PHAR303 - Respiratory Toxicants; Air Pollution
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
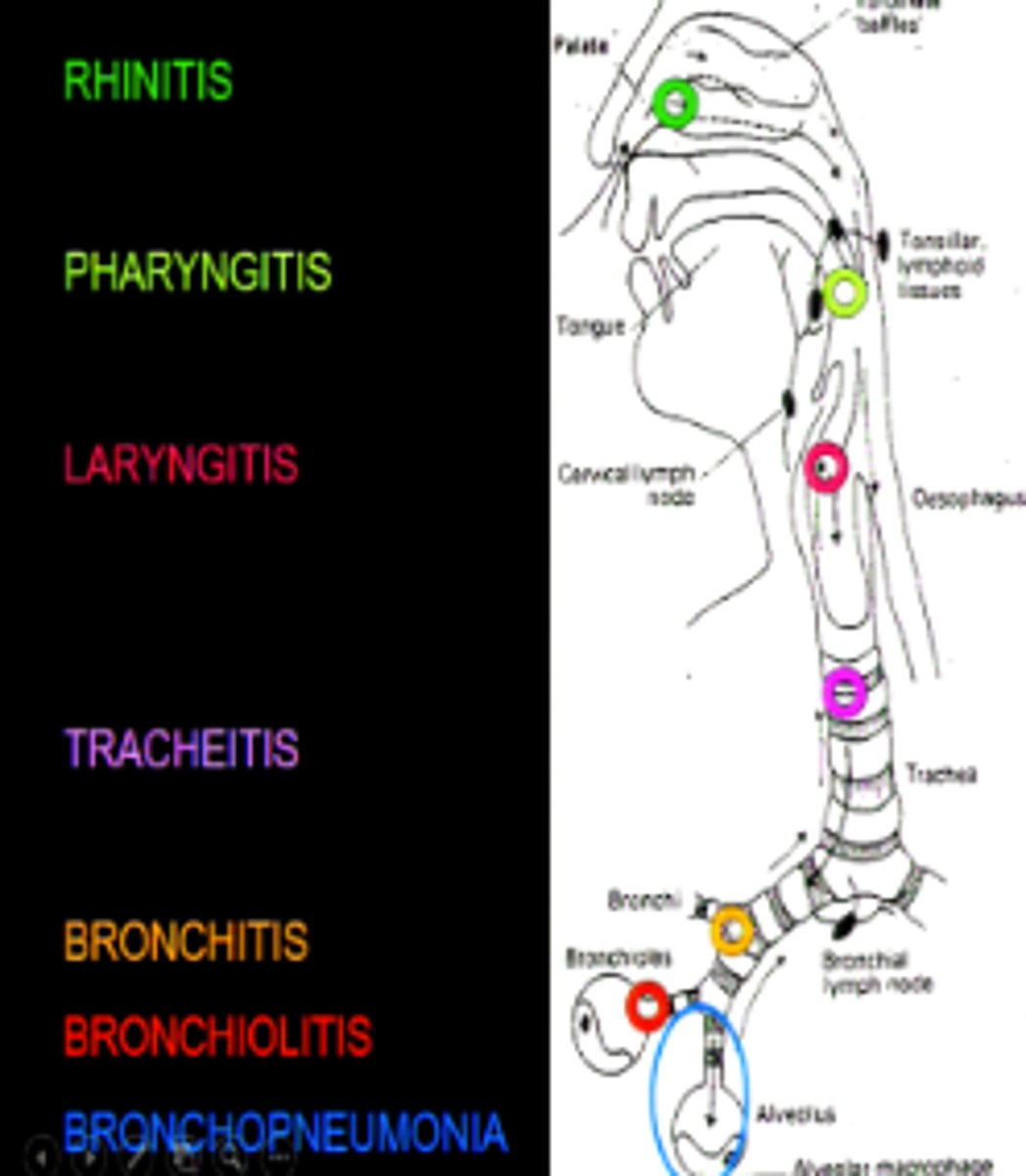
What are the three layers of the bronchus?
In the bronchus, there is an epithelial layer, muscle layer & cartilage layer.
What are the two types of cells found in the epithelium cells?
The epithelium layer has both the ciliated and the goblet cells.
What do the cilated cells do?
The ciliated cells continuously beat to move mucus upwards, thereby cleaning the airways
What do the goblet cells do?
The goblet cells release mucus. Mucus traps any contaminants, and prevents it from moving further into the respiratory system to the site of gas exchange.
What is the mucocillary escalator?
Together, mucus and cilia cells work together to generate the mucociliary escalator, a major defense mechanism in the respiratory system.
What exists in the bronchioles of the lungs?
There exist clara cells with a high concentration of CYP450 enzymes which can metabolize pollutants.
What is the role of the aveoli?
The alveolus are the site of gas exchange
What is the role of the macrophages the alveoli?
Alveolar phagocytes, primarily macrophages, patrol the lungs for microorganisms and pollutants that are inhaled and consume them. Upon consumption, the macrophages then ride the mucociliary elevator and become deposited into the GI tract (i.e. swallowed).
Air pollution harms the cardiovascular system, renal system, and the nervous system. True or false.
True.
What are the major health issues related to air pollution?
Ischaemic heart disease (30%)
Cerebrovascular disease (18%)
From pollutants getting into the bloodstream to the heart/brain.
Lung cancer (6%)
COPD (17%) – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Another major issue is infections and deaths from respiratory disease which are seen in children. (18% in children under 5 and 11% in children over 5)
If children are heavily exposed to air pollution, they are more likely to die of respiratory diseases.
Why is burning fossil fuels (e.g. coal) a problem?
Burning fossil fuels typically releases sulfuric or nitric acid which:
1. Are responsible for acid rain. This can acidify lakes and destroy the environment. The extent of damage depends on the environment
2. Contributes to temperature inversions in the winter.
What is smog?
Smog is a combination of smoke and fog, which is formed from the photochemical reaction of combustion smoke in the air.
Why is smog more common in the summer?
Due to the light-dependence of the reaction, there tends to be more smog during the summer. The prevalence of cars during the season also contributes to increased levels of smog.
What is the biggest source of smog?
The biggest source of smog is automobile exhaust. (e.g. disel exhaust)
Why is disel exhaust a big contributor to smog?
Produces ultrafine particles (<0.1 μm) as well as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxides, sulfur oxides and formaldehydes.
The ultrafine particles are the most dangerous type of exhaust that can be inhaled since they will go straight into the circulation.
Diesel exhaust inhalation causes inflammation and airway cytotoxicity.
Effects of diesel exhaust are potentiated by ozone, because pollutants interact.
What are the components of smog?
1. Ozone
2. Particulate matter
3. Nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides
4. Carbon monoxide
What is ground level ozone?
Ground-level ozone is generated through the reaction of a radical oxygen atom with the dioxygen molecule. The release of the radical oxygen atom from nitrogen dioxide in the atmosphere is powered by sunlight.
How is ground level ozone different from upper ozone?
Ground-level, or inner level, ozone layer is different from the upper ozone layer.
The upper ozone layer is located in the stratosphere, and protects the earth from the damaging effect of UV rays from the sun. (No human exposure)
Humans may be exposed to ozone through the ground-level ozone located in the troposphere. The ozone in this region is “bad” and can damage lung tissue and plants.
How does ozone's mechanism work?
The mechanism through which ozone acts is through injury to the epithelium, which then triggers cytokine release and inflammation.
What are the adverse effects of ozone exposure?
1. Lung damage, which can then lead to decreased lung function
2. Ozone exposure can also cause or exacerbate chronic respiratory conditions.
3. Ozone may also increase the risk of a respiratory infection by decreasing the function of certain lung defense mechanisms.
What kind of lung damage may ozone cause?
Impair mucus production
Impair epithelial cell barrier
Irritate throat & nose
Increased vulnerability to infections/chronic respiratory diseases due to epithelial injury
Risk of developing emphysema
Increased inflammation in various areas of the respiratory tract (Fig 3) & edema
Eye irritation
Free radical production (ROS species)
How is the severity of the effects of ozone determined? Which groups are at the greatest risk?
Severity of the effects of ozone is related to exposure and vulnerability of the affected person.
Children and patients with pre-existing diseases are at greatest risk of ozone symptoms.
What is the composition of particulate matter?
The exact composition of particulate matter varies between cities, but it will often be composed of sulphate, nitrate, organic C, elemental C, salt and soil.
How do we categorize particulate matter?
coarse (2.5-10 μm), fine (<2.5 μm) particles, and ultrafine particles (< 0.1 μm).
What determines the fate of the inhaled particulate?
Larger particles (2.5 - 10 μm) tend to get stuck on the larger airways (ie. bronchi) and can be removed by the mucociliary elevator, or macrophages riding the mucociliary elevator.
Particles <2.5 μm are considered dangerous, as they can penetrate deeper into the lungs, and may also enter the systemic circulation.
The smaller the particle, the farther out it gets and the more likely it is to stick around.
The mortality is directly proportional to the _______ of fine and ultrafine particles, because these can exert effects on the rest of the body.
concentration
What adverse effects can small particulate exposure cause?
1. Small particles exacerbate asthma, COPD, interstitial lung diseases, lung fibrosis cancer, and acute lung injury.
2. Small particles also activate T cells and cytokines in the immune system, which can further damage the tissue by triggering airway inflammation.
3. Small particles can also reach the nervous system and cause inflammation and damages.
What are the three ways in which particulate matter can enter the brain?
1. olfactory bulb
2. respiratory system
3. gut microbiota-brain axis
What damage does particulate matter do to the brain? What are the consequences?
Damage to neurons = neurodegeneration
Damage to microglia = Damage to the microglia and activation of the microglia and release of cytokines can cause a cycle where neurons are destroyed.
Damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) = Damage endothelial cells of BBB and/or the tight junctions between endothelial cells, leading to capillary damage. As a result, there can be increased permeability across the BBB.
What are the different adverse effects that ULTRAFINE particles can cause on the brain?
I .Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation
2.Changes in miRNA expression levels
3. Autophagy
4.PKA/CREBlBDNF signaling pathway
Brain Derived Neurotrophic actor
5. Disorders of the fibrinolytic and autonomic dysfunction
6."Gut-microbiota-brain" axis
What is the two main sources of air pollutants that contribute to the ground level ozone and fine particulate matter?
The two main sources of air pollutants leading to ground level ozone and fine particulate matter is home firewood burning and transportation (road, rail, air, marine)
What can nitorgen oxide and sulfur oxides do in the atmosphere?
These compounds can react with other components of the atmosphere to form nitric and sulfuric acids.
What is acid rain? What adverse effects does it have on the environment?
The mixing of these nitric and sulfuric acid with water vapour in clouds can lead to acid rain.
Acid rain can affect soil pH, which can make agriculture difficult.
Acid rain is also corrosive, which puts many outdoor historical monuments and sites in danger.
What is sulfur dioxide?
A water-soluble irritant gas that triggers airway nociceptors.
Atmospheric sulfur dioxide is produced by ______ and it is an irritant that is absorbed in the upper airways.
(the burning of) coal
What is effect of sulfur dioxide n the human body?
1. bronchoconstriction (due to cell injury)
2. mucus secretion (due to proliferation of goblet cells)
This can lead to acute or chronic bronchitis.
What is nitrogen dioxide?
This comes from gas heaters, stoves, smog and is a side stream of tobacco smoke. Farmers may also be exposed due to silage.
.
The different components of the smog come from many different places.
What is effect of nitrogen dioxide n the human body?
The airway injury is similar to that of ozone
What is effect of carbon monoxide in the human body?
This affects the circulation by forming carboxyhemoglobin.
How can risk assessment for air pollution be done?
This can be done by:
Epidemiology testing
Clinical studies
Laboratory tests in animals and plants.
What are lung function tests?
People who have been exposed to pollutants can be tested or researchers can have people briefly inhale a toxic compound to see the acute effects on the lungs.
What does the lung function test aim to find out?
Difference between intermittent exposure (when you are exposed a few times a week) and chronic exposure (like if you live near a highway).
Impacts on other species.
Different pollutant-pollutant interactions & their mechanisms of interaction (i.e. ozone potentiates diesel exhaust compounds)
If tolerance develops from long-term exposure (since the body usually reacts with changes.)
What is temperature inversions?
Normally, the pollutants will go up with the warm air (warm air rises) until it reaches colder air that is way above what we face ground-level. (Fig 5, top)
But in the winter, the cold air layer is below the warm air (inversion), in the ground level – causing pollutants in the air to get trapped in the ground level. (Fig 5, bottom)
When are temperature inversions common?
Temperature inversions are common in the winter.
Why do we have both summer and winter smog?
Overall, we have both winter smog (due to temperature inversion) and summer smog (due to increased photoactivation)
Indoor air pollutants include:
Pathogenic microorganisms (moulds, bacteria, viruses)
Allergic microorganisms (moulds, bacteria)
Respirable particles (smoke, dust, pet hairs, dust mites, etc.)
Volatile organic compounds (formaldehydes, cooking products, hair sprays, pesticides)
Radon (decay product of uranium)
What is COPD?
COPD is a consequence of air pollution, particularly that resulting from smoking.
COPD is characterized by spasm of airways, inflammation and mucus production.
What are the three components to COPD?
It has 3 components/diseases:
Bronchitis
Emphysema
Asthma
How does smoking contribute to COPD?
Smoking can damage every part of your body:
pneumonia
13 different types of cancer
vascular diseases
If flavouring can be consumed, why can it not be inhaled?
The combustion of these flavorings can produce new compounds that may be dangerous to us.
Furthermore, humans were evolved to digest these flavourings, not inhale them. The lungs lack many of the enzymes of the GI tract & liver, so would not be able to as effectively metabolize and detoxify the flavourings.
What was the mouse vaping study?
A mouse study exposed the animals to different “flavours” of e-cigarette smoke for 3 hours/day for 2 weeks. This exposure mimics the level that humans are exposed to, and the goal of the study was to see if they would be more susceptible to infection. (Figure 6)
What were the results of the mouse vaping study?
Macrophage levels increased and there were altered cytokines in lung fluid.
There is increased vulnerability to influenza and streptococcal pneumonia depending on the amount of e-cigarette they are exposed to (macrophages impaired, more virus/bacteria in all parts of the lung). This would lead to weight loss and death.
What are the adverse effects of vaping?
Increases airborne concentrations of particulate matter and nicotine in indoor environments
Induce acute endothelial cell dysfunction II formation of reactive oxygen
Species/oxidative stress/' DNA damage and mutagenesis// cancer and adverse reproductive outcomes increase in asthma exacerbations II
Young people who begin with e-cigarettes are more likely to transition to combustible cigarette use and become smokers