Pulmonology MSA Anatomy/Physiology Quiz pgs 177-184
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Respiratory System/Tract
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting especially of the nose, nasal passages, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
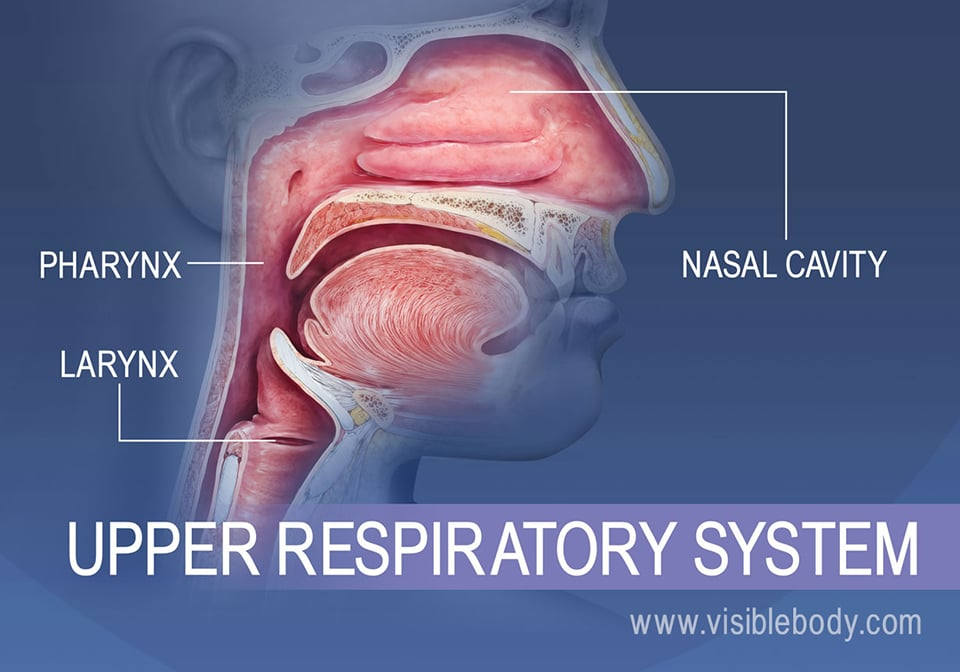
upper respiratory system
nose, nasal cavity, pharynx
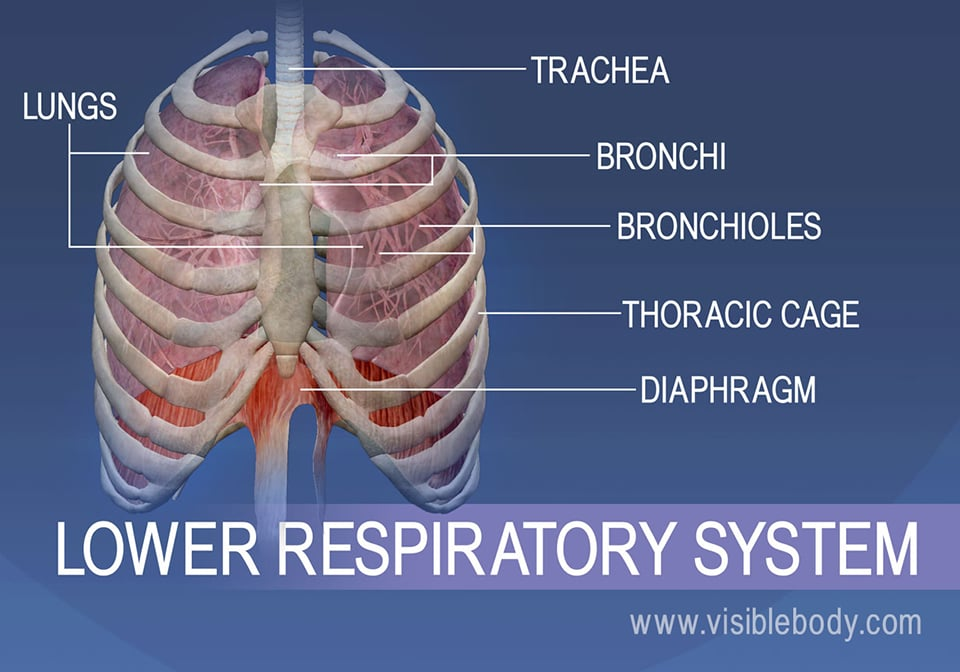
lower respiratory system
larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, thorax
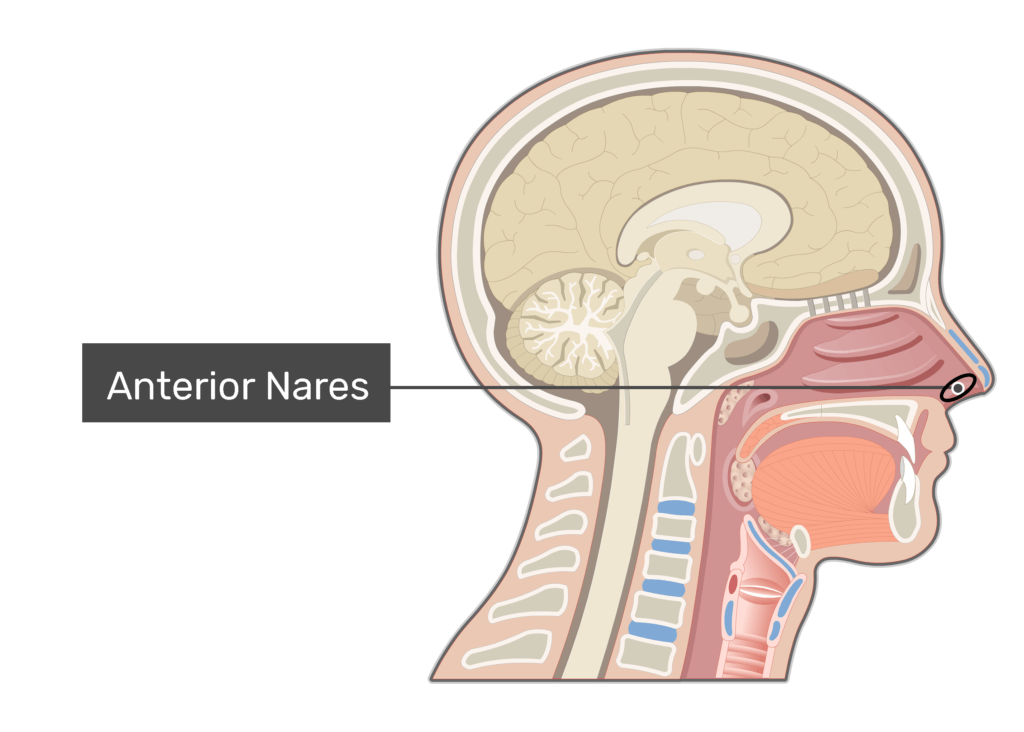
Nares
nostrils
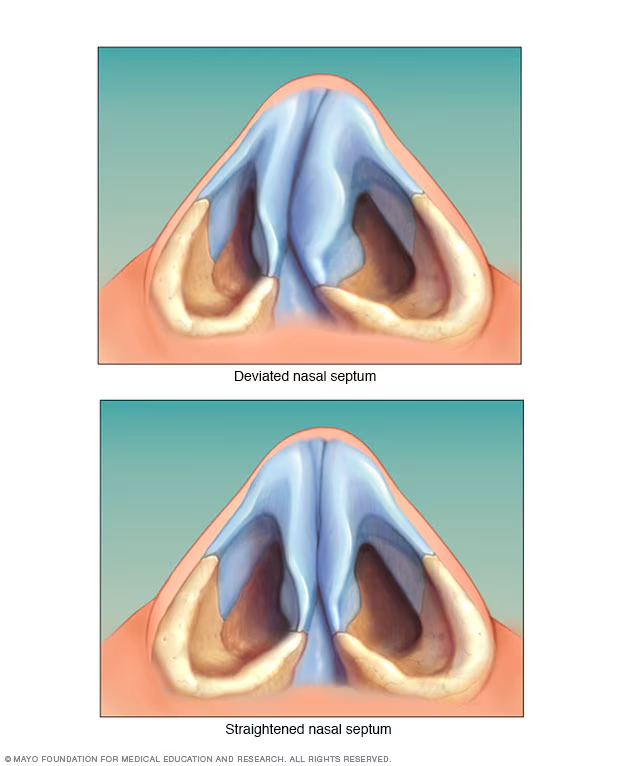
Nasal septum
a wall of cartilage that divides the nose into two equal sections
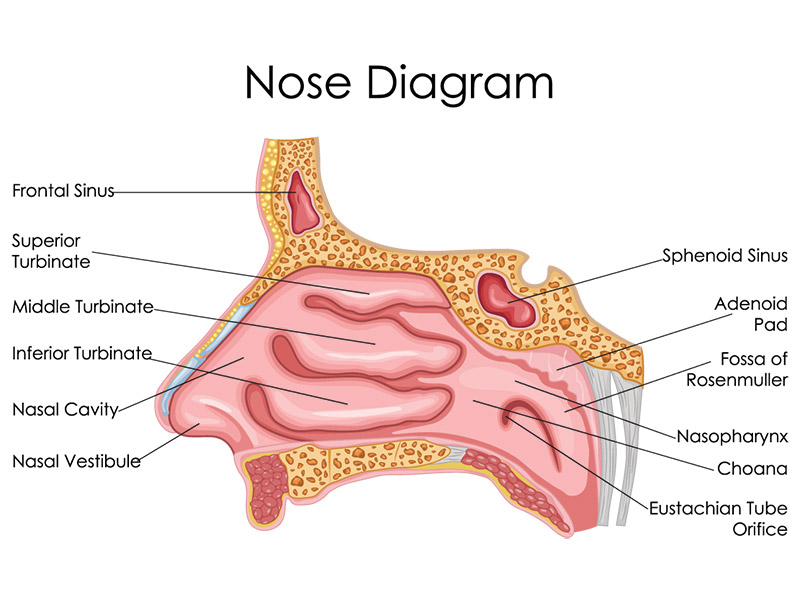
