BIOL 185L - Other Eukaryotes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
A. Eukarya, Protist, Archaeplastida, Chloroplastida (green algae)
B. Unicellular, filamentous, colonial, multicellulae
C. flagellated, unicellular, colonial, filamentous, multicellular, no mobility
D. Chlorophyll a & b
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. Label the following types under this secondary clade.
C. List some characteristics.
D. Pigment types
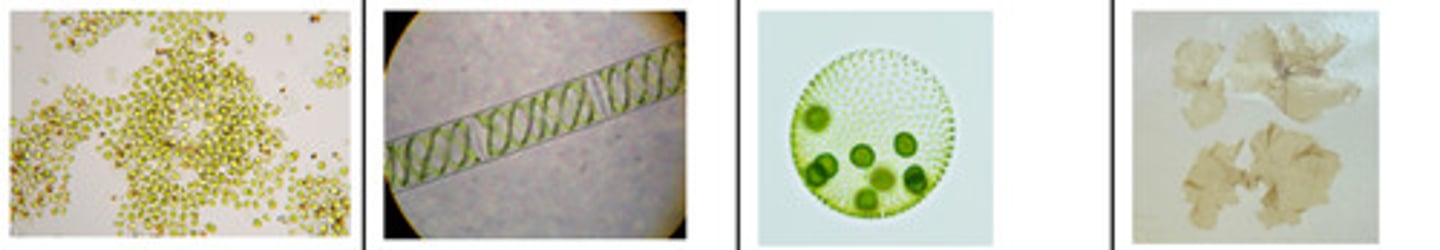
A. Eukarya, Protist, Archaeplastida, Rhodophyceae (red algae)
B. some (coraline algae) with calcification
C. Chlorophyll a & d
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List some characteristics.
C. Pigment types

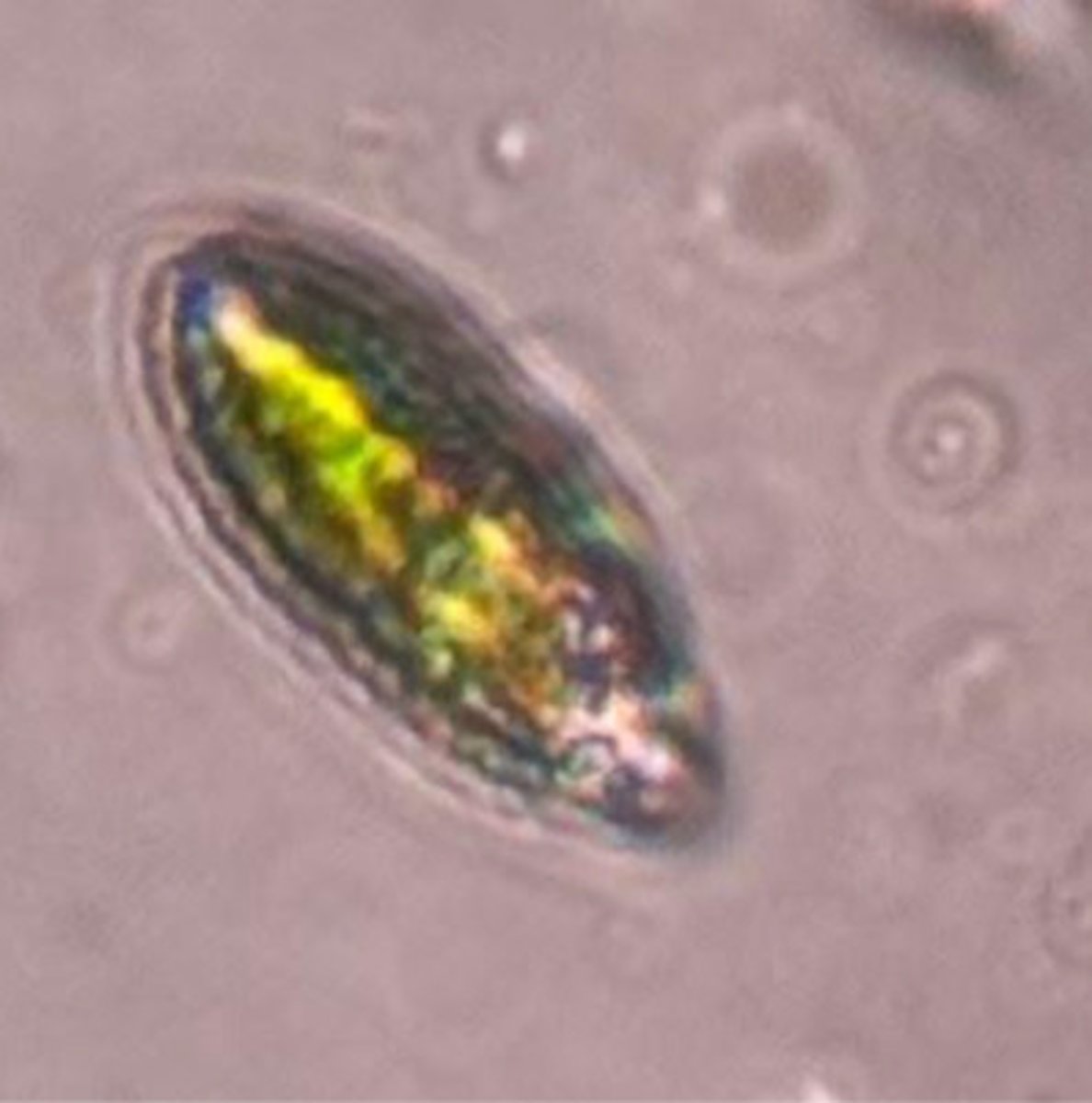
A. Eukarya, Protist, Excavata, Euglenida
B. green, unicellular, flagellated, chloroplasts
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List some characteristics.
