks`

describe and explain how the structure and properties of different carbohydrates suit them to their role as energy storage molecules in plants and animals (6)

describe and explain how the structure and properties of lipids suit them to their role as energy storage molecules in plants and animals (4)

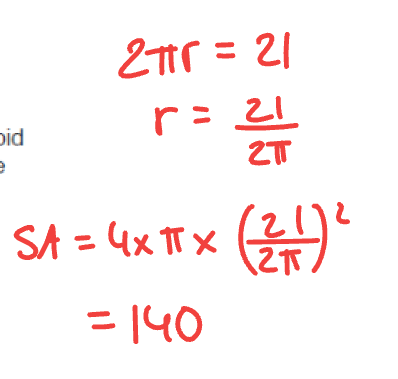

1 mark
Lipids less dense than protein
explain how water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with nitrate ions (NO3-) (2 marks)
water molecules are polar
nitrate ion is negatively charged
hydrogen bonds form between H on water and O on nitrate