Blood Composition and Function in the Circulatory System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Circulatory System
Connects heart, lungs, and tissues for blood flow.
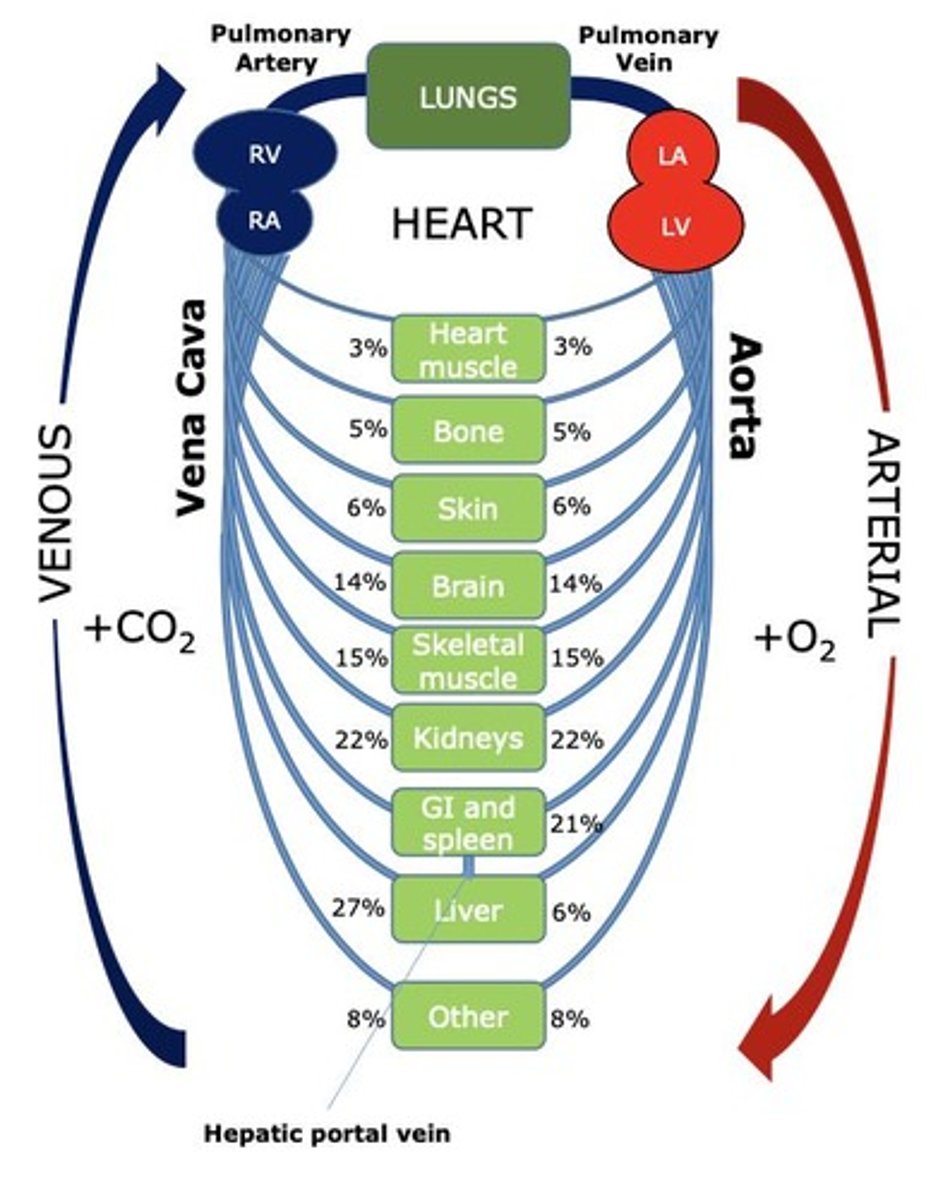
Blood Volume
Average adult blood volume is approximately 5 liters.
Blood Circulation Rate
14,000 liters circulate every 24 hours.
Arteries
Thick-walled vessels carrying blood away from heart.
Veins
Thinner-walled vessels returning blood to heart.
Blood Pressure
Force exerted by circulating blood on vessel walls.
Systolic Pressure
Maximum arterial pressure during heart contraction.
Diastolic Pressure
Minimum arterial pressure between heartbeats.
Hypotension
Abnormally low blood pressure causing weak symptoms.
Hypertension
Abnormally high blood pressure risking health issues.
Oxyhaemoglobin
Bright red form of haemoglobin carrying oxygen.
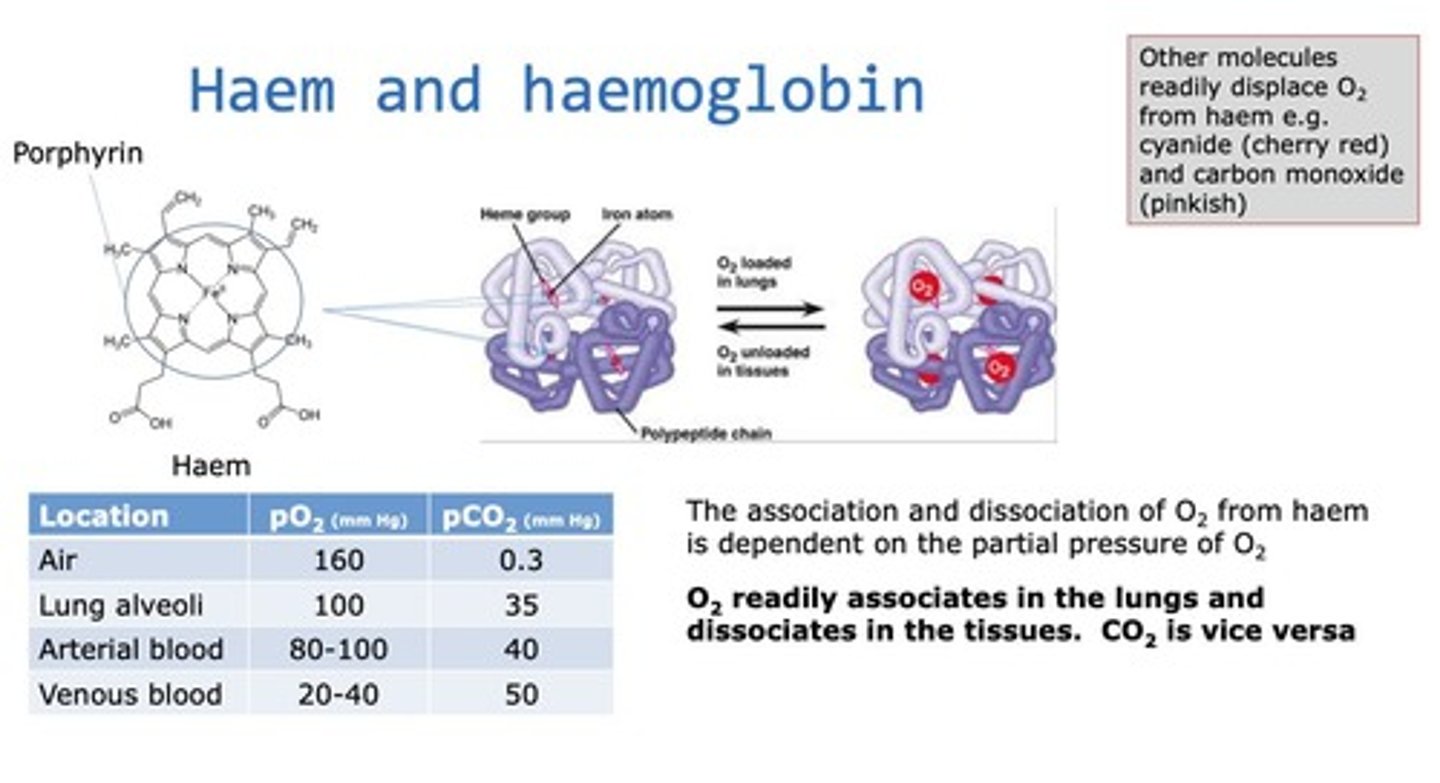
Carbaminohaemoglobin
Dark red form of haemoglobin carrying carbon dioxide.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells responsible for oxygen transport.
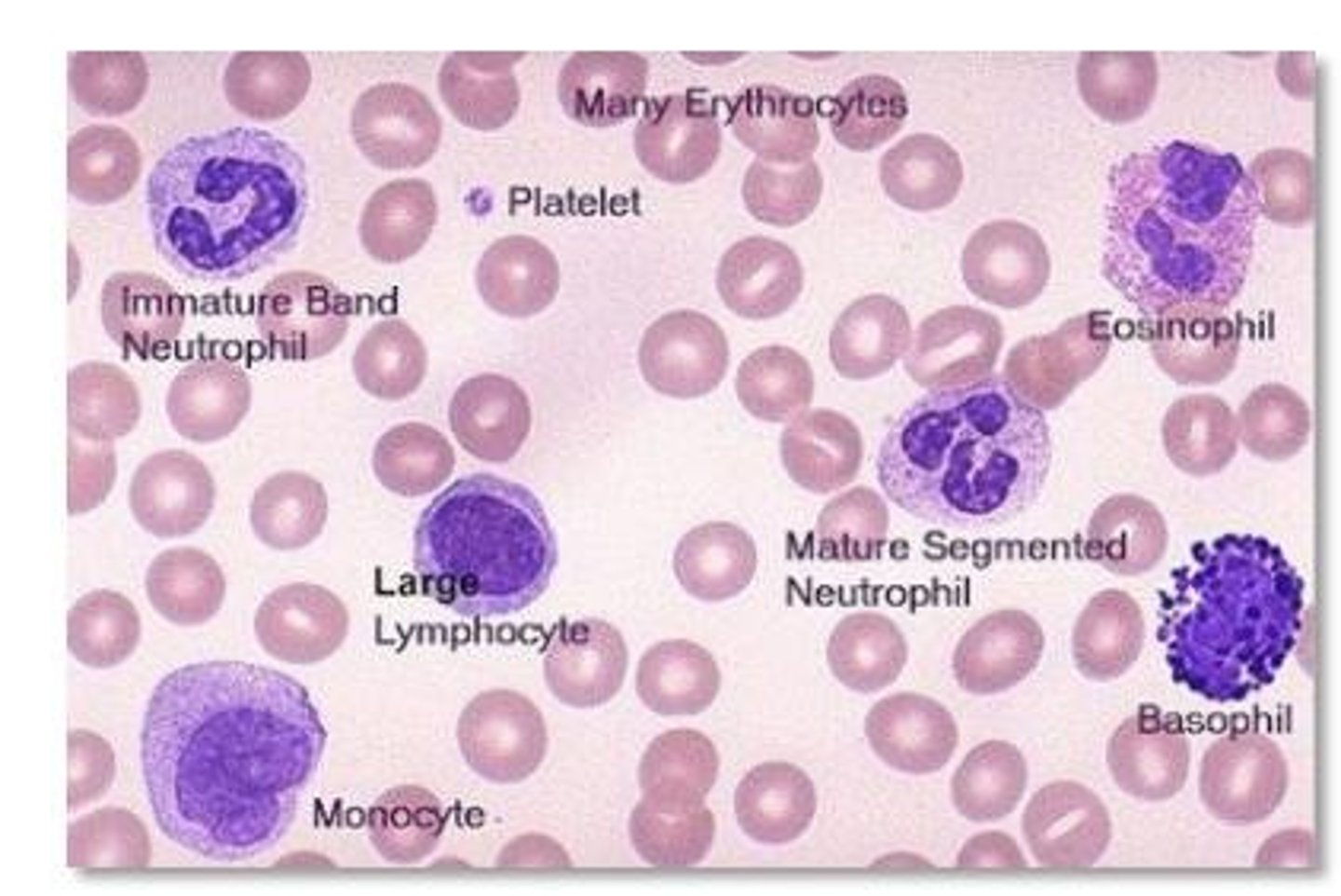
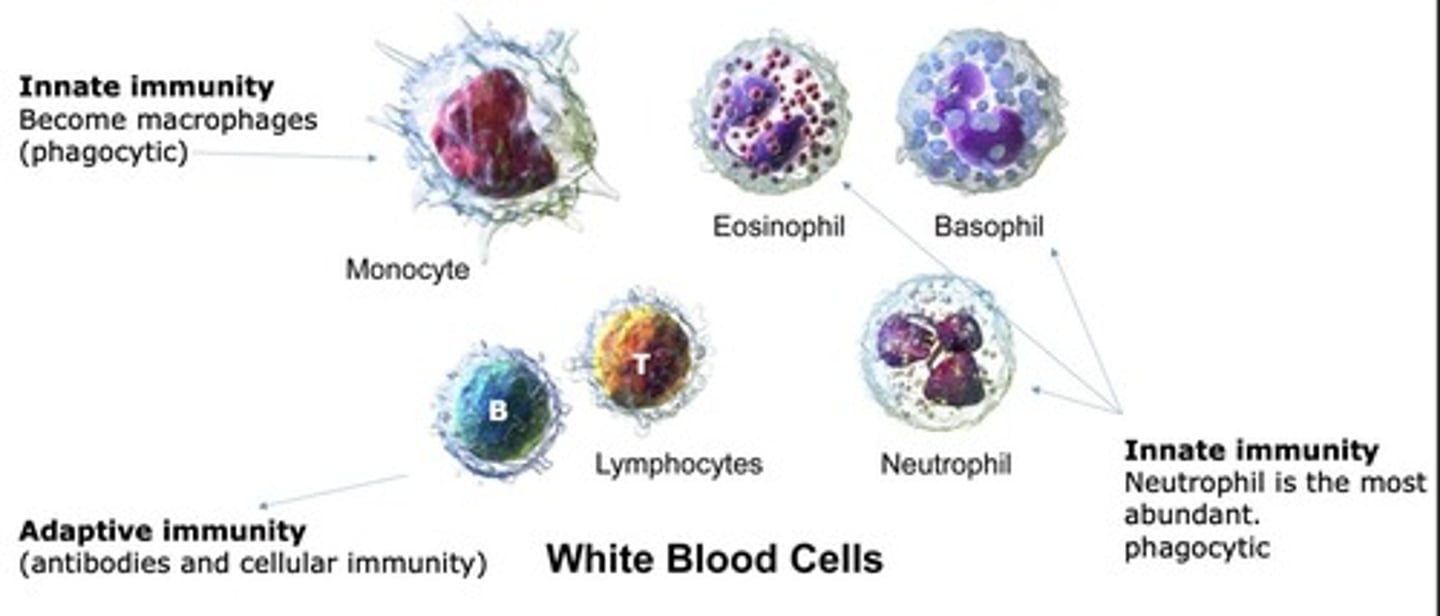
Leukocytes
White blood cells involved in immune defense.
Platelets
Cell fragments aiding in blood clotting.
Albumin
