Chemistry - UNIT 4
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
metallurgy
the science that deals with procedures for extracting metal from ore
Reduction - old definition
substances that can react with metal compounds that can reduce it to its pure form
Oxidation - old definition
substances that reacts with metal to produce a metal compound
oxidation state
positive or negative number corresponding to the apparent charge that an atom in a molecule or ion would have if the electron pairs in covalent bonds belonged entirely to the more electronegative atom
redox
during a chemical reaction, electrons get transferred between atoms
this reaction can be shown through half reactions
oxidizing agent
the reactant that becomes reduced oxidizes the other reactant
gains electrons
ex. Mg2+, any cations, O2, F2, non-metals
reducing agent
the reactant that becomex oxidized reduced the other reactant
loses electrons
ex. Mg, anions, metals, F-, O2-
glavantic cells
galvanic cell (voltaic cell) makes up part of a battery
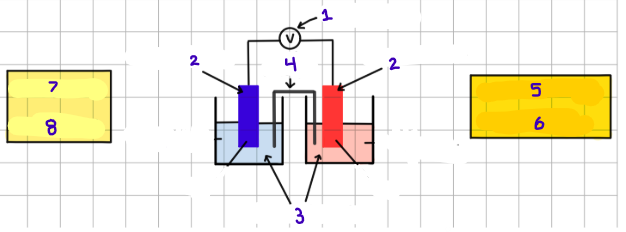
label the parts of galvanic cell
voltmeter
electrodes
electrolytes
salt bridge
cathode (+)
reduction
anode (-)
oxidation
cell notation → a | b || c | d
a & d: electrodes
b & c: electrolytes
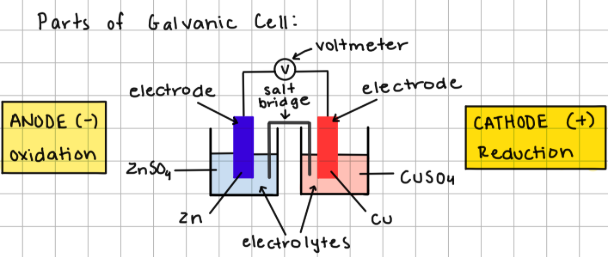
each beaker of a galvanic cell is a
half cell
electrolyte
solution containing ions
electrodes
solids undergo redox reaction
cathode (+)
where reduction reaction occurs
anode (-)
where oxidation reaction occurs
salt bridge/u-tube
contains cations/anions
what is ΔE
energy difference between cathode and anode per unit of charge at standard conditions
energy of electricity (voltage)
standard reduction potentional
the ability of a standard half-cell to compete for electrons
galvanic cells with inert electrodes
when you have a redox reaction where a metal is not involved, you must use an inert electrode
an inert electrode is an unreactive solid that connects ions in a solution involved in the redox reaction (ex. carbon - graphite, Pt)
ΔE is negative
non-spontaneous, galvanic cell will not work
ΔE is positive
spontaenous
what is the purpose of galvanic cells
to produce electricity
which cell needs a power source?
electrolytic cell
what are the 2 purposes electrolytic cells
seperatre ions in a solution
discharge ions (remove the charge
what is the sign of cathode in a electrolytic cell?
negative, reduction
what is the sign of anode in a electrolytic cell
positive, oxidation
what are the differences between an electrolytic cell and galvanic cell
signs change
electrolytic cell has no salt bridge
galvanic cell has a voltmeter, electrolytic cell has a battery
galvanic cell has 2 beakers, electrolytic cell has 1 beaker
faraday’s law
mass of an element consumed or produced at an electrode is direct to the charge transfered
What did Michael Faraday investigate
the relationship between electricity and electro chemical charges
What does Q mean
quanitity of charge transformed by a current per second measured in Columbs
how to caclulate current
I = Q/t
What is faraday’s constant
96500
formula to calculate moles
ne = Q/F