Natural Selection Vocab Quiz
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
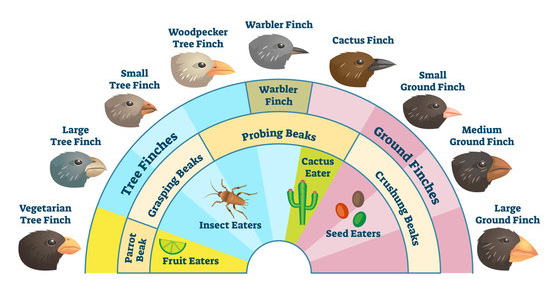
Adaptive Radiation
Period of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptations allow them to fill different ecological roles in their communities.
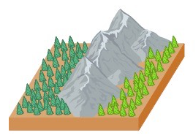
Allopatric Speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
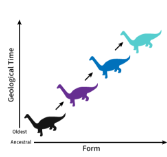
Anagenesis
The gradual evolution of a species without branching, where one species emerges from another over time.
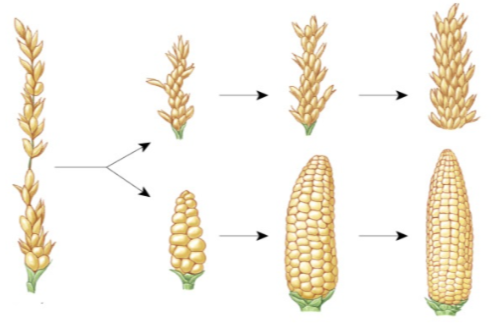
Artificial Selection
The selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to encourage the occurrence of desirable traits.
Biogeography
The scientific study of the past and present geographic distributions of species.
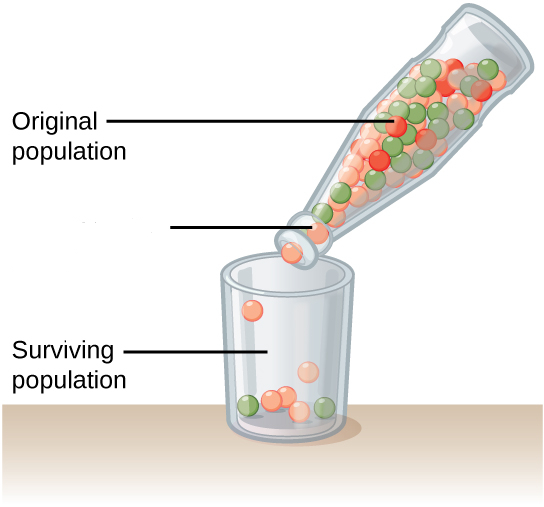
Bottleneck Effect
Genetic drift that occurs when the size of a population is reduced, as by a natural disaster or human actions. Typically, the surviving population is no longer genetically representative of the original population.

Catastrophism
The principle that events in the past occurred suddenly and were caused by different mechanisms than those operating today.
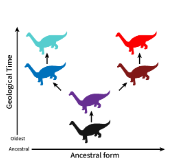
Cladogenesis
A pattern of evolutionary change that produces biological diversity by budding one or more new species from a parent species that continues to exist.
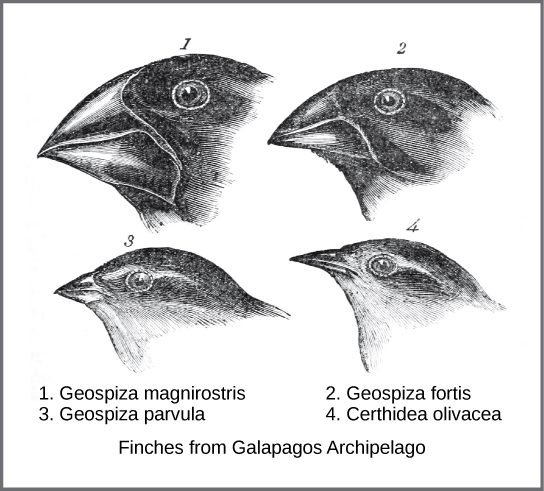
Descent with Modification
The process by which species evolve over time through variations that are inherited by offspring, leading to adaptations in response to environmental changes.

Fossils
Preserved remnant or impression of an organism that lived in the past.
