Chapter 18 The Eighteenth Century: European States, International Wars, and Social Change
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Enlightened Absolutism
A type of monarch that would emerge in the eighteenth century who are said to have followed the principles of the philosophes of the Enlightenment.

Pocket Boroughs
A corrupt system of voting for and choosing deputies for the English House of Commons based on corruption and even open bribery at times.

War of Austrian Succession
A war triggered by Austria putting a women in charge of the empire, Maria Theresa. Prussia used this as an excuse to declare war and take the iron rich Austrian Provence of Silesia.

Junker
A Prussian nobleman. Fredrick the Great was able to use many of them as officers in his large and powerful army, this made them have a greater bond and sense of loyalty to him and to the country.

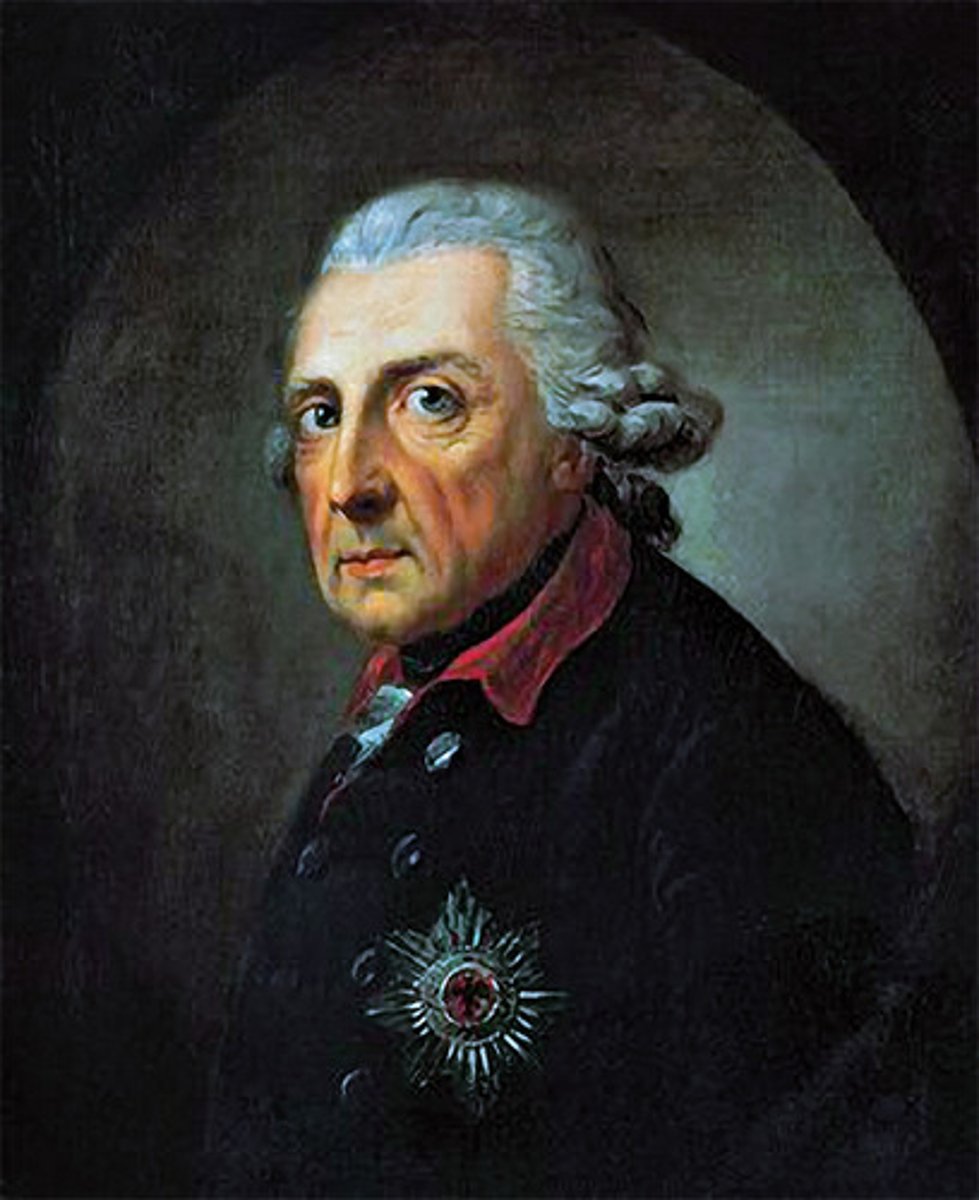
Frederick II, aka Frederick the Great
He is said to be one of the most cultured and best educated monarchs in all of Europe. He was influenced by the thoughts of the Enlightenment but also was known for his strict discipline and military victories during the Seven Years War.

Prussian Militarism
This term can best be summed up by a government official... "Prussia was not a country with an army, but an army with a country which served as headquarters and food magazine."

