Ped Dentistry Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
information to collect to create a differential dx and develop tx plan options
-med history: ROS, meds, allergies, sx history
-dental history: previous dental visits (continuity of care), caries experience, trauma, family dental history (caries risk assessment, malocclusion, environmental risk factors, attitudes towards dentistry), oral hygiene practices, diet, fluoride exposure
-clinical exam: intraoral and extraoral
-radiographic exam
-caries risk assessment
radiographic assessment of pediatric patients
-radiographs should be taken based on individual considerations- there is no set frequency that applies to all pts
-considerations in determining radiology prescription:
-risk assessment: caries history, fluoride status, diet
-trauma
-anomalies (supernumerary, missing permanent teeth, mesiodents)
-absence or presence of contacts (kids have generalized spacing→when first permanent molars erupt, they push teeth forward which creates contacts)
-active decay
children should take over brushing at age
-~8
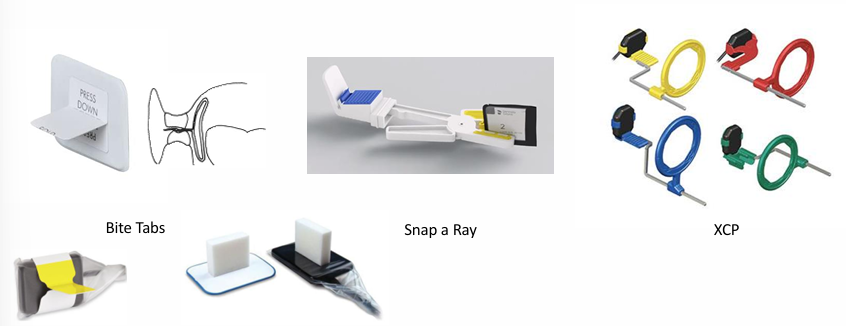
child preparation and management for radiographs
-euphemisms (camera, selfie)
-role models
-contour film- not possible with digital sensors, can damage phosphor plates
-”edge ease” (cushions that go around sensor)
-distraction
-parental help
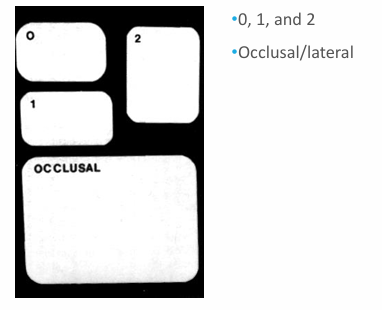
film sizes
-generally use 2 in adults
-0-1 in kids
radiographic tools
radiographic techniques
-bite wings
-periapicals
-maxillary and mandibular occlusals
-extraoral/lateral film
-soft tissue radiograph
-panoramic radiographs
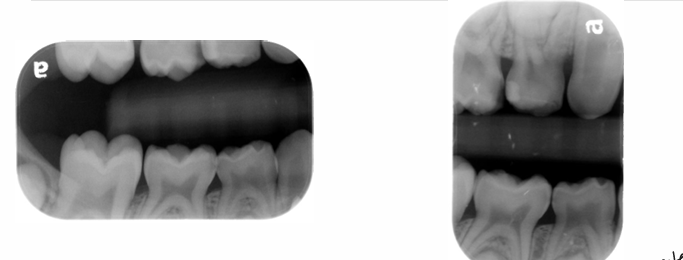
bite wing radiograph
-mesial surface of canine to distal surface of 1st permanent molar
-distal contact of canine to mesial contact of last tooth in arch
horizontal v. vertical bitewing
