Neuro Exam 1
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Which hemisphere is responsible for language?
Left
When Joe saw an image in his right visual field, which hemisphere processed this information?
left
These neurons are located only within the central nervous system and connect neurons together like links in a chain.
Interneurons
Which of the following organelles generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell?
Mitochondria
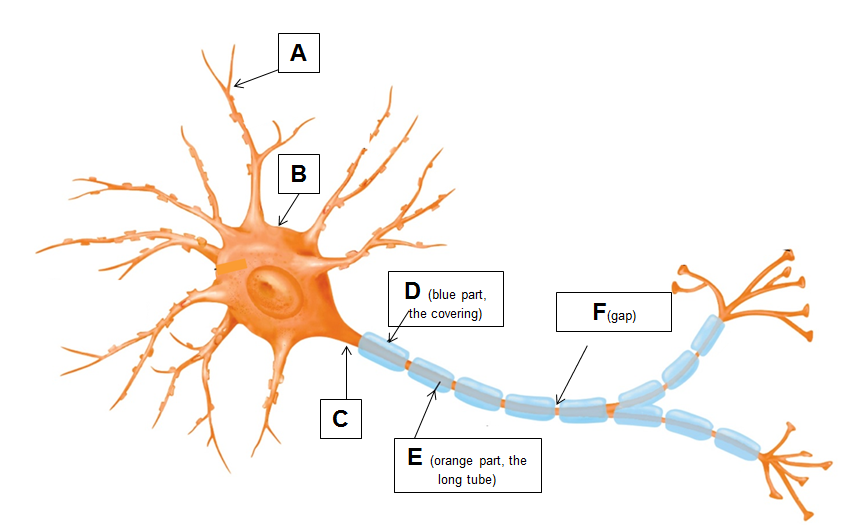
Identify the following parts:
a. dendrite
b. soma
c. axon hillock
d. myelin sheath
e. axon
f. node of ranvier
are supporting cells that can provide myelination to multiple axons at once.
Oligodendrocytes
_____ are multi-function glial cells that clean up debris and structurally support neurons in the brain.
astrocytes
Imagine that your corpus callosum has been sectioned to minimize your epileptic seizures. Suppose that your left nostril is plugged with cotton and that a fresh rose has been placed near your right nostril. Under these conditions, you would be most likely to:
use your left hand to select a hidden plastic flower

Imagine that your corpus callosum has been sectioned to minimize your epileptic seizures. You are asked to look directly at the dot, as the following image is flashed for a moment. Under these conditions, you would be mostly likely to:
verbally report seeing a dog
imagine that your corpus callosum has been sectioned to minimize your epileptic seizures. You are asked to look directly at the dot, as the following image is flashed for a moment: Under these conditions, you would be mostly likely to (there are 2 correct answers - marik both):
use your right hand to draw a dog
use your left hand to draw a fish
the three types of neurons according to functioning are:
afferent, motor, interneuron
which is NOT a characteristic of axons?
clustered around the cell body like tree branches
unilateral neglect from damage to the right parietal lobe involves:
the inability to notice objects placed to the left side of a person
Which part of the nervous system plays a dominant role in preparing the body for times of emergency or stress?
sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
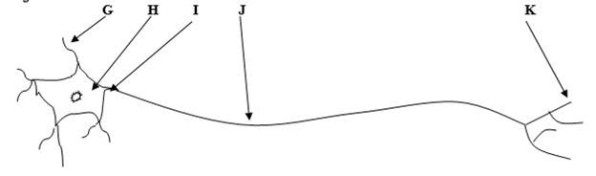
use the space below to label each part of this cell indicated by the letters
g: dendrite
h: soma
i: axon hillock
j: axon
k: terminal buttons
this part of the neuron is responsible for releasing neurotransmitters.
terminal buttons
the central nervous system is comprised of the:
brain and spinal cord
which system calms you down?
parasympathetic
which nerve controls the heart and digestive functions?
vagus
which nerve controls face and jaw muscles?
trigeminal
which cranial nerve is responsible for vision?
optic
the trigeminal nerve is primarily responsible for:
facial sensation and chewing
which cranial nerve controls the muscles of facial expression?