Major blood protein maintaining osmotic pressure.
Fibrinogen
Protein essential for blood coagulation process.
Immunoglobulins
Antibodies providing specific immune responses.
Hematopoiesis
Formation of blood cells from stem cells.
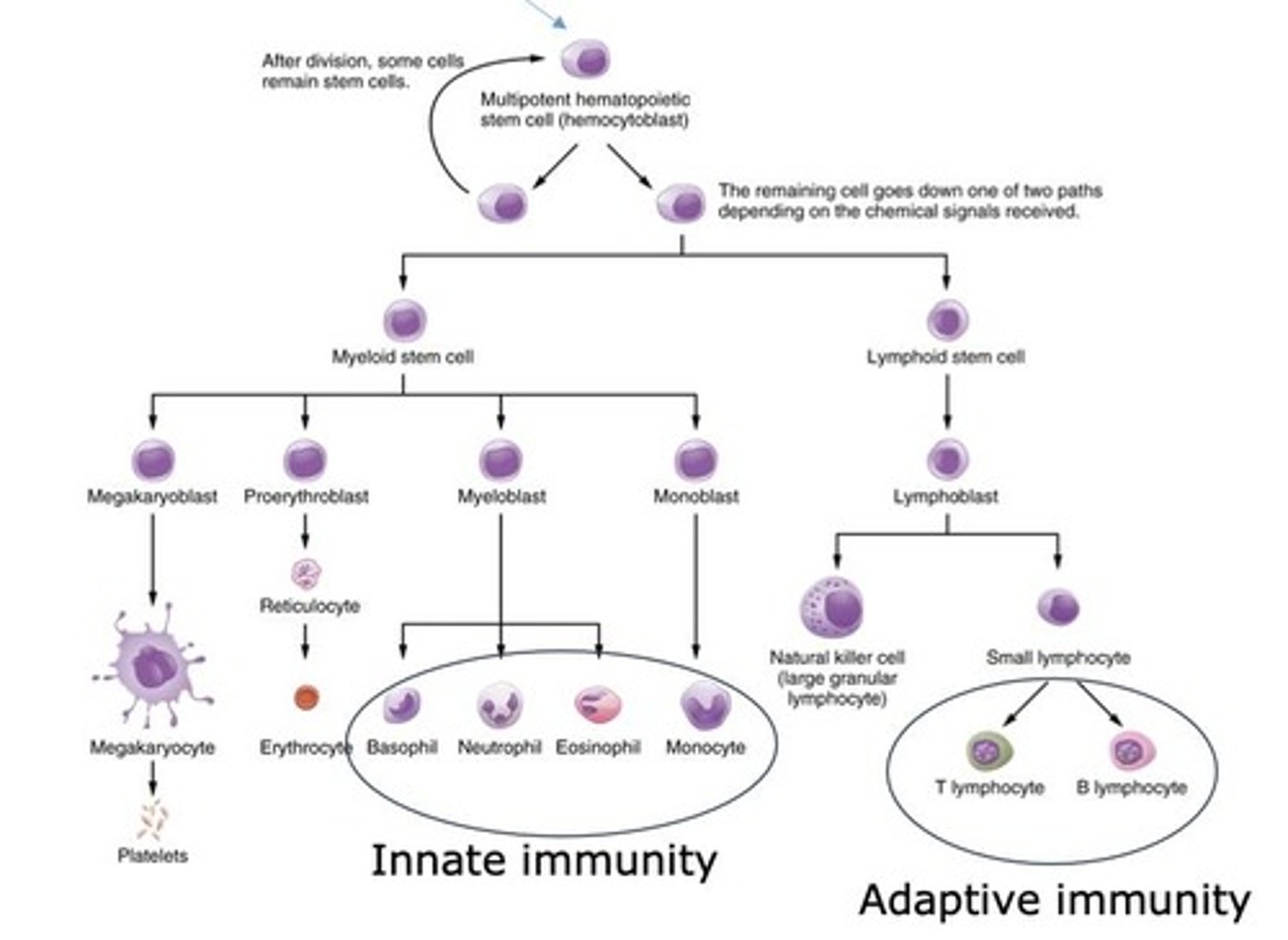
CD34+ Stem Cell
Multipotent stem cell for blood cell development.
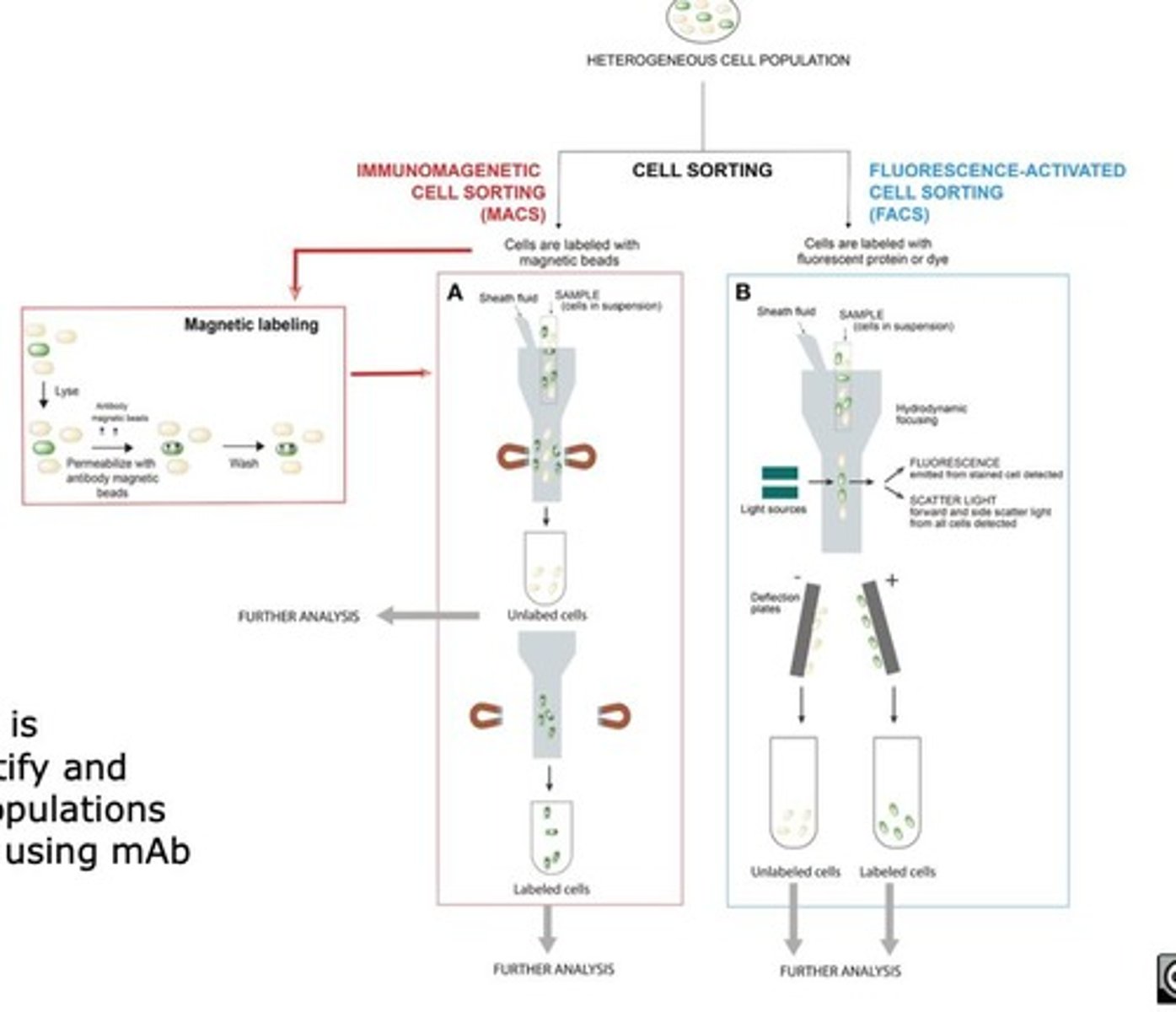
Immunophenotyping
