Chemistry Unit 2 (copy)
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB chem test study unit 2 by katie on 4/30. Not sure how deep we have to go into the essential question, "How has atomic theory changed over time?". Will ask Ms.Ravo.... someone remind me pls
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
John Dalton 1803
Made Democritus’ idea into a theory. Matter is composed of atoms, atoms of the same element are identical, atoms combine in whole numbers to create compounds. A reaction rearranges atoms
JJ Thompson
Discovers electron, and its negative charge (first subatomic particle, and Dalton is wrong). Proposed that cathode rays were streams of particles much smaller than atoms.
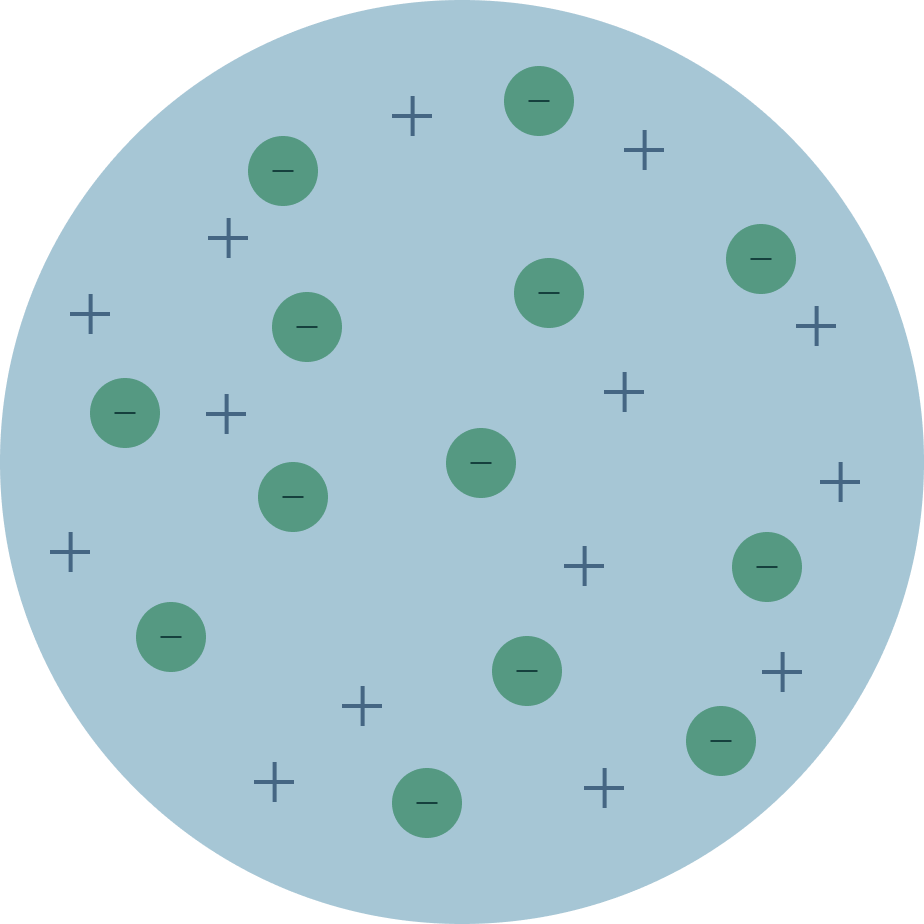
PLUM MODEL shows neg electrons in a pool of pos electrons.
Atom
smallest thing of an element that shows all the characteristics of that element. electrically NEUTRAL
Ernest Rutherford: Gold Foil Experiment 1911
Directing alpha particles (+) to a gold foil, watching it scatter. Found most particles go straight through the foil, while some scatter, showing the existence of the nucleus, and that an atom is mostly empty space.
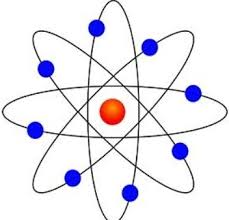
Bohr Model
Planetary Model, electrons travel in orbitals, each orbital has a definite energy.