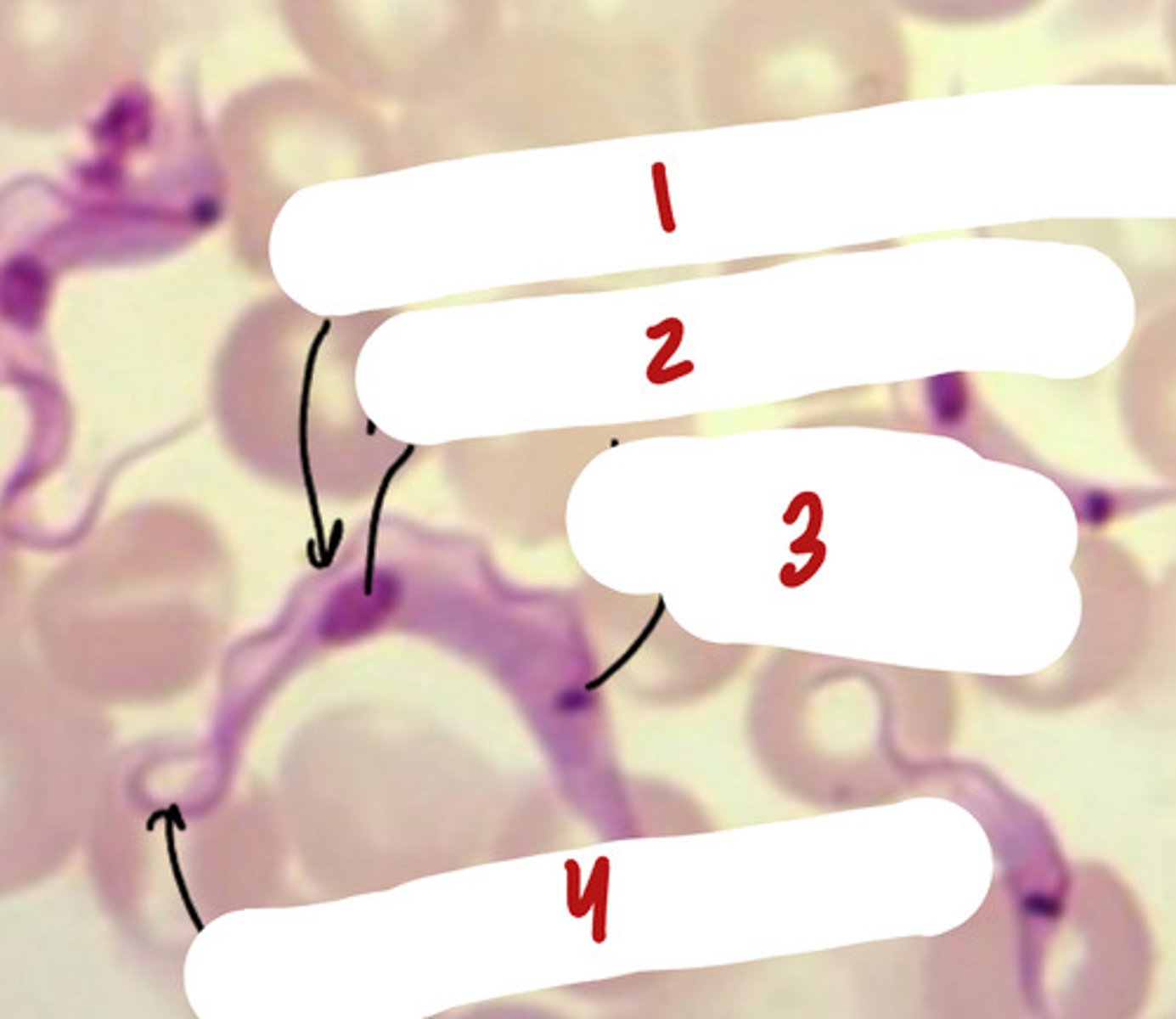
A. Eukarya, Protist, Excavata, Kinetoplasta
B. 1- undulating membrane (mobility), 2- nucleus (gene info), 3- kinetoplast (protein & carbohydrate synthesis), 4- flagellum (motility)
C. unicellular, flagellated, undulating membrane, nucleus, kinetoplast, sleeping sickness disease
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. Label the following with their function.
C. List some characteristics.
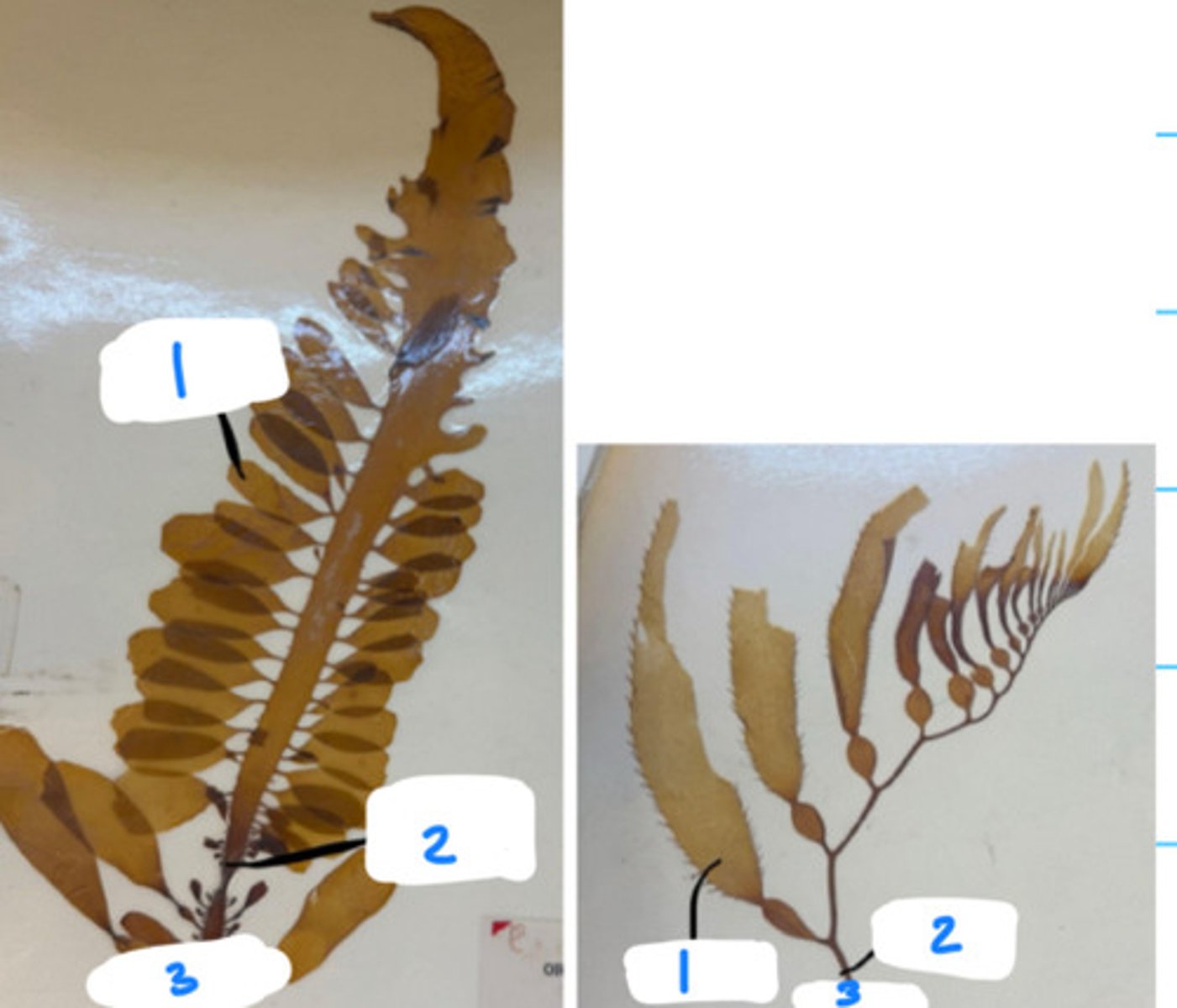
A. Eukarya, Protist, Stramenopila, Phaeophyceae (brown algae)
B. 1- blade, 2- stipe, 3- holdfast
C. Chlorophyll a & c
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. Label the following. 3 would be pointing at the base below the endpoint of 2
C. Pigment types?

A. Eukarya, Protist, Stramenopila, Bacillariophyta (diatoms)
b. unicellular/colonial, photosynthetic, silica skeleton
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List the characteristics.
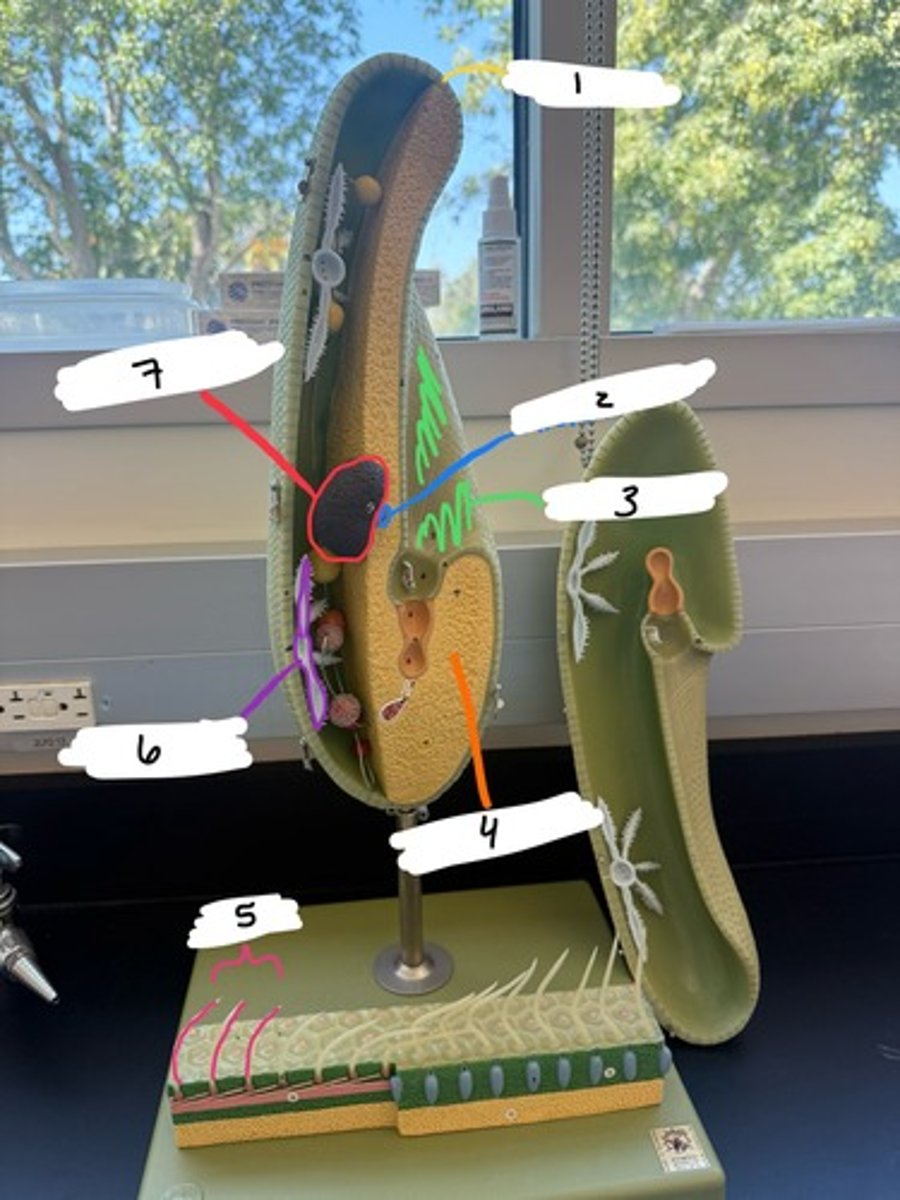
A. Eukarya, Protist, Alveolata, Ciliophora (ciliates), Paramecium
B. 1- ectoplasm (movement), 2- micronucleus (sexual reproduction), 3- oral groove (collect & transport food), 4- endoplasm (cell metabolism), 5- cilia (motility), 6- contractile vacuoles (osmoregulation), 7- macronucleus (metabolism & cell growth)
C. cilia to move, macronucleus, micronucleus, oral groove
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade, Species name
B. Label the following with functions.
C. List the characteristics.
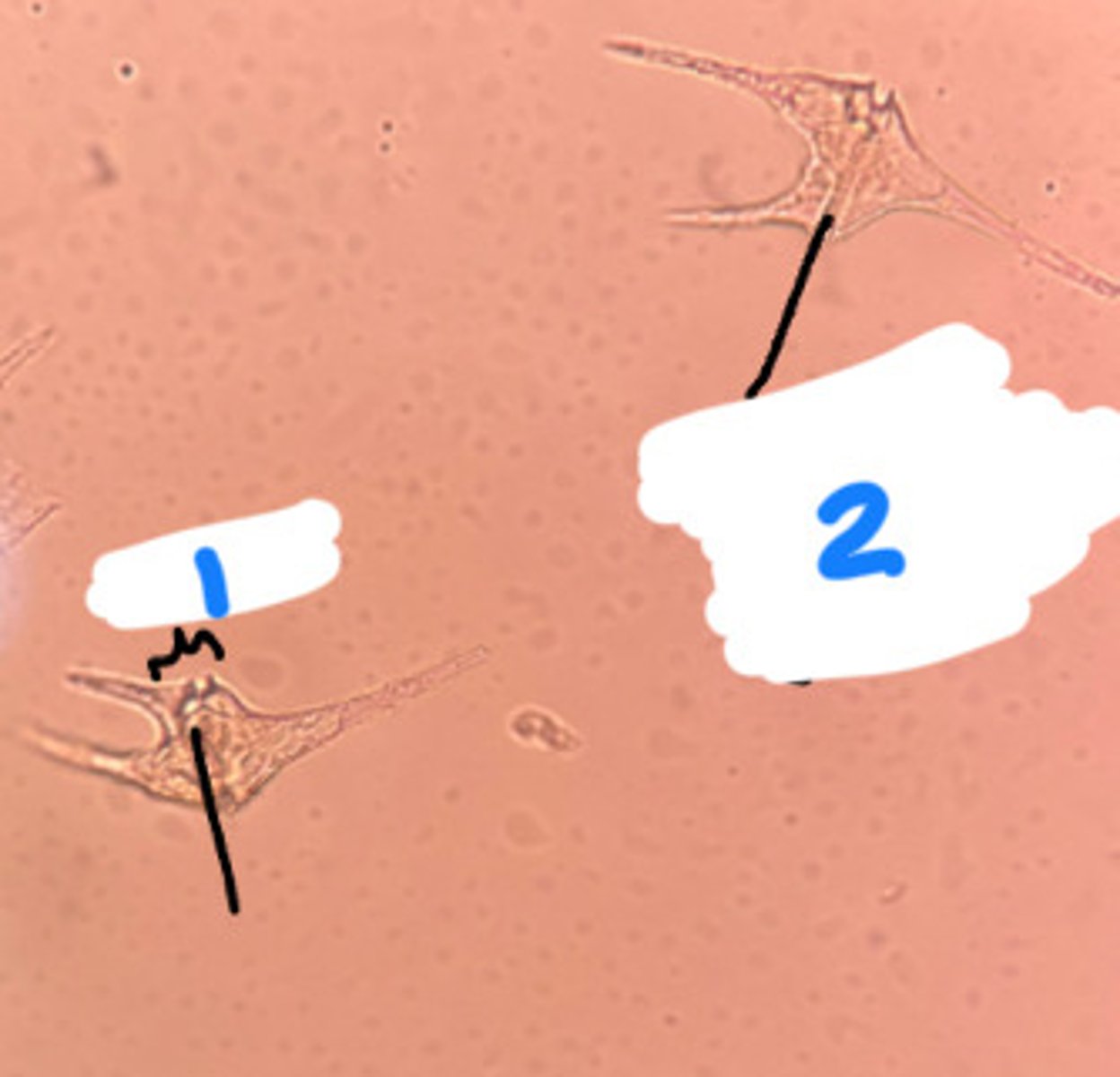
A. Eukarya, Protist, Alveolata, Dinozoa (dinoflagellates)
B. Groove (locomotion), Transverse flagellum in groove (movement)
C. cellulose plates, flagella, mostly autotrophs, some heterotrophs
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. Label the following with functions.
