Pharmacology - Antimicrobial Drugs
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is an Infection?
Occurs when pathogens invade causing harm or disease.
Immune system is overwhelmed.
Bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites.
Antimicrobial Therapy
Use of medications to treat infections due to bacteria, viruses, fungi.
Use selective toxicity to kill or otherwise control microbes without destroying host cells.
Why Antimicrobials Matter
Commonly prescribed
High-risk if used incorrectly
Nursing priority: safety and education
3 things to remember:
Allergy? If yes, what is it? Is it a side effect or and allergy reaction?
Opportunistic Infection (Super Infection) - Yeast infections, oral thrush
Organ Toxicity - Liver and kidney (possibly ears)!!!
How Antibacterials Work
Destroying cell wall that is present in bacteria.
Inhibiting conversion of enzyme unique for a particular bacterium’s survival.
Impairing protein synthesis in bacteria’s ribosomes
Disrupting bacterial synthesis or function of DNA and RNA
Inhibiting metabolic pathways.
Classification of Antibacterial Medication
Defining which microbes are susceptible to each medication.
Narrow-spectrum antibodies
Identifying the mechanism of action of each antibacterial medication.
Bactericidal - I’m killing that bacteria in the pt.
Bacteriostatic - I am slowing or stopping the growth of bacteria to stop it from replicating.
Selecting Antibodies
Identity of causative agent
Sensitivity of infecting organism to antimicrobial
Other factors (location of infection, age, allergies, immune status)
Culture and Sensitivity
Identifies organism
Laboratory testing of bodily fluids (blood, urine, sputum, and wound drainage)
Targeted therapy
May take days
Antibiotic Resistance
Bacteria adapt and survive (skipped doses and incomplete therapy)
Misuse allows resistance
Nurses reduce risk
Superinfections
Normal microbiome destroyed
Opportunistic infections
Examples of signs/symptoms: diarrhea, thrush, vaginitis
Antibiotics Affecting Bacterial Cell Wall
Penicillins (Penicillin G potassium)
Beta-lactamase inhibitors: amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (Augmentin)
Cephalosporins (Cephalexin, first generation)
Vancomycin
Pharmacological action
Destroy the bacterial cell walls causing destruction of microorganisms.
Penicillin Complication
Allergies, anaphylaxis
Renal impairment
Hyperkalemia, dysrhythmias, hypernatremia
At risk for superinfection, GI distress, C. diff
Interaction: PCN in the same IV solution as aminoglycosides inactivates the aminoglycoside
Nursing Administration: Penicillin
Instruct patients to report any findings of an allergic response
Assess for allergy to PCN or cephalosporins
Complete the entire course of therapy, even if manifestations resolve
Use an additional contraceptive method
C&S sample taken before starting antibiotic to identify infective microorganism.
Cephalosporins
Multiple Generation
First Generation - Cefazolin
Second Generation - Cefaclor
Third Generation - Ceftriaxone
Fourth Generation - Cefepime
Fifth Generation - Ceftaroline
Broad-spectrum with a high therapeutic index that treat a wide variety of infections
Cephalosporin Complications
Allergies, hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, possible cross-sensitivity to penicillin
GI distress
Bleeding tendencies
Thrombophlebitis with IV infusion
Renal insufficiency
Pain with IM injection
Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis (caused by Clostridioides difficile)
Nursing Administration: Cephalosporins
Complete the entire course of therapy even if manifestations resolve
Take PO with food
Store PO suspensions in a refrigerator
Interactions
Disulfiram reaction (intolerance to alcohol) when alcohol and cephalosporins are taken concurrently.
Vancomycin
Commonly used in hospitals
Poor absorption through GI tract
Treats infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and streptococcal infection
Treat antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to Clostridium difficile
Vancomycin Complication
Ototoxicity (rare and reversible)
Infusion reactions (red man syndrome - related to rapid infusions) IM and IV injection-site pain
Renal toxicity
Neutropenia (rare and reversible)
Nursing Administration - Vancomycin
Monitor vancomycin trough levels routinely after steady state reached
Administer slowly to avoid transfusion reaction
Remember this Image!!
Okay!!
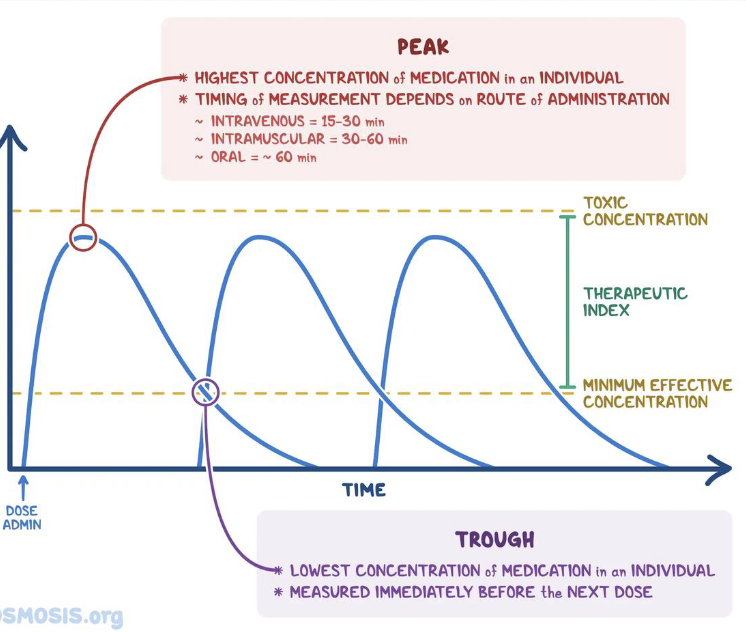
Antibiotics Affecting Protein Synthesis
Macrolides (Prototype: Erythromycin)
Exemplars: Azithromycin
Tetracyclines (Prototype: Tetracycline)
Exemplars: Doxycycline, Minocycline
Aminoglycosides (Prototype: Gentamicin)
Exemplars: Tobramycin, Neomycin, Streptomycin
Macrolide Complications
GI discomfort (nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain)
Prolonged QT intervals
Ototoxicity with high-dose therapy
Interactions - Macrolides
Erythromycin inhibits metabolism of:
Antihistamines
Theophylline
Carbamazepine
Warfarin
Digoxin
Metabolism of erythromycin is inhibited by:
Verapamil
Diltiazem
Antifungals
Nefazodone
Nursing Administration - Macrolides
If given to treat STD, abstain from intercourse until they finish their medication and manifestations resolve or partners have been treated.