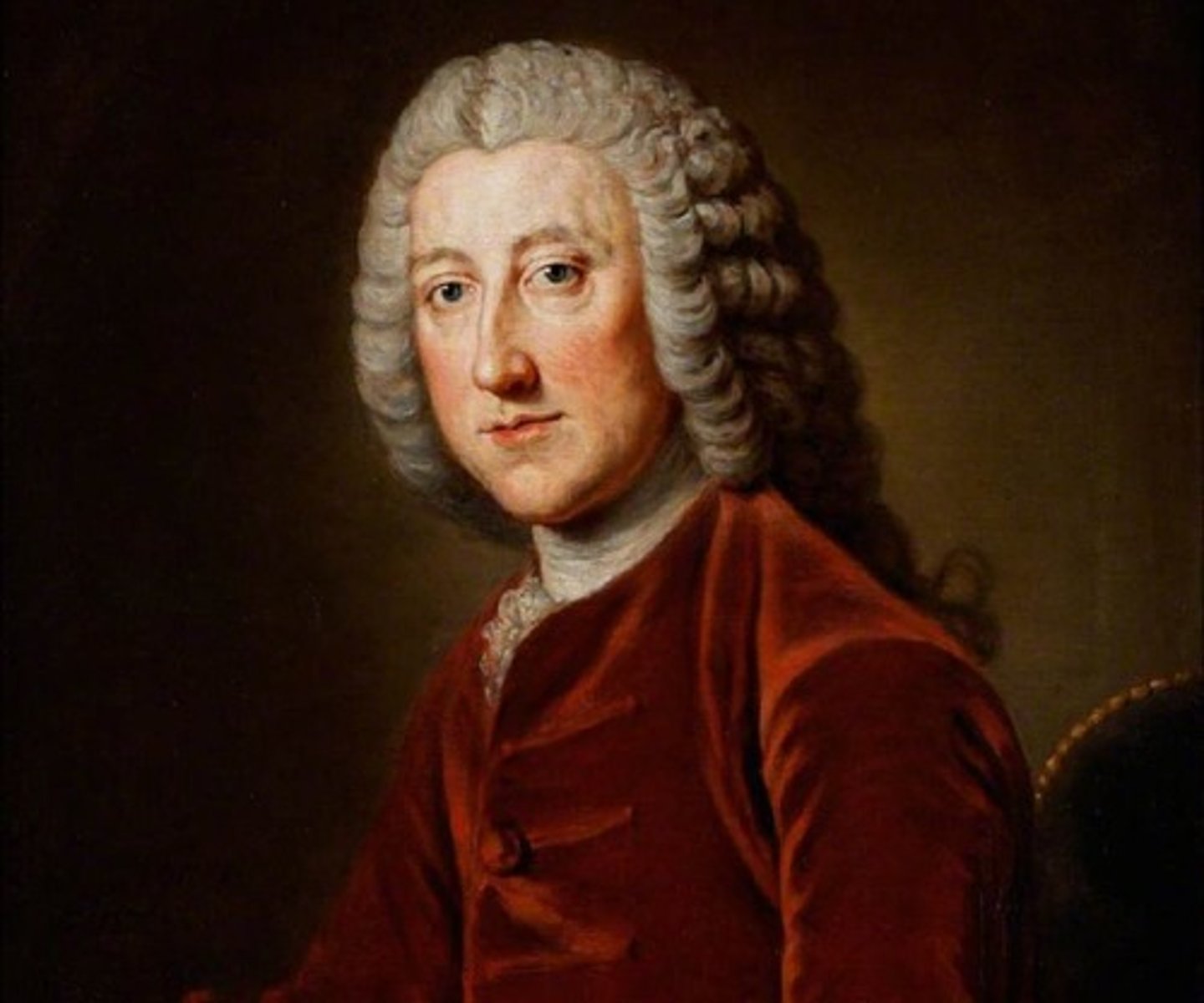
William Pitt the Elder
English Prime Minister that fostered imperial ambitions by adding Canada and India to the Empire by taking part in the Seven Years War.

