7. Ear diseases (Otitis externa, media, interna) & skin adnexes
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
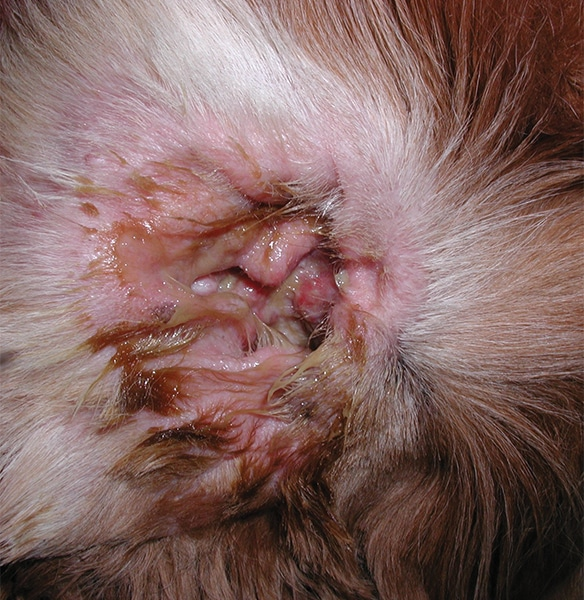
What is otitis externa?
Inflammation of the external ear canal distal to the tympanic membrane; the ear pinna may or may not be involved
What are some primary causes of otitis externa?
Allergy
Autoimmune diseases (pemphigus)
Endocrine disorders
Epithelialisation disorders
Parasites (Otodectes, Notoedres, Sarcoptes)
Viral infections (canine distemper)
Miscellaneous causes: foreign bodies like grass, overcleaning, and medication reactions
What are some clinical signs of otitis externa?
Headshaking, odour, pruritus, pain on manipulation of the ear, exudate, and erythema
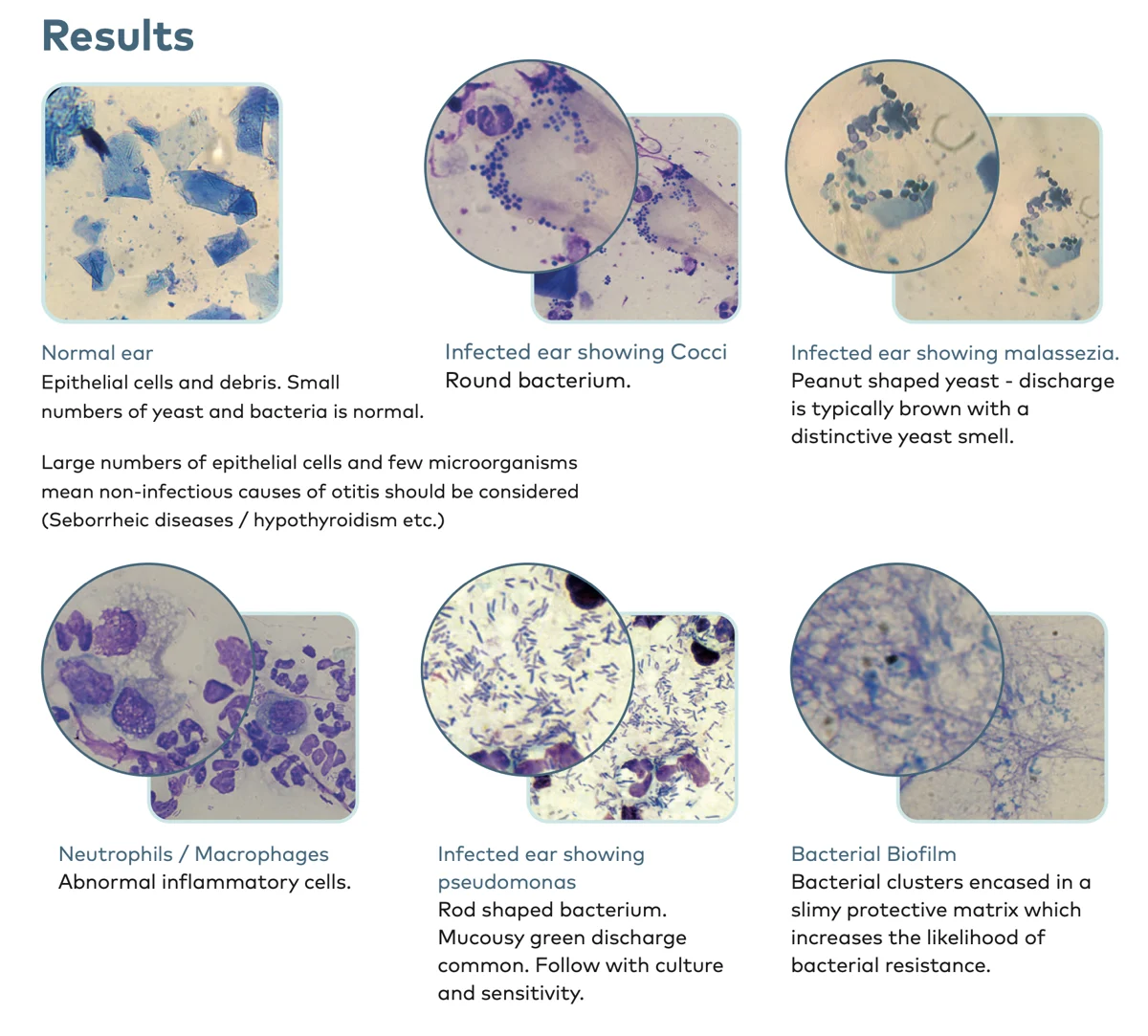
How can the type of cerumen help with diagnosis of otitis externa?
