Oral Communication || 1st Semester || Midterms
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Communication Barrier
Factors that stop communication from effectively occurring
Language Barrier
Different languages
Semantic Barrier
Different interpretations of the words
Syntactic Barrier
Grammar mistakes and errors
Physical/Environmental Barrier
Physical limitations like noise
Physiological Barrier
Disabilities
Emotional/Psychological Barrier
Failure to express feelings or emotion
Cultural Barrier
Different understandings due to different cultures
Kinship
Families and organizations
Sexuality or Gender
Some countries are open and closed
Religion
Some have specific religions that change understanding and clothing
Cultural Taboos
Includes many taboos universal and per culture
Dress Code
How one should dress in one country vs another varies
Food and Eating Habits
How people eat or what they use to eat also varies from culture to culture
Communication
Two way process by which information is exchanged between people through common systems
communicare
Latin word of communication means working as one
Verbal Communication
Words and language
Oral Language
Speaking and active listening
Written Language
Written text
Sign Language
Gestures to represent words
Non-Verbal Communication
Communication through body language and gestures
Facial Expressions
Emotion through a person's face
Gestures
motions of a speaker's hands or arms during a speech
Paralinguistics
-Tone of voice
-Loudness, pitch, etc.
Body Language and Posture
Can convey certain information about how an individual feels or thinks about a situation; (defensive postures, arm-crossing, and leg-crossing);
Proxemics
-Distance between persons
-Personal space
Eye Gaze
refers to where someone is looking
Haptics
Touching through communication
Appearance
the way that someone or something looks
Artifacts
used to communicate nonverbally
such as selecting your avatar online to
represent your identity.
Sender
initiates the communication process
Message
core content of the
communication, consisting of emotions,
information or ideas
Receiver
an individual who receives or
interprets the message
Channel
or the way the
message is delivered.
Feedback
switching of roles and it is when
we gauge the reaction
Noise
to only disruptions or barriers
in the communication process and it can
cause a conflict.
sender, message, receiver, feedback, and noise
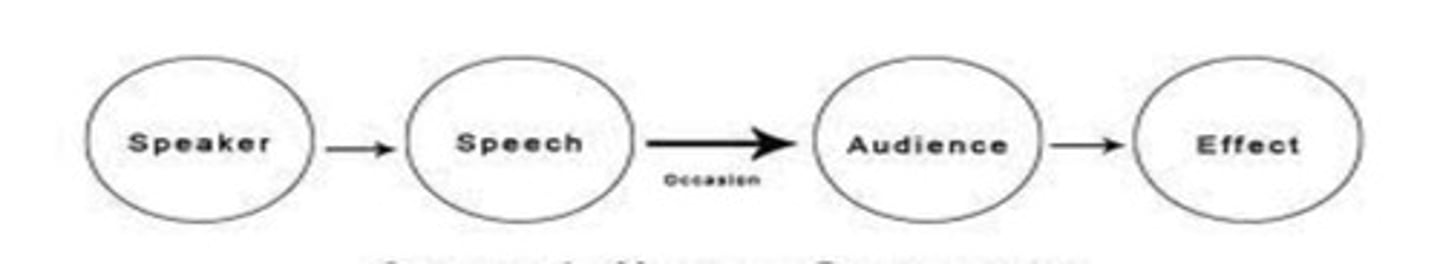
Aristotle Model
Focused on public speaking than interpersonal communication
Laswell's Model
Who says what to whom with what effect?
