Chap 5: Sensation and Perception
0.0(1)Studied by 28 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Source: Barron's AP Psychology
Last updated 6:06 AM on 1/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
Transduction
* Translation of stimuli into neural impulses
* These impulses first travel to the thalamus, then onto different cortices
* These impulses first travel to the thalamus, then onto different cortices
2
New cards
Sensory Adaptation
Decreasing responsiveness to stimuli due to constant stimulation
3
New cards
Sensory Habituation
Our perception of sensations is partially due to how focused we are on them
4
New cards
Cocktail Party Phenomenon
The ability to focus one's attention on a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli
5
New cards
Process of Light Entering the Eye
1. Reflected light first enters through the cornea (a protective covering) that focuses the light
2. Light goes through the pupil
* Muscles that control the pupil (iris) to let more or less light in
3. Accommodation: light that enters the pupil is focused by the lens. As light passes through the lens, the image is inverted.
4. The focused inverted image projects on the retina which has specialized neurons that are activated by the different wavelengths of light
6
New cards
Process in each layer of cells within the eye
* First layer of cells are directly activated by light (rods and cones)
* If enough rods and cones fire in an area of the retina, they activate the next layer of bipolar cells.
* If enough bipolar cells fire, the next layer, **ganglion cells**, are activated
* The axons of the ganglion cells make up the optic nerve that sends these impulses to the **lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)**, which is an area of the thalamus
* From there, the messages are sent to the visual cortices located in the occipital lobes of the brain
* If enough rods and cones fire in an area of the retina, they activate the next layer of bipolar cells.
* If enough bipolar cells fire, the next layer, **ganglion cells**, are activated
* The axons of the ganglion cells make up the optic nerve that sends these impulses to the **lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)**, which is an area of the thalamus
* From there, the messages are sent to the visual cortices located in the occipital lobes of the brain
7
New cards
Blind Spot
The spot where the optic nerve leaves the retina and has no rods or cones
8
New cards
Optic Chiasm
Spot where the nerves cross each other
9
New cards
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel
* Discovered that groups of neurons in the visual cortex respond to different types of visual images.
* Feature detectors for vertical lines, curves, motion, etc.
* Feature detectors for vertical lines, curves, motion, etc.
10
New cards
Trichromatic Theory
* 3 types of cones in the retina: cones that detect blue, red, and green
* Cones are activated in different combinations to produce all the colours of the visible spectrum
* Cannot explain some visual phenomena
* Cones are activated in different combinations to produce all the colours of the visible spectrum
* Cannot explain some visual phenomena
11
New cards
Opponent-Processing Theory
* Sensory receptors arranged in the retina come in pairs
* Red/Green, Yellow/Blue, Black/White
* If one sensor is stimulated, its pair is inhibited from firing
* Can explain visual phenomena
* Red/Green, Yellow/Blue, Black/White
* If one sensor is stimulated, its pair is inhibited from firing
* Can explain visual phenomena
12
New cards
Afterimages
* If you stare at one colour for a while and then look at a white or blank space, you will see a colour afterimage.
* If you stare at green, the afterimage is red. If you stare at blue, the afterimage is yellow.
* If you stare at green, the afterimage is red. If you stare at blue, the afterimage is yellow.
13
New cards
Colourblindness
* Dichromatic: cannot see either red/green or blue/yellow shades.
* Monochromatic: can only see shades of grey
* Monochromatic: can only see shades of grey
14
New cards
Amplitude
The height of the wave and determines the loudness of the sound (decibels)
15
New cards
Frequency
* Length of the waves and determines the pitch (megahertz)
* High-pitched sounds have high frequencies, and the waves are densely packed together.
* Low-pitched sounds have low frequencies, and the waves are spaced apart.
* High-pitched sounds have high frequencies, and the waves are densely packed together.
* Low-pitched sounds have low frequencies, and the waves are spaced apart.