C. List the characteristics.
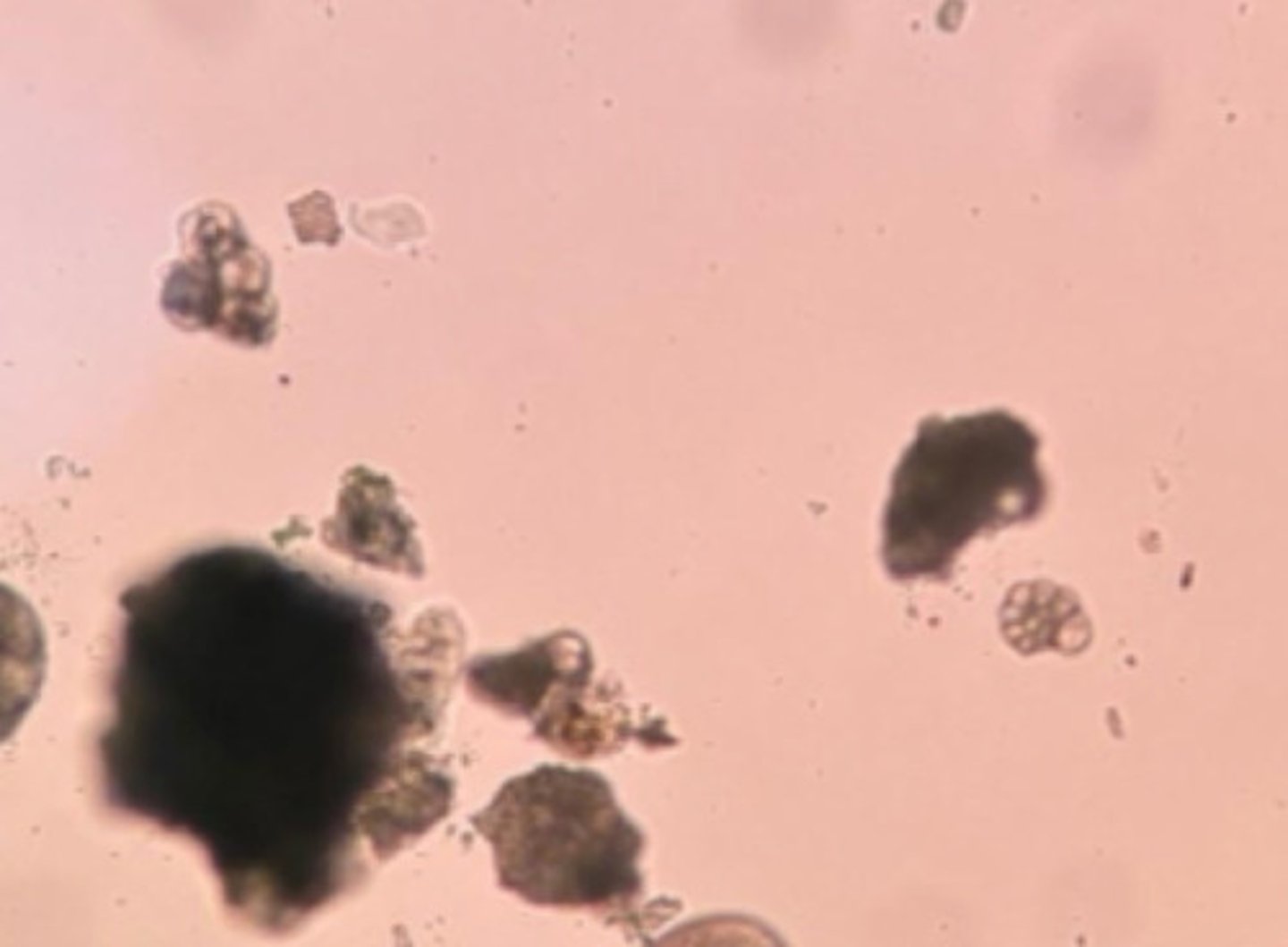
A. Eukarya, Protist, Rhizaria, Foraminifera
B. Calcium carbonate test
*close up: looks like mollusk shells
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List the characteristics.
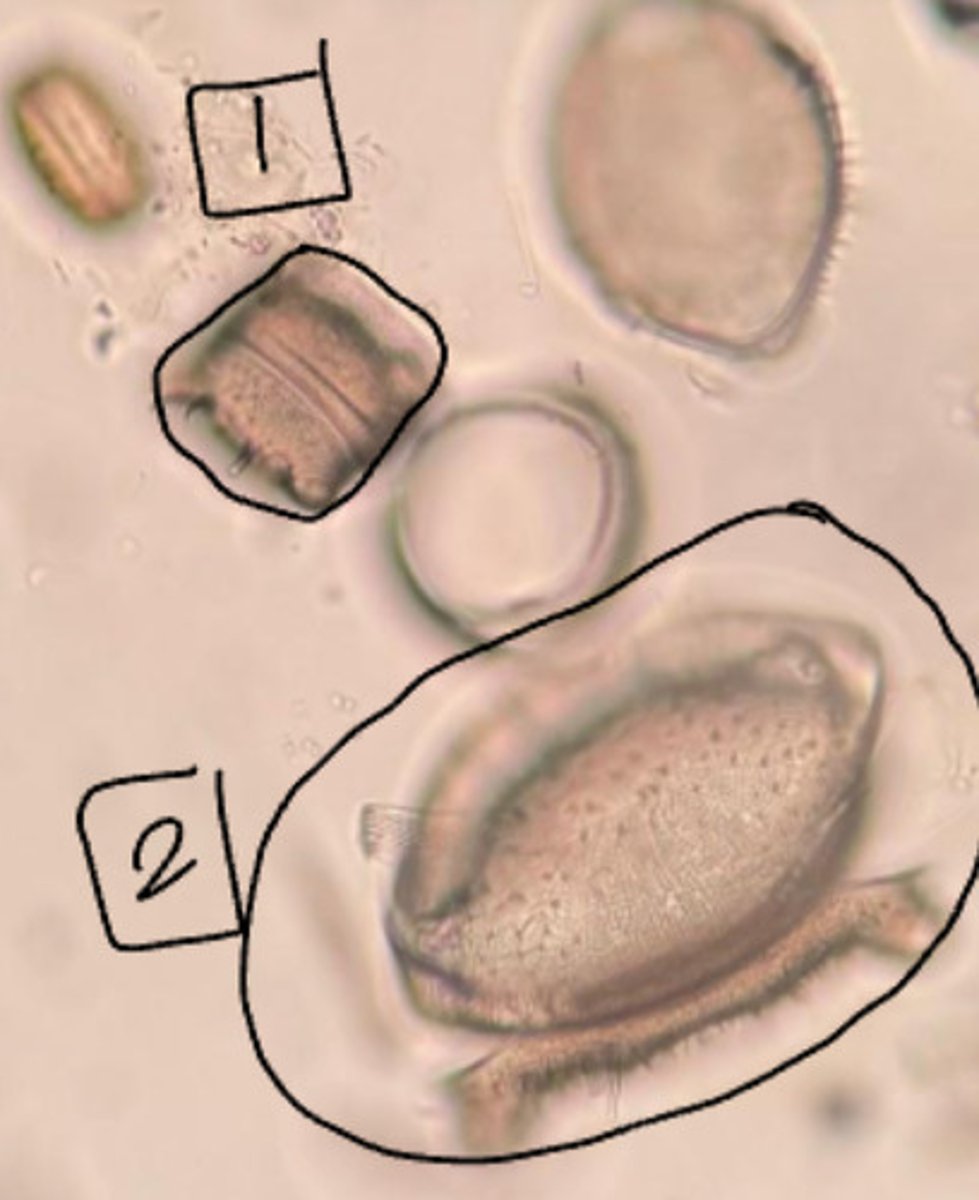
A. Eukarya, Protist, Rhizaria, Radiolaria
B. silica skeletons, axopodia
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List the characteristics.