-vertical easier to tolerate for pts who gag
occlusal radiographs
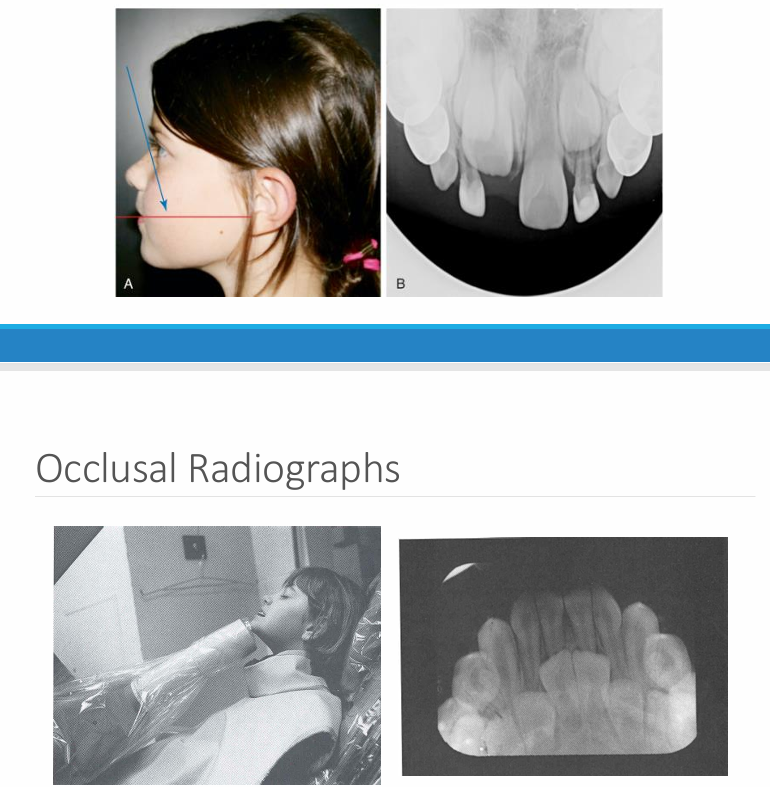
occlusal v. periapical radiographs
-occlusal: can often visualize the whole arch, angulation can vary
-periapical: a section of the arch that shows the whole tooth crown to apex- position film as if taking an occlusal
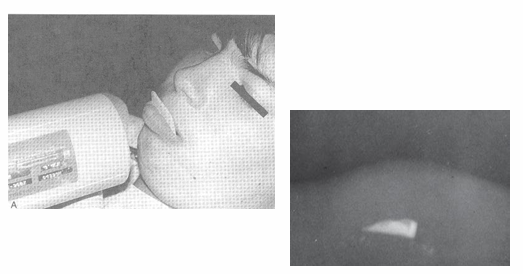
trauma
-soft tissue radiograph
-indicated after trauma to locate piece(s) of fractured tooth
panoramic radiograph
-evaluate growth and development
-take pans in children if unerupted teeth exist that should be erupted
-some practitioners say every 3 yrs starting at age 6
-look at overall development of child
-23, 24, 25, 26, 1st year molars present = good time to take pan
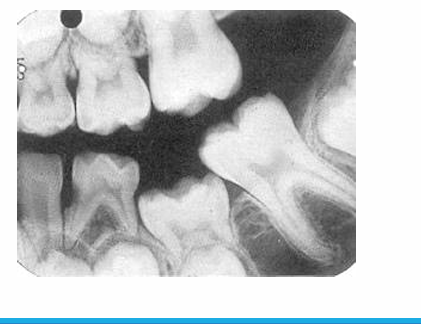
-anomaly: ankylosis
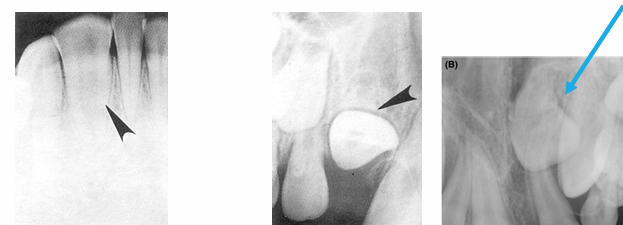
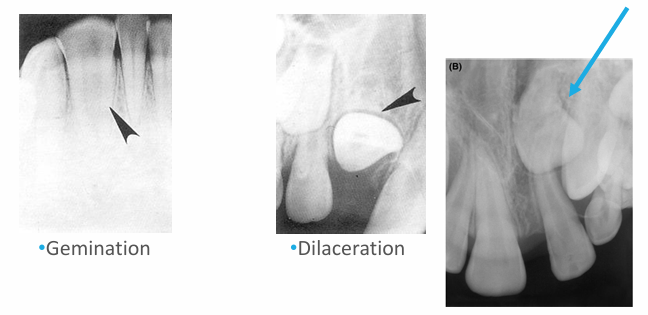
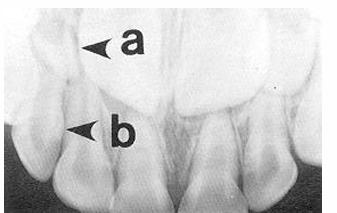
-peg lateral
-supernumerary primary lateral
-count the teeth
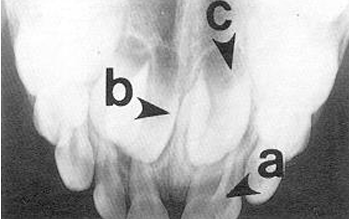
-fusion
-supernumerary tooth
-missing lateral
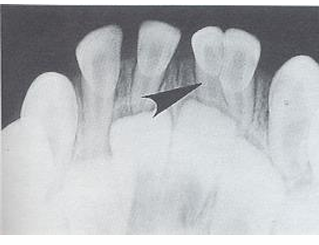
-concrescence: cementum fuses together
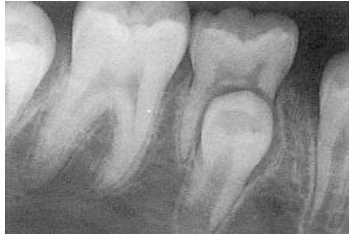
-unfavorable resorption pattern of roots
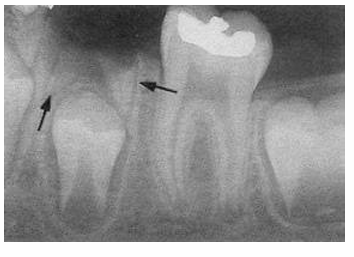
-retained primary root tips
-common in kids with high caries → don’t get tx and teeth just crumble
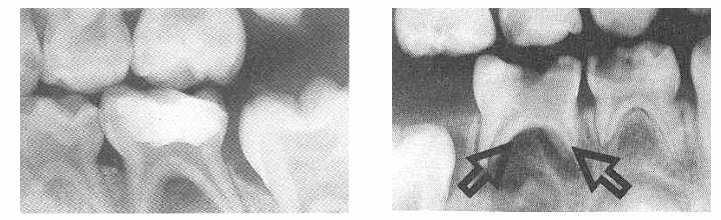
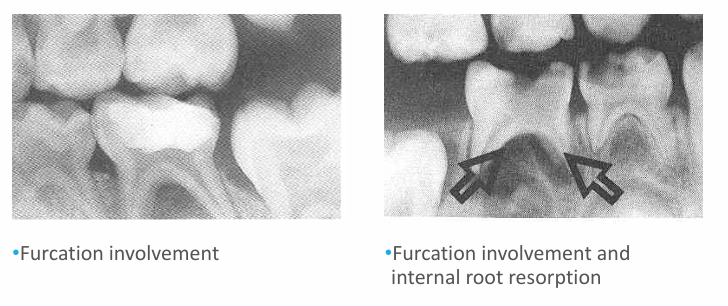
may take ____ demineralization to occur before it will be evident radiographically
-30-70%
dental erosion
-progressive irreversible loss of dental hard tissue that is chemically etched away from the tooth surface by intrinsic and/or extrinsic process that does not involve bacteria
-consequences of dental erosion: lack of enamel, hypersensitivity, discoloration, crazing/fractures, increased wear, restorations