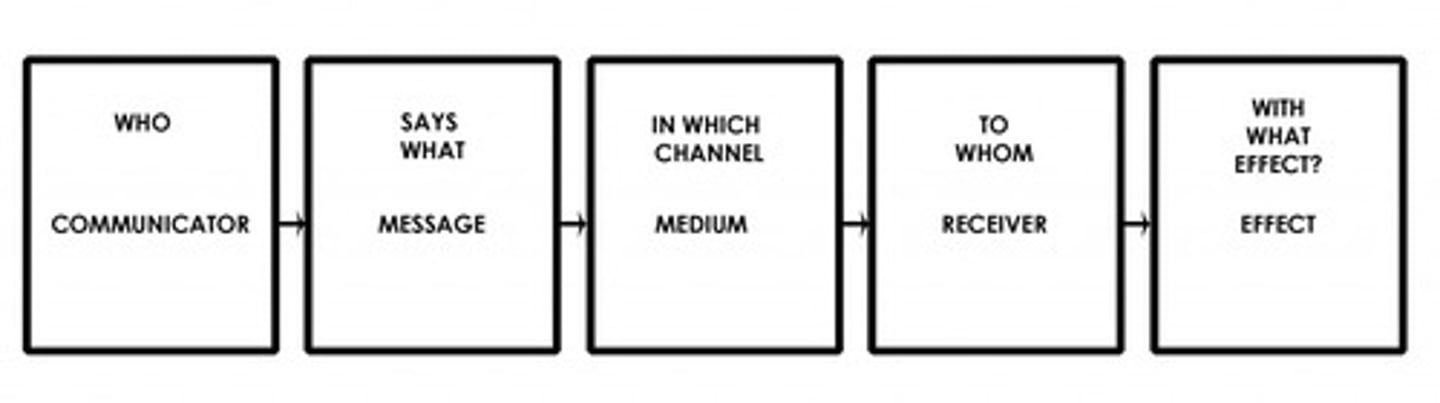
Shannon and Weaver Model
Mother of all communication models
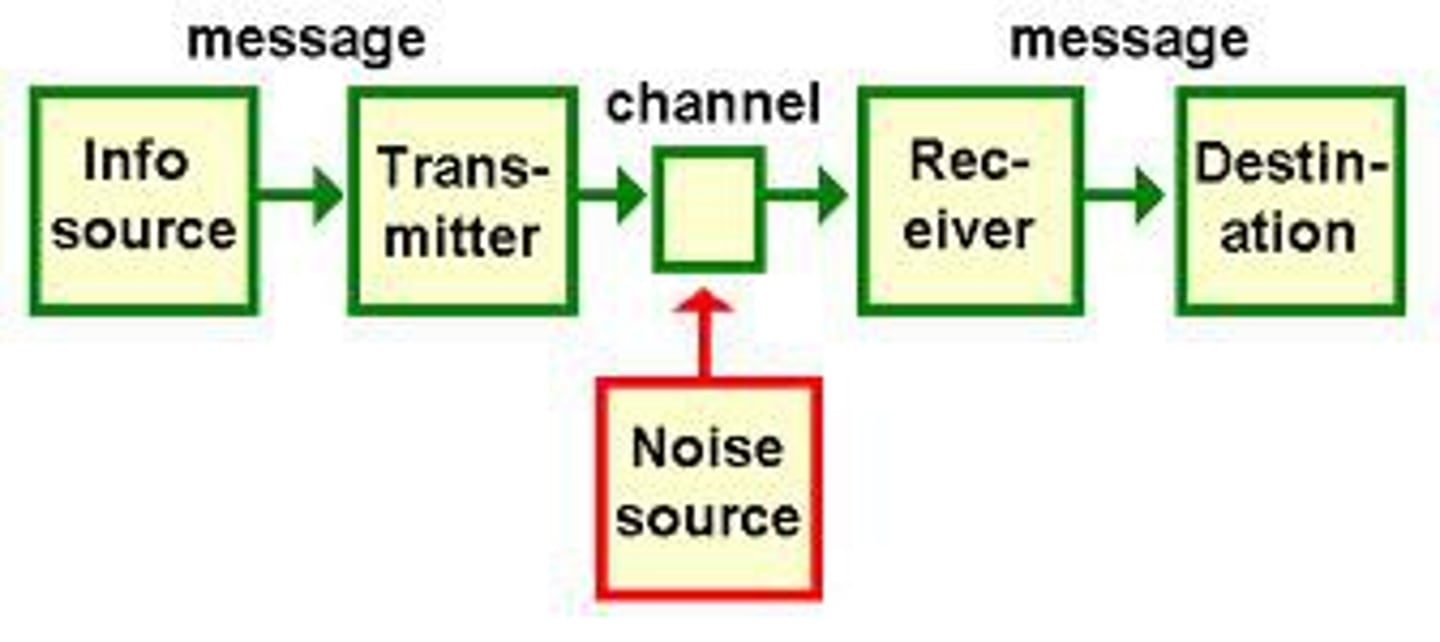
Schramm's Model
Both the sender and receiver take turns in exchanging information
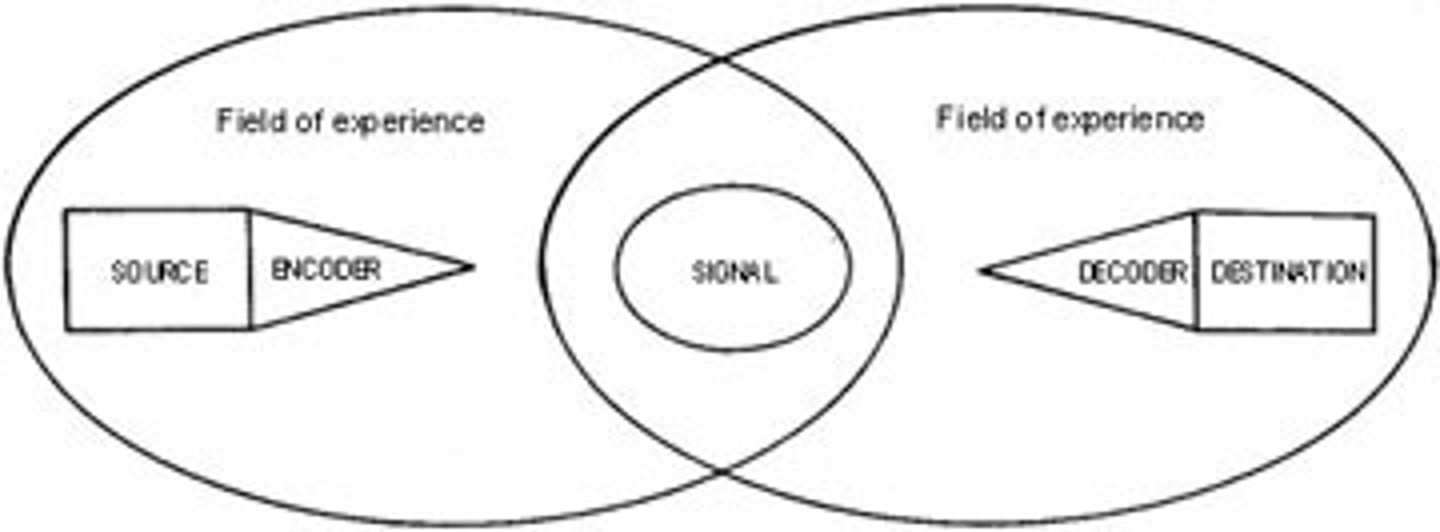
