Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final aerobic stage of cellular respiration (aka: electron transport chain)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
The series of proteins and organic molecules found in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
The electron transport chain
The energy released in the ECT is captured as a:
Proton gradient
What are the two main electron acceptors in the ETC
NAD+ and FAD
How many protons can NAD+ and FAD each accept?
2; NADH+H and FADH2
What is the final electron accepter in the ETC
O2
Name complex I
NADH dehydrogenase
Name complex II
Scuinate dehydrogenase
Name complex III
Cytochrome bc1
Name complex IV
Cytochrome c oxidase
Where does the ETC occur in eukaryotic cells?
Innermitochondrial membrane
Where does the ETC occur in prokaryotic cells?
Plasma membrane
This complex accepts two electrons from NADH+H+ and transfer them, through Fe-S clusters, to a lipophylic molecule, ubiquinone (Q), which gets converted to ubiquinol (QH2)
Complex I or NADH dehydrogenase
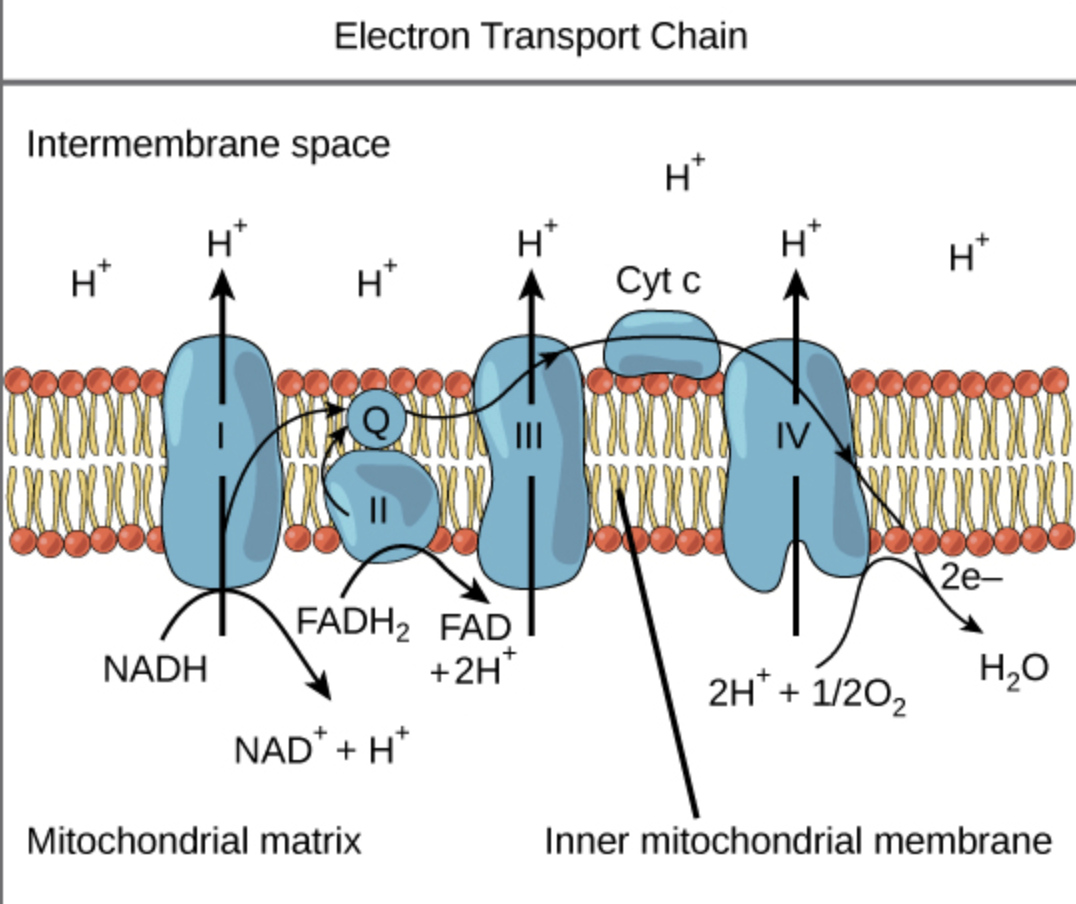
This oxidizes succinate to fumarate and transfers both released electrons to FAD, yielding FADH2
Complex II or succinate dehydrogenase
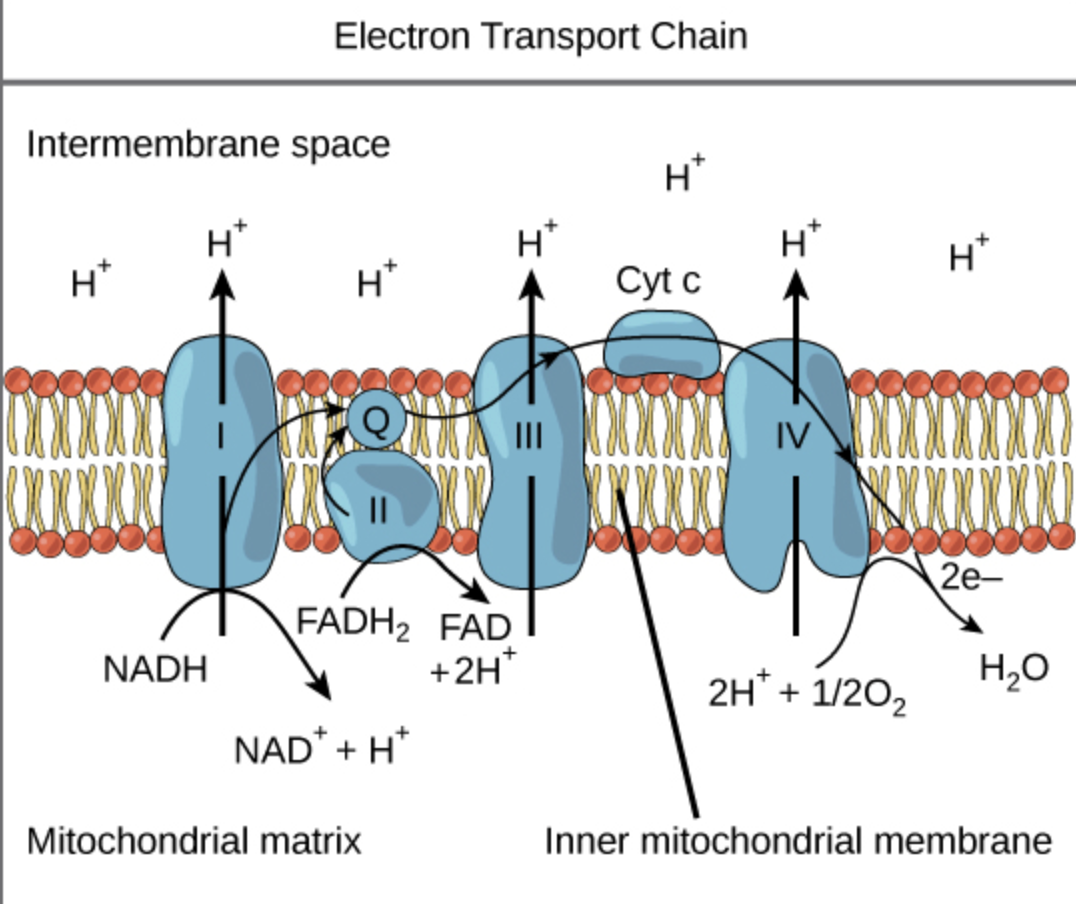