Seven Years War
The war that would see France lose most of it's overseas empire, England become the dominant European economic and naval power and Prussia become a recognized major military power on the European continent.
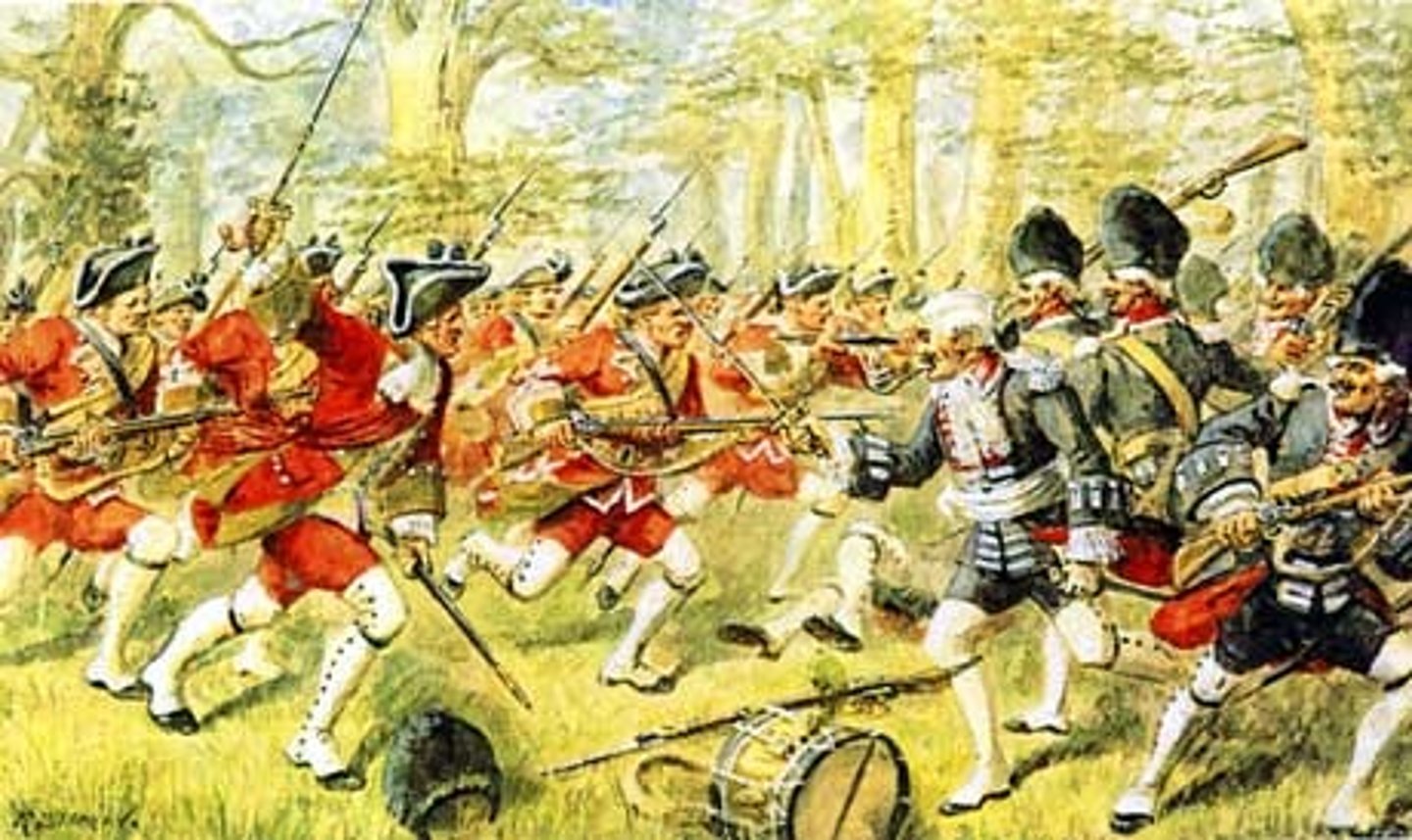

The French and Indian War
The name given to the Seven Years War that took place in North America. France would lose this war and have