16
New cards
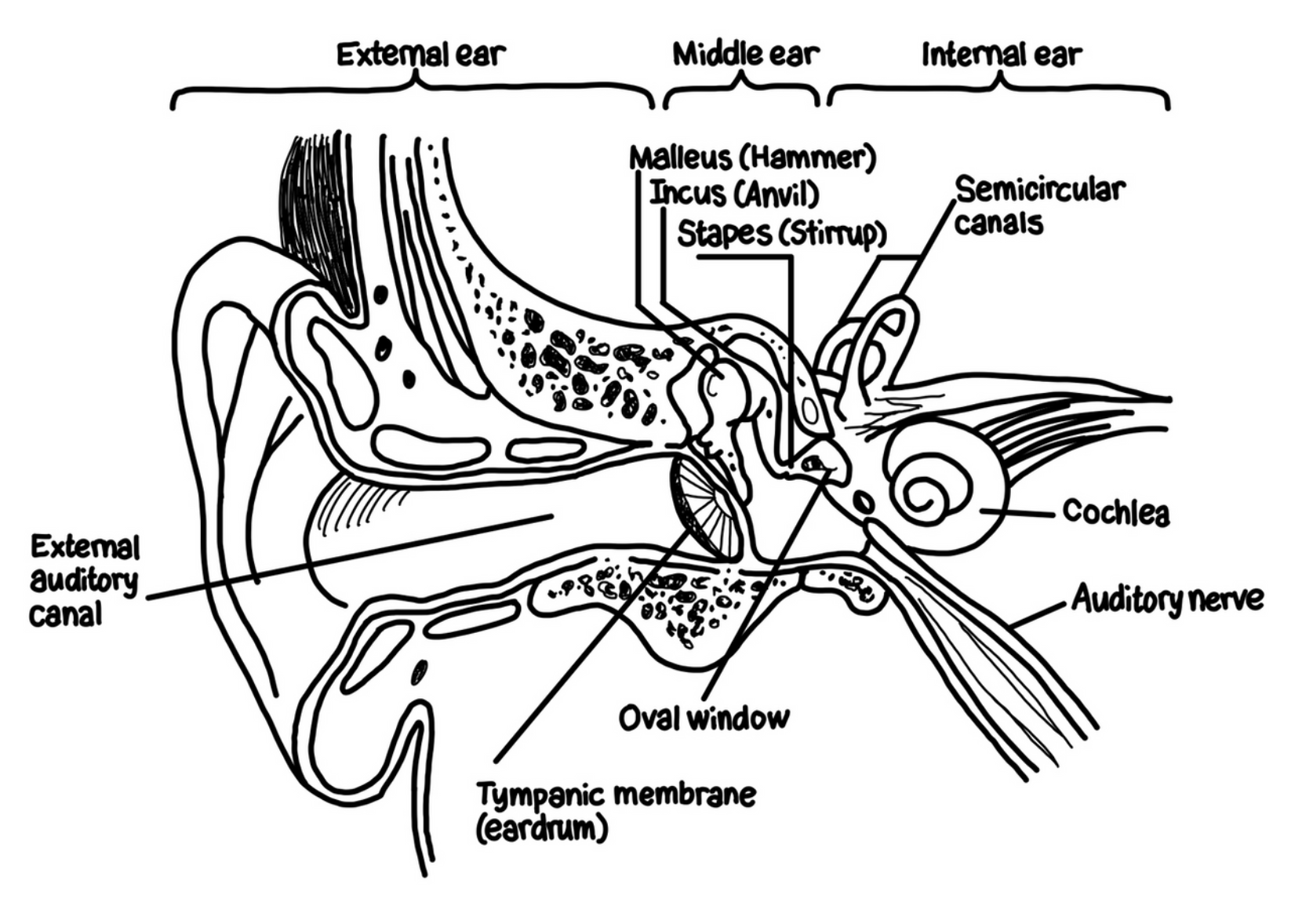
Process of hearing
* Sound waves are collected in your outer ear (pinna) and travel down the ear canal until they reach the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
* The membrane vibrates as the sound waves hit it and is attached to the first in a series of 3 small bones (collectively known as the **ossicles**)
* Eardrum connects with the **hammer** (malleus), which connects to the **anvil** (incus), which connects to the **stirrup** (stapes)
* The vibration of the eardrum is transmitted by these 3 bones to the **oval window** which is attached the to cochlea, a structure shaped like a snail’s shell filled with fluid. As the oval window vibrates, the fluid moves.
* The floor of the cochlea is called the basilar membrane. It’s lined with hair cells connected to the **organ of Corti**, which are neurons activated by the movement of the hair cells. When the fluid moves, the hair cells move and transduction occurs. The organ of Corti fires, and these impulses are transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
* The membrane vibrates as the sound waves hit it and is attached to the first in a series of 3 small bones (collectively known as the **ossicles**)
* Eardrum connects with the **hammer** (malleus), which connects to the **anvil** (incus), which connects to the **stirrup** (stapes)
* The vibration of the eardrum is transmitted by these 3 bones to the **oval window** which is attached the to cochlea, a structure shaped like a snail’s shell filled with fluid. As the oval window vibrates, the fluid moves.