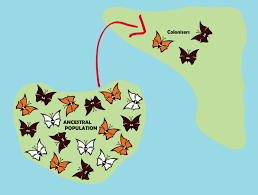
Founder Effect
Genetic drift that occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population and form a new population whose gene pool composition is not reflective of that of the original population.
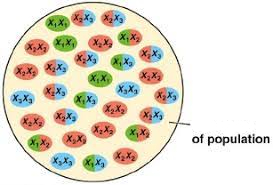
Gene Pool
The aggregate of all copies of every type of allele at all loci in every individual in a population. The term is also used in a more restricted sense as the aggregate of alleles for just one or a few loci in a population.
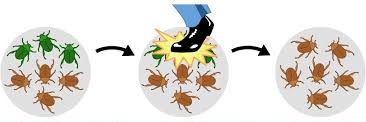
Genetic Drift
A process in which chance events cause unpredictable fluctuations in allele frequencies from one generation to the next. Effects of _______ _____ are most pronounced in small populations.
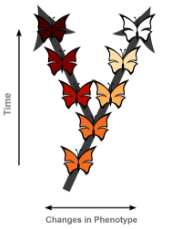
Gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly but steadily, with small incremental changes over long periods of time.
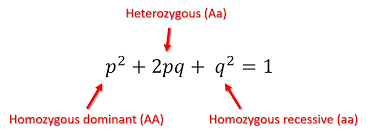
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
The state of a population in which frequencies of alleles and genotypes remain constant from generation to generation, provided that only Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles are at work.
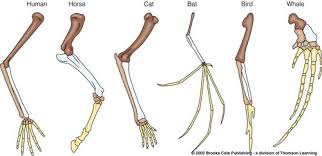
Homologous Structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
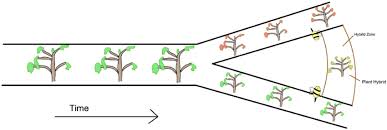
Hybrid Zone
A geographic zone in which members of different species meet and mate, producing at least some offspring of mixed ancestry.

Macroevolution
Evolutionary change above the species level. Examples of _________________ change include the origin of a new group of organisms through a series of speciation events and the impact of mass extinctions on the diversity of life and its subsequent recovery.
Microevolution
Evolutionary change below the species level; change in the allele frequencies in a population over generations.
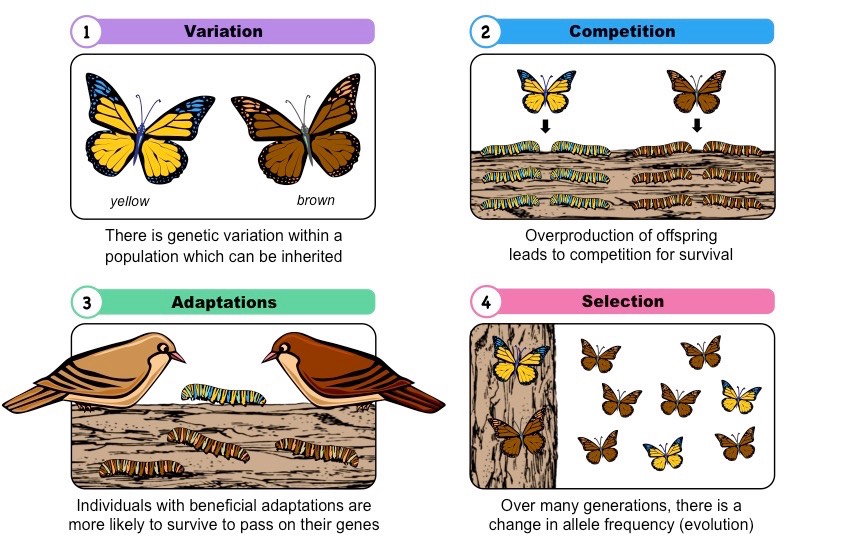
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Polymorphism
The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs of a certain species within the same population.
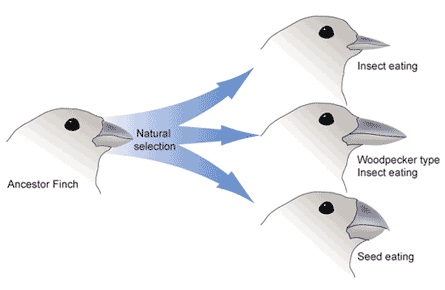
Speciation
An evolutionary process in which one species splits into two or more species.