signs of enamel erosion
-broad concavities on cusp tips (mandibular molars)
-smooth silky glazed appearance
-increased incisal translucency
-”raised” amalgam restorations (enamel wears away but amalgam does not)
-loss of surface anatomy in young children
-hypersensitivity
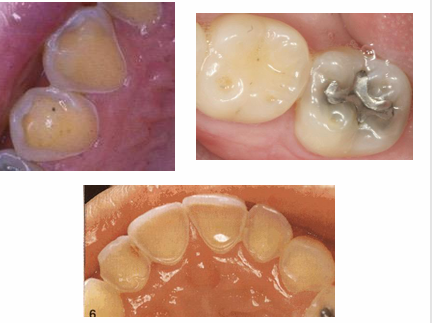
dental erosion as a sign of systemic disease
-bulimia nervosa: lingual surfaces of anterior teeth
-GERD
titratable acidity
-critical pH of enamel = 5.5
-measure of the amount of alkali which needs to be added to an acid in order to neutralize at pH 7.0
-indicates the amount of available acid, both bound and free hydrogen ions; erosive potential of a substance
dental caries
-disease of microbial origin
-communicable
-largely preventable
-described as a “silent epidemic”: 5x more common than asthma
dental caries- bacteria and biofilm
-initiated by pathogenic bacteria- Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacilli, and Streptococcus sobrinus
-formation of a complex structure called biofilms
-dental plaque biofilm: unremoved plaque promotes the caries process
-can explain biofilm as “teeth wearing sweaters”, “sugar bugs”, “sugar bug nest”
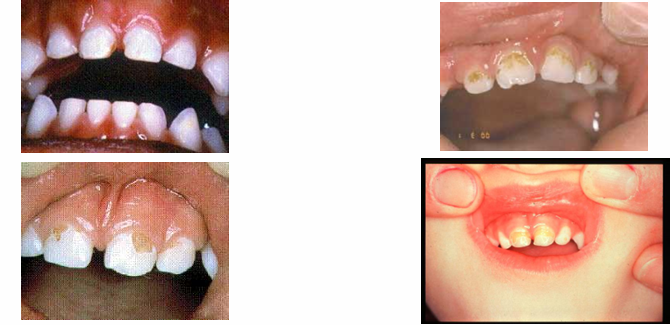
early signs of decay
-white spot lesions
-not as visible when dry → become chalky
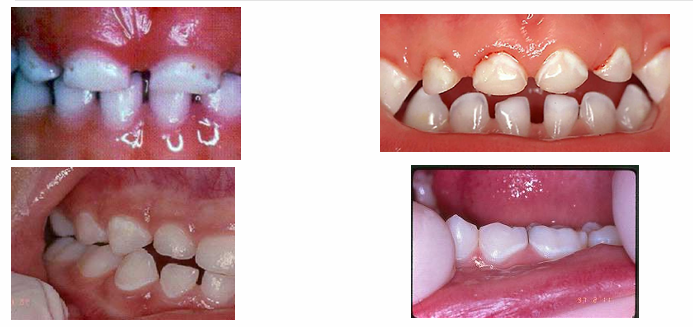
later signs of decay
-enamel breakdown
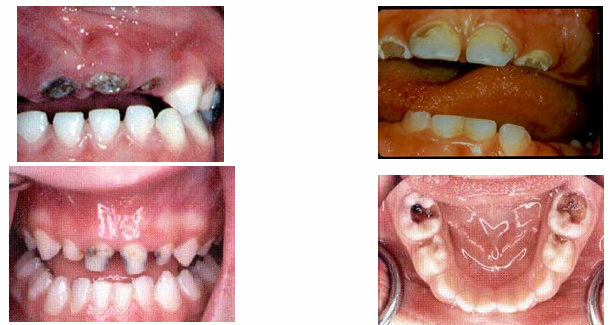
advanced/severe decay
-decay that extends all the way to the gingiva anteriorly or very extensively occlusally in the posterior
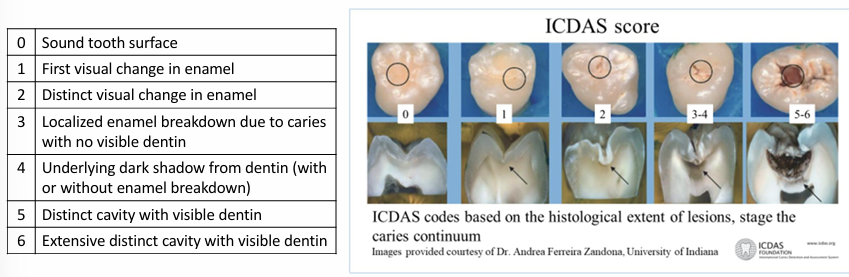
ICDAS score
sequalae of ECC
-extreme pain
-spread of infection
-difficulty chewing
-poor weight gain
-extensive and costly dental treatment
-risk of dental decay in permanent dentition
-malocclusion
-missed school and work days
-impaired language development
-inability to concentrate in school
-reduced self-esteem
-possible facial cellulitis requiring hospitalization
-possible systemic illness
-death
dental infections
-can spread more quickly in children → tissues more compliant
high risk groups
-children with special health care needs
-children from low socioeconomic and ethnocultural groups
-children with suboptimal exposure to topical or systemic fluoride
-children with poor dietary and feeding habits
-children whose caregivers and/or siblings have caries
-children with visible caries, white spots, plaque, or decay
caries prevention- fluoride varnish
-5% NaF or 2.26% fluoride in a viscous resinous base in an alcoholic suspension with flavoring agent
-has not been associated with fluorosis
-application does not replace the dental home or is equivalent to comprehensive dental care
-ensure teeth are super dry before applying- otherwise will just slide off the teeth
additional fluoride exposures
-fluoride mouthwashes, Rx toothpastes and gels
-reservoir in saliva/vestibule → don’t want to eat/drink & have reservoir deplete
caries prevention- flossing
-once a day, preferably at night
-whenever any two teeth touch
dental sealants
-noninvasive procedures
-helps prevent pit and fissure caries (account for almost 80% of all dental caries in children)
-seals deep, narrow grooves
-BEWARE of the poorly placed sealant → can create a plaque trap
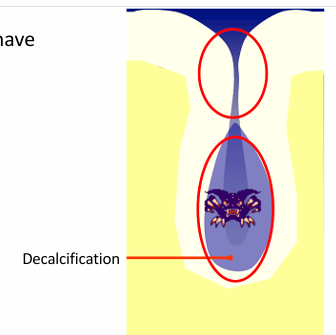
fissures caries model
-once the organic plug fails, bacteria have access to the depths of the fissure
-fissure walls are in close apposition
-unable to detect caries
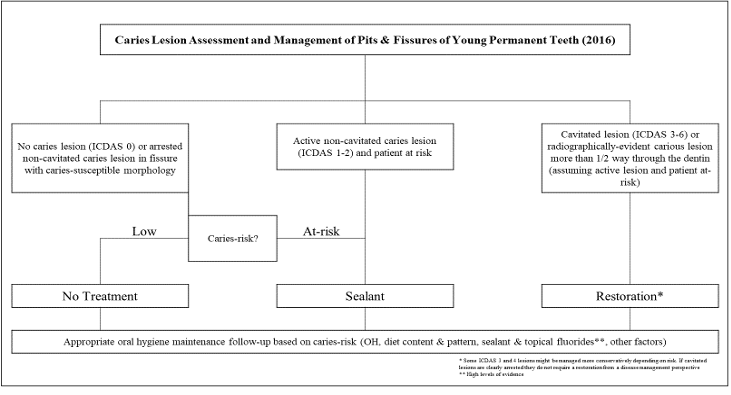
clinical pathway for occlusal surface management
restorative dentistry
-adhesive dentistry: retention and resistance forms of cavity preparation do not apply, therefore more conservative, isolation is CRITICAL (moisture makes composite fail)
