animal and plant cell
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
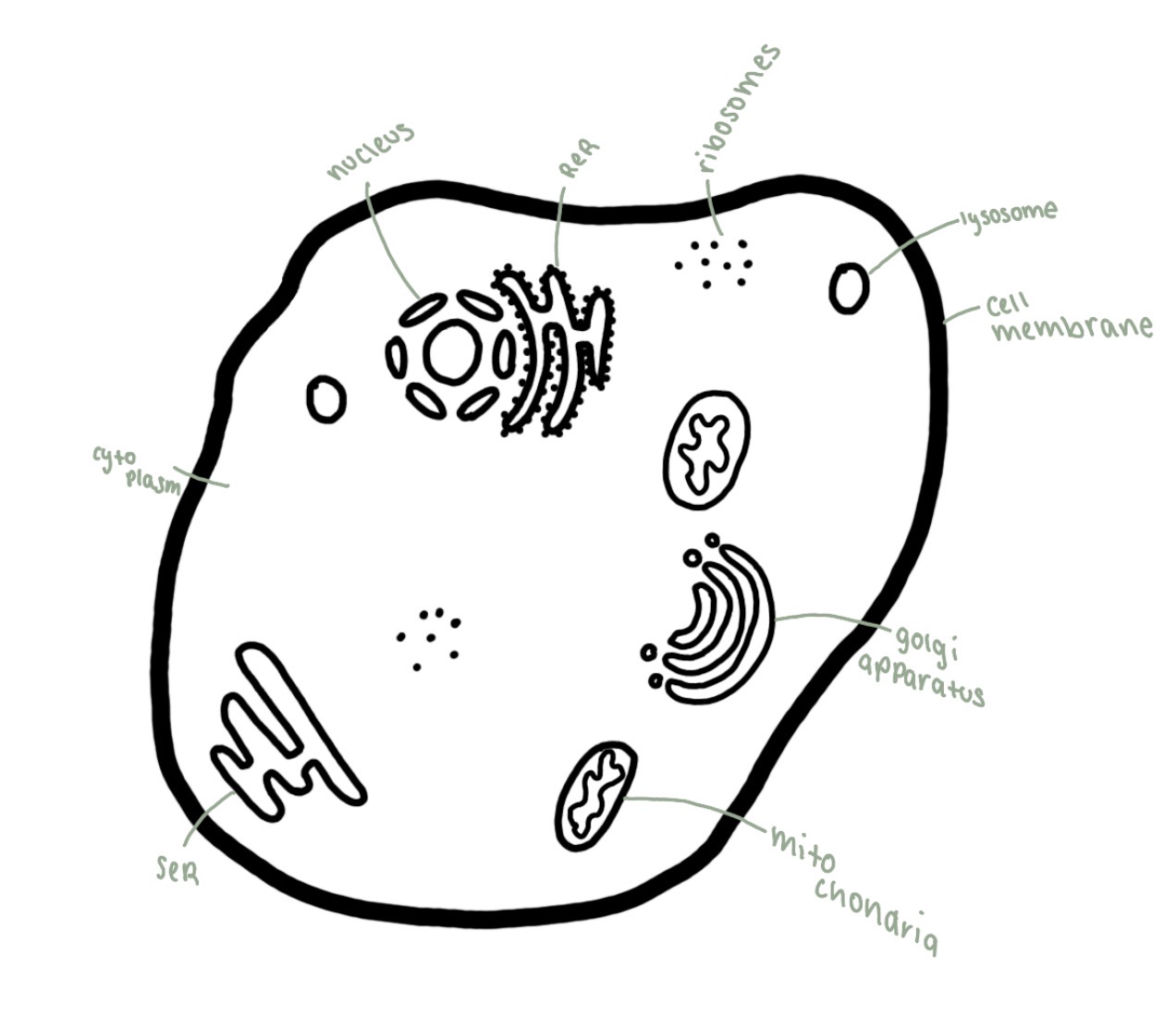
animal cell
plant cell
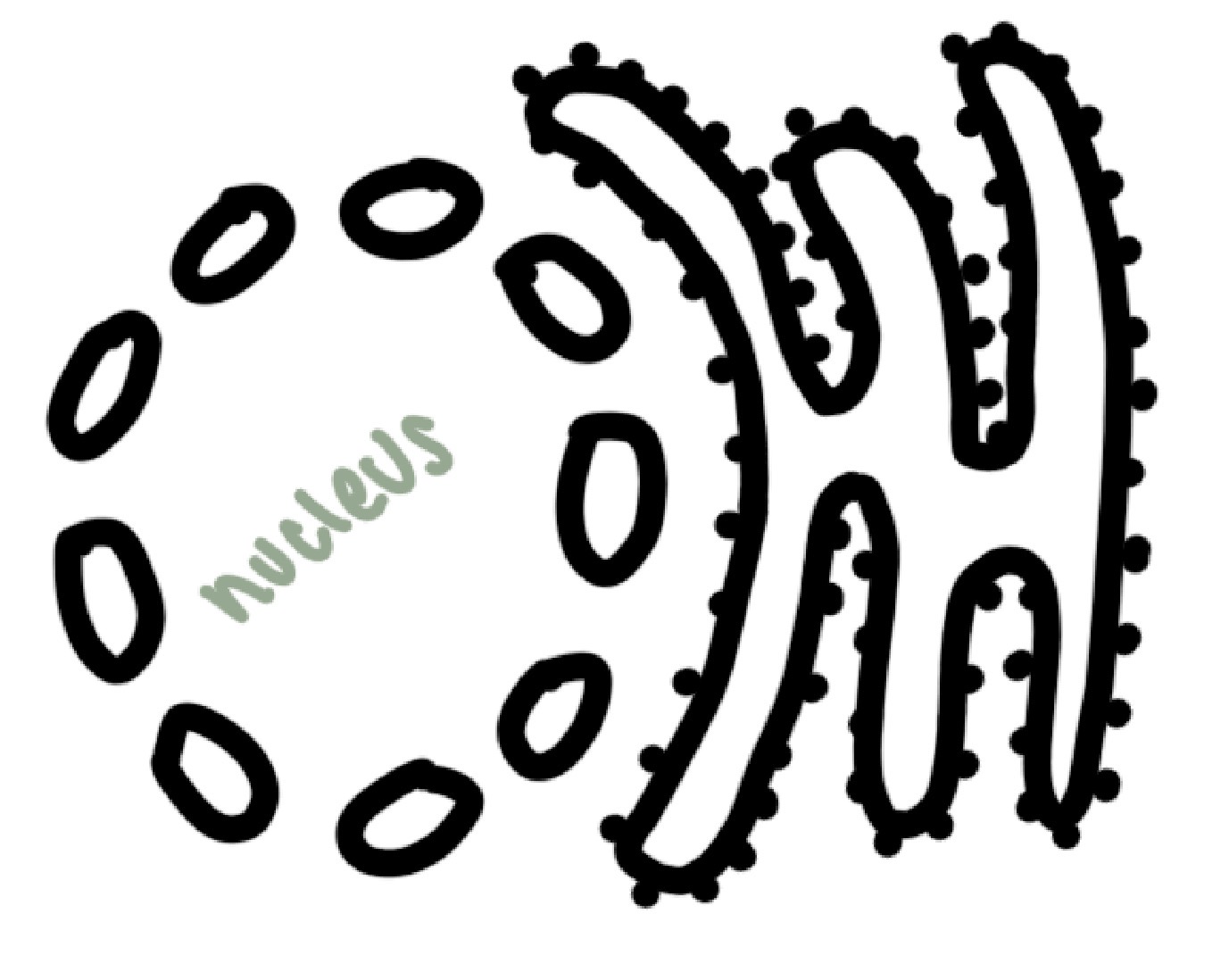
nucleus
10-12 micrometers
contains genetic material, dna
controls cell activity by making molecules for protein synthesis
makes ribosomes and rna