Sympatric Speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area.
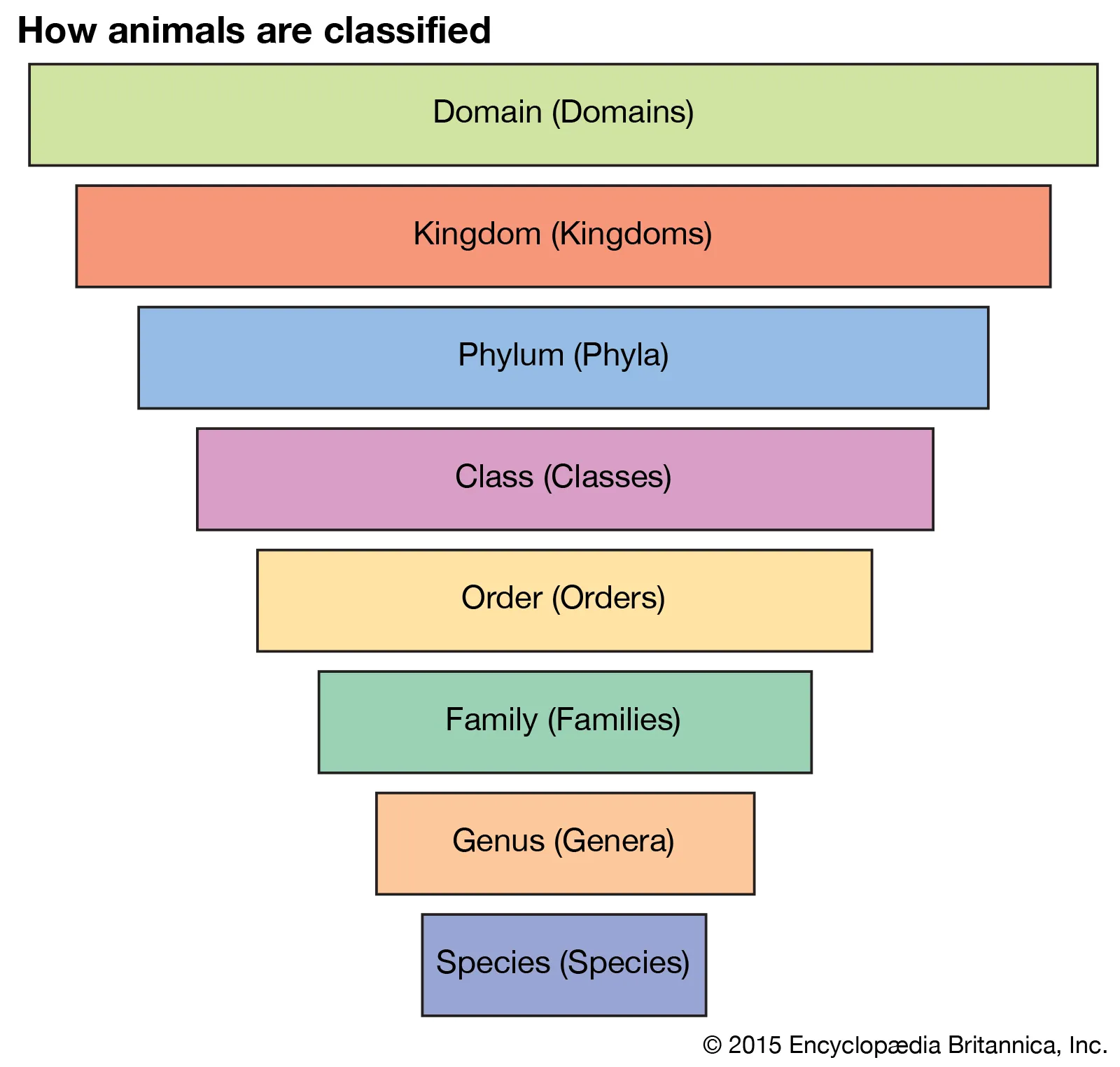
Taxonomy
A scientific discipline concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life.
Uniformitarianism
The principle stating that mechanisms of change are constant over time.
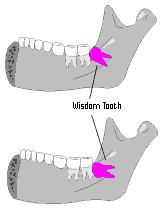
Vestigial Organs/Structures
A feature of an organism that is a historical remnant of a structure that served a function in the organism’s ancestors.