Orbitals closer to the nucleus has lower energy
Schrodinger: 1926
The Wave Mechanical Model: likelihood of finding an electron at a certain place
Electrons move like particles and waves
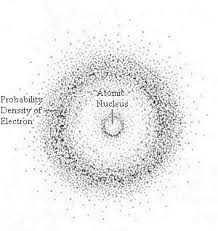
Electrons move like….
particles AND waves
Chadwick: 1932
Discovers neutron, same mass as a proton, electrically neutral

Protons location and weight
Nucleus and 1 amu

Neutron location and weight
nucleus and 1 amu
Electron location and weight
Outside the nucleus, 0 amu

Atomic Number
number of protons
Isotopes
differing number of neutrons (carbon -12…. add mass number at the end)
Isotope Notation
top is mass # and ottom is atomic #
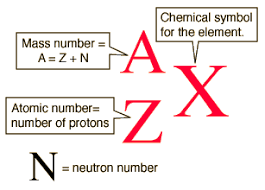
Ions
when protons do not equal electrons (charged)
Relative atomic mass
The average mass of an atom of an element taking into account all of its isotopes and their relative abundance (how often they show up naturally )
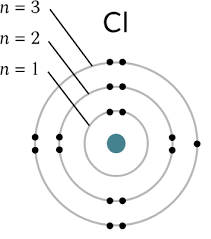
Energy levels/shells and their max # of e
2n² shows the maximum number of electrons that a shell can accommodate
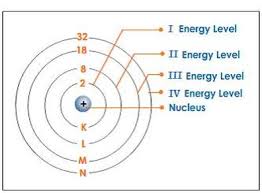
Valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell
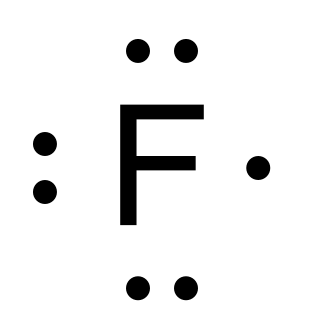
Lewis electron dot structures
Showing # of valence electrons (clockwise)
Electron config
Li: 2—1
Sulfur : 2—8—6
Energy levels divided up into Sublevels/subshells, with letters…
s, 2. p , 6. d, 10 and f, 14. (max # of electrons)
FULL electron config
1s22s22p6……
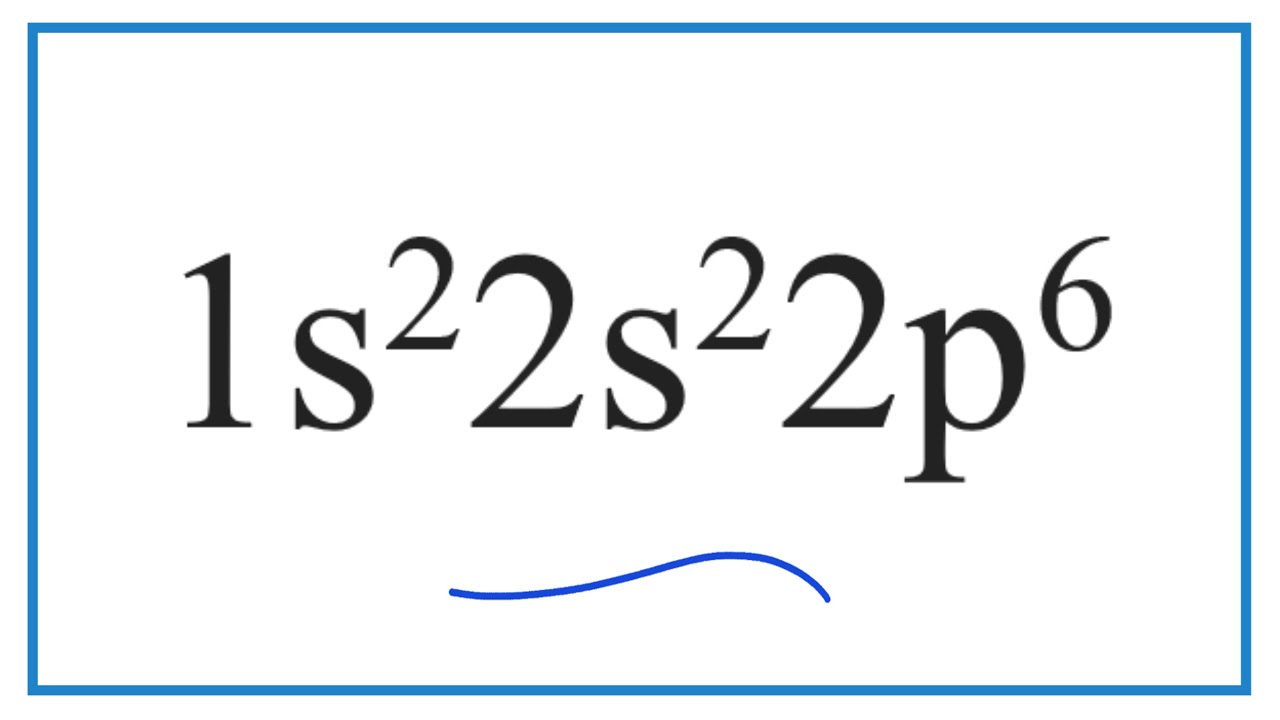