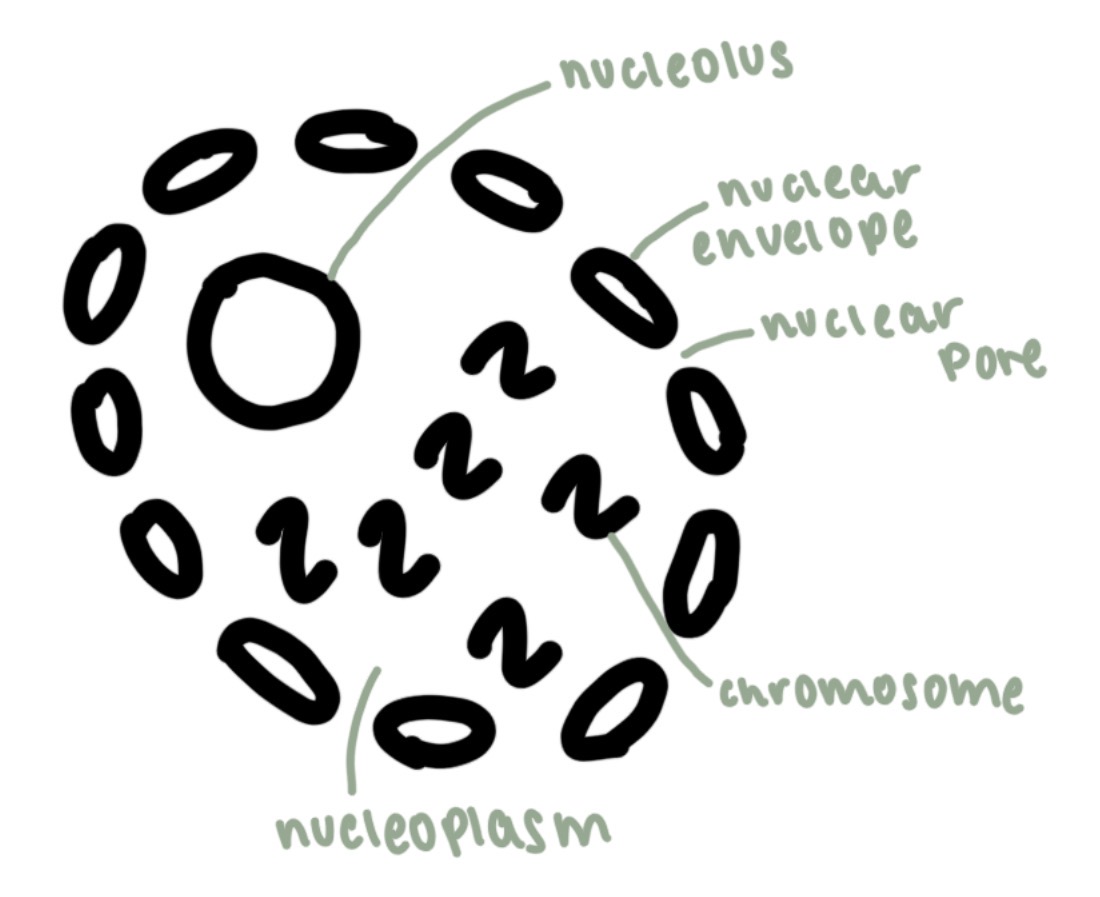
nucleolus
makes ribosomes
nuclear envelope
controls the exits and entry of molecules
chromosome
long, linear strands of dna
nuclear pore
allows large molecules to pass out e.g mrna
mitochondria
1-10 micrometers
site of aerobic respiration , atp
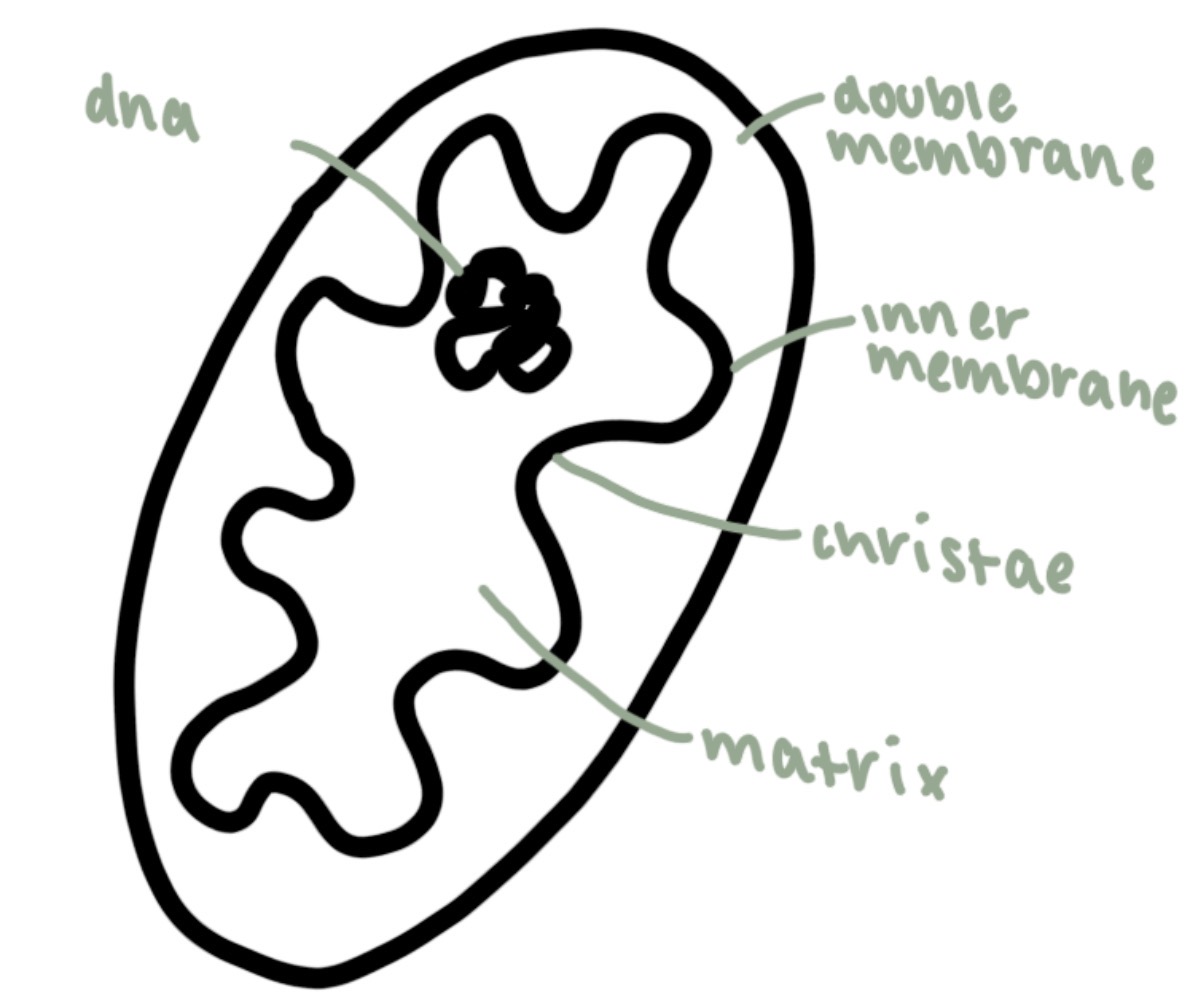