to give up much of its territory as well as its claim to its holdings in Canada.

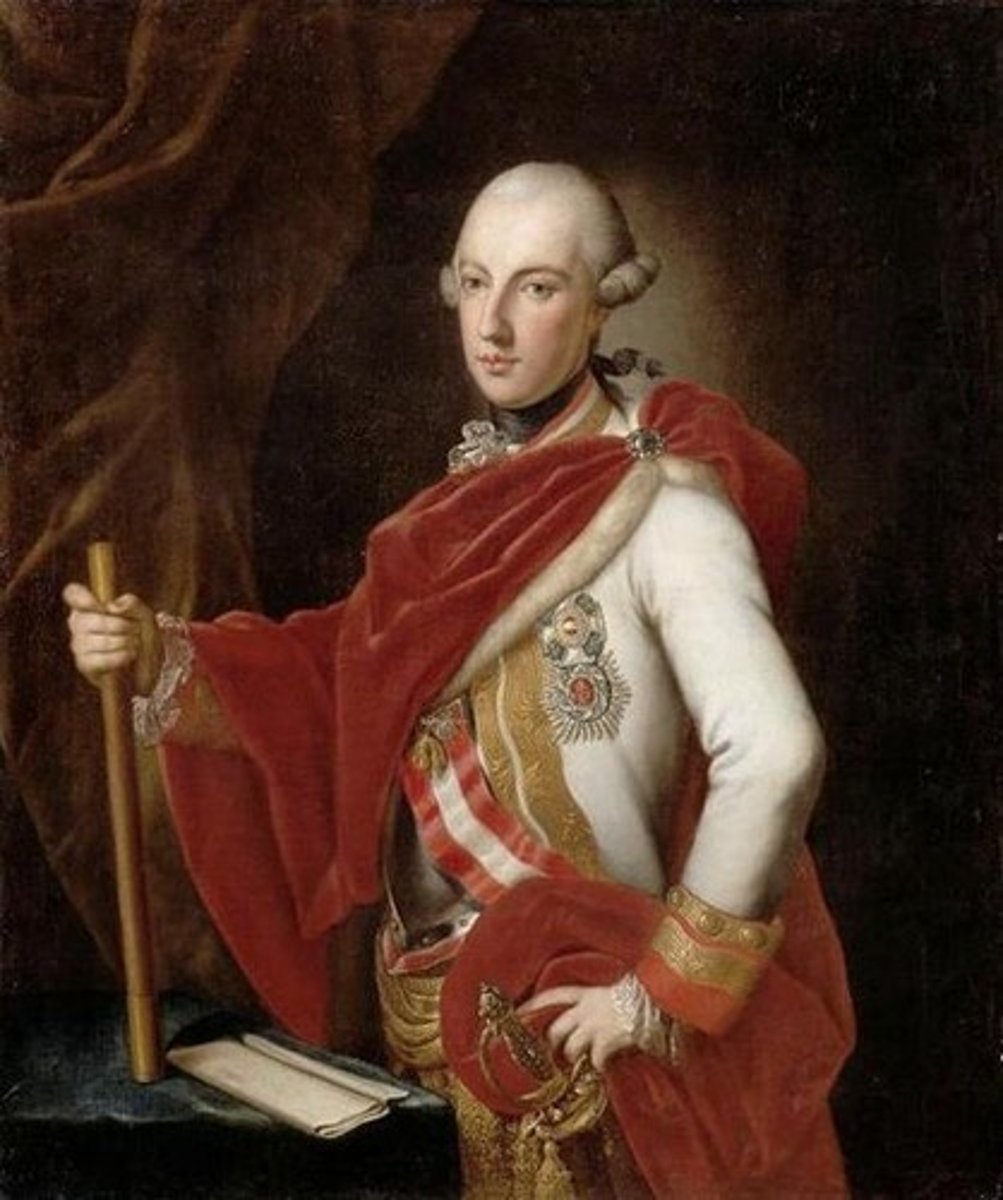
Joseph II
The Emperor of the Habsburg Empire. He was perhaps the most true to the idea of an Enlightened Despot and instituted many reforms in the Empire, such as abolishing serfdom and pushed for religious freedoms. Sadly many of his reforms were undone after his death.

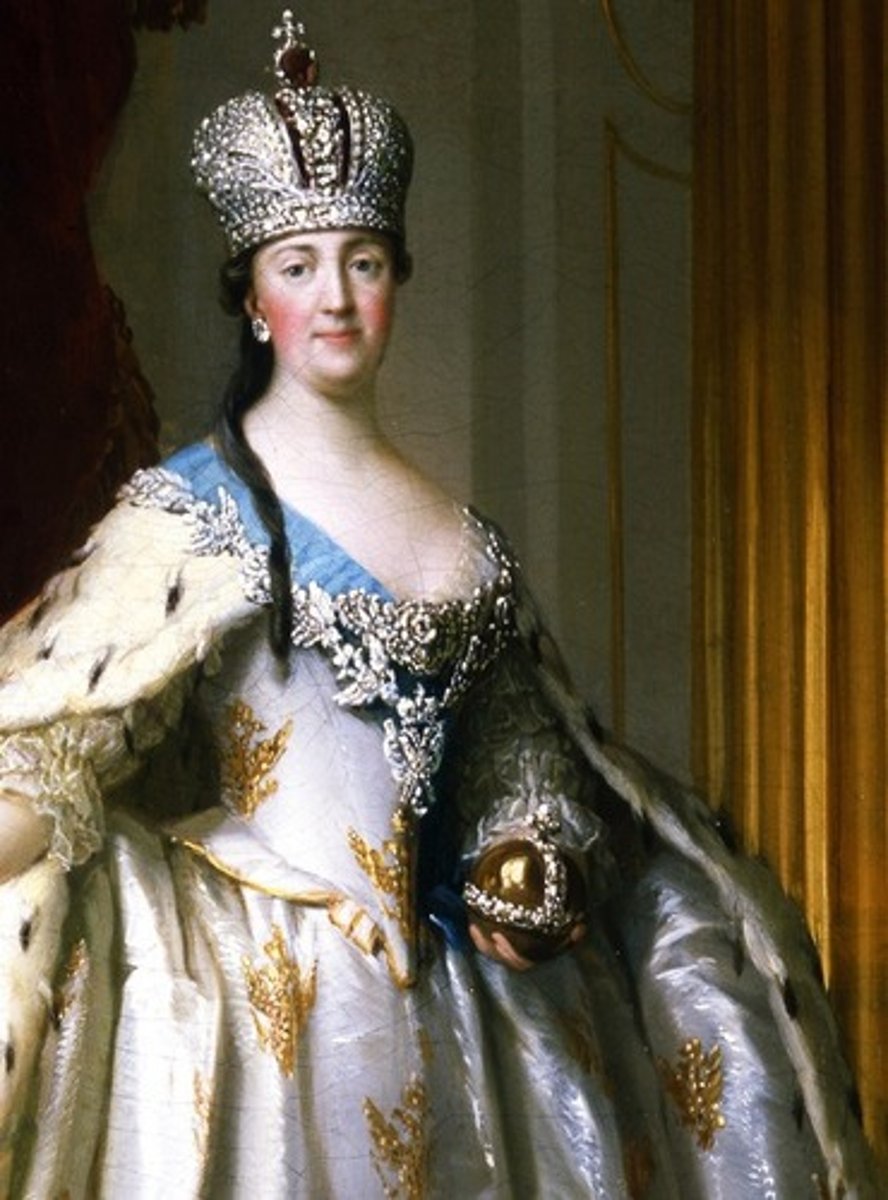
Catherine the Great
The Empress of the Russian Empire. She undertook some reforms for her people but was realistic enough to keep them moderate enough to keep the political forces happy that could remove or even kill her, the earlier fate of her husband, Peter III.

Pugachev's Rebellion
An uprising led by a illiterate Cossack that pushed for more rights for the poor in Russia. It was brutally crushed and was known for its great violence. Catherine the Great would respond with even more repression after the failed uprising.

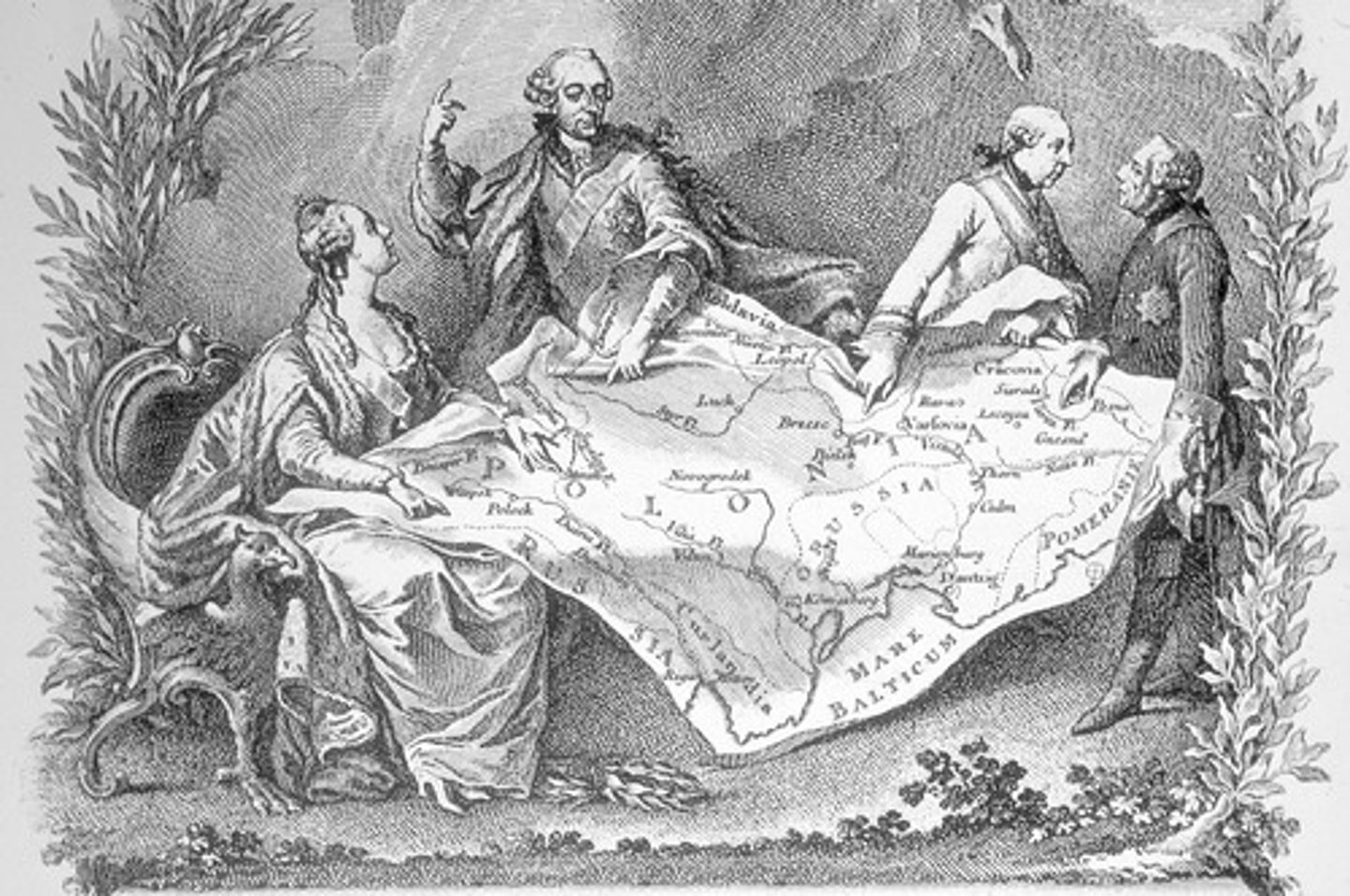
Partition and destruction of Poland 1795
This state paid the price for decades of weak, corrupt leadership and government. They were divided up by their powerful neighbors, Austria, Prussia and Russia.
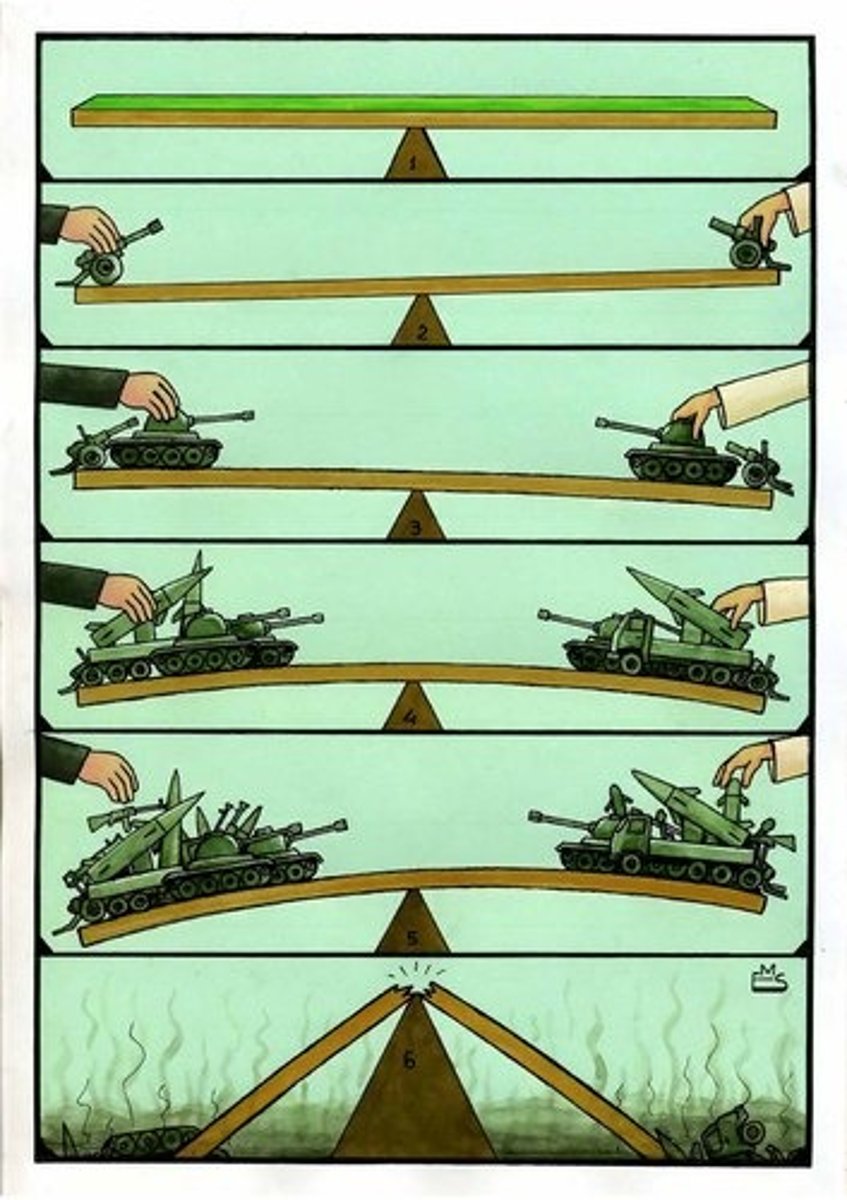
Balance of Power
This concept became very important in European affairs. The idea was to not let any one power become too powerful. Alliances and sides in wars would change over the years to allow for shifting in levels of power.
Reason of State
The concept of leadership that emerged in the eighteenth century that had leaders thinking about the long term needs and goals of their nations beyond their own lifetimes.

