Monomers and Polymers
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
amino acid
monomer that makes up proteins
has a central carbon atom that bonds to: a carboxylic group, an amino group, a hydrogen atom and an R group
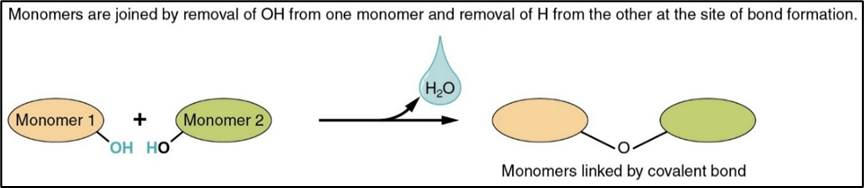
condensation reaction
chemical process when 2 molecules combine to form a more complex one whilst eliminating a simple substance(usually water)
how many biological polymers are formed
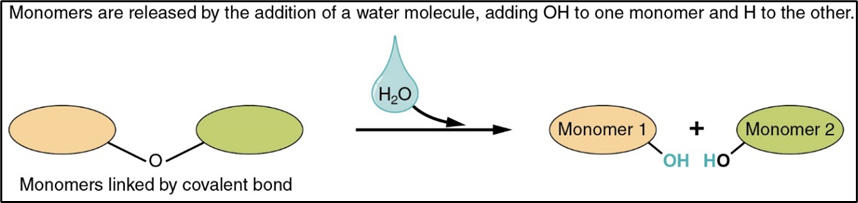
hydrolysis
breaking down of large molecules into smaller ones by addition of water molecules(like the opposite of condensation)
nucleotide
a compound made of an organic base and ribose sugar linked to a phosphate group
nucleotides form monomers of nucleic acids e.g DNA
organic molecules
any molecule containing carbon that can be found in living things. The 4 classes are:
carbohydrates: respiratory substrates that provide energy for cells, used for structure in cell membranes and cell walls
proteins: main component of many cellular structures, form enzymes and chemical messengers e.g RNA
lipids: can be used as respiratory substrates to provide energy for cells, from a bilayer in cell membranes and make up some hormones
nucleic acids: form polymers(DNA and RNA) to makeup genomes.They code for the sequence of amino acids to makeup all proteins
what supports the theory that all organisms share a common ancestor
all organisms use the same nucleic acids as genetic material
all build proteins using the same 20 amino acids
all use lipids and carbohydrates as energy stores and to make up their cell membranes and walls
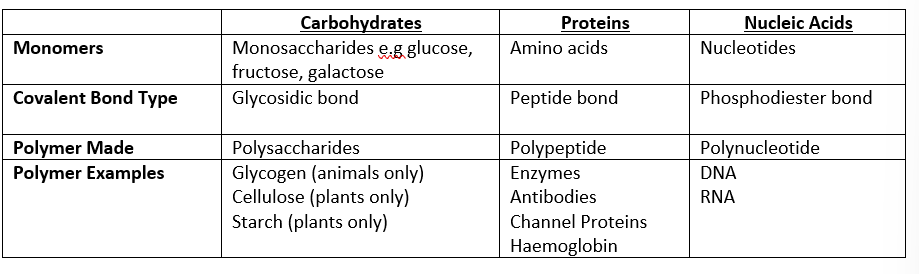
monomer, covalent bond type, polymer made and polymer example for carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids