Lids, Lashes, & Dry Eye
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Peterson's Ocular Disease Lecture UMSL School of Optometry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
homeostasis
According to the DEWS II report, the main goal of DED treatment is to restore ____________.
Advanced age
Female sex
Asian race
Extreme heat or cold weather
Low humidity
Refractive sx
Contact lenses
Certain medications
Technology use
What are the 9 risk factors of Dry Eye Syndrome?
Keratoconjunctivitis sick (KCS)
Historic term for dry eye referring to any degree of dryness; typically referring to aqueous deficiency dry eye
Xerophthalmia
Severe dry eye due to Vitamin A deficiency
Xerosis
Extreme eye dryness and keratinization secondary to cicatricial disease
Sjogren Syndrome
Autoimmune inflammatory disease; attack on the salivary and lacrimal glands (dry eyes, dry mouth)
Meibomian glands
Glands of Zeis
Glands of Moll
Glands of Wolfing & Krause
What 4 glands are present in the eyelid?
Glands of Moll
What glands in the eyelid are apocrine glands and partake in immune defense?
Glands of Wolfing & Krause
What glands in the eyelid undergo merocrine secretion and empty into the fornix of the eye?
Glands of Zeis
What glands in the eyelid undergo holocrine secretion and secrete sebum onto lashes?
Gland of Wolfing
Gland of Krause
Gland of Moll
Gland of Zeus
Identify the following glands within the eyelid based on the image (1-4).
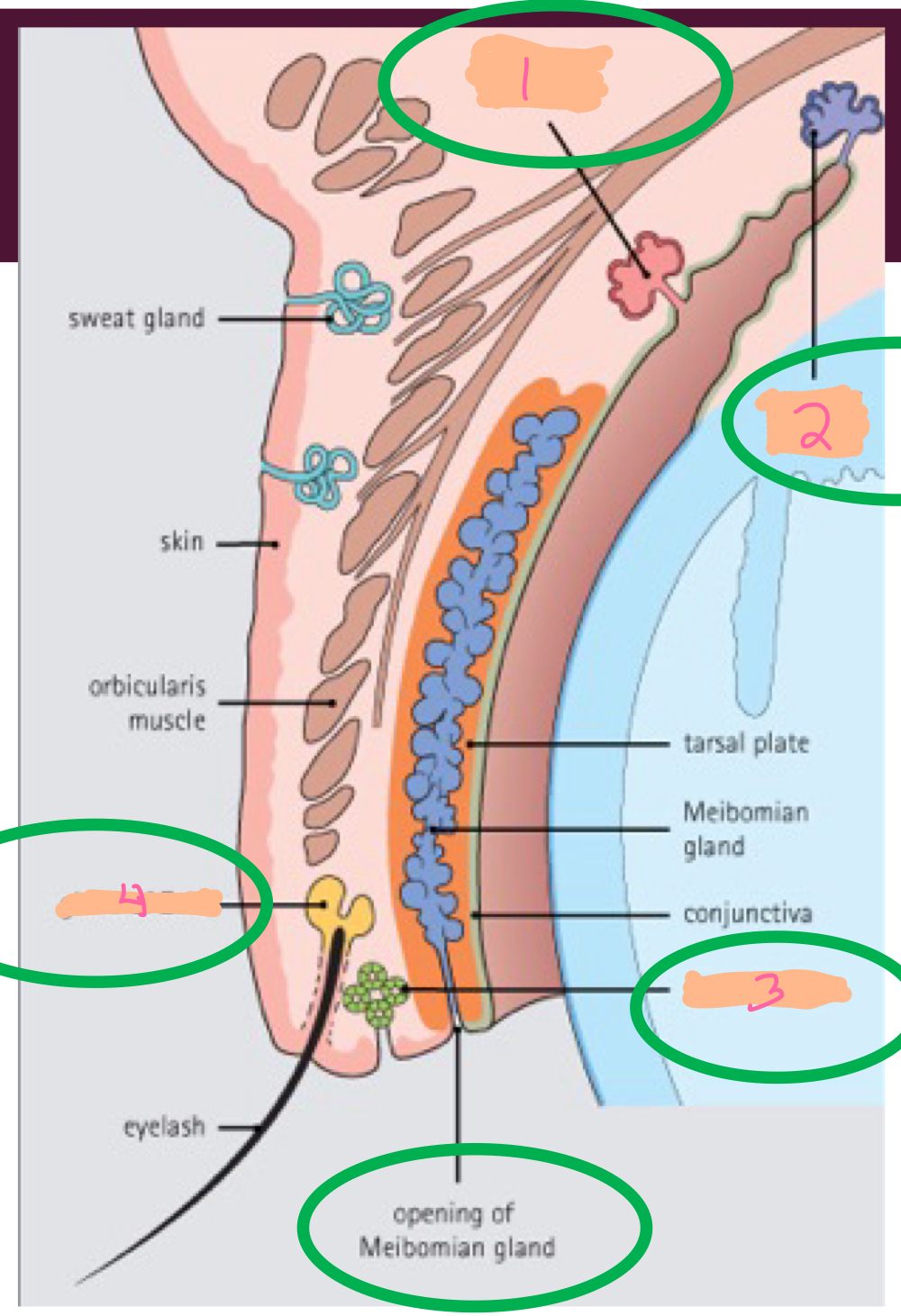
Lipid layer
Aqueous layer
Mucin layer
What are the 3 layers of the tear film?
meibomian glands
What gland is responsible for secreting the lipid layer of the tear film?