Dark, dry cerumen = parasites
Moist, yellow, odourous = bacterial
Brown, waxy, acidic = yeast
Yellow, oily = keratinisation disorder
What should you do if the eardrum is ruptured?
Avoid applying drugs directly into the ear canal (ototoxic); administer oral antibiotics or antifungals instead
What are the three steps of ear cleaning during otitis externa treatment?
Irrigation with a cleansing liquid (warm saline or emulsion),
Massaging the ear canal
Removing excess liquid and debris with cotton
What are some topical antibacterial agents used for otitis externa?
Gentamicin, neomycin, enrofloxacin, and tobramycin
What are some surgical treatments for otitis externa?
Lateral wall resection (Zepp's procedure)
Partial ear canal ablation
Total ear canal ablation (TECA)
When must the tympanic bulla be removed?
In TECA (total ear canal ablation) for severe otitis media
What is otitis media?
Inflammation of the tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, stapes, tympanic bulla, and tympanic cavity
What are some clinical signs of otitis media?
Head shaking, rubbing or scratching the affected ear, head tilting or rotation, facial nerve paralysis (ear droop, lip droop, ptosis), and Horner's syndrome (miosis, ptosis, enophthalmos, protrusion of the nictitating membrane)
What is otitis interna?
Inflammation of the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibules
What is the treatment for otitis interna?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics (amoxicillin with clavulanic acid, enrofloxacin).
Tympanic membrane ruptures typically heal within 4 weeks.
Treatment of tumours (radiation/chemotherapy). Hearing may recur even after deafness
What are parts of the skin adnexa?
Sweat gland, sebaceous gland, hair follicle, and nails
What are examples of diseases of the skin adnexa?
Sebaceous adenitis
Supracaudal gland hyperplasia
Claw infections
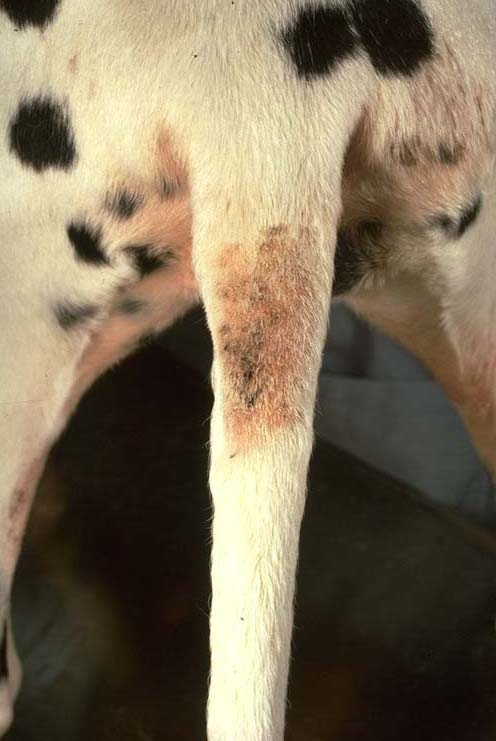
What are some causes of claw infections?
Secondary bacterial or fungal infections
Endocrine disorders
Allergies
Autoimmune disorders
Neoplasia
What is onychogryphosis?
Abnormal, excessive development and curving of your dog's claws. Seen in leishmaniasis.
Why is it important to check the tympanic membrane in otitis externa?
Check if infection has spread, if it's ruptured etc
What should be done if the tympanic membrane is ruptured in otitis externa?
a thorough ear flushing, usually under sedation
Oral antibiotics & antifungal medications are used in many cases
Systemic corticosteroids - beneficial if severe inflammation & pain
Some patients will require surgery - severe, irreversible changes of the outer ear with concurrent middle ear infection
Most ruptured eardrums heal without surgery within 3-5 weeks.
What quick test can you use to determine if otitis externa is caused by bacteria or yeast?
Smear & stain w/ diff quick