Week 2 - X-ray Diffraction
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
X-Rays
High energy EM radiation
Usually wavelengths in the Amstrong range 10^-10m
Production of X-Rays
Bombardment of target with energetic electrons which undergo collisions and scattering, resulting in the production of X-rays
Bremsstrahlung X-rays
Continuous X-ray which results from electrons changing direction when travelling in proximity to the target nucleus
Kinetic energy of incoming electron - energy of emitted X-ray photon
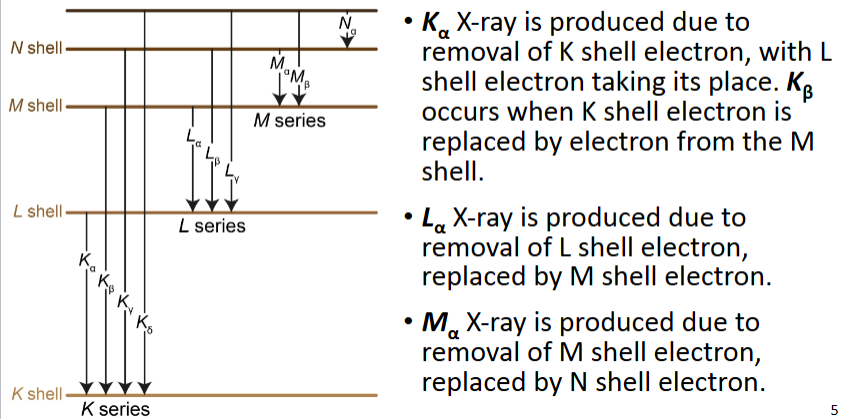
Characteristic X-ray
Result from incoming electron knocking out electron from atomic shell of target
KE incoming e- > binding energy of shell e-
Vacancy filled with e- from outer shell resulting in the emission of X-ray photon with characteristic energy equal to the difference in binding energies of shells involved
Characteristic X ray series between shells
Diffraction
Interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/opening
Constructive interference
2 sets of waves meet in phase
Path difference between 2 waves is nλ
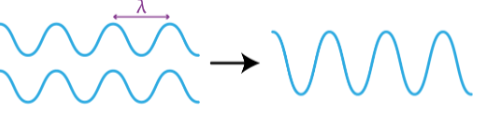
Destructive interference
2 sets of waves meet completely out of phase
Path difference is (n+1/2)λ
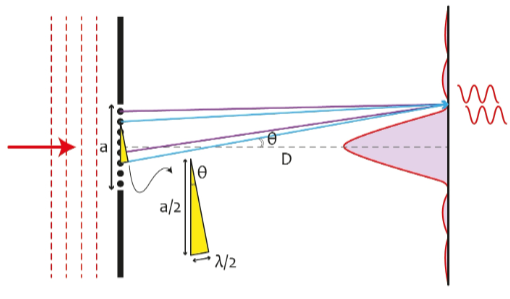
Fraunhofer single slit diffraction
Diffraction from crystal lattice planes
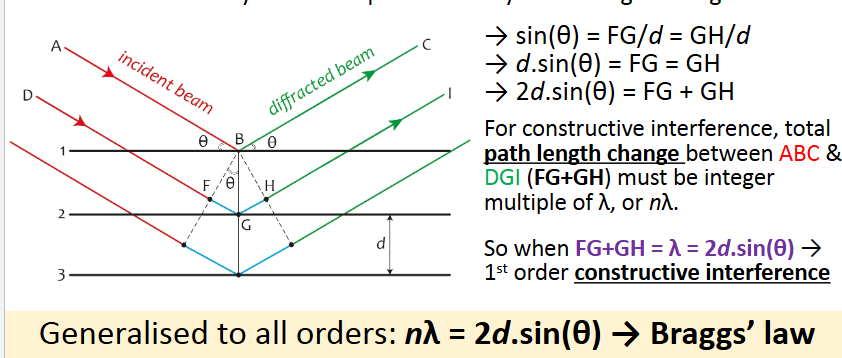
Diffraction with monochromatic beam
Angularly dispersive XRD
Diffraction with white light
Energy dispersive XRD
Single crystal XRD
Detailed information about internal lattice of crystaline substances to provide a mineral IDP
Powder XRD
Can analyse single crystal or rock powder with lots of randomly oriented fragments so sample doesn’t need to be rotated
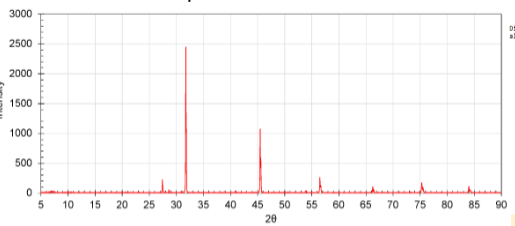
Example of powder XRD
Peaks correspond to diffraction on different lattice planes
Key equations