Hormonal contraceptive effectiveness decreased with various antibiotics.
Administer oral preparations on an empty stomach, with 8oz of water, unless GI upset occurs.
Tetracycline Complications
Gi discomfort (including esophageal ulceration)
Yellow or brown tooth discoloration, hypoplasia of tooth enamel
Hepatotoxicity
Photosensitivity
Superinfection
Interactions - Tetracyclines
Absorption of tetracyclines reduced with:
Milk products
Calcium and iron supplements
Laxatives containing magnesium
Antacids
Doxycycline increased risk of digoxin toxicity
Nursing Administration - Tetracyclines
Take tetracyclines on an empty stomach with 8 oz of water (may be taken with food if GI distress occurs)
Do not take lying down (increased risk of esophageal ulceration)
Administer at least 1 hr before or 2 hrs after chelating agents
Complete entire course of therapy; use additional contraception
Aminoglycosides - Complications
Ototoxicity
Nephrotoxicity
Intense neuromuscular blockade (results in respiratory distress, muscle weakness)
Hypersensitivity
Interactions - Aminoglycosides
Penicillin inactivates aminoglycosides when in the same IV solution.
Concurrent administration with other ototoxic drugs increases risk for ototoxicity
Concurrent administration with skeletal muscle relaxants increases risk for neuromuscular blockade
Nursing Administration - Aminoglycosides
Most are parenteral
Neomycin also has oral and topical formulations
Tobramycin also has inhalation formulation
Base acquisition of aminoglycoside level on dosing schedules
Once-a-day dosing (blood sample only necessary for measuring trough levels)
Divided doses
Peak: 30 mins after IM; 30 min after completion of IV
Trough: right before next dose
Fluoroquinolones (Prototype: Ciprofloxacin)
Exemplars: Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin
Action: Inhibition of an enzyme necessary for DNA replication
Complications: GI discomfort, Achilles tendon rupture, superinfection, phototoxicity, cardiac dysrhythmias (QT interval prolongation)
Interactions: Antacids, dairy products decrease absorption plasma levels of theophylline and warfarin increase with concurrent use
Nursing Administration - Fluroquinolones
D/C other IV infusions or another IV site when administering cipro IV
Lower doses for patients who have impaired kidney function
Administer cipro IV in dilute solution slowly over 60 mins in a large vein.
Sulfonamides
Prototypes:
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim
Prevent synthesis of tetrahydrofolate (folic acid derivative, essential for production of DNA, RNA, proteins)
Sulfonamides Complications
Hypersensitivity (including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)
Photosensitivity
Blood dyscrasias
Crystalluria
Kernicterus
Hyperkalemia
Interactions & Nursing Administration - Sulfonamides
Increased effects of warfarin, phenytoin, sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemics (monitor levels, give lower dosages during therapy)
Use back-up contraception method
Increase fluids (at least 2000 ml/day unless contraindicated)
Urinary Tract Antiseptics
Nitrofurantoin
Injures bacteria by damaging DNA
Complications: GI discomfort, hypersensitivity, blood dyscrasias, peripheral neuropathy, headache, drowsiness, dizziness
Nursing administration
Turns urine rust-yellow to brown and can stain teeth
Take with food
Avoid crushing, chewing, or opening capsules (possibility of teeth staining)
Antifungals
Amphotericin B given IV (systemic mycoses); Ketoconazole (superficial and system mycoses); nystatin (Candida infections of intestines, vagina, skin, mouth)
Complications: Infusion reactions, thrombophlebitis, nephrotoxicity, electrolyte imbalance, bone marrow supression
Interactions & Nursing Administration - Antifungals
Additive nephrotoxic risk when take with aminoglycosides
Azoles increase risk of multiple drugs, including digoxin, warfarin, and sulfonylurea antidiabetics drugs
Nursing Administration
Amphotericin B is highly toxic and should be infused slowly (over 4-6 hours IV)
Observe solution for precipitation and discard if present (use filter to prevent infusion of undissolved crystals)
Universal Nursing Responsibilities
Assess for allergies
Obtain cultures before starting therapy
Monitor for therapeutic effect
GI distress
Superinfection (C. diff diarrhea)
Hypersensitivity reactions
Monitor for adverse effects (complications)
Minitor renal and hepatic functions (as appropriate)
Ensure correct administration
Infection control measures
Patient Education
Complete the full course
Do not skip doses
Report any reactions (severe diarrhea, rash or itching, signs of superinfection)
Do not share medication
Nursing Evaluations of Medication Effectiveness
Antibiotics are effective when signs and symptoms of infection improve or resolve
Clinical improvement
Laboratory improvement
VS stabilization
Radiologic or objective findings (improving chest X-ray in pneumonia, improved wound appearance)
Time frame expectation (improvement usually seen within 24-72 hours)