inner membrane
folded to increase surface area
matrix
contains enzymes for the reactions and dna
rough endoplasmic reticulum
system of membranes connected to the nucleus with ribosomes on the outer surface
synthesise, modify and transport protiens
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
system of membranes
synthesises, stores and transports lipids and carbohydrates
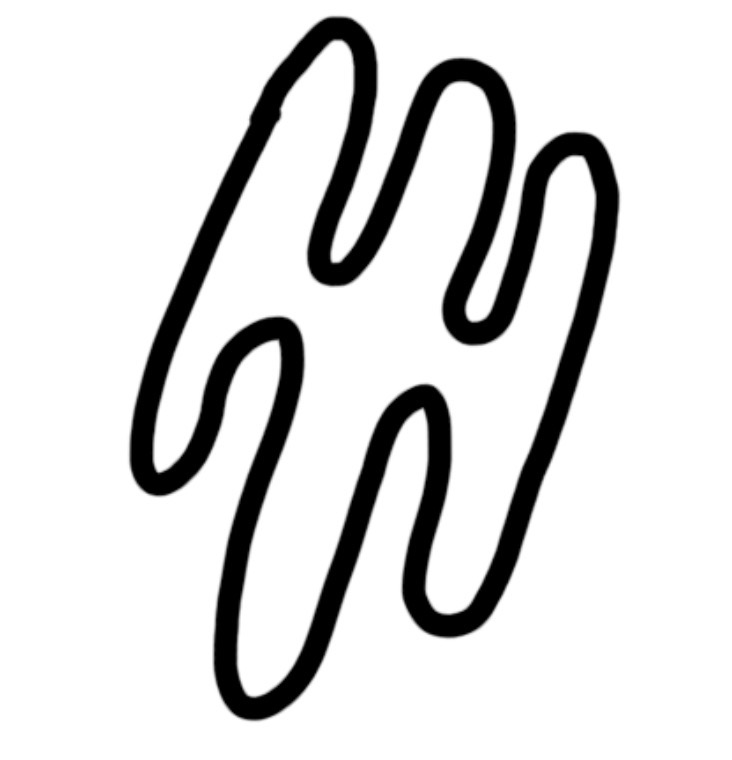

golgi apparatus
membranes forming a series of flattened sacs with vesicles
modifies and transports proteins, secretes enzymes and produces lysosomes
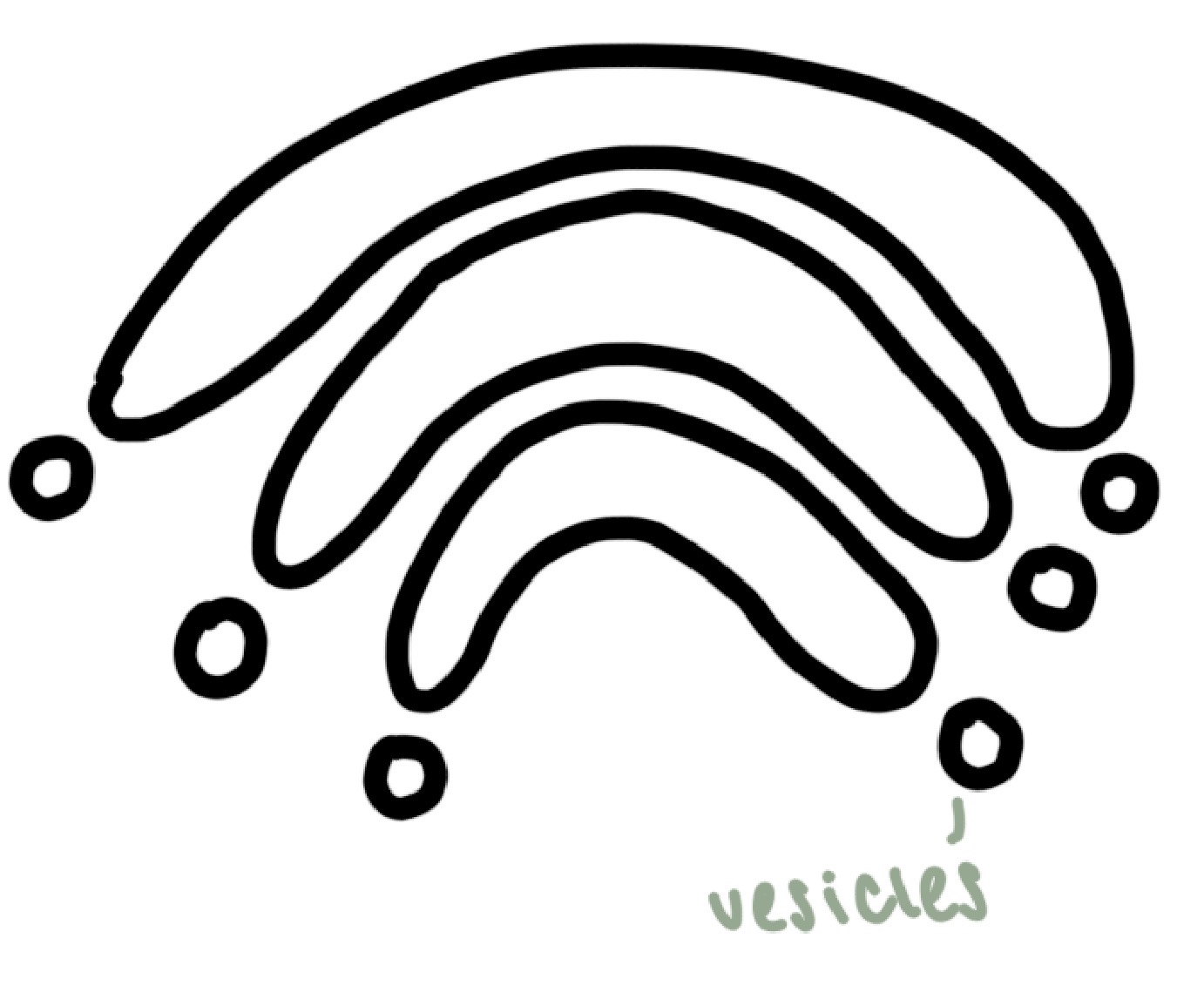

lysosomes
small vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes
phagocytosis, recycles damaged organelles
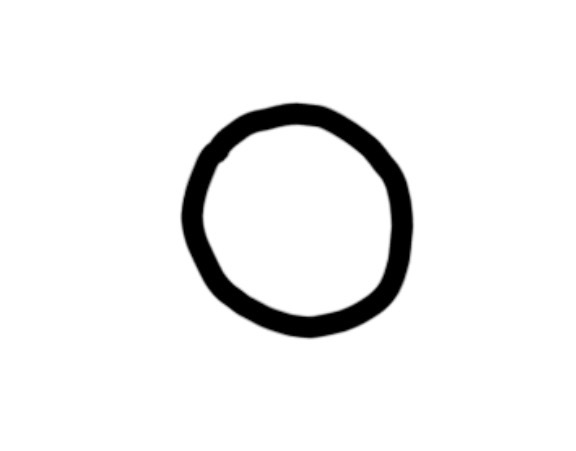

ribsosomes
2 subunits made of protein and rna
performs protein synthesis (translation)
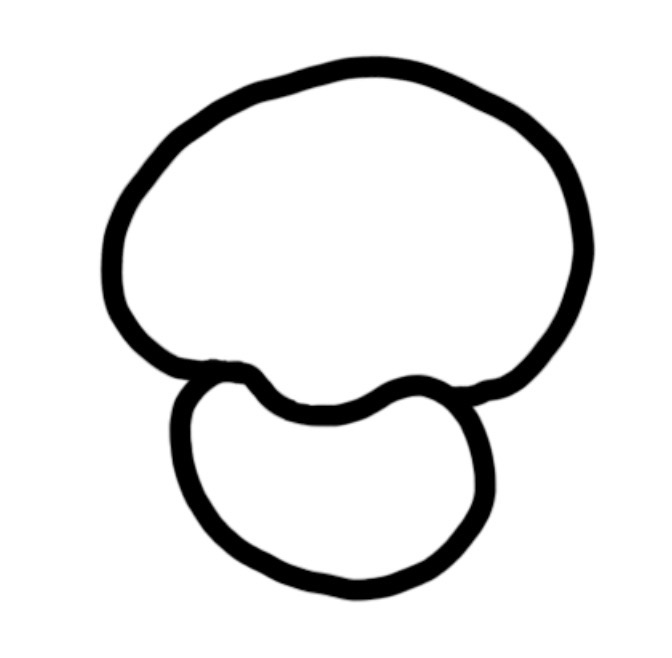

centrioles
helps pull apart the chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis
chloroplasts