This accepts electrons from ubiquinol and transfers them to cythocrome c
Complex III or cytochrome bc1
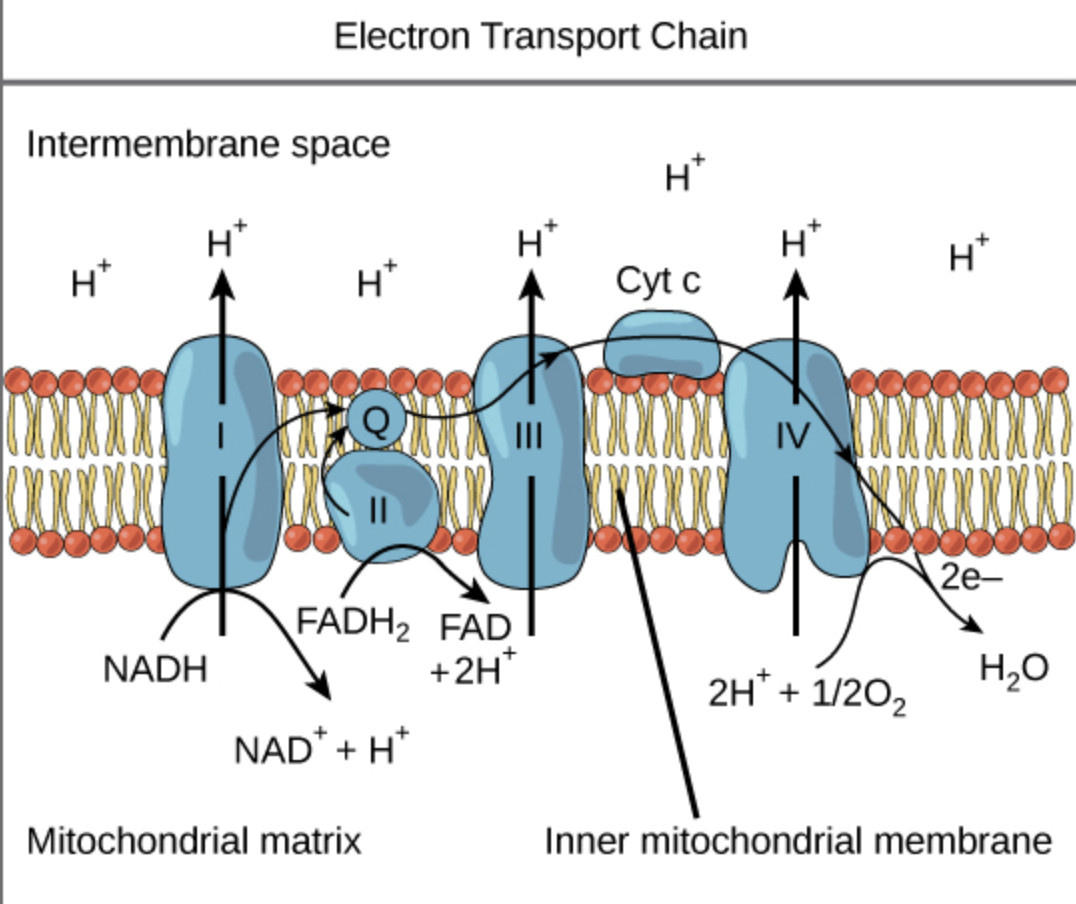
This receives four electrons from cythocrome c and transfers them to O2
Complex IV or cytochrome c oxidase
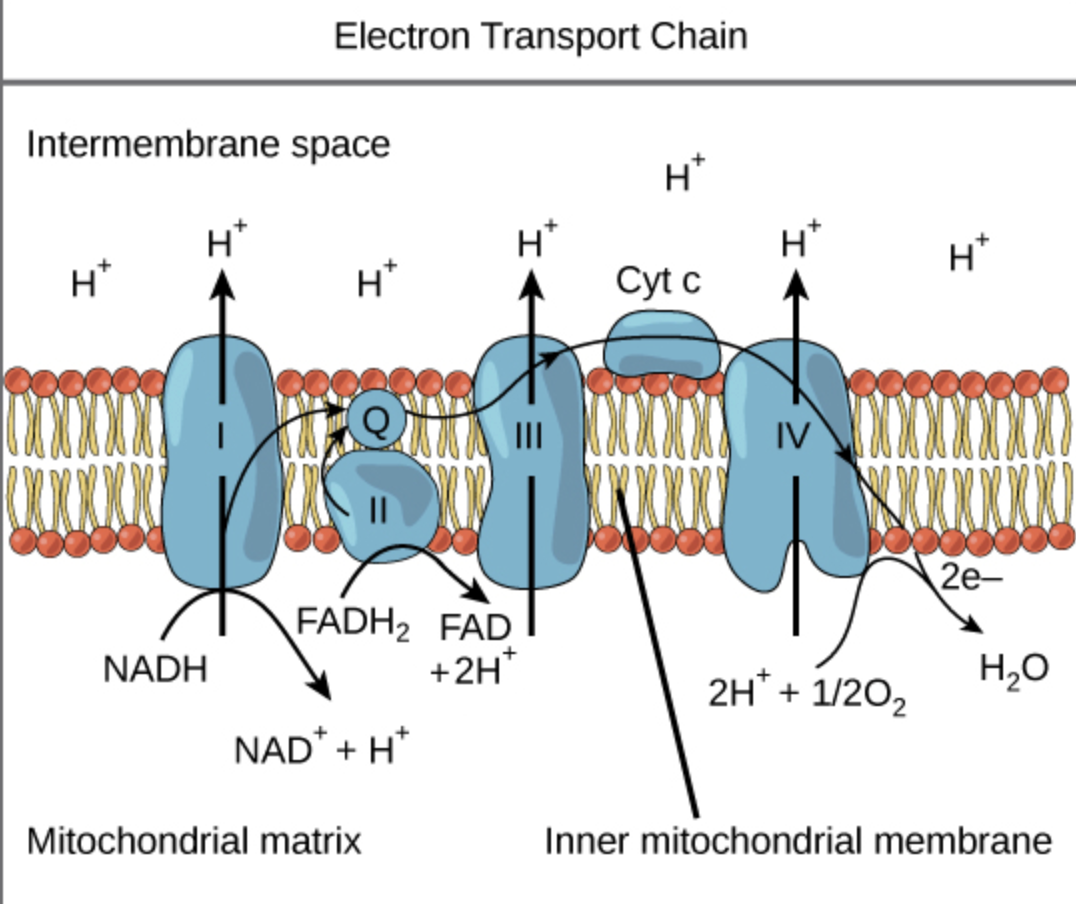
Where is H+ transferred from and to?
From the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space
Special protein that transports H+ back into the mitochondrial matrix
ATP synthase
Two main components of APT synthase
Intermembrane proton channel (F0)
Catalytic protein complex (F1) facing the mitochondrial matrix