turbinates (nasal conchae)
Three long, bony projections (superior, middle, and inferior) on either side of the nasal cavity. They break up and slow down inhaled air.
mucous membrane
Lines the nasal cavity and turbinates, warms and moisturizes air and produces mucus
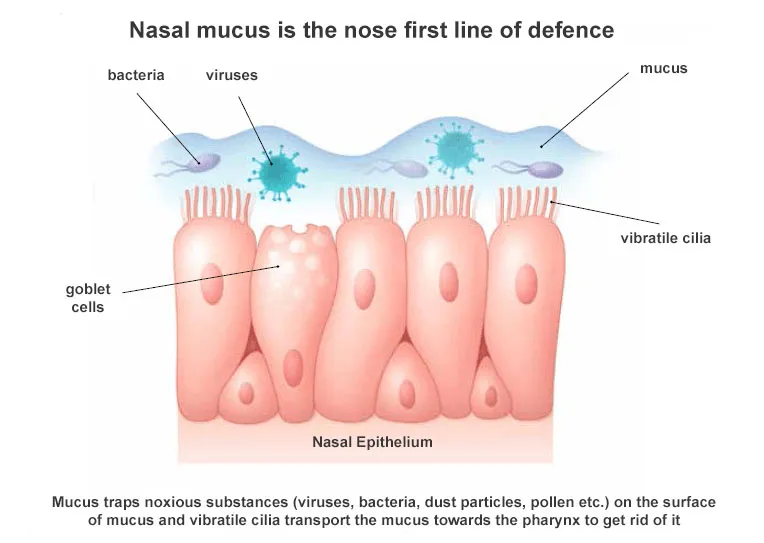
Mucus
a slimy substance produced in the nose and throat to moisten and protect them
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
three parts of the pharynx
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
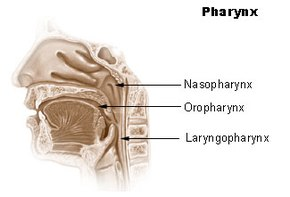
nasopharynx
region of the pharynx at the back of the nose and above the soft palate
oropharynx
area of the pharynx posterior to the mouth.