-amalgam restorations: follow GV Black’s principles of cavity preparation, less conservative (need bulk of amalgam to ensure success), more forgiving in terms of moisture control
-full coverage restorations: stainless steel crowns, preformed ceramic crowns
-other tools: silver diamine fluoride (SDF)
preventive resin restorations (PRR)
-a single or multiple, small, discontinuous, carious pits or fissures
-may extend into enamel, dentin, or DEJ
-excavated and restored with resin
-occlusal surface sealed for prevention
composite/resin restorations
-involves the excavation of a single, larger carious lesion followed by restoration with a resin based material
bonding tips
-etch for the appropriate length of time: too long = etch patterns that extend too deeply causing adhesives to not be able to penetrate the demineralized zone; usually 15-20 seconds
-ensure ideal dentin moisture conditions: ethanol adhesives do not require as much moisture, apply indirect air to dry, do not dessicate
-pay attention to application time and technique: watch the clock to avoid counting too fast
-scrub adhesive when recommended by manufacturer: usually scrub dentin to increase bond strength, scrubbing enamel will usually decrease bond strength, treat enamel more delicately and dentin more aggressively
-thin and dry the adhesive properly: gentle air spray at half an inch from the surface
-light cure close to the surface with a compatible light
-first increment of composite in a thin layer (0.2mm)
-thoroughly clean contamination: if contamination during bonding, clean and re-etch for 5 seconds
resin based composites- resin matrix (Bis-GMA) with inorganic filler particles
-filler content: filled v. unfilled, flowable (less filler) v. packable (more filler), anterior v. posterior composite
-particle size: macro, microfilled, and hybrids
-BPA = endocrine disruptor? → scrub top of composite with water
glass ionomer cements
-fluorosilicate glass powder (base) combined with a water soluble polymer (acid)
-set via chemical rxn
-contain fluoride
-Ketac cement, Fuji II or IX, Fuji Triage- used as sealants
resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI)
-glass ionomers with a light polymerized resin component
-dual cure
-increased mechanical properties
-physiochemically bonds to tooth structure
-biocompatible, moisture
-similar coefficient of thermal expansion as dentin (good dentin replacement material)
-ion leachability- fluoride release (anti-cariogenic)
-minimal polymerization shrinkage
preventive materials
-fluoride gels, foam, and varnish: remineralization of decalcified enamel
-sealants: indicated for preventing and arresting incipient lesions, available as clear/white, filled/unfilled, resin/RMGI
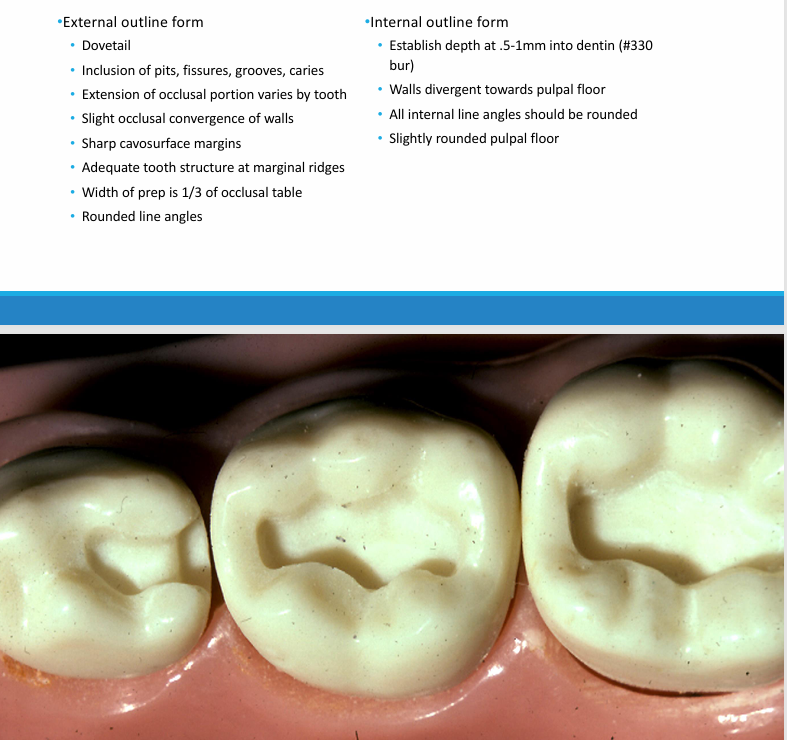
steps in class I restoration
-appropriate anesthesia
-rubber dam isolation/isodry
-cavity preparation
-excavation of remaining caries
-etch for 20 seconds
-wash and dry
-prime and bond
-light cure
-place resin (in increments)
-light cure
-polish
-check occlusion
features of a primary tooth class I restoration
features of a primary tooth class II restoration
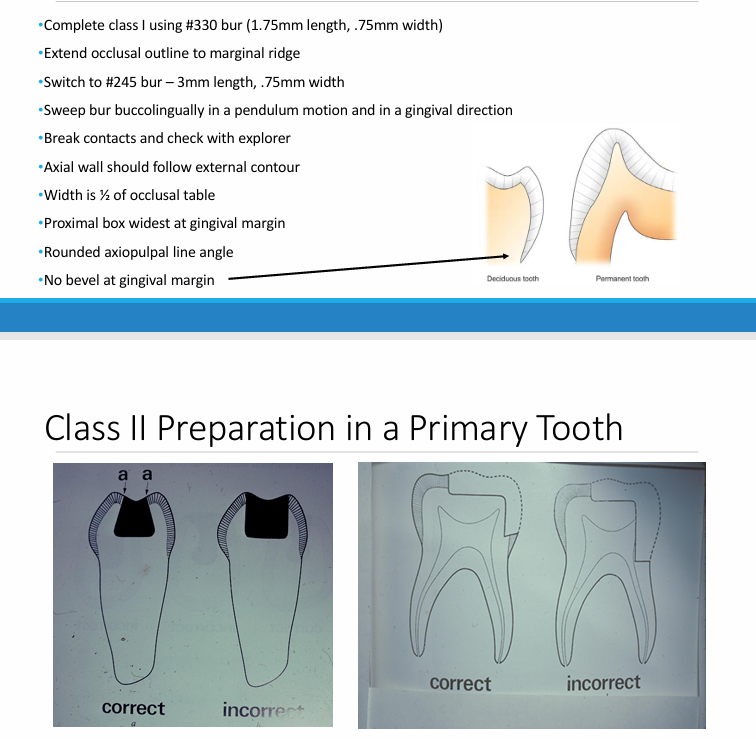
matrix bands and retainersq
-contour, insert, and place wedge
-purpose: restoration of proximal contact
-examples: Tofflemire, T-band, denovo band, compositight
-Fendermate wedges
amalgam
-no polymerization shrinkage
-moisture forgiving
-excellent mechanical properties
-esthetics
-mercury toxicity
stainless steel crowns
-full coverage, metallic, definitive restoration
-available pretrimmed and pre-contoured
-durable and cost-effective
-single visit
-most predictable restoration for primary dentition
stainless steel crowns indications and contraindications
-indications: restoration of primary and young permanent teeth with multiple carious surfaces, class II lesions where the caries extend beyond the anatomic line angles, primary teeth after pulpotomy or pulpectomy procedures, hypoplastic teeth, hereditary anomalies, patients at high caries risk
-contraindications: esthetics, metal allergy
steps of preparation and placement of SSC
-evaluate pre-operative occlusion
-administer appropriate local anesthesia
-place rubber dam (clamp adjacent tooth)
-caries removal
-crown preparation
-selection and trial placement of SSC
-contour and crimp SSC if necessary
-evaluate occlusion
-cementation
SSC preparation
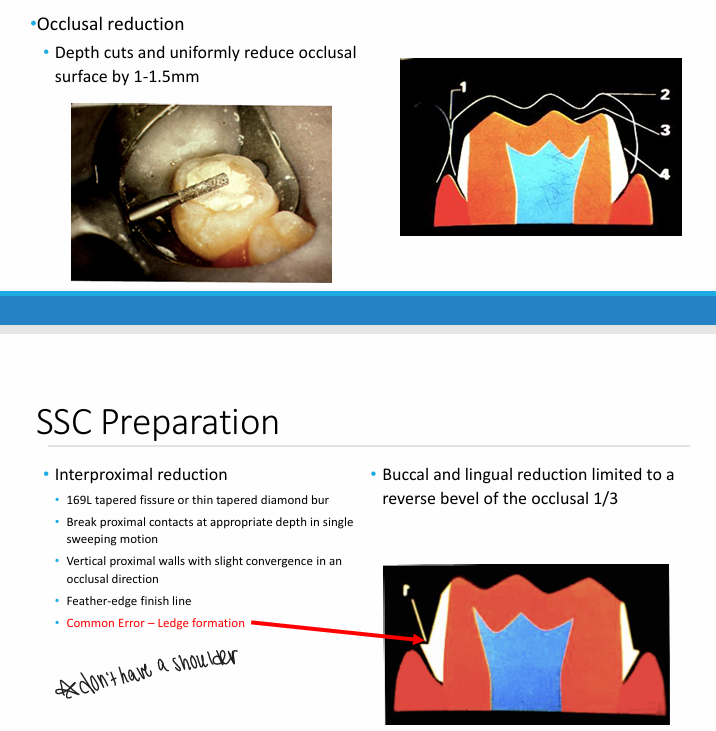
crown selection, try-in, and cementation
-select smallest crown that restores pre-existing proximal contacts
-occlusal dimensions of SSC should be same as pre-op tooth
-most commonly used molar SSC is size 4
-place or seat crown from lingual to buccal
-push crown over the buccal bulge for snap fit
-check margins for close cervical adaptation extending 1mm subgingivally
-remove dam and check occlusion
-remove crown
-dry, do not desiccate tooth
-fill crown with GI cement
-seat crown
-remove excess with damp gauze, explorer, and knotted floss
prefabricated ceramic crowns
-requires path of insertion
-no mechanical retention
-technique sensitive
-requires more reduction
-esthetic
interim therapeutic restoration (ITR)
-used to restore, arrest, or prevent the progression of caries lesions in young patients, uncooperative patients, or patients with special health care needs or when traditional cavity preparation and/or placement of traditional dental restorations are not feasible and need to be postponed
-involves removal of caries using hand or rotary instruments with caution not to expose the pulp
-leakage minimized by removing as much caries as possible from the periphery