Technique to identify specific cell populations using antibodies.
Coagulation Cascade
Proteolytic activation process leading to blood clotting.
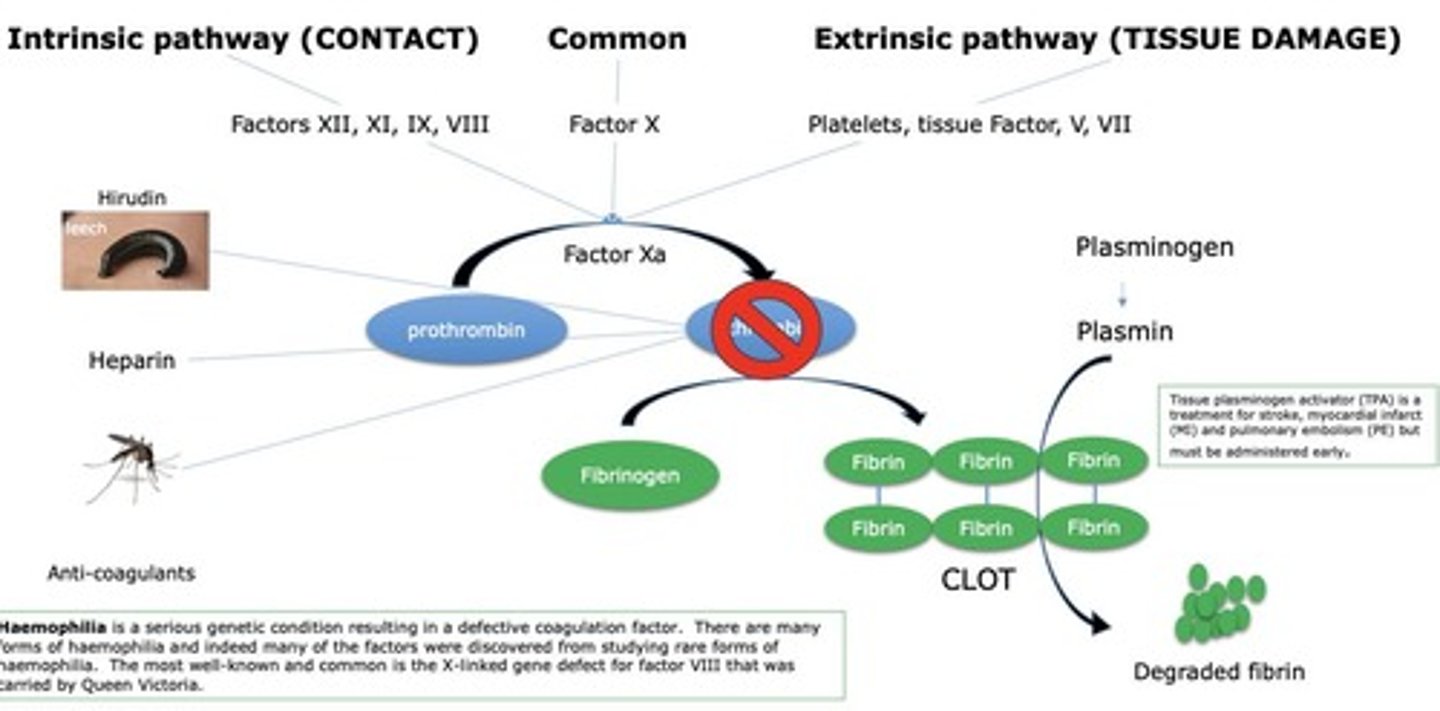
Thrombin
Key enzyme converting fibrinogen to fibrin.
Plasminogen
Inactive precursor converted to plasmin for clot dissolution.
Complement System
First line of defense against pathogens in immunity.
Opsonization
Coating of pathogens to enhance phagocytosis.
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
Lytic pore formed by complement proteins to kill bacteria.
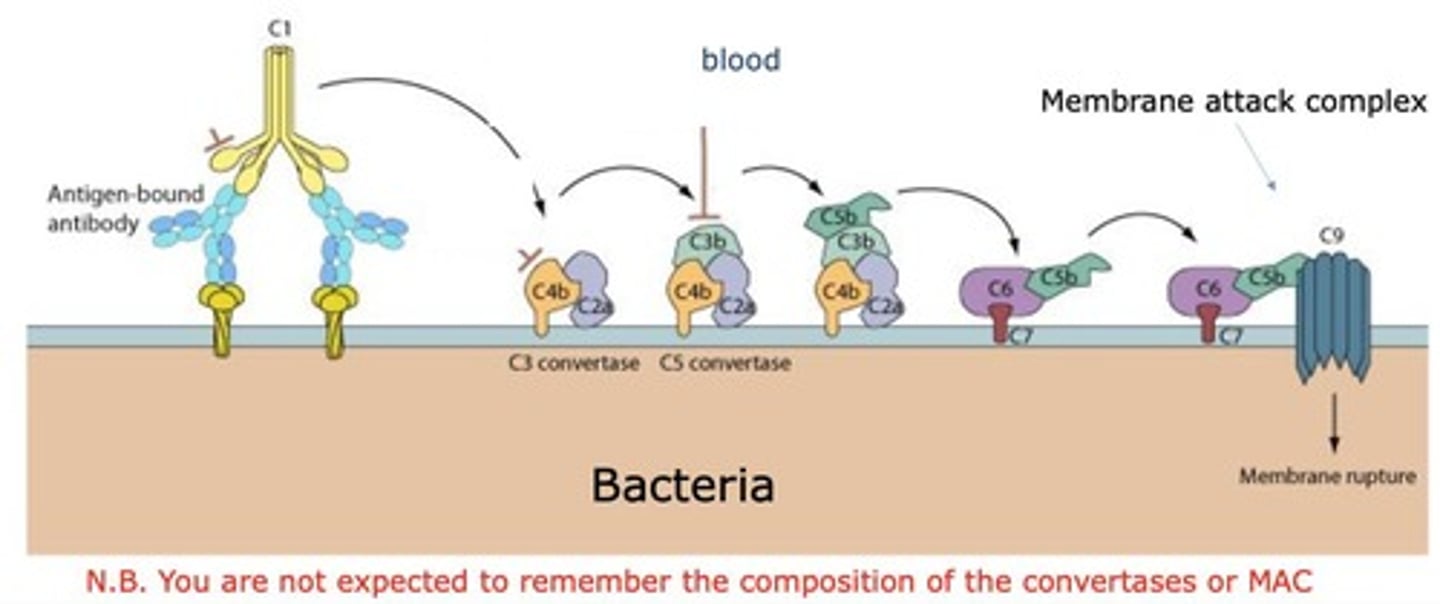
Anaphylatoxins
Small fragments attracting and activating phagocytes.
TPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator)
Medication used to dissolve blood clots.