laryngopharynx
lower part of the pharynx, posterior to the larynx (voice box) opening into the larynx and esophagus
Cilia
Small hairs that move in waves to carry mucus and foreign particles toward the throat where they can be swallowed or expelled by coughing
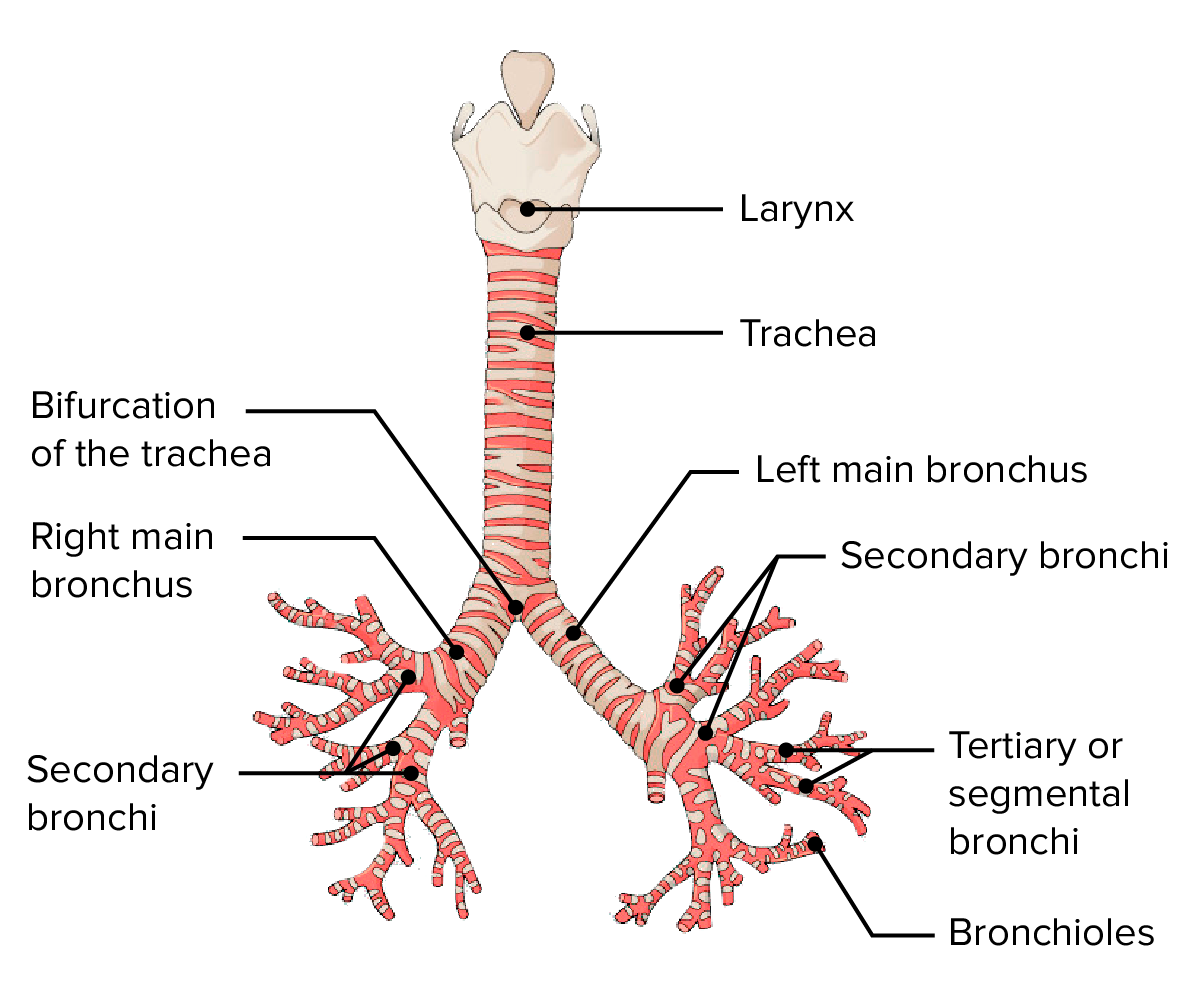
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
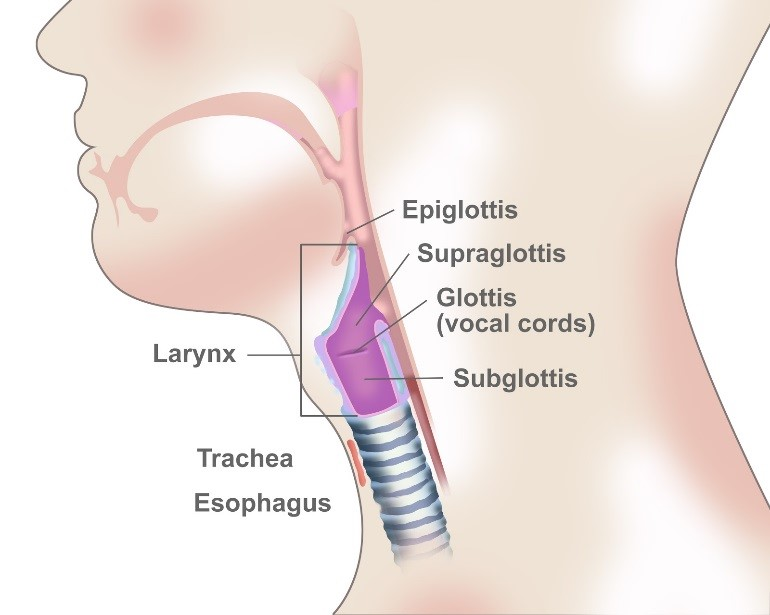
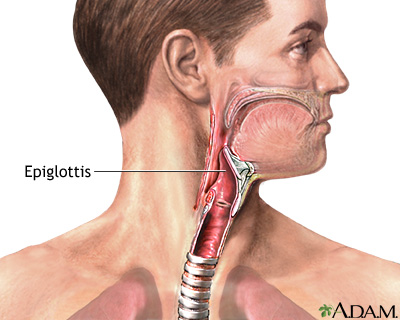
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