* The floor of the cochlea is called the basilar membrane. It’s lined with hair cells connected to the **organ of Corti**, which are neurons activated by the movement of the hair cells. When the fluid moves, the hair cells move and transduction occurs. The organ of Corti fires, and these impulses are transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
17
New cards
Place Theory
* Hair cells in the cochlea respond to different frequencies of sound based on where they are located in the cochlea.
* Some bend in response to high pitches and some to low.
* We sense pitch because the hair cells move in different places in the cochlea
* Some bend in response to high pitches and some to low.
* We sense pitch because the hair cells move in different places in the cochlea
18
New cards
Frequency Theory
* Place theory accurately describes how hair cells sense the upper range of pitches, but not the lower tones.
* Lower tones are sensed by the rate at which the cells fire.
* We sense pitch because the hair cells fire at different rates (frequencies) in the cochlea.
* Lower tones are sensed by the rate at which the cells fire.
* We sense pitch because the hair cells fire at different rates (frequencies) in the cochlea.
19
New cards
Conduction Deafness
Occurs when something goes wrong with the system of conducting the sound to the cochlea (in the ear canal, eardrum, hammer/anvil/stirrup, or oval window).
20
New cards
Nerve (sensorineural) Deafness
* Occurs when the hair cells in the cochlea are damaged, usually by loud noise.
* Prolonged exposure to loud noise can permanently damage the hair cells in your cochlea, and these hair cells do not regenerate.
* Prolonged exposure to loud noise can permanently damage the hair cells in your cochlea, and these hair cells do not regenerate.
21
New cards
Gate-Control Theory
* Some pain messages have a higher priority than others.
* When a higher priority message is sent, the gate swings open for it and swings shut for a low priority message, which we will not feel.
* Endorphins (pain-killing chemicals) also swing the gate shut
* When a higher priority message is sent, the gate swings open for it and swings shut for a low priority message, which we will not feel.
* Endorphins (pain-killing chemicals) also swing the gate shut
22
New cards
Papillae
Taste buds are located on papillae, which are the bumps you can see on your tongue.
23
New cards
Process of Olfaction
* Molecules settle in a mucous membrane at the top of each nostril and are absorbed by receptor cells located there.
* **Receptor cells** are linked to the olfactory bulb, which gathers the messages from the **olfactory receptor cells** and sends this info to the brain.
* **Receptor cells** are linked to the olfactory bulb, which gathers the messages from the **olfactory receptor cells** and sends this info to the brain.
24
New cards
Why is smell a powerful trigger of memories?
Impulses from other senses, except smell, go through the thalamus first before being sent to the cortex, but info from our sense of smell go directly to the amygdala (emotional impulses) and then to the hippocampus (memory).
* This direct connection to the limbic system may explain why smell is such a powerful trigger for memories.
* This direct connection to the limbic system may explain why smell is such a powerful trigger for memories.
25
New cards
Vestibular Sense
* Tells us about how our body is oriented in space.
* 3 semicircular canals filled with fluid in the inner ear give the brain feedback about body orientation
* When position of your head changes, the fluid moves in the canals, causing sensors in the canals to move.
* The movement of these hair cells activate neurons and their impulses go to the brain.
* 3 semicircular canals filled with fluid in the inner ear give the brain feedback about body orientation
* When position of your head changes, the fluid moves in the canals, causing sensors in the canals to move.
* The movement of these hair cells activate neurons and their impulses go to the brain.
26
New cards
Kinaesthetic Sense
* Tells us about the position and orientation of specific body parts.
* Receptors in our muscles and joints send info to our brain about our limbs.
* This info, along with visual feedback, lets us keep track of our body.
* Receptors in our muscles and joints send info to our brain about our limbs.
* This info, along with visual feedback, lets us keep track of our body.
27
New cards
Absolute Threshold
The smallest amount of stimulus we can detect
28
New cards
Subliminal
Used to describe stimuli below our absolute threshold
29
New cards
Difference Threshold (Just-Noticeable Difference)
The smallest amount of change needed in a stimulus before we detect a change.
30
New cards
Weber’s Law
* Computes the difference threshold
* States that the change needed is proportional to the original intensity of the stimulus. The more intense the stimulus, the more it will need to change before we notice a difference.
* Each sense varies according to a constant, but the constants differ between the senses.
* Constant for hearing is 5%, constant for vision is 8%
* States that the change needed is proportional to the original intensity of the stimulus. The more intense the stimulus, the more it will need to change before we notice a difference.
* Each sense varies according to a constant, but the constants differ between the senses.
* Constant for hearing is 5%, constant for vision is 8%
31
New cards
Signal Detection Theory
* Investigates the effects of the distractions and interference we experience while perceiving the world.
* Tries to predict what we will perceive among competing stimuli
* Takes into account how motivated we are to detect certain stimuli and what we expect to perceive
* All the above factors are called the **response criteria**
* Tries to predict what we will perceive among competing stimuli
* Takes into account how motivated we are to detect certain stimuli and what we expect to perceive
* All the above factors are called the **response criteria**
32
New cards
False Positive
When we think we perceive a stimulus that is not there.
33
New cards
False Negative
When we don’t perceive a stimulus that is present.
34
New cards
Top-Down Processing
* We perceive by filling in gaps in what we sense.
* Occurs when you use your background knowledge to fill in gaps in what you perceive
* Occurs when you use your background knowledge to fill in gaps in what you perceive
35
New cards
Schemata
Mental representations of how we expect the world to be based on our experience
36
New cards
Perceptual Set
Predisposition to perceiving something in a certain way; influenced by schemata
37
New cards
Backmasking
Supposed hidden messages musicians recorded backward in their music
38
New cards
Bottom-Up Processing
* We use only the features of the object itself to build a complete perception.
* Feature detectors in the visual cortex allow us to perceive basic features, such as lines, curves, motions, etc
* Our mind builds the picture from the bottom up using these basic characteristics
* Feature detectors in the visual cortex allow us to perceive basic features, such as lines, curves, motions, etc
* Our mind builds the picture from the bottom up using these basic characteristics
39
New cards
Figure-Ground Relationship
What part of a visual image is the figure and what part is the ground or background?
40
New cards
Gestalt Rules of Perception
We normally perceive images as groups, not as isolated elements. (Proximity, Similarity, Continuity, Closure)
41
New cards
Proximity
Objects that are close together are more likely to be perceived as belonging in the same group.
42
New cards
Similarity
Objects that are similar in appearance are more likely to be perceived as belonging in the same group.
43
New cards
Continuity
Objects that are arranged in a continuous line or curve are more likely to be perceived as belonging to the same group.
44
New cards
Closure
Similar to top-down processing. Objects that make up a recognizable image are more likely to be perceived as belonging in the same group even if the image contains gaps that the mind needs to fill in.
45
New cards
Constancy
Our ability to maintain a constant perception of an object despite changes in angle of vision, variations in light, etc.
46
New cards
Size Constancy
Objects closer to our eyes will produce bigger images on our retinas, but we take distance into account in our estimations of size. We keep a constant size in mind for an object (if we are familiar with the typical size of the object) and we know that it does not grow or shrink in size as it moves closer or farther away.
47
New cards
Shape Constancy
Objects viewed from different angles will produce different shapes on our retinas, but we know the shape of an object remains constant. This also depends on our familiarity with the usual shape of the object.
48
New cards
Brightness Constancy
We perceive objects as being a constant colour even as the light reflecting off the object changes.
49
New cards
Stroboscopic Effect
* Images in a series of still pictures presented at a certain speed will appear to be moving.
* Examples: movies, flip books
* Examples: movies, flip books
50
New cards
Phi Phenomenon
* A series of lightbulbs turned on and off at a particular rate will appear to be one moving light.
* Examples: movie marquees, holiday lights
* Examples: movie marquees, holiday lights
51
New cards
Autokinetic Effect
If a spot of light is projected steadily onto the same place on a wall of an otherwise dark room and people are asked to stare at it, they will report seeing it move.
52
New cards
Eleanor Gibson
Used the visual cliff experiment to determine when human infants can perceive depth.
53
New cards
Visual Cliff Experiment
* Used to determine when human infants can perceive depth
* Infant is placed onto one side of a glass-topped table that creates the impression of a cliff.
* Found that an infant old enough to crawl will not crawl across the visual cliff, implying the child has depth perception.
* Infant is placed onto one side of a glass-topped table that creates the impression of a cliff.
* Found that an infant old enough to crawl will not crawl across the visual cliff, implying the child has depth perception.
54
New cards
Monocular Cues
* Depth cues that do not depend on having two eyes
* Linear perspective, relative size cue, Interposition cue, texture gradient, shadowing
* Linear perspective, relative size cue, Interposition cue, texture gradient, shadowing
55
New cards
Binocular Cues
Cues that depend on having two eyes
56
New cards
Binocular (Retinal) Disparity
Since each of our eyes sees any object from a slightly different angle, the closer the object is, the more disparity there will be between the images coming from each eye.
57
New cards
Convergence
* As an object gets closer to our face, our eyes must move toward each other to keep focused on the object.
* The more the eyes converge, the closer the object must be.
* The more the eyes converge, the closer the object must be.