VII
the vestibulocochlear nerve is associated with which senses?
hearing and balance
the vagus nerve is known for its role in:
heart rate and digestion
which of the cranial nerves are both sensory and motor?
trigeminal, facial, vagus, and glossopharyngeal
list the twelve cranial nerves
olfactory
optic
oculomotor
trochlear
trigeminal
abducens
facial
auditory
glossopharyngeal
vagus
accessory
hypoglossal
olfactory:
smell
optic:
vision
oculomotor:
eye movement
trochlear:
eye movement
trigeminal:
jaw, chewing
abducens:
eye movement
facial:
facial expression
auditory:
hearing
glossopharyngeal:
taste, swallowing
vagus:
heart, digestion
accessory:
neck and shoulder
hypoglossal:
tongue
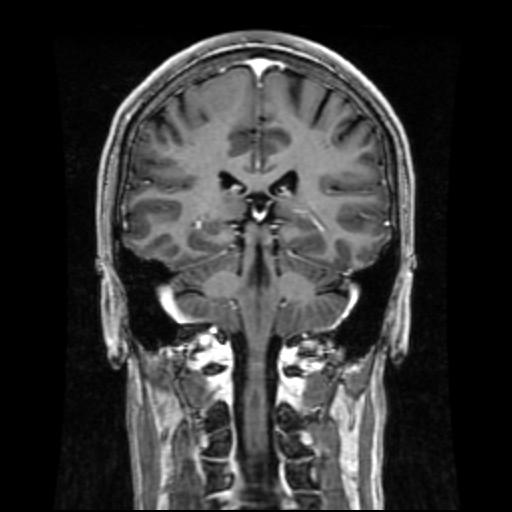
what view is this?
coronal
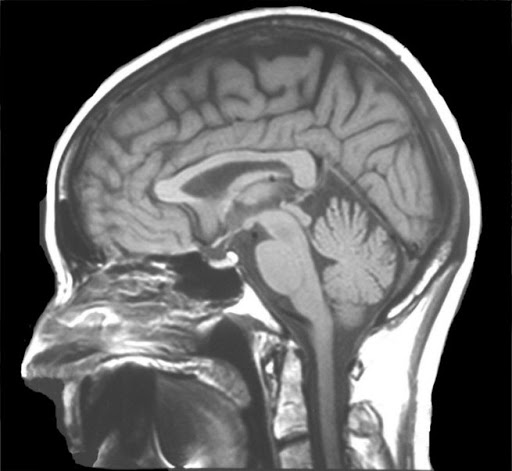
what view is this?
sagittal
your nose is ____ rostral to the back of your head.
rostral
the ventricles are filled with:
cerebrospinal fluid
the toughest layer of the meninges is:
dura mater
which substructure of the hindbrain is associated with sleep and arousal?
reticular formation
where is the primary motor cortex located?
frontal lobe
list the three major ways to section the human brain ( planes, not hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain)
coronal, horizontal, sagittal
the nose is ___, whereas the back of the head is ___.
rostral, caudal
the term “neuraxis” refers to:
an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain
What term means “above” when referring to the human brain?
superior
assume that electrical stimulation of the right motor cortex elicits limb movements on the left side of the body. In this instance, we would descrive this as a(n) ___ organization of motor cortex and the muscles of the body.
contralateral
the order of the meningeal layers from the surface of the brain outward (so inside to outside layers) are:
pia, arachnoid, dura
what are the meningeal layers?
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
the ___ is the soft and spongy layer of the brain meninges.
arachnoid membrane
the four hollow and interconnected spaces within the brain form the:
ventricles
a ___ is a large groove found in the surface of the human cortex.
fissure
what would be expected following damage to the cortex that lies just in front of the central sulcus?
difficulty in controlling the muscles of the body
which plane is shown here?
coronal
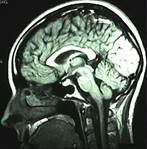
which plane is shown here?
sagittal
which substructure of the forebrain acts like a sensory relay?
