Astronomy 152
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Astronomy
as the study of the objects that lie beyond our planet Earth and the processes by which these objects interact with one another.
The universe is a total of
Energy, Matter, Space, Time
Matter
any substance that has mass and occupies space (volume), forming everything from stars and planets to gas clouds, and is fundamentally composed of elementary particles like quarks and leptons (electrons)
Energy
fundamentally the capacity to do work or cause change
Dark Matter
Astronomers have no solid definition of “dark matter.” It has mass (hence it being matter) because it creates gravity. It does not interact with matter, light, or energy. Most abundant form of matter- shapes the structure of the universe
Potential Energy
Stored energy that is ready to do work
Kinetic Energy
When energy is doing work, typically in motion
Conserved
When energy can be converted from one form to another
Joule (J)
International Unit for Energy
Space is a backdrop
(Theory for what is the nature of space) Space could stretch out infinitely, you could venture as far out as nothingness. Allows for the idea of an infinite universe
Space is a frame
(Theory for what is the nature of space) Space is whit is between two pieces of matter. No reference points, how can you define a space between nothing and nothing. If matter is finite, then space must be finite as well
Time
What can be measured as a clock OR a progression of events from the past, through the present, and into the future
Arrow of Time or Second Law of Thermodynamics
One directional flow of time, which means time only flows in a singular direction- forward
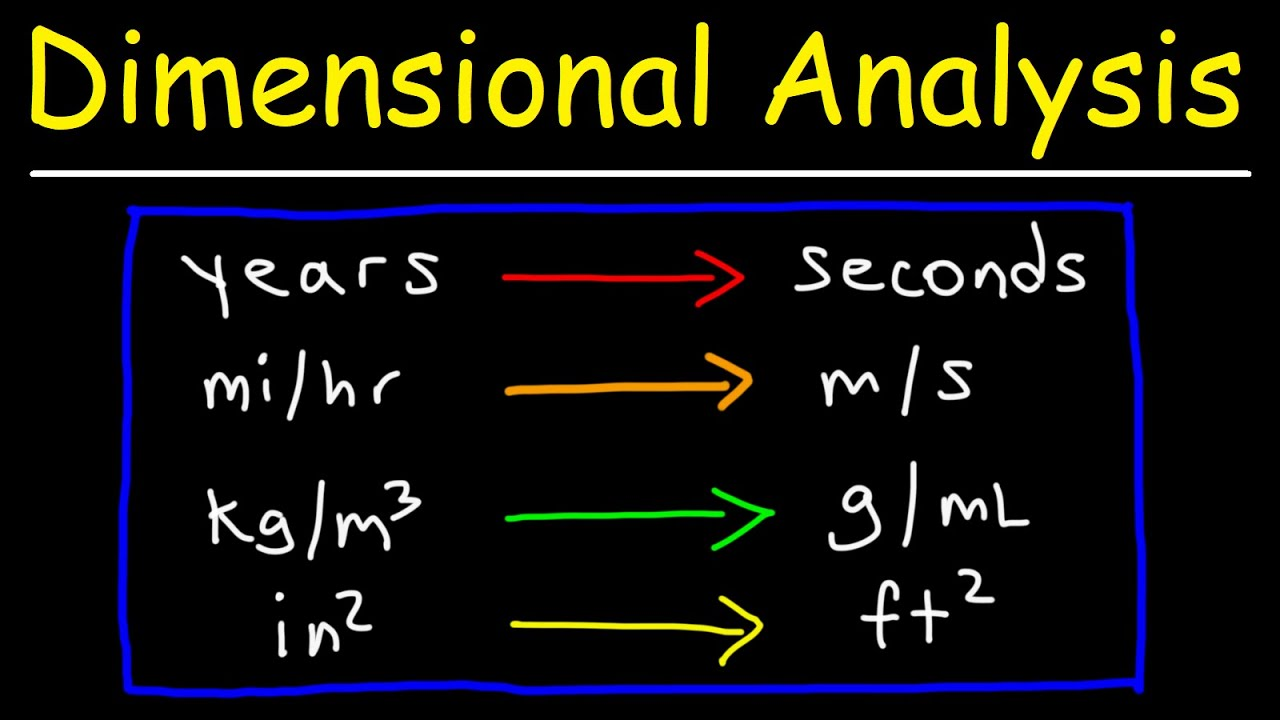
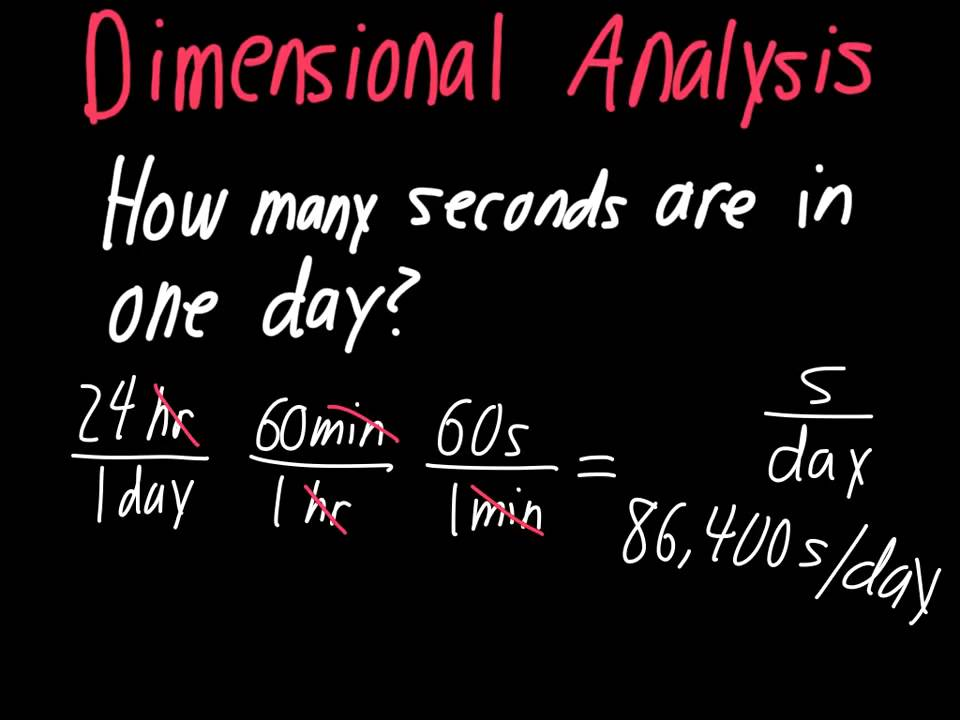
Dimensional Analysis
A problem-solving method that uses the fact that any number or expression can be multiplied by one without changing its value
Trigonometry
Triangulation & Parallax
The way scientists know that a hypothesis in astronomy is a reasonable description of nature is to _____.
do experiments and observations about the predictions of the hypothesis
The Astronomical Unit (AU) as defined by astronomers is _____.
the average distance between the Earth and the Sun
When the Earth passes directly between the Sun and Mars, the Earth and Mars are closest to each other. If Mars is 1.52 AU from the Sun and there are 1.5 ✕ 108 km in 1 AU, how many times will the width of the U.S. (2,530 miles) fit end-to-end between Mars and Earth?
Mars is 1.52 AU from the Sun. How many times further away from the Sun is Mars than the Earth? (The distances in AU are relative to the distance between the Sun and the Earth, so however many AU a planet is away from the Sun is how many times farther it is from Sun than Earth.)
1.52 times further away
When the Earth passes directly between the Sun and Mars, the Earth and Mars are closest to each other. If Mars is 1.52 AU from the Sun and there are 1.5 ✕ 108 km in 1 AU, how many times will the width of the U.S. (2,530 miles) fit end-to-end between Mars and Earth?

Now we need to determine how many kilometers there are between the Earth and Mars in this configuration.
We first have to subtract the distance between the Earth and the Sun from the distance between the Sun and Mars.
0.52 AU
78,000,000 km
When the Earth passes directly between the Sun and Mars, the Earth and Mars are closest to each other. If Mars is 1.52 AU from the Sun and there are 1.5 ✕ 108 km in 1 AU, how many times will the width of the U.S. (2,530 miles) fit end-to-end between Mars and Earth?

4050 km
When the Earth passes directly between the Sun and Mars, the Earth and Mars are closest to each other. If Mars is 1.52 AU from the Sun and there are 1.5 ✕ 108 km in 1 AU, how many times will the width of the U.S. (2,530 miles) fit end-to-end between Mars and Earth?
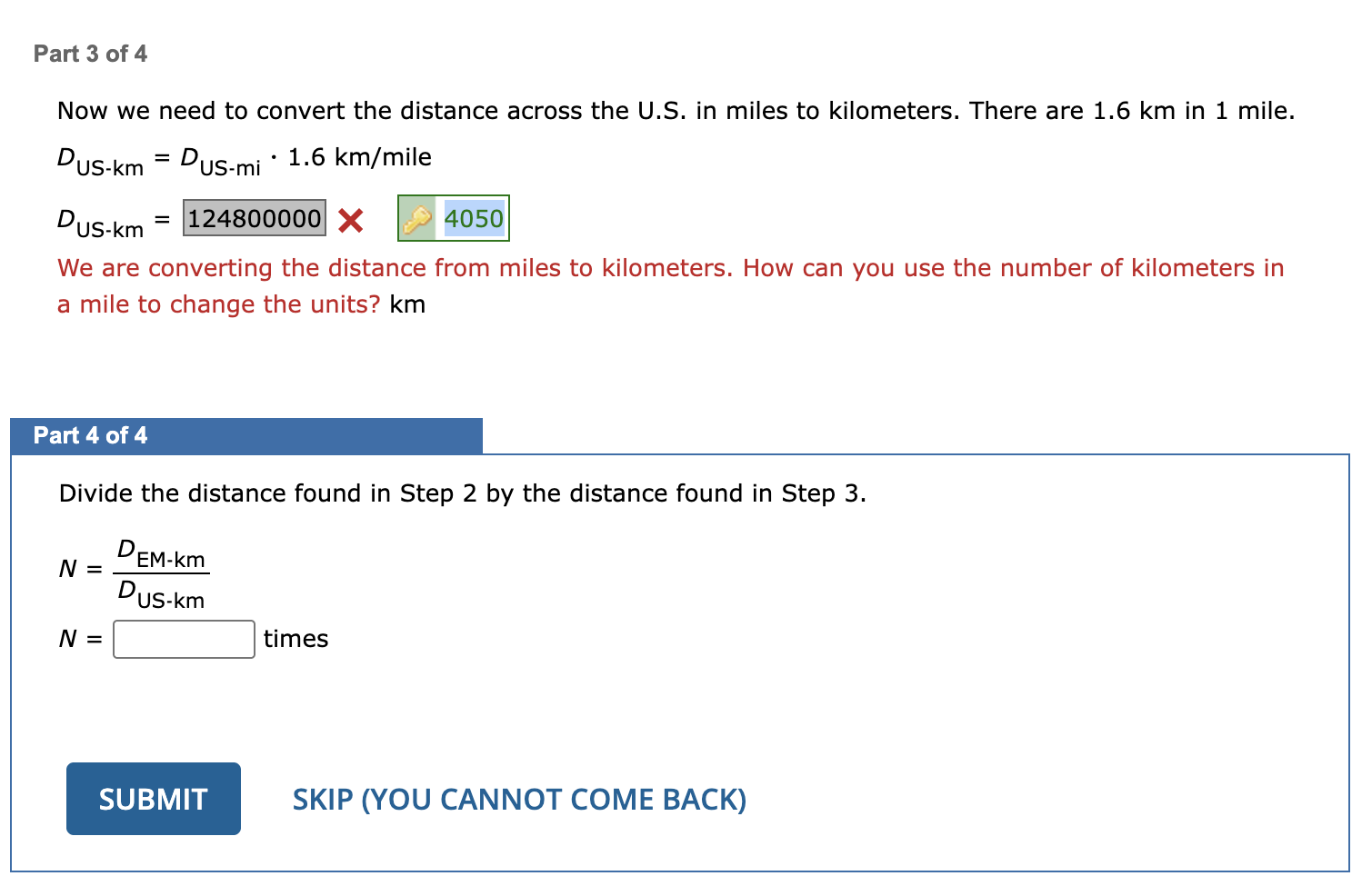
N=18519 times
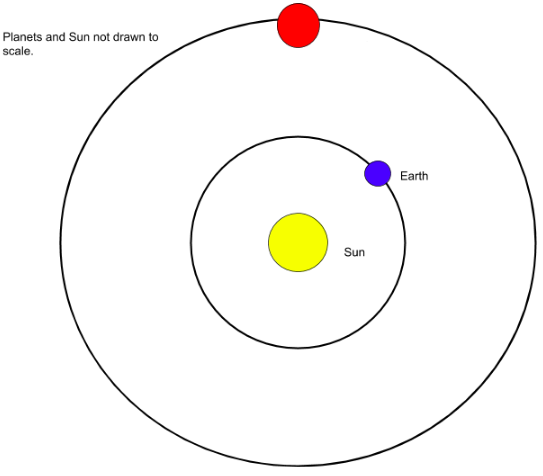
The Earth and Mars are 1.3 AU apart. How many minutes does it take for us to send a radio signal to communicate with the Curiosity rover? (Assume the Curiosity rover is near the surface of Mars, and ignore the distance between the Curiosity rover and Mars in your calculations.)

195000000 km
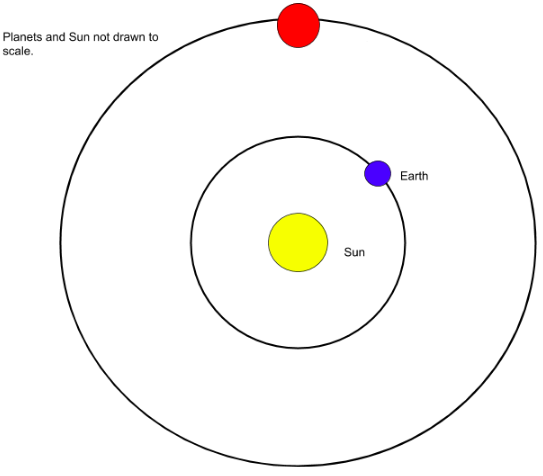
The Earth and Mars are 1.3 AU apart. How many minutes does it take for us to send a radio signal to communicate with the Curiosity rover? (Assume the Curiosity rover is near the surface of Mars, and ignore the distance between the Curiosity rover and Mars in your calculations.)

650 s
The Earth and Mars are 1.3 AU apart. How many minutes does it take for us to send a radio signal to communicate with the Curiosity rover? (Assume the Curiosity rover is near the surface of Mars, and ignore the distance between the Curiosity rover and Mars in your calculations.)

60 seconds
10.8 minutes
What is a constellation as astronomers define it today? What does it mean when an astronomer says, I saw a comet in Orion last night?
How many degrees does the Sun move per day relative to the fixed stars?
1°
How many days does it take for the Sun to return to its original location relative to the fixed stars?
365
From where on Earth could you observe all of the stars during the course of a year?
the equator
What fraction of the sky can be seen from the North Pole?
50%
What is an asterism?
An easily-recognizable group of stars that does not belong to a constellation
What is a constellation as astronomers define it today? What does it mean when an astronomer says, "I saw a comet in Orion last night"?
A constellation is a well-defined area of the sky with borders. The comet would be within Orion's border.
Explain why more stars are circumpolar for observers at higher latitudes.
At higher latitudes, the celestial pole is higher in the sky.
What is the latitude (in degrees) of the North Pole?
90° North
What is the latitude (in degrees) of the South Pole?
90° South
he stars rise and set perpendicular to the horizon
Earth's equator (0° latitude)
the stars circle the sky parallel to the horizon
either the North or the South Pole (90° North or South latitude)
the celestial equator passes through the zenith
Earth's equator (0° latitude)
in the course of a year, all stars are visible
Earth's equator (0° latitude)
the Sun rises on March 21 and does not set until September 21 (ideally)
the South Pole (90° South latitude)
Constellation Figure
88 officially recognized, IAU-defined, specific areas of the night sky (covering both hemispheres) often imagined as mythical, animal, or object shapes. Examples include Orion the Hunter, Ursa Major (Great Bear), Leo the Lion, and Pegasus the Flying Horse, which represent symbolic, rather than literal, celestial patterns


Asterism
recognizable, informal patterns of stars in the night sky that are not among the 88 formally defined constellations
Constellation vs Asterism vs Constellation Figure
Key Differences:
Constellation: A specific, surveyed area of the sky. It is a region, not just a shape.
Asterism: A popular, unofficial grouping of stars, often brighter, that creates a shape (e.g., Orion's Belt, Summer Triangle). Asterisms can be inside a single constellation or span multiple constellations
Constellation Figure: The "dot-to-dot" picture (like a bear or hunter) that defines the traditional, imaginative shape within a constellation.
YouTube +4
Examples & Relationships:
Ursa Major is the official constellation (a region of the sky).
The Big Dipper is an asterism (a shape) located inside the Ursa Major constellation.
The Great Bear is the constellation figure representing Ursa Major
Right assention (RA, symbol a)
is an equatorial coordinate used in astronomy to define a celestial object's east-west position, acting similarly to longitude on Earth