exceptions when doing full electron config and WHY
Chromium and Copper, because the last sublevel is 4 or 9, and they would be happier at 5 or 10. (take one from the second to last level)
How to write condensed config
use [noble gas]
What are orbitals
region of space where there is a high chance an electron is gna be there
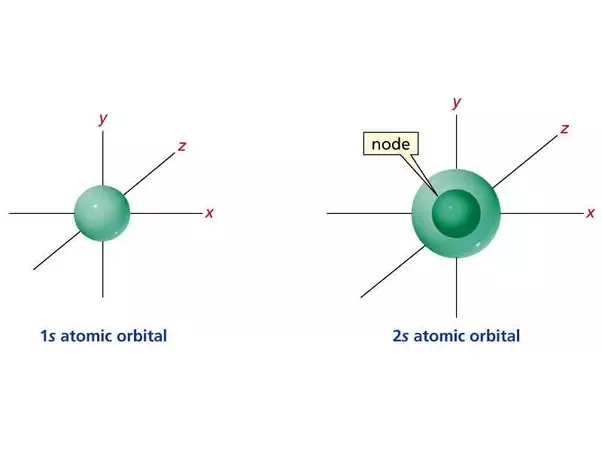
1s and 2s orbitals
SHPERICAL and 2s is bigger.
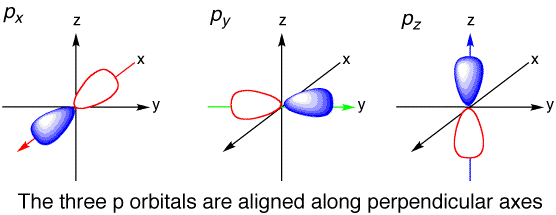
px, py, and pz orbitals
DUMBELL SHAPED
Orbital diagrams
most detailed e config, orbitals are boxes, arrows representing the spinning of opposite directions.
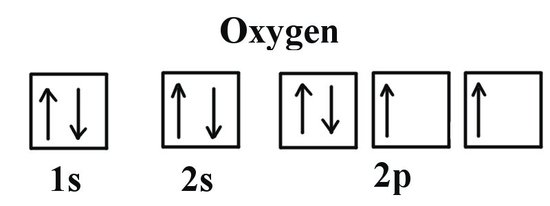
Pauli Exclusion Principle
A maximum of two electrons in each orbital, but only if they have opposite spins.
Hund’s Rule
fill in all the spaces in the boxes with one before going in for seconds,,, basically
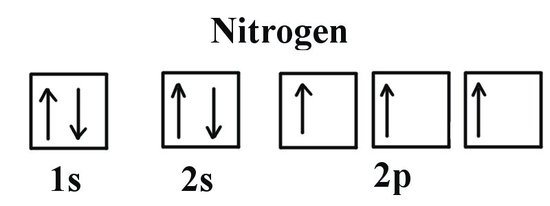
which electrons are removed first
highest energy level, the ones furthest away from nucleus CAUSE THEY HAVE LEAST ATTRACTION
what is isoelectronic ill do this lkater damn
idfk
Proof that supports electron config?
Flame test…. we shld look more into this.
Flame test
atoms of different elements produce different flame colors when heated with a Bunsen burner, producing light of distinctive color when an electric discharge is passed through a vapor of an element.
WHY does the flame test do that…
The flame test excites electrons in atoms, causing them to release energy in the form of light at specific wavelengths, which corresponds to different colors.