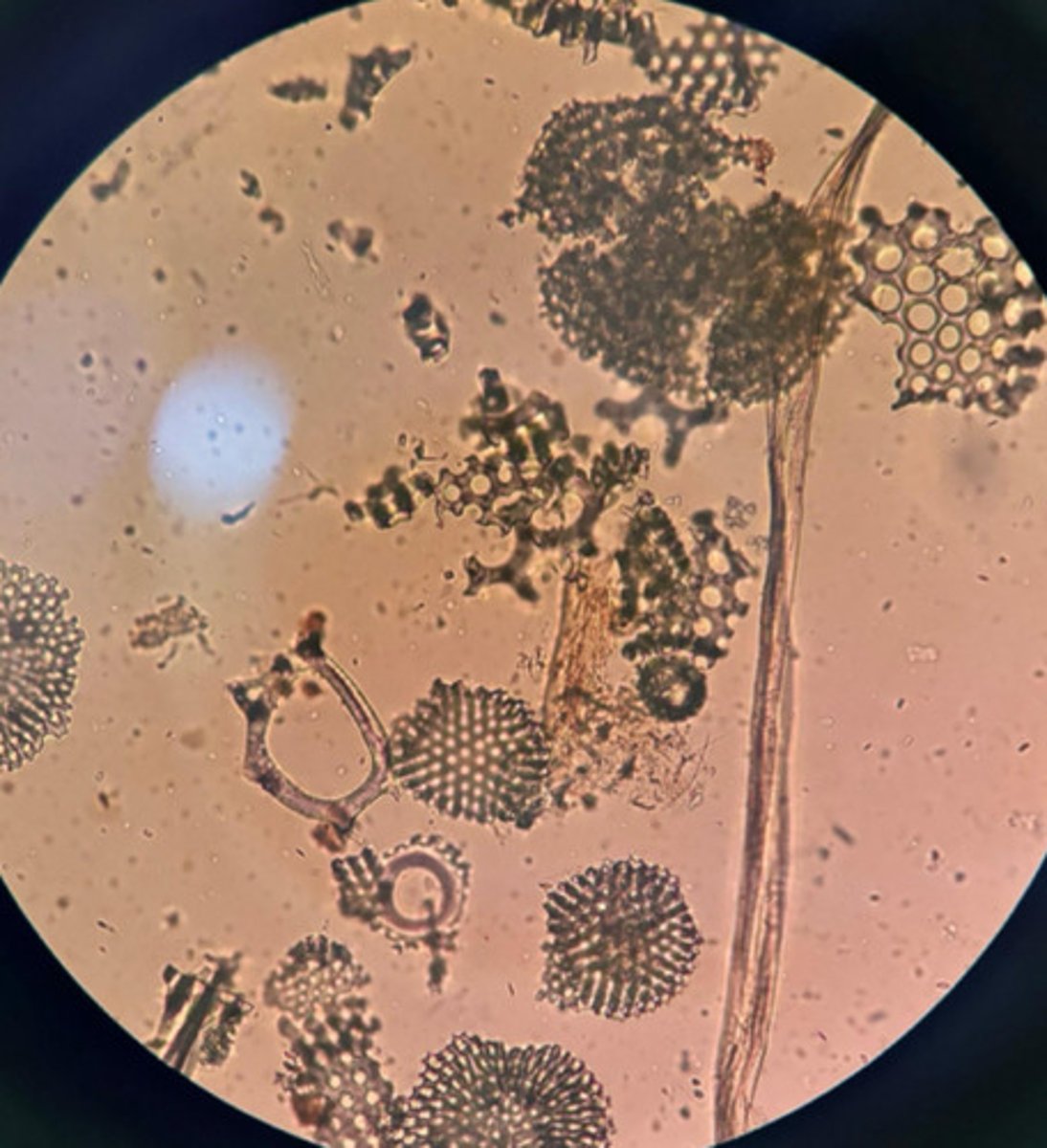
A. Eukarya, Protist, Rhizaria, Radiolaria
B. axopodia (locomotion, capture prey)
C. silica skeletons, axopodia
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. Label the blank with function.
