Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Deformation
Change in the shape or size of an object due to applied forces.
work
To produce deformation in an object, we must do ____.
force, exerted, distance
Whether you pluck a guitar string or compress a car’s shock absorber, a _____ must be _______ through a _______.
That all the work is initially stored in the deformed object as some form of potential energy.
What should be concluded when the only result of the work is deformation, and no work goes into thermal, sound, or kinetic energy?
Conservative force
The force on the spring is what type of force?
Potential energy
The energy stored in the spring when the spring is extended or compressed, is what type of energy?
W = ∫(from xi to xf) F_x dx = ∫(from xi to xf) -kxdx = [(-1/2)kx^2]from xi to xf = -[(1/2)k(x_f)^2 - (1/2)k(x_i)^2] = -[U_f - U_i] = -ΔU
Write down the integral equation showing how the block oscillates in one dimension with the force of the spring acting parallel to the motion.
It means the position at which the energy stored in the spring is equal to 0.
In the spring, what does its equilibrium position marked as x_i = 0m means?
U = (1/2)k(x^2)
Formula for the potential energy inside the spring whenever it gets stretched or compressed to a certain distance (in the deformation of the spring).
K = (1/2)m(v^2)
Equation for the kinetic energy of the mass.
simple harmonic oscillator
In ___________________, the energy oscillates between kinetic energy of the mass and potential energy stored in the spring.
dissipative
The total energy is the sum of the potential energy and kinetic energy when no ___________ forces are there, which is the case with SHM of the mass and spring system.
(1/2)k(A^2)
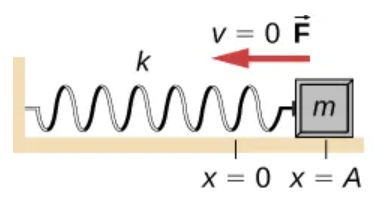
(1/2)m(-vmax^2)
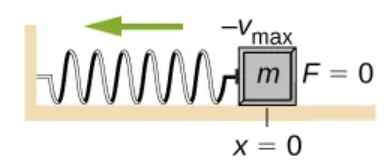
(1/2)k(-A^2)
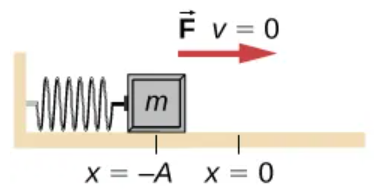
(1/2)m(vmax^2)
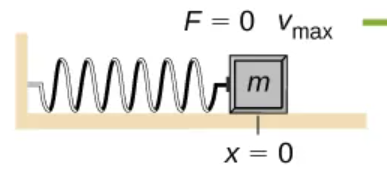
Elastic potential energy
An object on a frictionless surface attached to a spring, the motion starts with all of the energy stored in the spring as….
kinetic energy, kinetic energy, equilibrium position, elastic potential energy
As the object starts to move the elastic potential energy is converted into ______________ becoming entirely ______________ at the _______________________. Then it is converted back into ______________________, by the spring as it is stretched or compressed.
Velocity
What becomes zero when the kinetic energy is completely converted?
Etotal = U + K = ((1/2)k(x^2)) + ((1/2)m(v^2))
Equation for the total energy of the spring-block SHM system.
x(t) = Acos(ωt + Φ)
Equation for the position of the block on a spring in SHM
v(t) = -Aωsin(ωt + Φ)
Equation for the velocity of the block on a spring in SHM
(cos(θ))^2 + (sin(θ))^2 = 1
Pythagorean identity
ω = (k/m)^1/2
Formula for angular frequency in SHM
Etotal = ((1/2)k(A^2)(cos(ωt + Φ)^2)) + ((1/2)m(A^2)(ω^2)(sin(ωt + Φ)^2))
Total energy equation (Substitute the position and velocity definitions of velocity)
Etotal = ((1/2)k(A^2)(cos(ωt + Φ)^2)) + ((1/2)m(A^2)(k/m)(sin(ωt + Φ)^2))
Total energy equation;
x(t),v(t) → ω
Etotal = ((1/2)k(A^2)(cos(ωt + Φ)^2)) + ((1/2)(A^2)k(sin(ωt + Φ)^2))
Total energy equation;
x(t),v(t) → ω → simplify
Etotal = (1/2)k(A^2)(cos(ωt + Φ)^2 + sin(ωt + Φ)^2)
Total energy equation;
x(t),v(t) → ω → simplify → Factorize
Etotal = (1/2)k(A^2)
Total energy equation of a spring-block SHM, which is a constant.
(Final form)
sine-squared function
In the spring-block SHM, the kinetic energy of the block oscillates as what type of a function?
cosine-squared function
In the spring-block SHM, the potential energy stored in the spring oscillates as what type of a function?
Yes, it is true
Is it true that the total energy for the Spring-Block SHM system is constant and is proportional to the amplitude squared?