Energy and frequency have a ____ relationship
direct
wavelength and frequency/energy have a ____ relationship
indirect

Continuous spectrum
White light is all the colors at once.
emission spectrum/line spectrum
light emitted by gas, only certain wavelengths of light pass

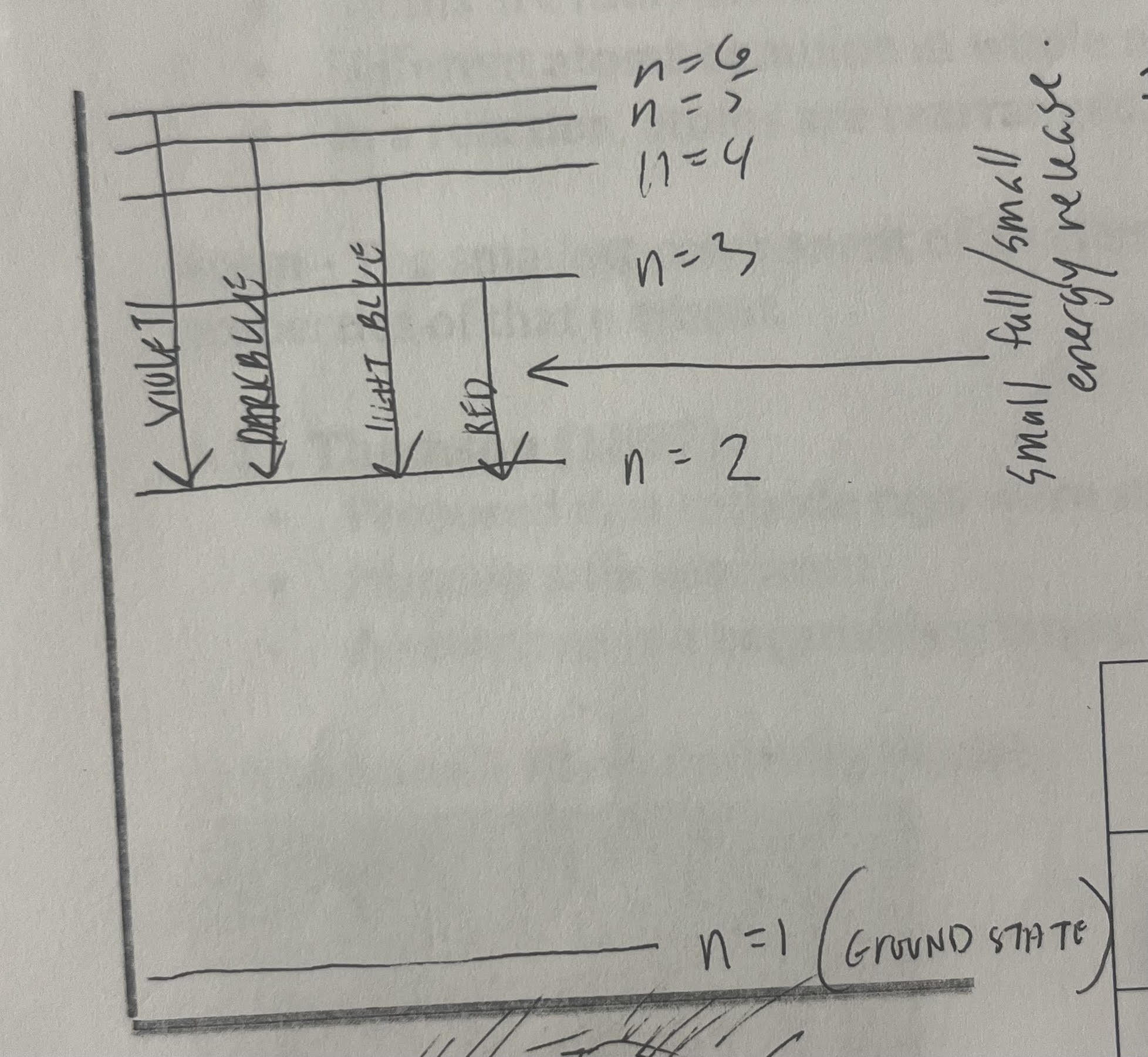
What happens to the lines as we go towards higher energy (violet)
they converge
How is the emission spectrum created
energy is given to the atom, where they enter the excited state
they fall back down to their ground state, releasing energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. One photon (packet of energy) is released for each electron transition)
How to write excited state config
Put an electron in another level basically.
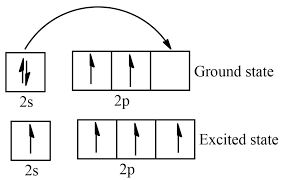
Visible light only falls to which level?
2