thalamus
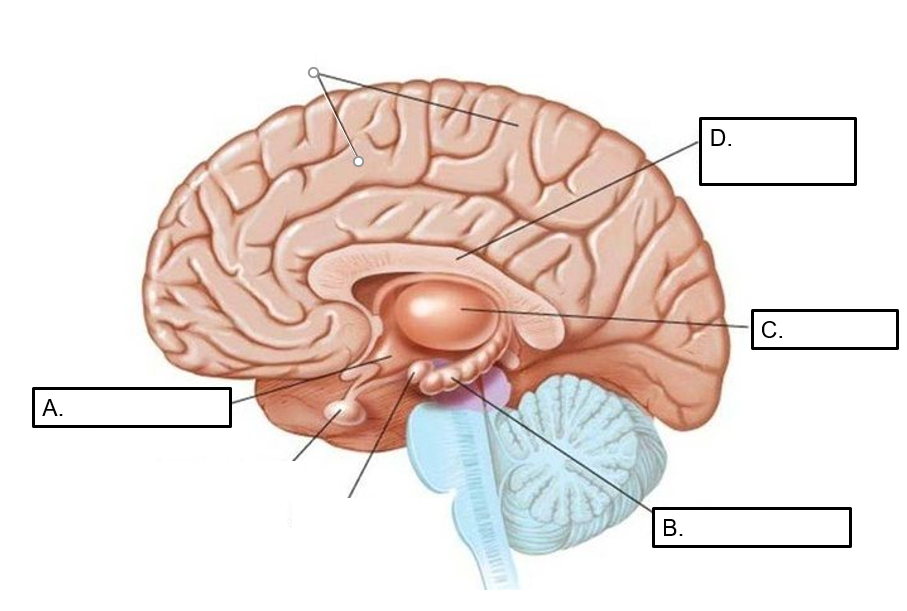
identify the following:
a: hypothalamus
b: hippocampus
c: thalamus
d: corpus calossum
at rest, where is the concentration of sodium and chloride ions highest?
outside the cell
the Na+/K+ pump removes ___ Na+ ions and adds ___ K+ ions.
3, 2
which passive forces push sodium ions into a restin gneuron?
electrostatic pressure and diffusion
cations have which kind of charge?
+
depolarization is a change toward:
positive
what is the resting potential in mV?
-70
what is the threshold potential in mV?
-55
which receptor requires energy and involves a G protein and second messenger?
metabotropic
sometimes after releasing neurotransmitters, vesicles simply break away and get filled with more neurotransmitters. what is this called?
kiss and run
where are calcium ions concentrated at rest?
outside of the cell
a cation would be attracted to:
an anion
which of the following is true of ion distribution across the axon membrane?
sodium ions are more concentrated outside the axon membrane
as a consequence of the activity of the sodium-potassium pumps,
intracellular sodium concentrations are kept low.
which of the following is true regarding the action potential?
it is an all-or-none electrical event
what events repolarizes the membrane potential from the peak of the action potential?
potassium ions move out of the cell
the nervous system codes for variation in the intensity fo incoming sensory stimuli by variations in the ___ of a neuron
firing rate
influx (entry) of ___ ions result in depolarization
Na+
central nervous system:
astrocytes, oligodendrocyte, microglia, ependymal cell
peripheral nervous system:
satellite cells, schwann cells
astrocytes and satellite cells:
blood brain barrier, debris, nutrition
oligodendrocyte and schwann cells:
myelination
microglia:
immune
ependymal cell:
CSF
The electrical charge of the membrane potential is the result of a balance between two passive forces. The first is ___ which is the process by which molecules evenly distribute in a medium (from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration). The second is ___ which is the process exerted by the attraction of cations and anions. There is a third, active force that helps maintain the concentration of sodium ions outside of the cell. It is called the ___ pump.
diffusion, electrostatic force, sodium-potassium
what can bridge the gap between adjacent cells?
neurotransmitter
when the action potential arrives as the synapse, it opens voltage gated potassium channels. This activates the vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane.
calcium
what is another name for a depolarizing signal?
EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential)
which of the following does NOT happen to serotonin after binding to the receptor?
enzymatic degredaded
ethanol has a therapeutic index around 10. recall benzodiazepines have a therapeutic index of over 100. which drug has a larger safety margin? that is, which drug is more difficult to over dose?
valium
relaxation is an effect of heroin. what is a withdrawal symptom you would expect?
agitation
drugs that are lipid soluble are absorbed:
faster
where are drugs usually metabolized?
liver
in order to cross the synapse between two cells, a substance called ___ is released from the first cell (pre-synapse) to activate or inhibit the second cell (post-synapse).
a neurotransmitter
which of the folloiwng is true of receptors?
neurotransmitters act on binding sites on receptors to exert their effects
after a vesicle fuses with the presynaptic membrane and releases its contents into the synaptic cleft, the membrane is
recycled to form new vesicles
with regard to release of neurotransmitter in the brain, “kiss and run” refers toth esituation in which the vesicle
releases most of its contents into the cleft, after which the vesicle breaks away from the presynaptic membrane and is refilled
influx of ___ or ___ ions result in depolarization
Na+, Ca+
drugs like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) prevent the reuptake fo serotonin. they are:
agonists
administering a molecule that is a precursor for the synthesis of a synaptic neurotransmitter would be expected to
increase the rate of synthesis and release of that neurotransmitter