Lacrimal gland
What gland is responsible for secreting the aqueous layer of the tear film?
goblet cells
What is responsible for the mucin layer of the tear film?
lipid layer
What layer of the tear film prevents evaporation and stabilizes the tear film?
aqueous layer
What layer of the tear film provides essential nutrients and oxygen to avascular cornea, assists in metabolic waste and debris removal, and protects ocular surface with bacteriolytic enzymes?
mucin layer
What layer of the tear film serves as the hydrophilic barrier to the corneal epithelium for wetting of the ocular surface?
Aqueous-deficient
Evaporative
What are the 2 main types of dry eye?
True
True/False: Dry eye disease is more of a continuum in its classification of being evaporative or aqueous deficient.
Tear Hyperosmolarity; pro-inflammatory mediators
What is the triggering event of all dry eye types in the cascade? What does this event cause the release of?
Noninvasive TBUT
Tear Osmolarity
Ocular surface staining
According to the DEWS II, diagnosing dry eye disease must have a positive result in at least one of what 3 diagnostic tests?
CN V1
In dry eye disease, there is a disruption between the lacrimal gland and neurons of the cornea that are part of what cranial nerve?
ocular sensitivity
Disruption to the lacrimal gland in dry eye disease leads to decreased secretions to the ocular surface followed by decreased _______________________.
Interrupts sensory innervation —> reduced corneal sensitivity —> decreased lacrimal gland feedback —> aqueous deficient dry eye
How does refractive surgery induce dry eye?
Aqueous deficient dry eye
What type of dry eye results from refractive surgery?
MMP-9 levels
What levels are specifically measured in InflammaDry dry eye testing?
inflammation
What is the key mechanism of ocular surface injury in eyes with DED?
Tear film disruption
Ocular surface cell damage
What 2 triggers stimulate protective immmunoregulatory and pro-inflammatory mechanisms?
Tear hyperosmolarity
What is the key trigger of inflammatory dry eye?
androgens; estrogens
In regards to hormones, ___________ are thought to suppress DED while ____________ are thought to promote DED.
lacrimal & meibomian glands
What is targeted in the influence of dry eye by hormones?
Transdermal 0.5% testosterone eyelid cream
What treatment is often used in post-menopausal women dealing with dry eye?
Epstein-Barr virus
Hepatitis C virus
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I
What 3 viral infections are associated with Sjogren Syndrome?
Other inflammatory diseases (RA, Lupus, Hepatitis, Myasthenia gravis, etc.)
Secondary Sjogren’s Syndrome results from what?
Aqueous-Deficient dry eye
What type of dry eye is associated with Sjogrens syndrome?
Anti-SSA (Rho)
Anti-SSB (La) antibodies
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA)
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
What 4 levels should be tested in blood work for diagnosing Sjogren’s?
Anti-SSA (Rho)
Anti-SSB (La)
What 2 levels in the blood are specific for Sjogrens?
The Sjö Test
What test for Sjogrens is 89% sensitive and 78.2% specific?
Refer to rheumatology for work-up
How should you manage a patient in which you suspect sjogrens?
Plaquenil
Methotrexate
What are 2 common forms of treatment for Sjogrens?
Dry mouth
Dry eyes
Dry nasal passages
Joint pain
What are 4 common symptoms of Sjogrens?
Topical corticosteroids
Restasis
Xiidra
What are the 3 main medications given for the ocular treatment of Sjogrens Syndrome?
Pilocarpine
What immunosuppressant medication is used in the ocular treatment of Sjogrens to promote parasympathetic output of the lacrimal gland?
Lacrimal deficiencies
Obstruction of lacrimal ducts
Neurosecretory/reflex block
Systemic drugs
What are 4 non-sjogren syndromes that cause aqueous-deficient dry eye?
Corneal surgery
Diabetes
Contact lens wear
What 3 ocular associations cause neurosecretory/reflex block?
Anti-depressants
Diuretics
β blockers
Antimuscarinics (Parkinson’s drugs)
What 4 main systemic drug types cause aqueous deficient dry eye?
Decrease lacrimal gland output
What effect do anti-cholinergic medications have on the lacrimal gland?
5 minutes
How long should you test a Schirmer’s test?
At least 15 mm; At least 10 mm
What is the expected Schemer’s result without anesthesia? With anesthesia?
>20 mm; < 6 mm
What is the expected Phenol Red Test results in a normal patient? Abnormal patient?
15 seconds
How long is the Phenol Red Test administered?
SM Tube
What dry eye assessment tests tear volume in 5 seconds?
0.3 mm
What is a normal lacrimal lake height?
a. Increased
b. Decreased
c. Decreased
Identify whether the following would be found in decreased or increased levels in DED.
a. Matrix Metalloproteinase
b. Lactoferrin
c. Lysozyme
Increased
Tear osmolarity is (increased/decreased) in dry eye.