Primogeniture
The practice of the oldest son receiving all the attention and largest share of the parents estate. This began to fall out of favor in this time period as the needs of all the children in the family became more recognized.

Infanticide
The practice of killing ones own children to save them from starving to death. This unfortunate practice took place in the lowest of classes and economic conditions.

Agricultural Revolution
The term used to describe the advances in farming technology and techniques during the eighteenth century.
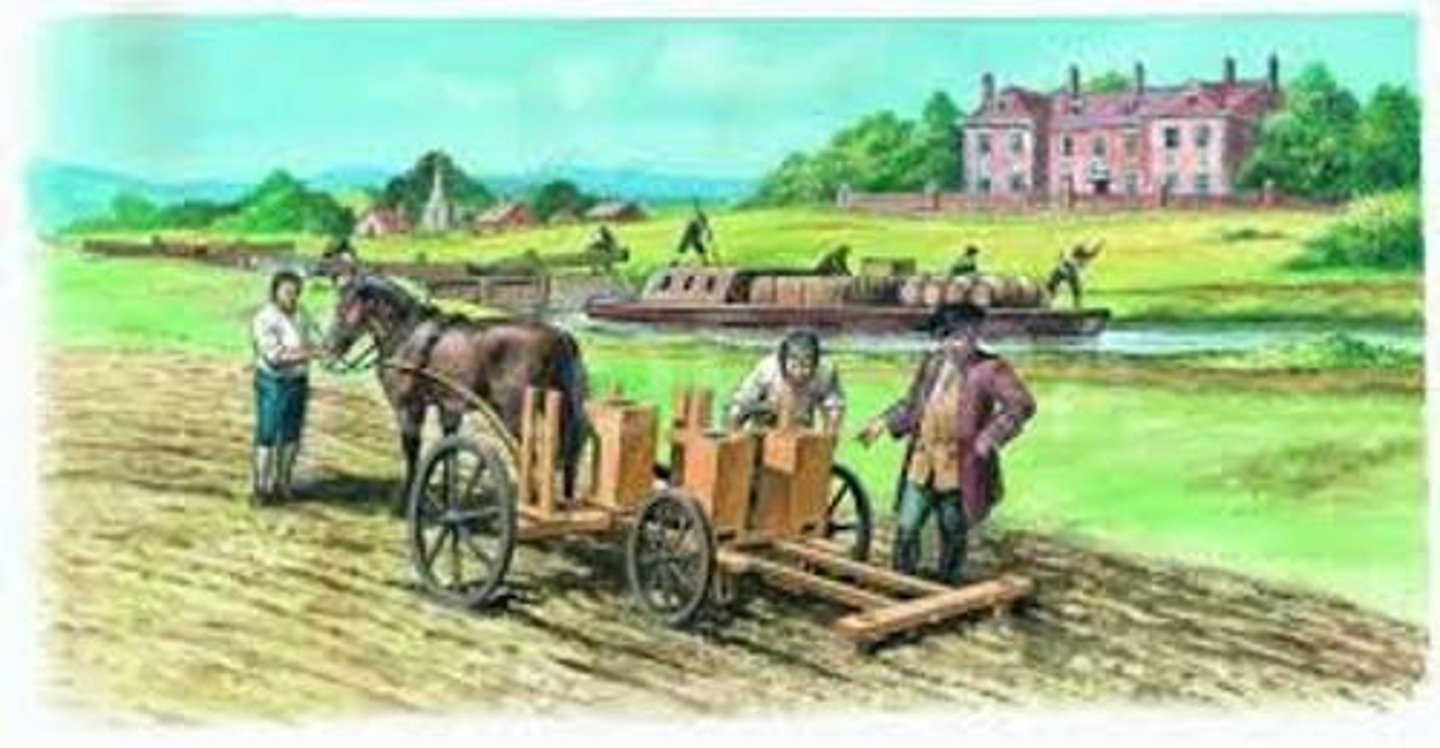