SMCR model
A communication model that identifies the Source, Message, Channel, and Receiver.
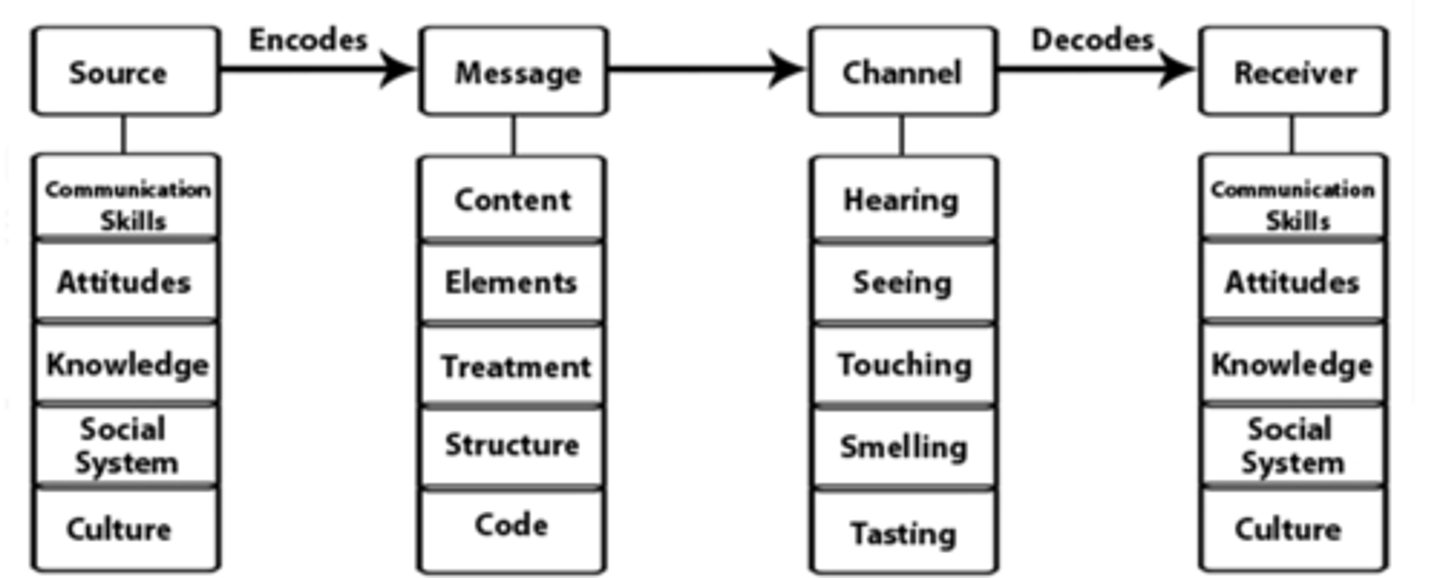
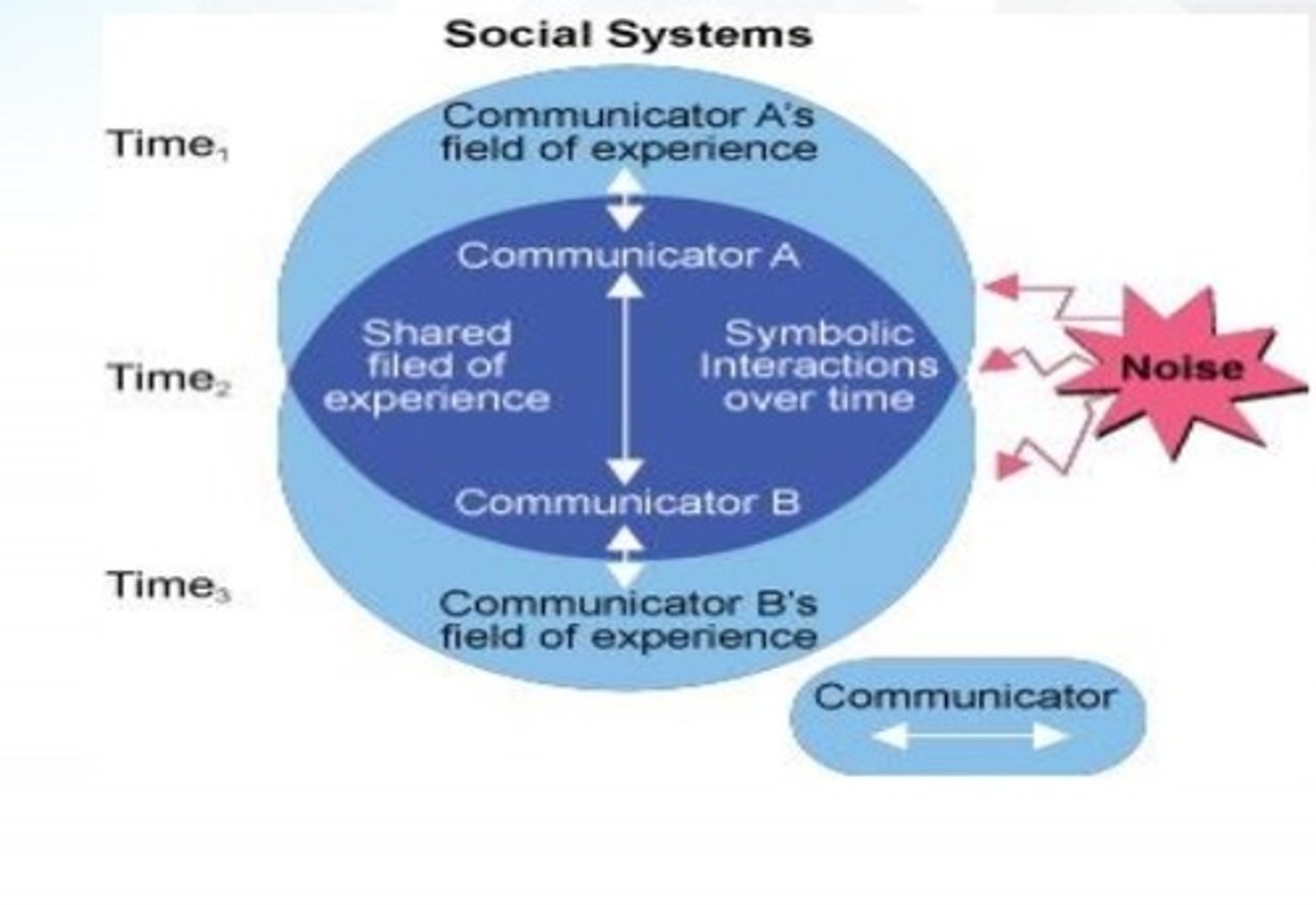
Wood's Model
Depicts communication as a continually changing process.
Linear Communication
one way and no feedback
Interactive Communication
-Schramms' is the only interactive model
-Both receiver and sender play the same role
Transactional Communication
-Wood's is the only interactive model
-The roles reverse or change