TearLab
What dry eye lab test has the highest predictive value for the diagnosis of dry eye disease among objective tests?
Sodium fluorescein
Rose bengal
Lissamine green
What are 3 ophthalmic dyes used to visualize dry eye observations?
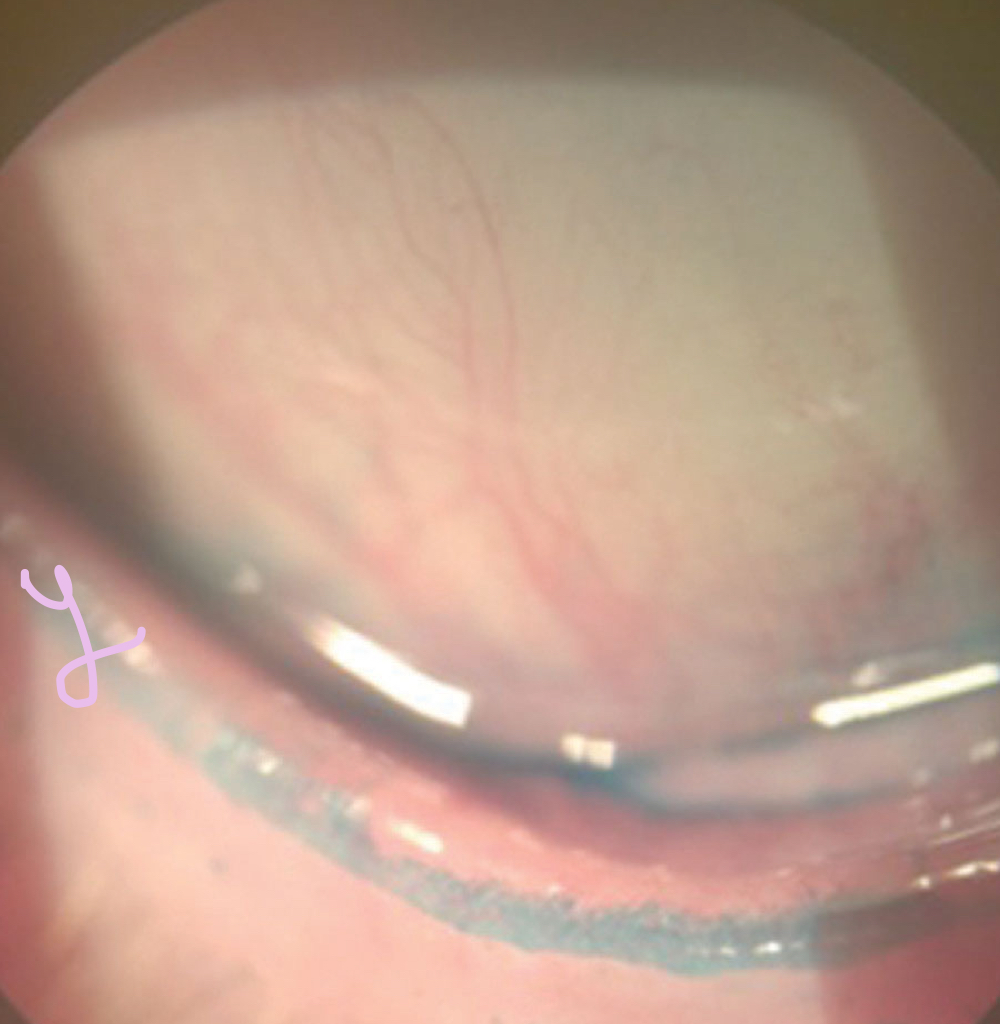
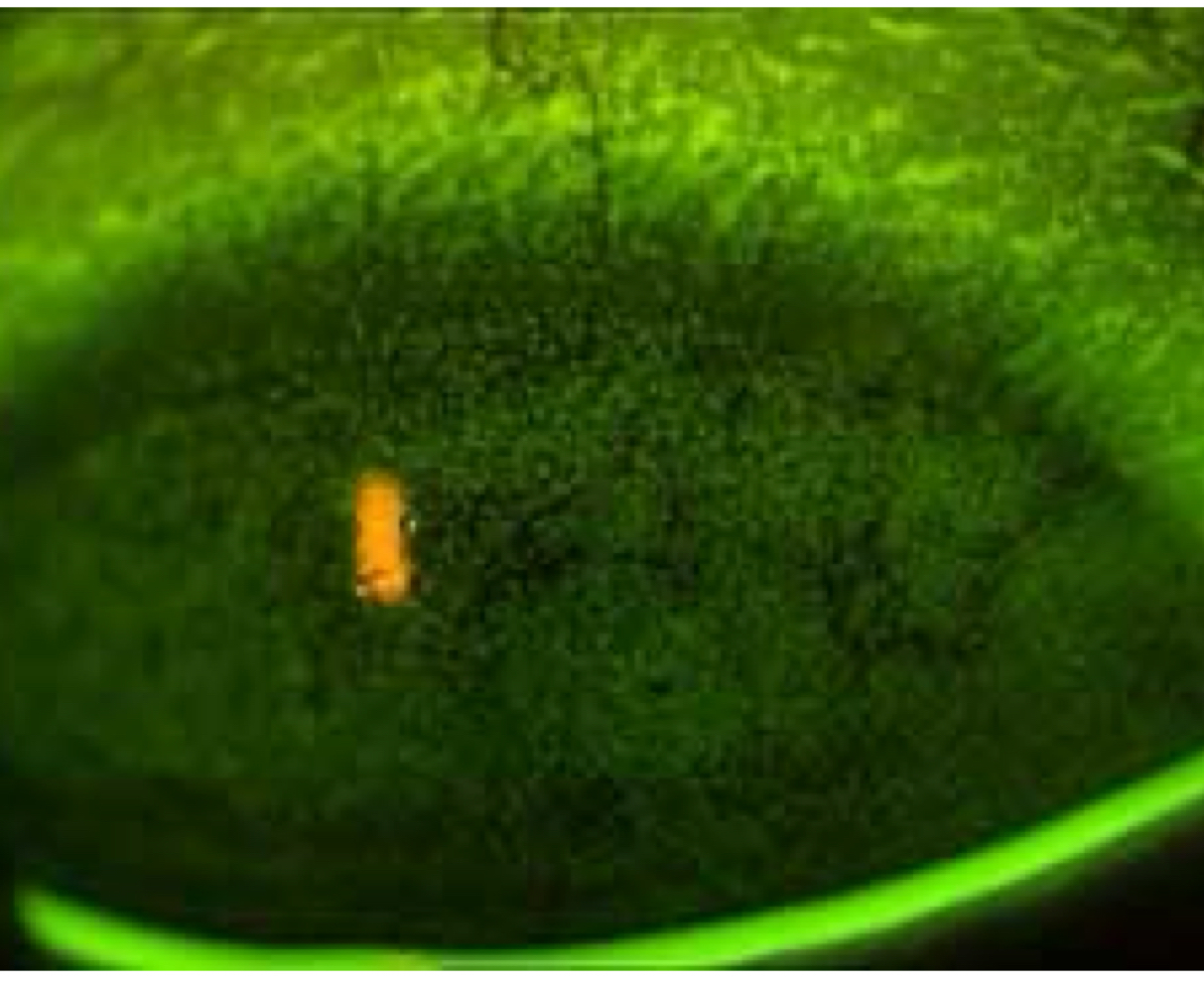
Lid wiper epitheliopathy
What lid staining defect is shown here? What dye was used?
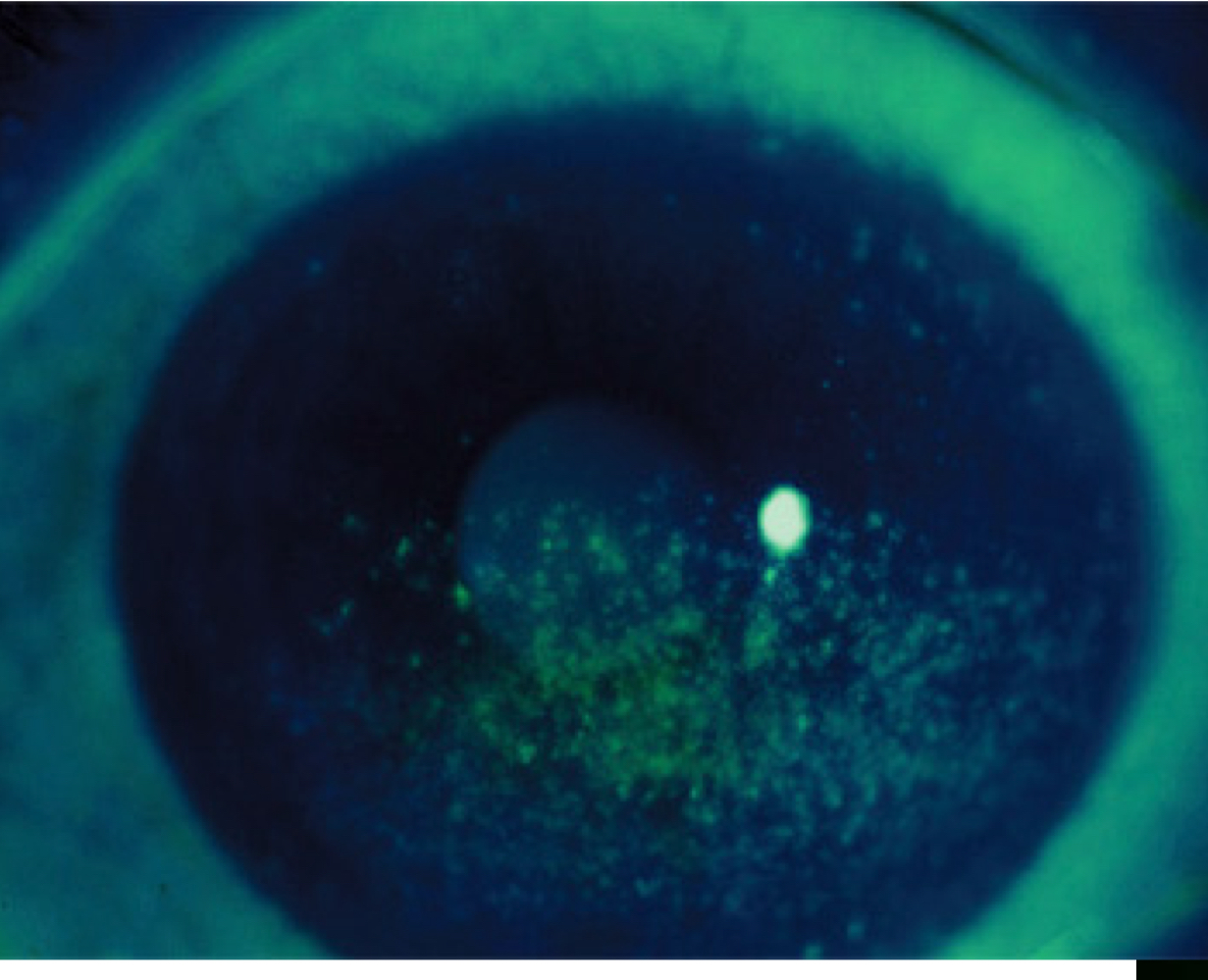
Lagophthalmos
This inferior corneal staining pattern indicates what condition?
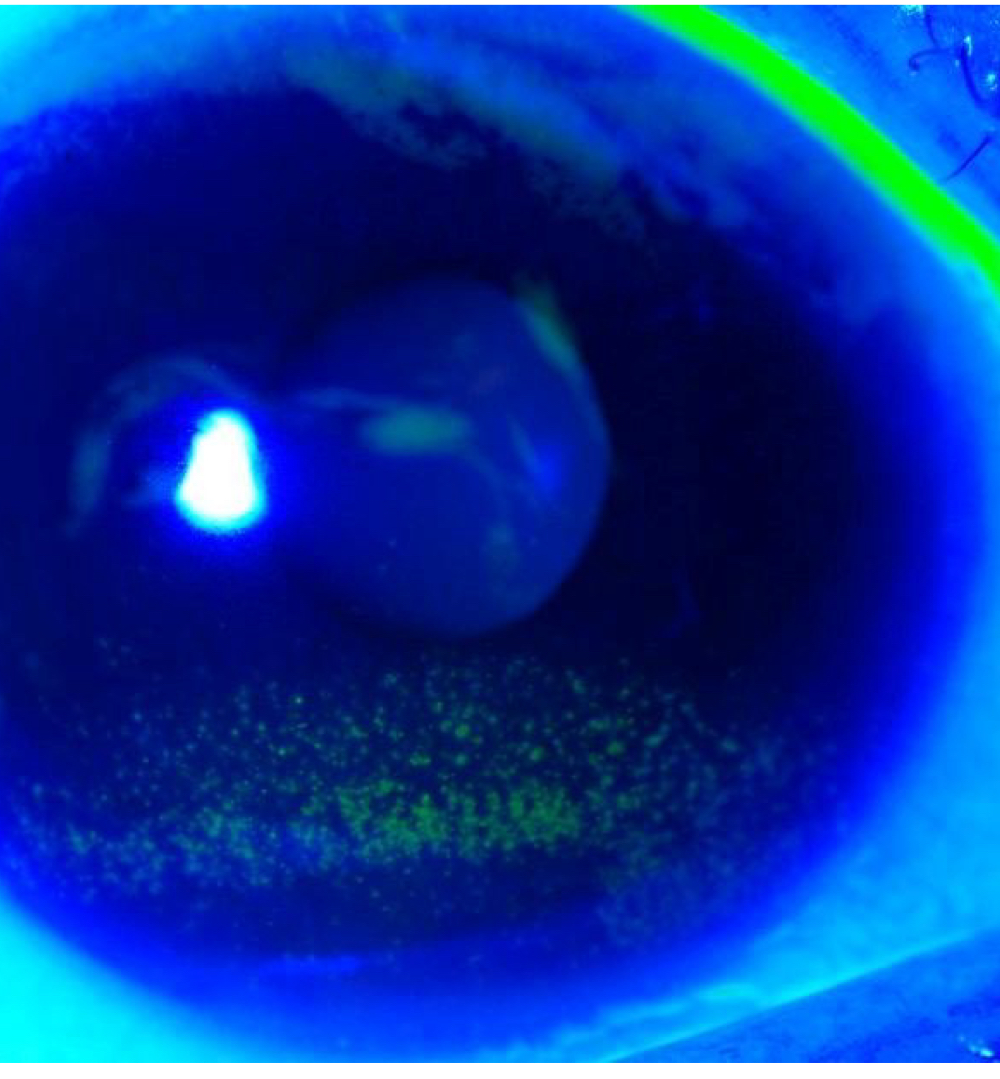
Lids/Lashes Toxicity to Cornea (i.e. blepharitis)
This inferior corneal staining pattern indicates what condition?
Aqueous deficiency
This type of staining pattern is common with what dry eye issue?
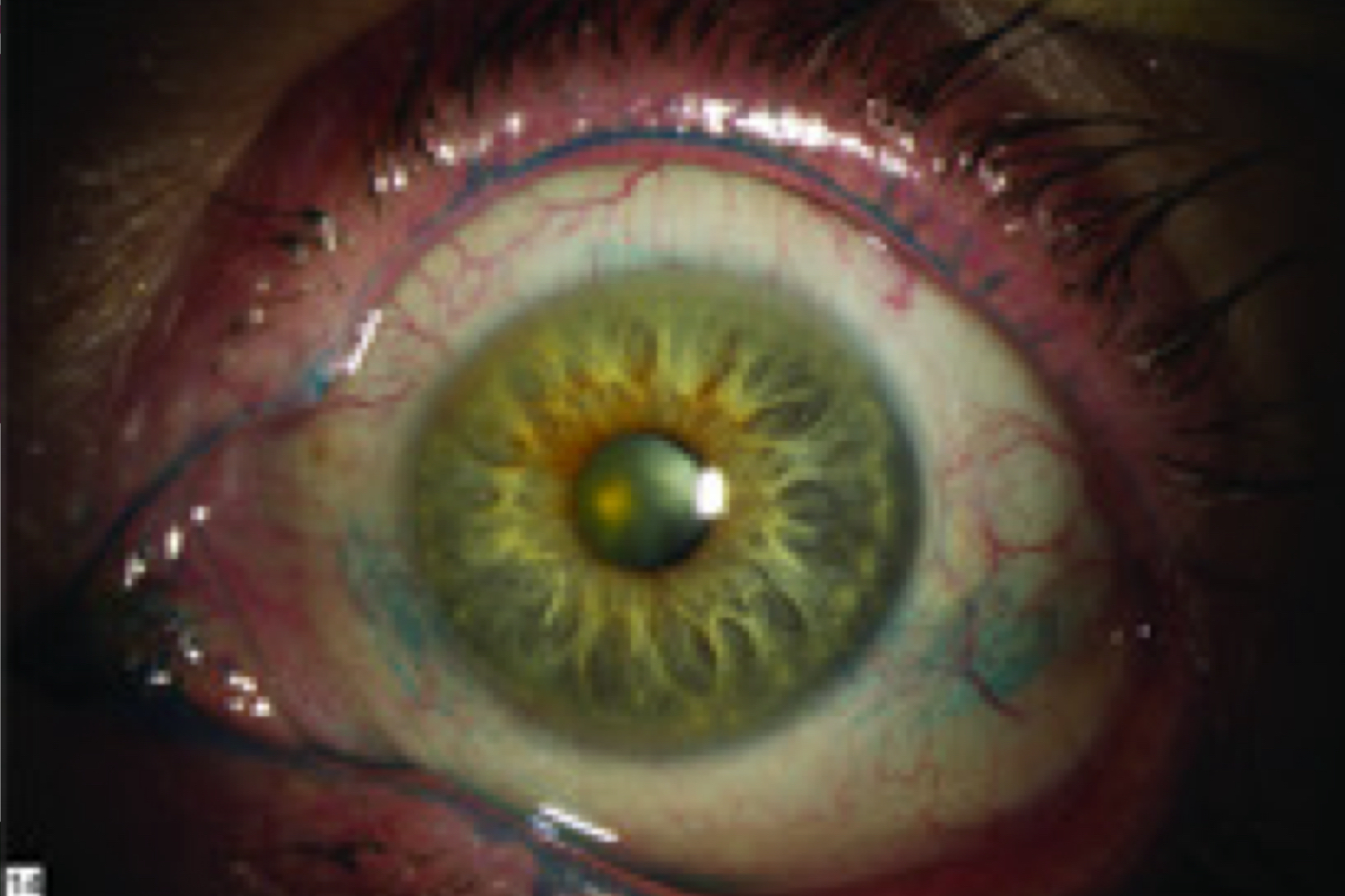
preservative sensitivity
The diffuse staining pattern shown here indicates what?
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD)
What is the most under diagnosed, under treated, and under appreciated disease in eye care?
meibomian glands
What gland is responsible for the lipid component of the tear film?
sebaceous glands
What type of glands are meibomian glands?
True
True/False: Meibomian glands are densely innervated.
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD)
What is most likely the most frequent cause of DED?
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD)
Chronic, diffuse abnormality of the meibomian glands, commonly characterized by terminal duct obstruction and/or qualitative/quantitative changes in glandular secretion; result in alteration of the tear film, symptoms of eye irritation, clinically apparent inflammation, and ocular surface disease
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
Leading cause of evaporative dry eye
Rosacea
What is an example of a secondary cause of meibomian gland dysfunction?
60
Up to _____% of rosacea patients show ocular manifestations.
Rosacea
Disease affecting sebaceous glands in the face
Asian populations
What ethnicity has the highest prevalence of MGD?
Anterior blepharitis
Contact lens wear
Demodex
What are 3 ocular associations of MGD?
Androgen deficiency
Menopause
Aging
Rosacea
Antihistamine use
Antidepressant use
What are 6 systemic associations of MGD?
Irritation & visual fluctuation
Tear film instability
Ocular surface compromise
What are 3 clinical features present with both aqueous-deficient & evaporative dry eye?
smoking
What environmental factor causes thickened meibum?
Loss of lipid layer —> evaporation of aqueous layer
What causes tear film instability in MGD?
Photophobia
Discomfort
Burning
Itching
Grittiness
FBS
What are 6 ocular symptoms of MGD?
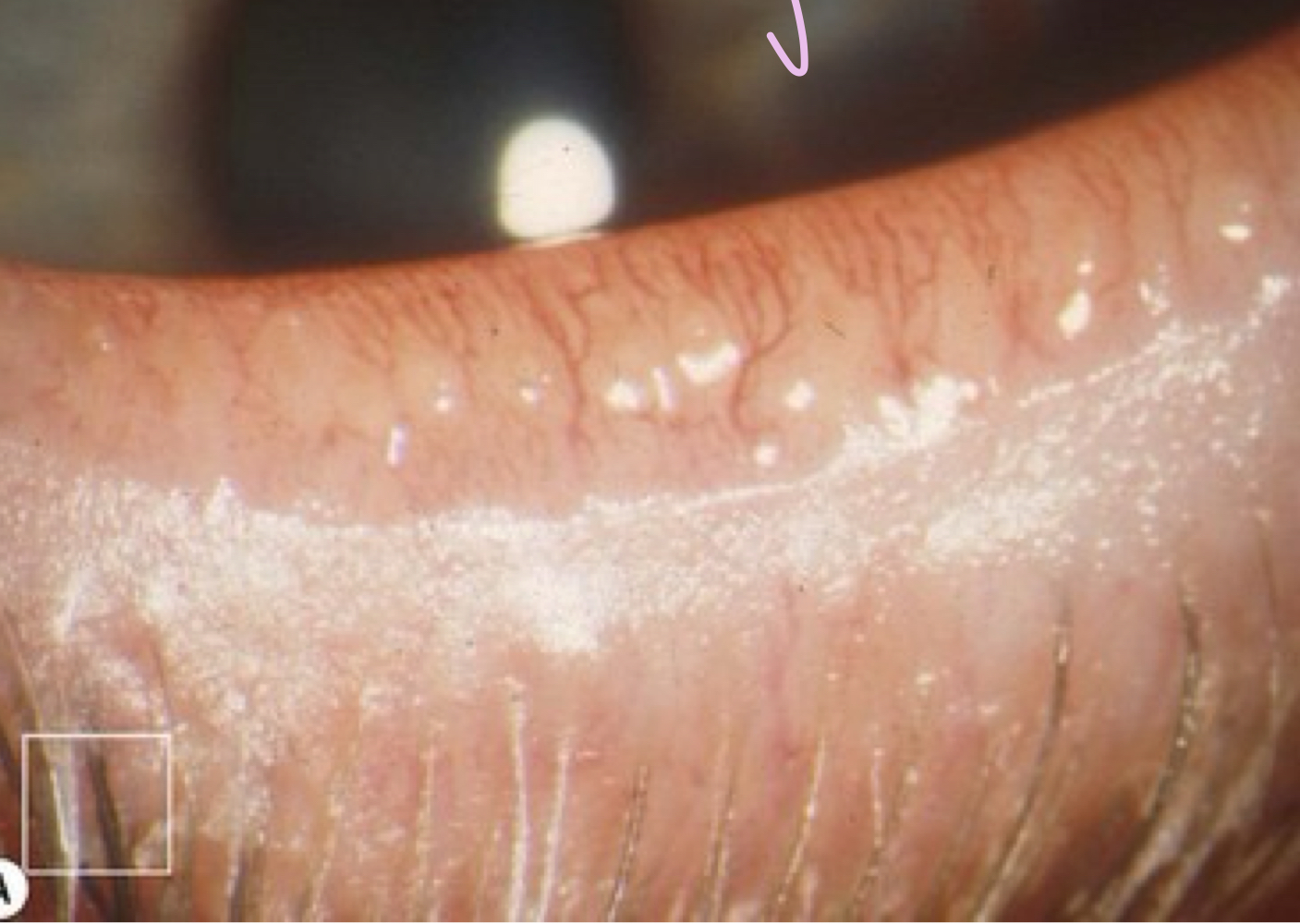
Telangiectasia of the lid margin
“Scalloped”, irregular lid appearance
What 2 features of the eyelid appearance indicate inflammation?
Inflammation
Capped glands
Saponification
What are 3 general appearances of the eyelid that aid in the diagnosis of MGD?
Telangiectasia of the lid margin
What is shown in the image?
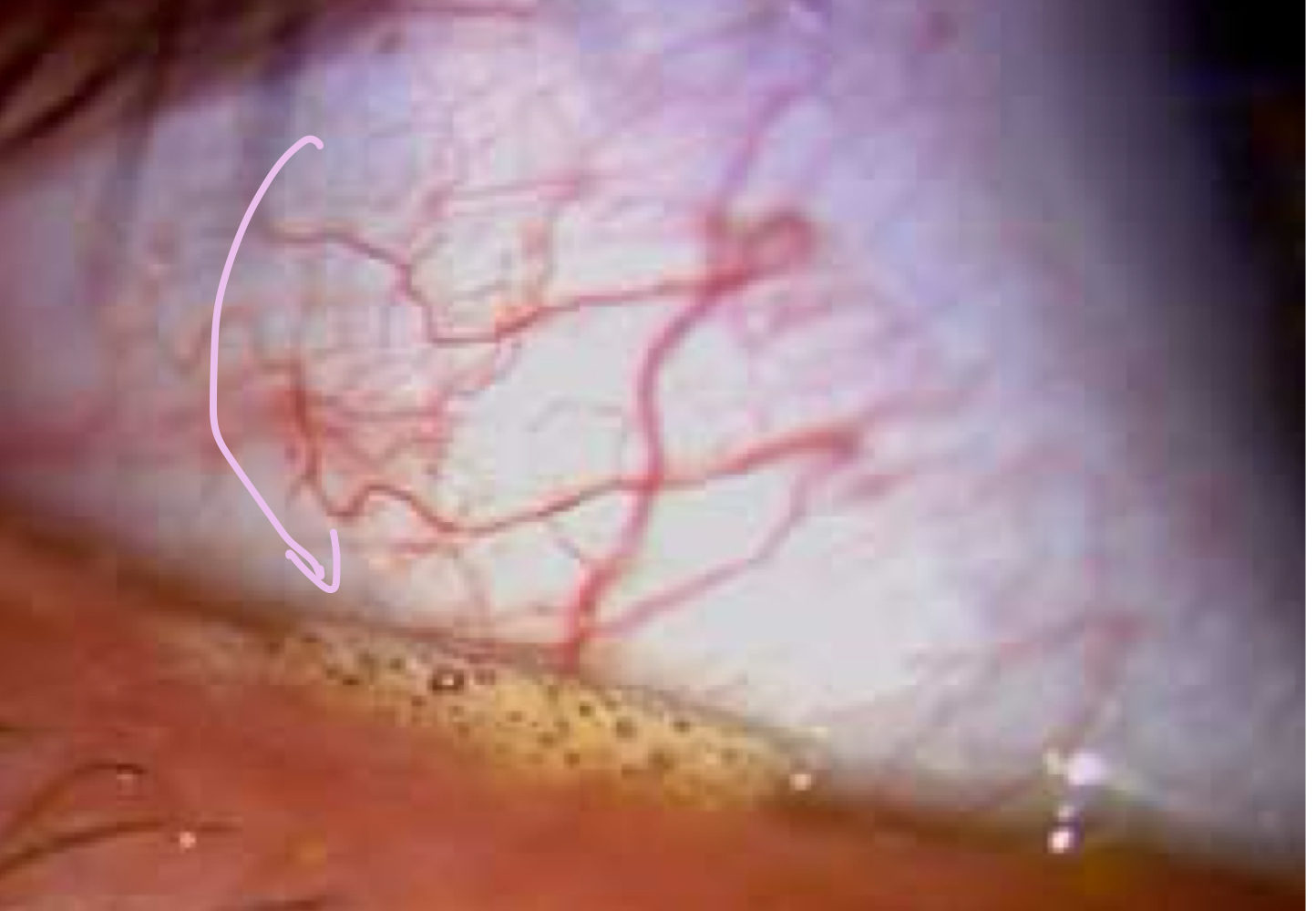
Saponification; bacterial enzymes react to the tear film
What ocular anomaly is indicated by the arrow in cases of MGD? What causes this to occur?
clear, liquid meibum
What secretion quality of the meibomian glands would you expect in a normal, healthy patient?
Sodium fluorescein
What stain should be used to analyze corneal staining in the diagnosis of MGD?
Lissamine green & Rose Bengal
What stain(s) should be used to analyze conjunctival staining in the diagnosis of MGD?
The ocular surface is protected by the tear film.
An Ocular Protection Index (OPI) > 1 indicates what?
Exposed ocular surface
An Ocular Protection Index (OPI) < 1 indicates what?
Divide TBUT by blink interval in seconds
How do you calculate Ocular Protection Index (OPI)?
Meibography
Allows imaging for direct visualization of meibomian gland morphology
atrophy
Missing meibomian glands seen in meibography indicates __________.
Analyze tear film instability
What is the purpose of TBUT testing in the diagnosis of MGD?
Expressibility
Quality
What 2 features are you assessing when you express meibomian glands?
Warm Compress (Bruder Mask)
Mechanical lid massage
In-Office expresssion
Treatment of accompanying anterior blepharitis
What are the 4 main conservative treatments of MGD?
compliance
What is the biggest problem with conservative treatment of MGD?
Improve tear osmolarity & reduce friction on ocular surface
What is the purpose of using artificial tears in the treatment of MGD?
Refresh Mega-3 drops
What type of artificial tears has a lipid layer supplementation (omega-3s) to aid in the treatment of MGD?
Refresh Mega-3
Retaine MGD
Systane Complete
What 3 drops discussed in glass directly target the lipid layer of the tear film & meibomian gland health?
False—no evidence of bacterial involvement
True/False: Topical antibiotics are a great form of treatment for MGD.