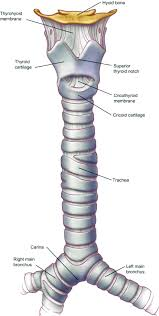
Lumen
The central opening within the trachea
cardiopulmonary
pertaining to the heart and lungs
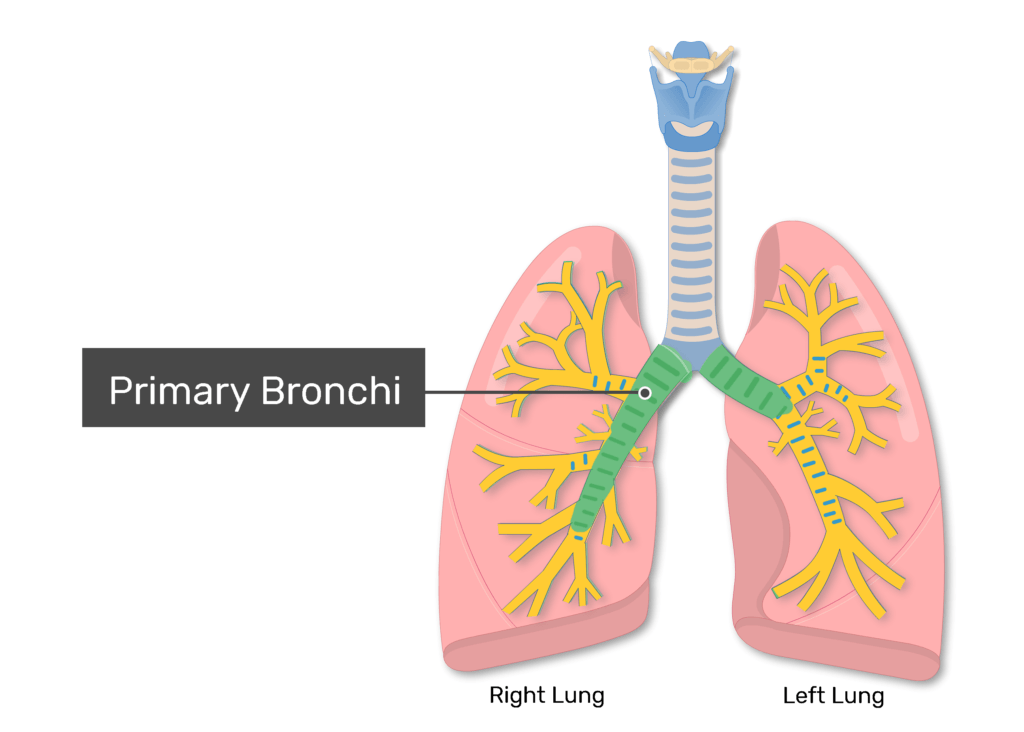
Bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
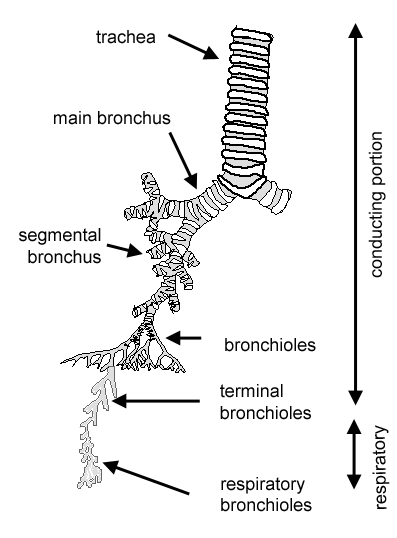
Bronchioles
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
Bronchopulmonary
pertaining to the bronchi and lungs
Bronchial tree
the branching system of bronchi and bronchioles conducting air from the windpipe into the lungs.
Lungs
two spongy organs, located in the thoracic cavity enclosed by the diaphragm and rib cage, responsible for respiration
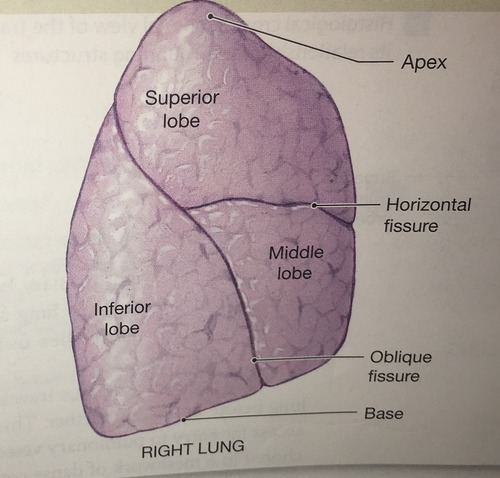
Lobes
Large divisions of the lungs that are visible on its outer surface
The lobes of the right lung
superior, middle, inferior
The lobes of the left lung
superior and inferior
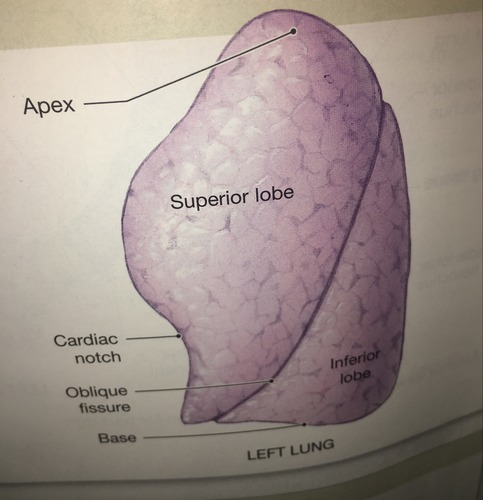
apex of the lung
uppermost portion of the lung
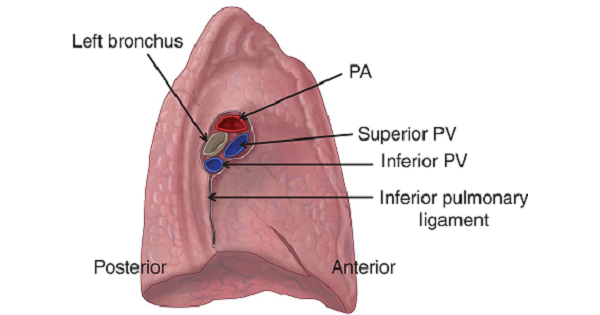
hilum of the lung
midline region where the bronchi, blood vessels, and nerves enter and exit the lungs
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
pulmonary surfactant
A compound excreted by alveoli, reduces surface tension and keeps the walls of the alveoli from collapsing with each exhalation
pulmonary parenchyma
essential parts of the lung, responsible for respiration; bronchioles and alveoli
Thorax
chest
Rib cage
protects the heart and lungs
Sternum
breastbone
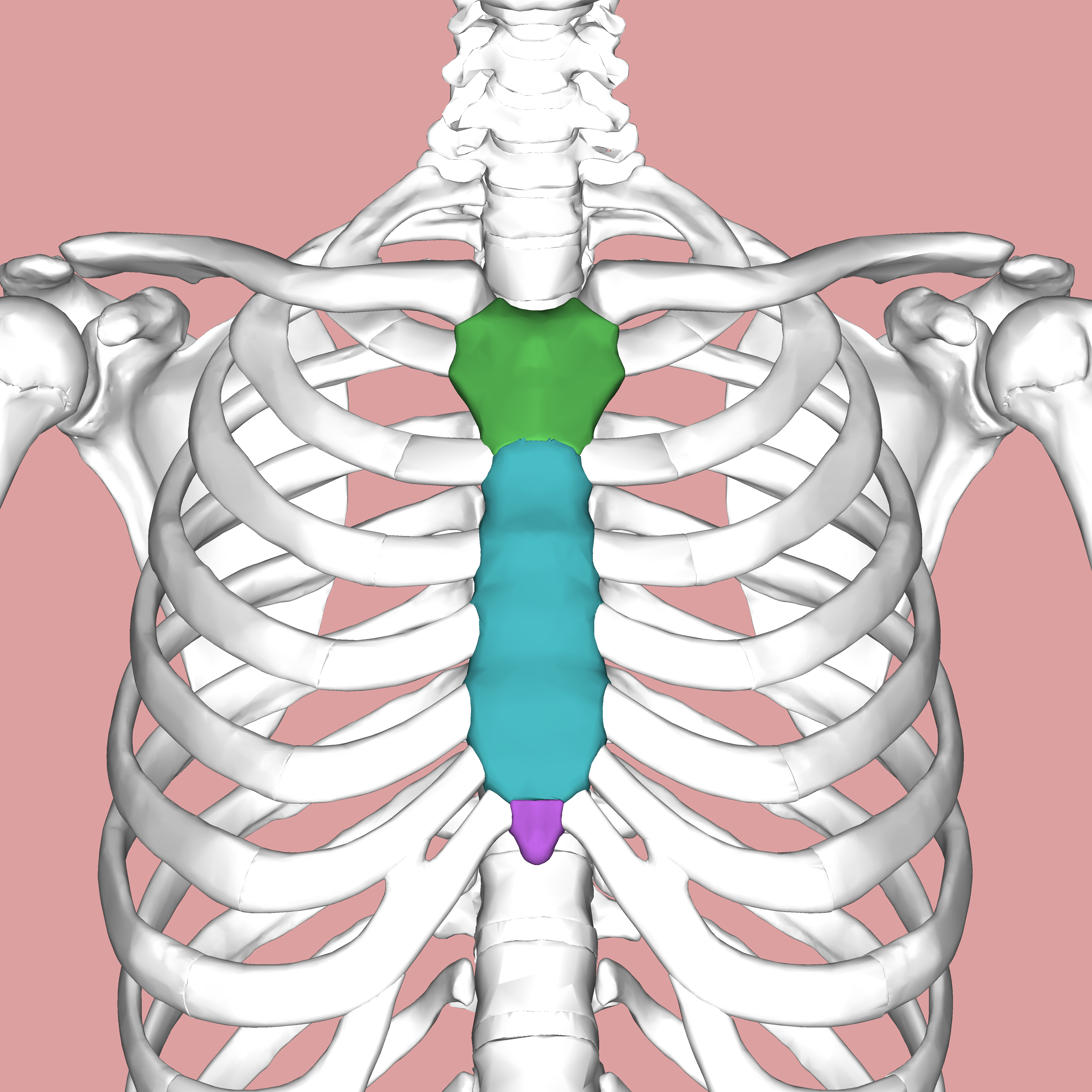
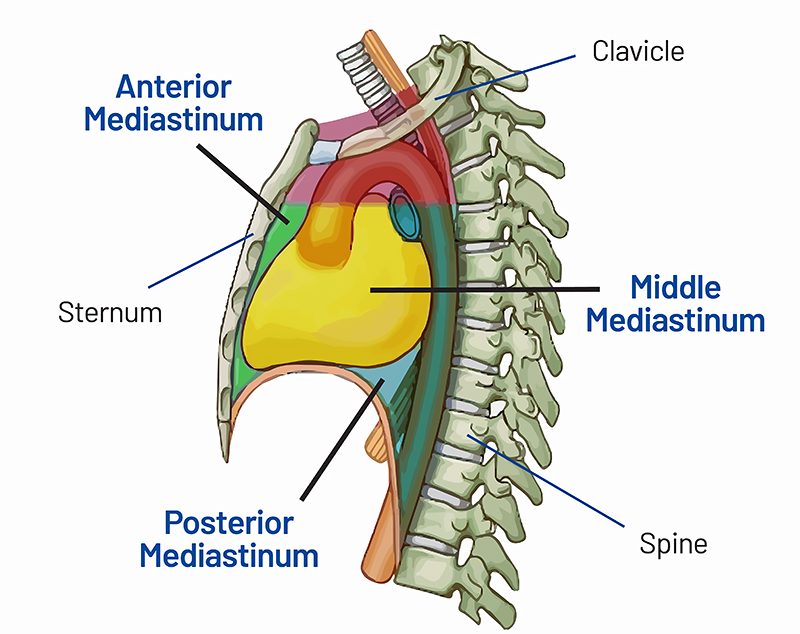
Mediastium
The middle section of the chest cavity located between the lungs. This cavity contains the heart and its veins and arteries, the esophagus, trachea, bronchi, the thymus gland, and lymph nodes.
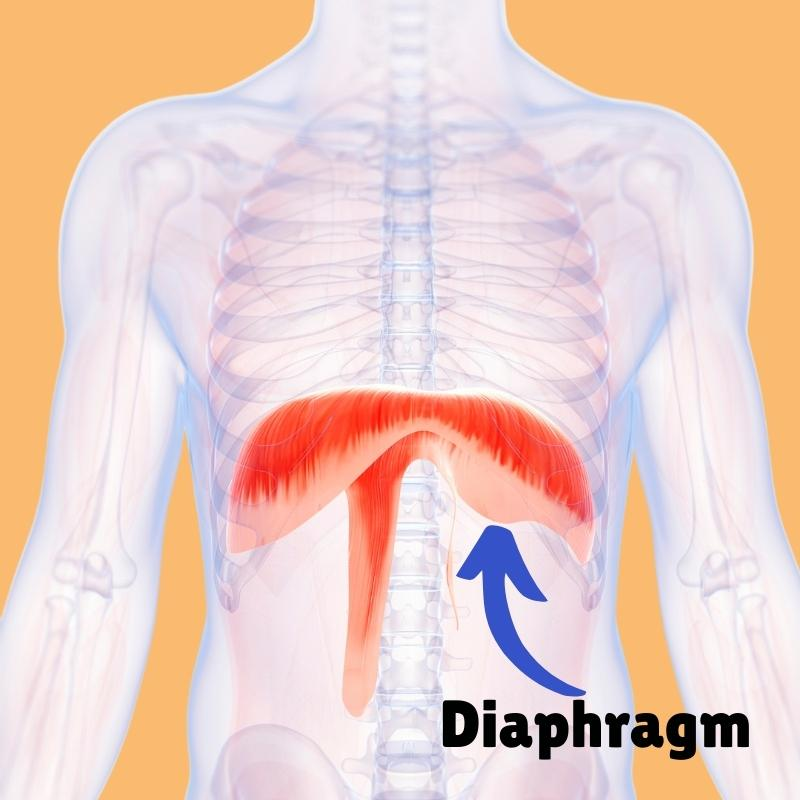
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
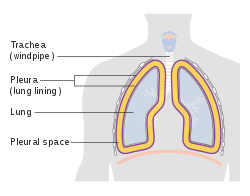
pleural cavity
contains the lungs
Pleurae
serous membranes that form an envelope between the lungs and the chest wall
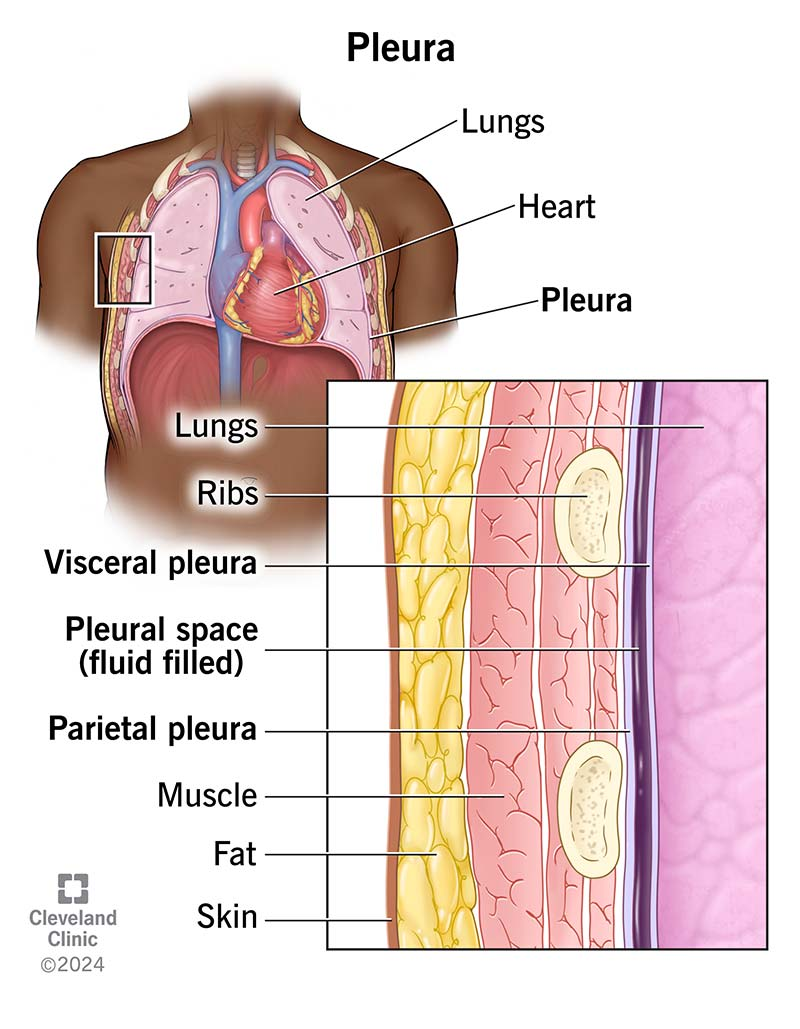
visceral pleura
inner layer of pleura lying closer to the lung tissue
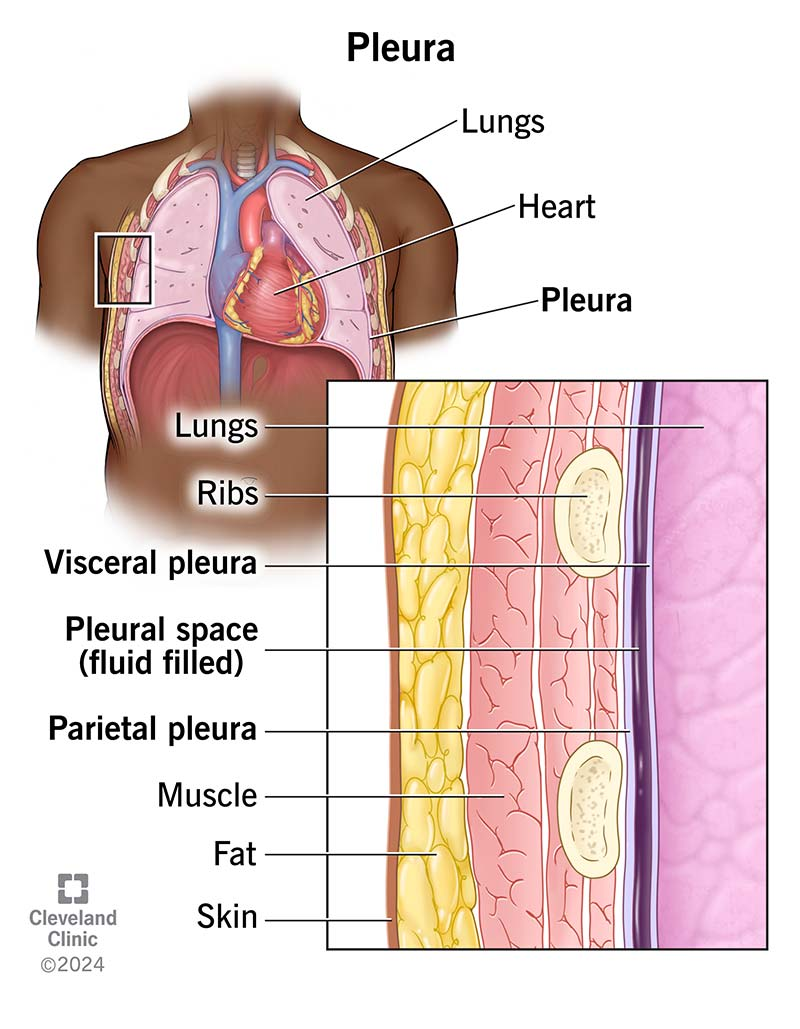
parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura lying closer to the ribs and chest wall
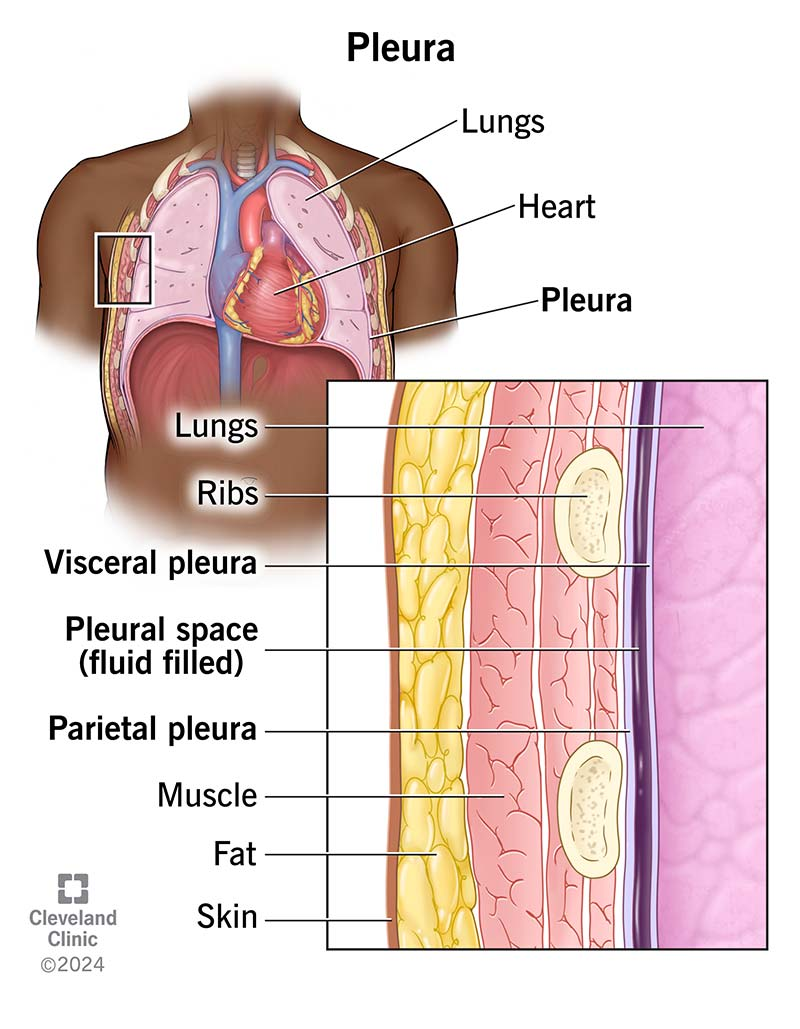
Pleural fluid
serous fluid necessary to prevent friction between the pleural membranes
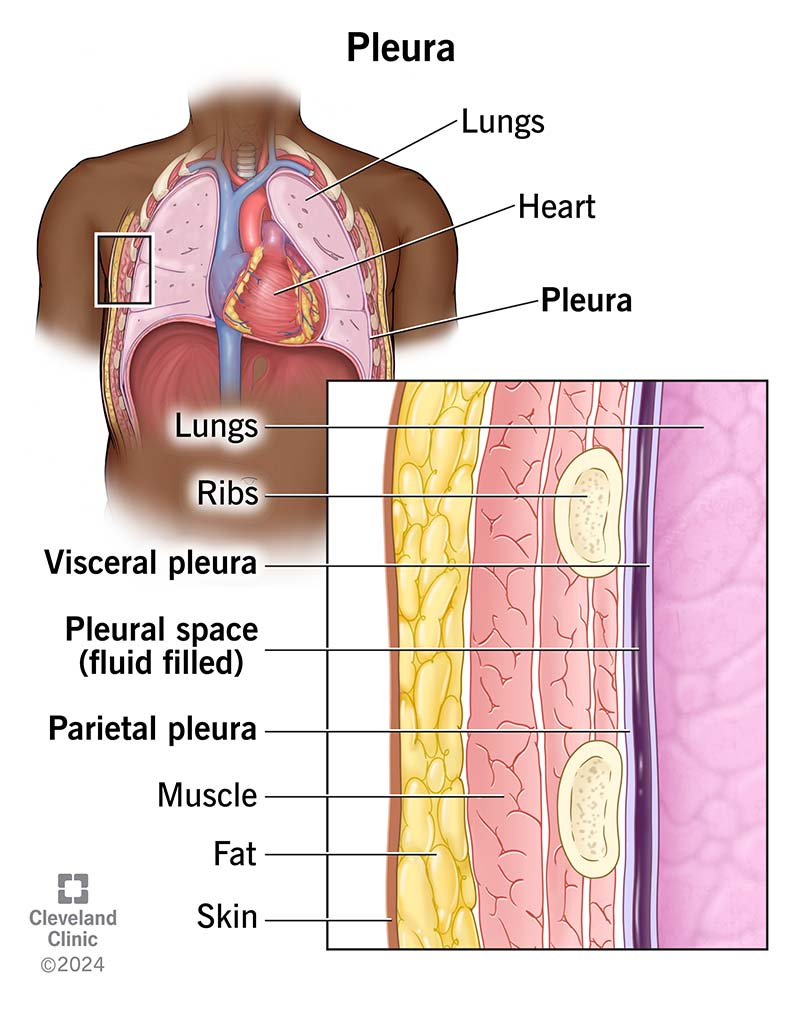
Pleural space
the area between the parietal and visceral pleurae; pleural fluid is excreted into this space