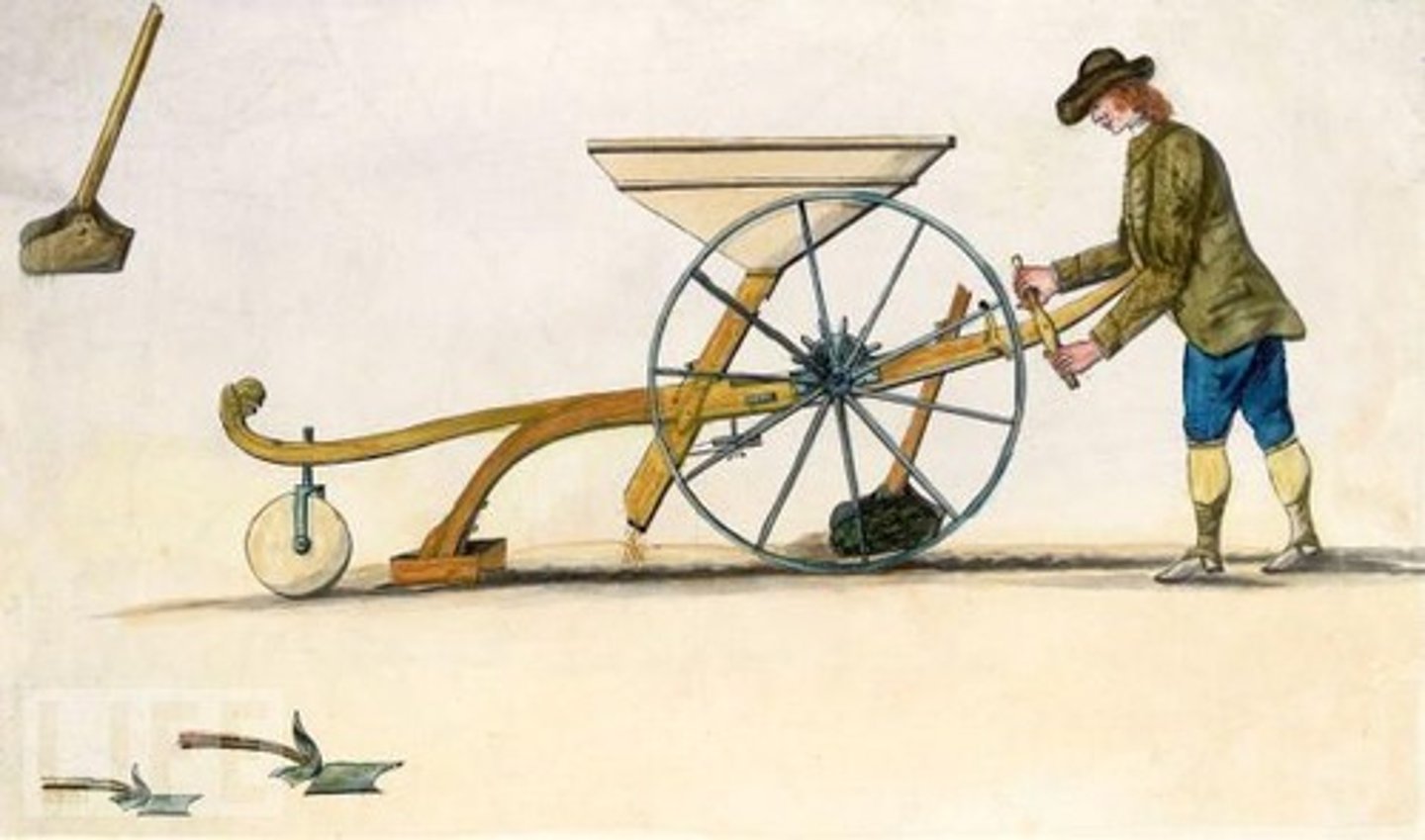
The Seed Drill
An invention by Jethro Tull that let farmers plant seeds in rows and also prevented birds from easily swooping down and eating the seeds before they could grow and produce food.
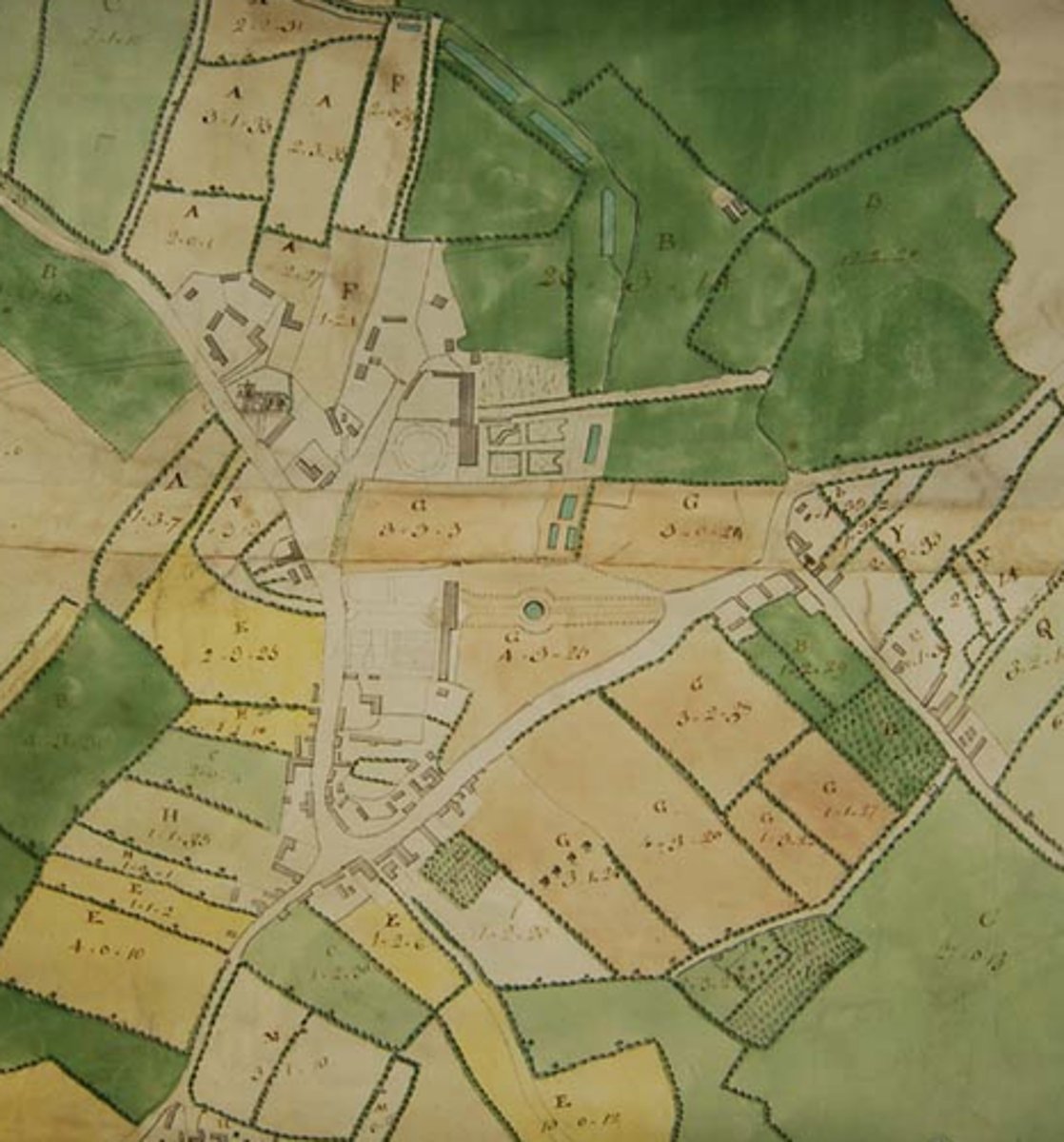
Enclosure Acts
An act of the English Parliament that let wealthy land owner enclose their lands, destroying the livelihood of many small farmers forcing them to become day laborers for the wealthy.
Cottage Industry
The term used where people would produce goods in their own homes and then sell them in markets. This predates the development of factories.