-restored with a fluoride releasing GI or RMGI
ITR- infected and affected dentin
-infected dentin: irreversibly denatured
-affected dentin: can be soft but the collagen network is capable of remineralization, reversible process
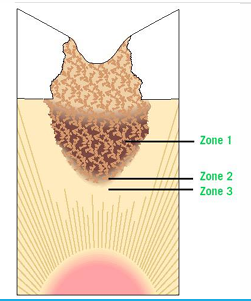
ITR- caries disinfection
-affected dentin has some viable bacteria
-30 second application of bactericidal agent such as Bentadine or Sodium hypochlorite may improve prognosis
-Consepsis: 2.0% chlorohexidine gluconate, scrub for 30s before etching
SDF
-38% SDF- colorless and odorless liquid with a pH of 10
-fluoride: remineralization of enamel and dentin
-silver ions: antimicrobial effect
-zombie effect of silver in killed bacteria cells
-creates an unfavorable environment for collagen enzyme activation = reduced dentin degradation
-studies consistently show more effective than fluoride alone at arresting caries
-does not reduce adhesion of resin or glass ionomer restorative materials
-FDA approved as a desensitizing agent, use for caries management is off label
SDF outcomes
-strong antibacterial effects on the cariogenic biofilm
-potent inhibitory effects on the activation of matrix metalloproteinases and cysteine cathepsins
-increases mineral density of enamel carious lesions and increases micro-hardness of dentin carious lesions
-ammonia stabilizes high concentrations in solution
SDF contraindications
-silver allergy
-esthetics: stains all carious lesions black, including white spot lesions, temporarily stains soft tissue (2 weeks), always get consent and show pictures of staining
minimally invasive dentistry
-silver modified atraumatic restorative technique (SMART fillings): placement of SDF, subsequent placement of GI material
-Hall Crown technique: placement of separators, removal of gross caries, cementation of appropriate sized crowns with GI cement