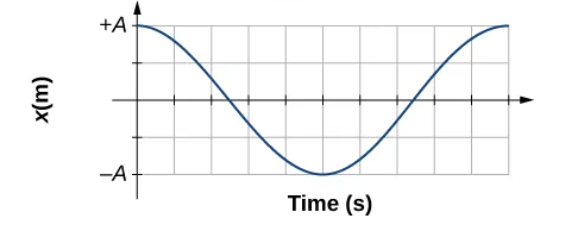
SHM Position v/s Time graph
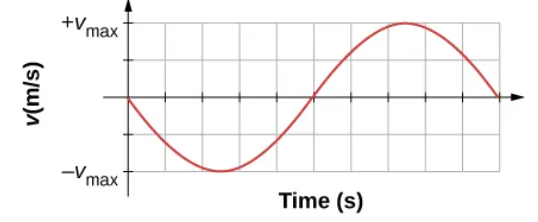
SHM Velocity v/s Time graph
(1/2)k(A^2)
1A
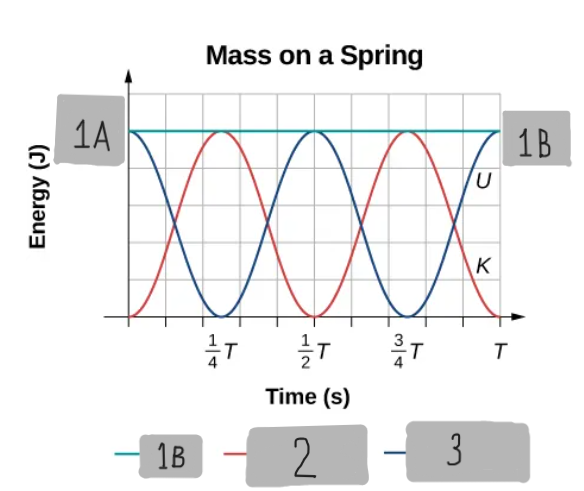
Etotal
1B
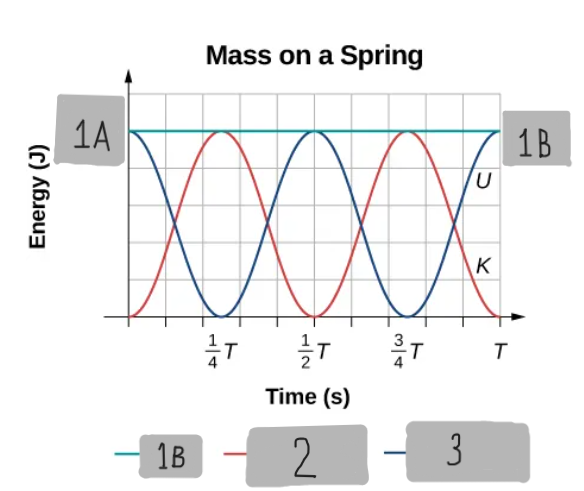
K = (1/2)m(v^2)
2
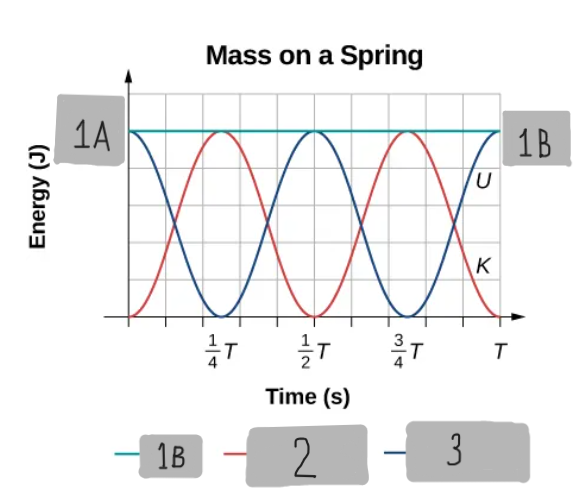
U = (1/2)k(x^2)
3
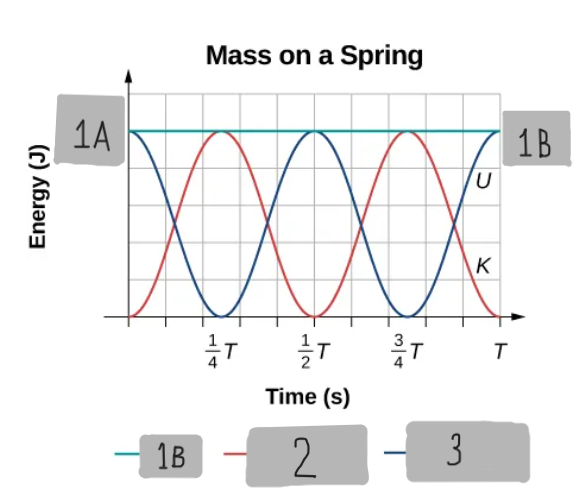
zero, maximum, equilibrium position, speed
When the kinetic energy is maximum, the potential energy is ____, This occurs when the velocity is ________ and the mass is at the ______________. Potential energy is maximum when the _____ is zero.
As a function of time or As a function of position
Two ways to graph the energy of SHM