Respiratory control centers
Centers in the brain that regulate the depth and rate of respiration
Phrenic nerve
Carries impulses to the diaphragm from the brain.
Respiration
Inhalation and exhalation of air.
Inhalation/Inspiration
breathing in
Exhalation/Expiration
breathing out
intercostal muscles
Muscles which move the rib cage during breathing.
Why is it necessary for the ribs to pull out during inhalation?
This movement enlarges the thoracic cavity and creates negative internal pressure that causes air to flow into the lungs
What happens to the lungs during exhalation?
The diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, the thoracic cavity returns to its previous size, and air flows slowly out of the nose.
Eupnea
A normal depth and rate of respiration
Ventilation
movement of air in and out of the lungs
external respiration
Movement of oxygen gas molecules from inhaled air into the alveoli and then into the blood. External respiration also involves the movement of carbon dioxide gas molecules from the blood into the alveoli and then into exhaled air. External respiration is the exchange of these two gases within the alveoli. The respiratory system and the blood perform this process together.
Gas transport
the process of carrying O2 and CO2 from the alveoli to the systemic tissues and vice versa. Performed by the cardiovascular system and blood
Hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment in red blood cells
Oxyhemoglobin
a bright red substance formed by the combination of hemoglobin with oxygen, present in oxygenated blood.
Internal respiration
Movement of oxygen gas molecules from the blood into the cells of the body. Also, the movement of carbon dioxide gas molecules from the cells into the blood.
Internal respiration is the exchange of those two gases between the blood and each cell. The blood and individual cells perform this process.
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
Metabolism
the combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials