Biological molecules: Carbohydrates
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What elements are carbohydrates made of
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
3 types of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
Name 3 monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
Name 3 disaccharides
sucrose, maltose, lactose
Name 3 polysaccharides
Starch, cellulose, glycogen
What is the classification of monosaccharides based on
Number of carbon atoms
Chemical formula for glucose, fructose, galactose
C6H12O6
Chemical formula for sucrose, maltose, lactose
C12H22O11
General formula for monosaccharides
CnH2nOn
Single sugar is a
Monosaccharide
How many orientations can glucose be in
Any
How many structural isomers does glucose have
2
Structural isomer meaning
Same molecular formula, different structure
Draw alpha glucose
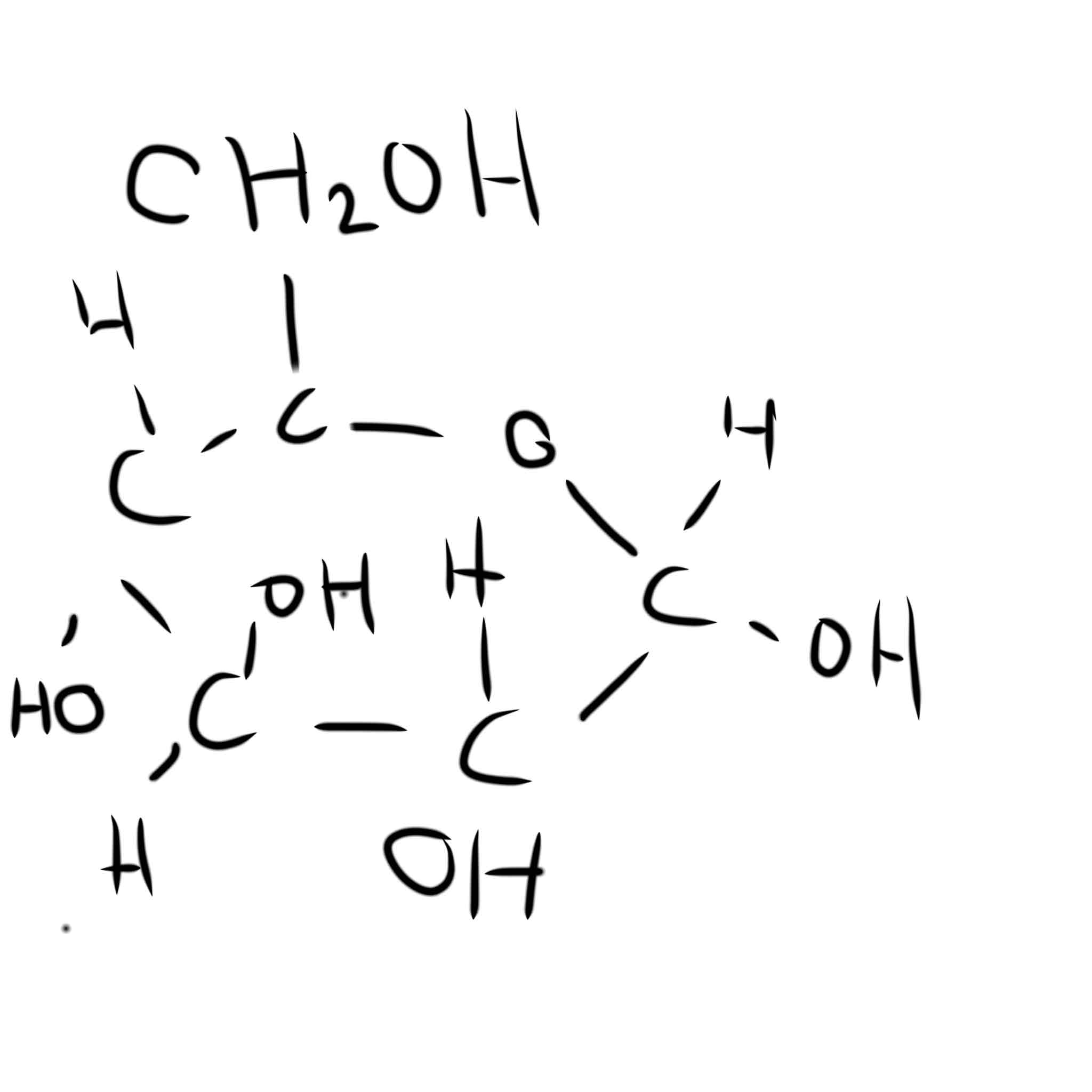
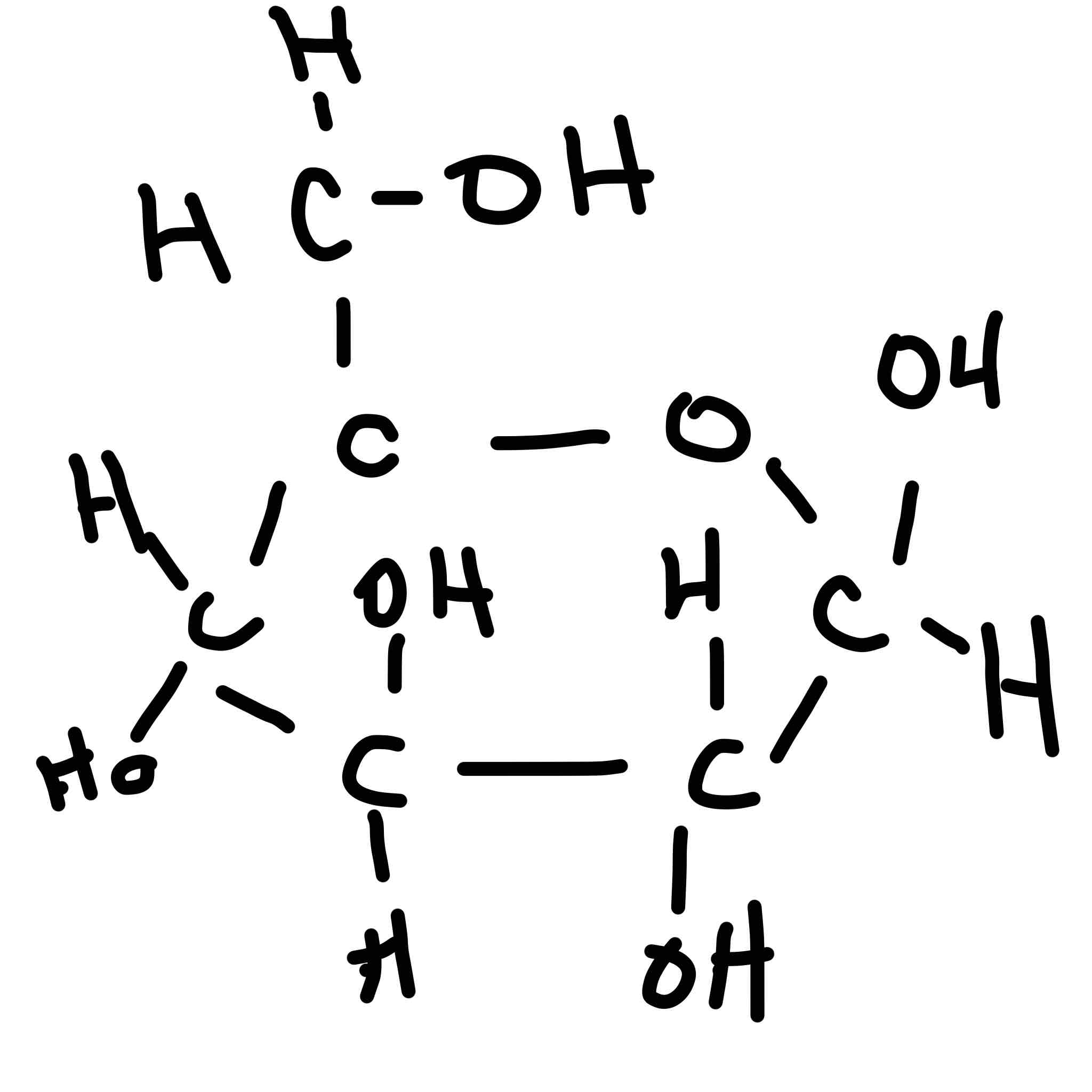
Draw beta glucose
a glucose + a glucose?
starch (storage molecule)
b glucose + b glucose?
cellulose (structure)
Describe a condensation reaction (3)
Smaller monomer joins to another, water molecule is removed.
Remainder = residue.
Produces polymer (larger molecule)
What kind of bond does a condensation reaction create?
Covalent / glycosidic bond
Glycosidic bond
bond formed as a result of condensation between to monosaccharides
2 alpha glucoses create
maltose + water
beta fructose + alpha glucose
Sucrose + water
galactose + alpha glucose
lactose + water
molecular formula for lactose, maltose, sucrose
C12H22O11
What are carbohydrates used for (2)
By body for fuels (respiration)
build cells
Monomers join together to form
Polymers
Hydrolisis (3)
opposite of condensation.
Polymer broken down into molecules.
Water is chemically added
Starch’s monomer
monomer = alpha glucose, mixture of 2 polymers
starch digested by
amylase
2 polymers that make up starch
amylose, amylopectin
Amylose structure + function link (2)
curly (forms helix) to be compact
only a 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Amylopectin structure (5)
Highly branched (1)
a 1-6 + 1-4 glycosidic bonds. (1)
Lots of terminal starch molecules (1) to allow many glucose units to be synthesised (1) and stored effectively (1)
Glycogens monomer
alpha glucose
Function of glycogen (3)
storage of glucose (1)
which allows for fast energy release when needed (1)
present in muscle tissue (1)
Function of starch
Store glucose for later energy use
Glycogen structure to function (4)
1-4, 1-6 alpha glycosidic bonds (1)
polymer = large molecule, insoluble, osmotically inert. (1)
Highly branched molecule = many terminal glucose molecules (1) = easily hydrolysed for energy released in respiration (1)
Cellulose monomer
beta glucose
Chemical equation for respiration
6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water
Cellulose structure to function (5)
beta glucose bonds 1-4, 1-6 (1)
alternate molecuules rotate 180 degrees (1)
parallel chains cross linked to form microfibrils for strength. prevents osmotic lysis in hypotonic solutions (2)
long straight chains (1)
Similarities between starch and cellulose (5)
C,H,O
carbohydrate
monomer: glucose
polysaccharide
alpha 1 -4 glycosidic bond
Other “polysaccharides” (3)
Contain nitrogen
Chitin: fungal cell wall
Peptidoglycon (meurin): component of prokaryotic (bacteria) cell wall