double membrane organelle with stacks of thylakoids containing chlorophyll and a fluid filled stomata
site of photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy (glucose)
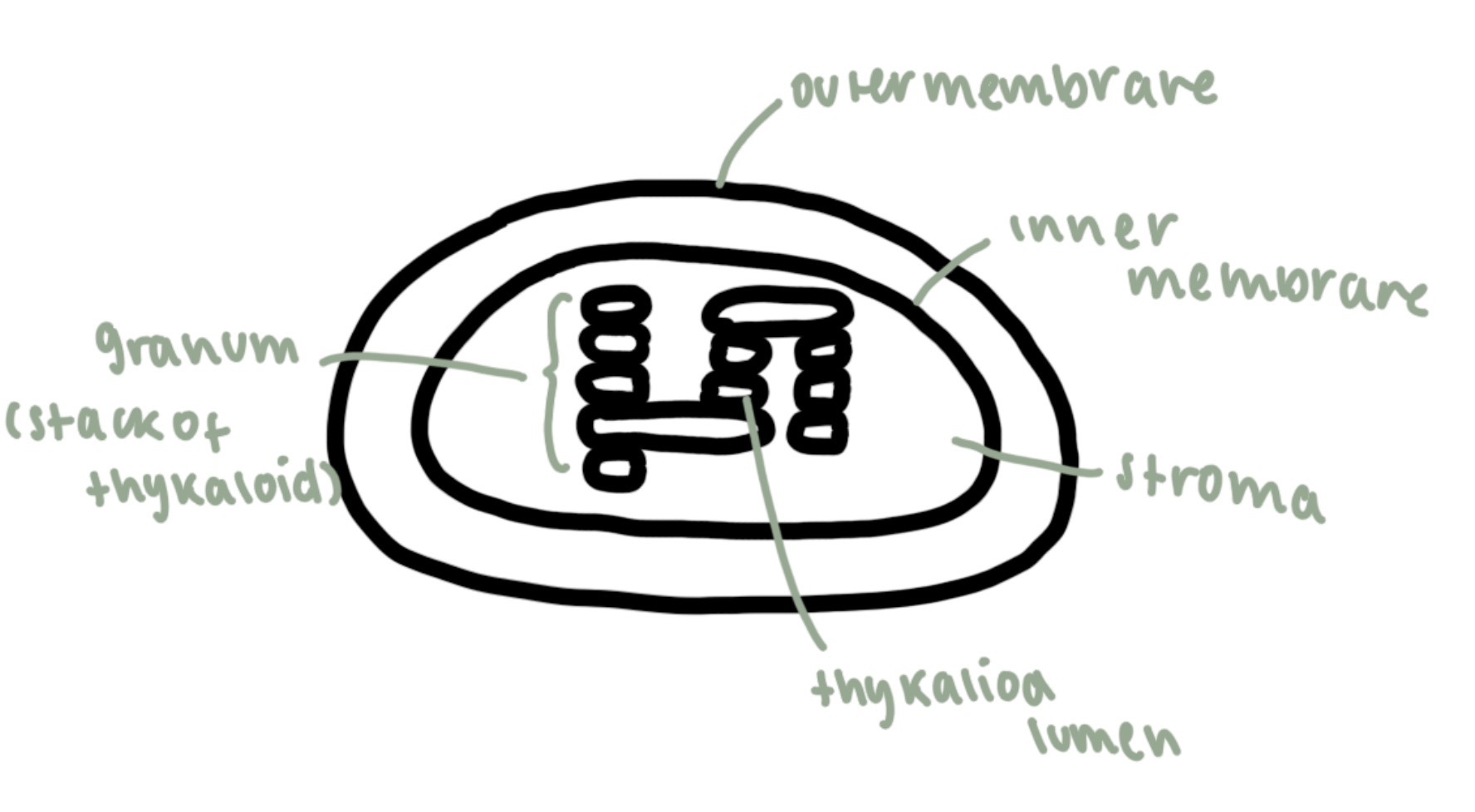
granum
stack of thykaloid
thylakoid lumen
contains chlorophyll, absorbing the light for photosynthesis
vacuole
a large membrane bound sac filled with cell sap
maintains turgor pressure, stores water, ions, pigments and other substances
cell wall
a rigid layer outside the cell membrane, composed of cellulose, chitin or polysaccharides
provides structural support, protection and helps maintain cell shape
plants: cellulose fungi: chitin