C. List the characteristics.
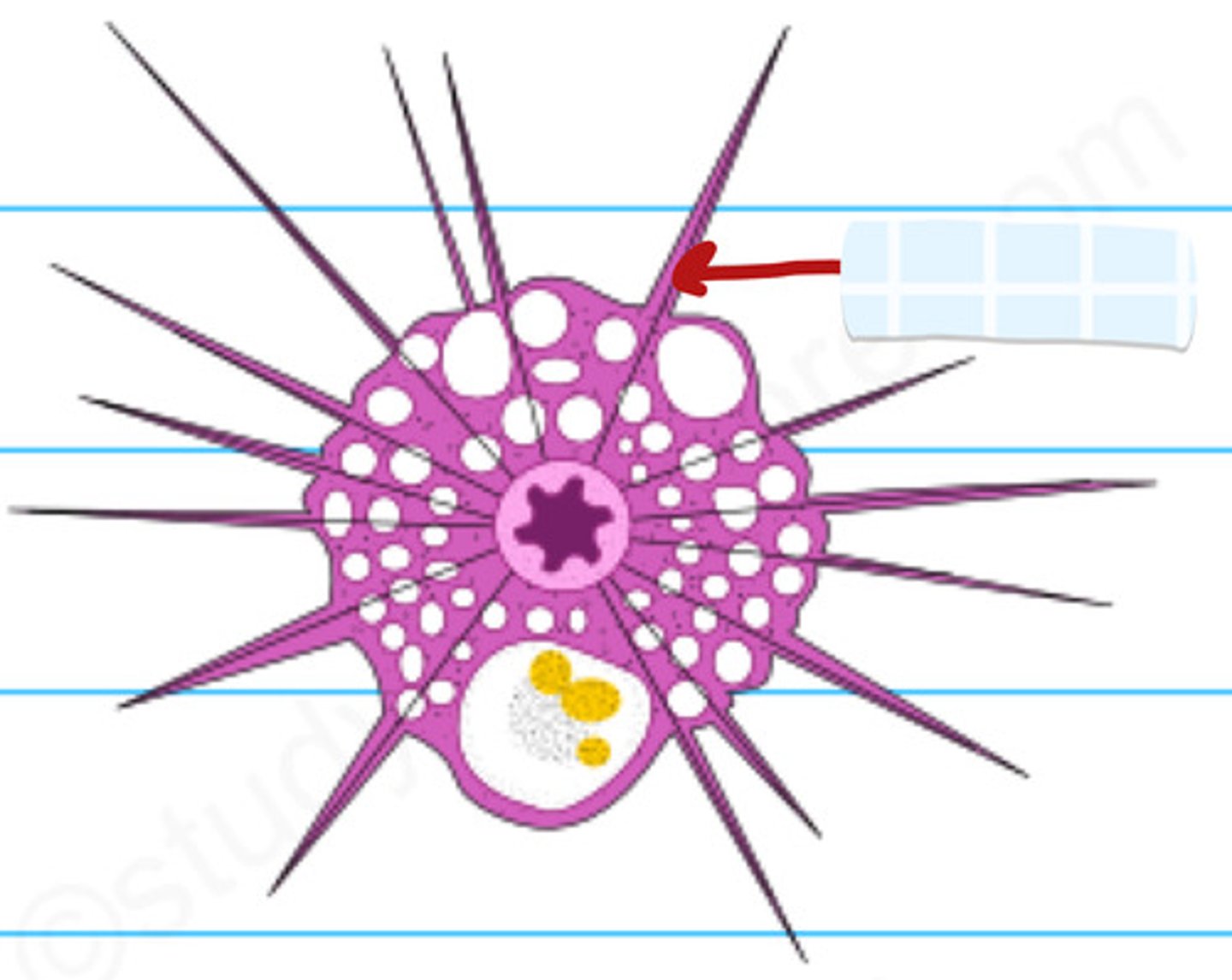
A. Eukarya, Protist, Amoebozoa (amoeboids), Tubulinea (amoeba)
B. moving pseudopods & cytoplasmic streaming, no flagella/cilia, ectoplasm, endoplasm, nucleus, vacuoles
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List the characteristics.
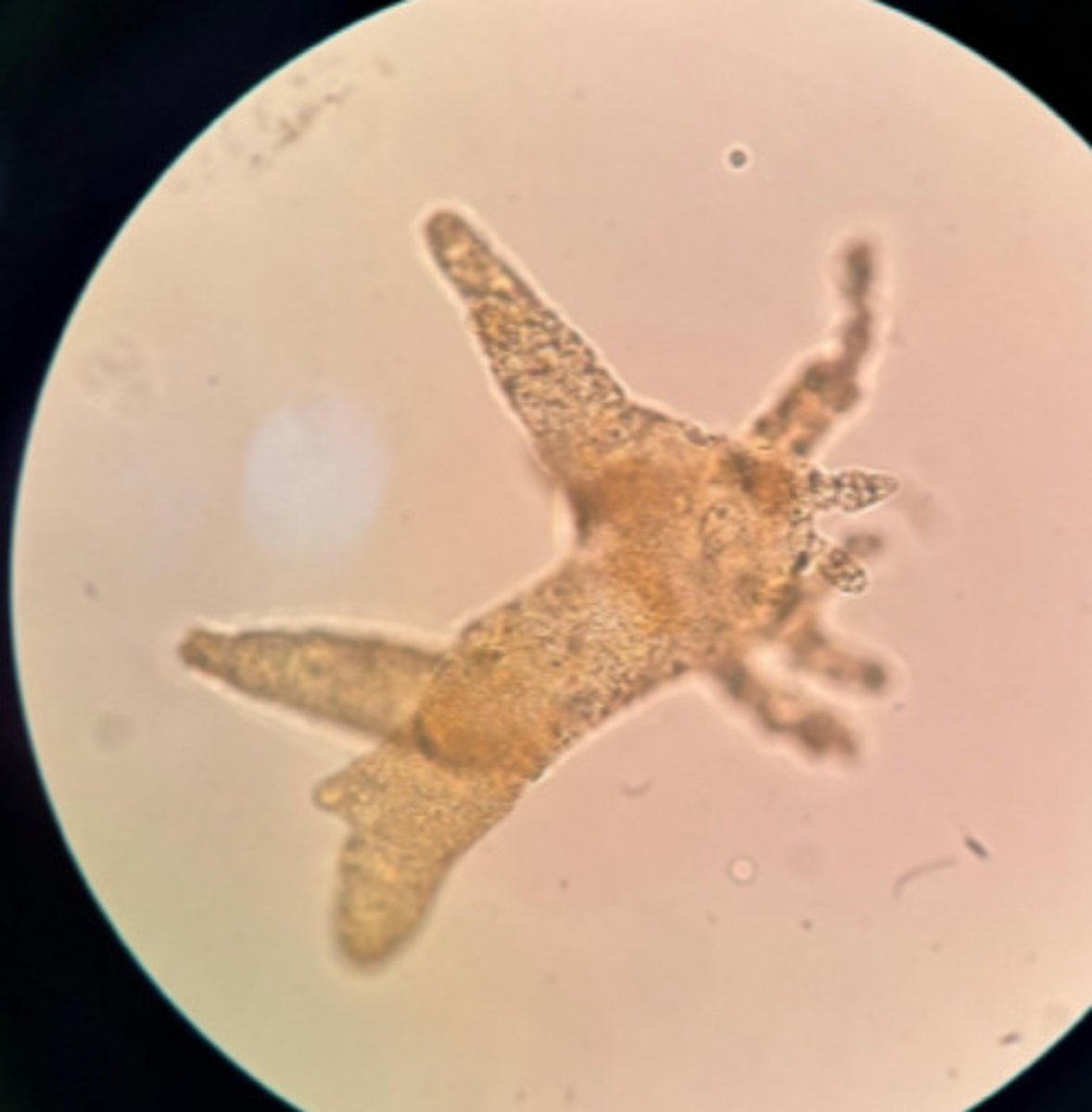
A. Eukarya, Protist, Amoebozoa (amoeboids), Tubulinea (amoeba)
B. 1- ectoplasm (mvmt), 2- pseudopod (locomotion & feeding), 3- food vacuole (digest food), 4- endoplasm (locomotion & metabolism), 5- nucleus (gene info), 6- contractile vacuole (osmoregulation)
C. moving pseudopods & cytoplasmic streaming, no flagella/cilia, ectoplasm, endoplasm, nucleus, vacuoles
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. Label the blank with function.
C. List the characteristics.
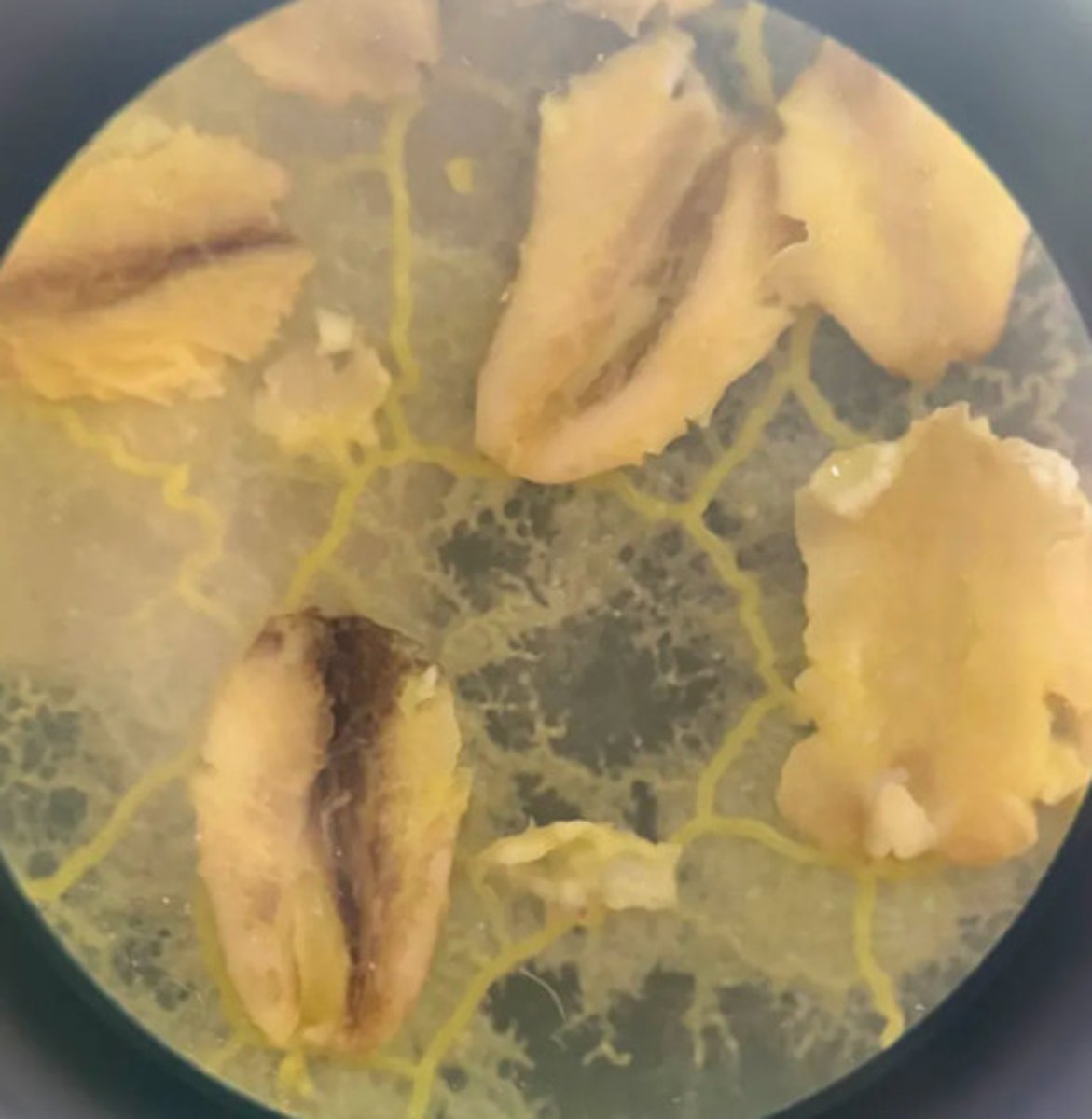
A. Eukarya, Protist, Amoebozoa (amoeboids), Eumycetozoa (slime molds)
B. cellular & acellular, plasmodium
A. Domain, Kingdom, Primary Clade, Secondary Clade
B. List the characteristics.