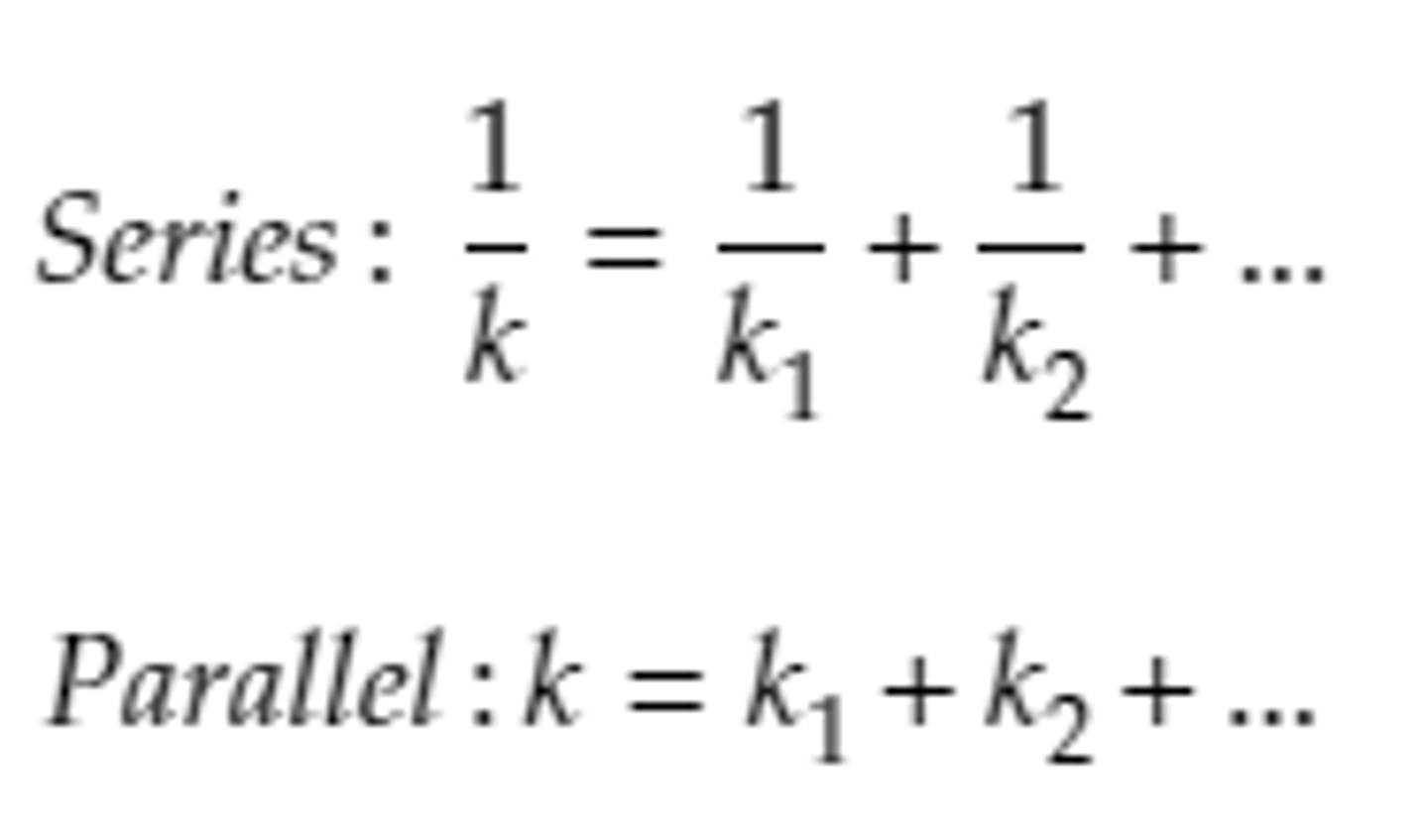Ch.7 Part 2 Hooke's Law and Young Modulus
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Hooke's Law
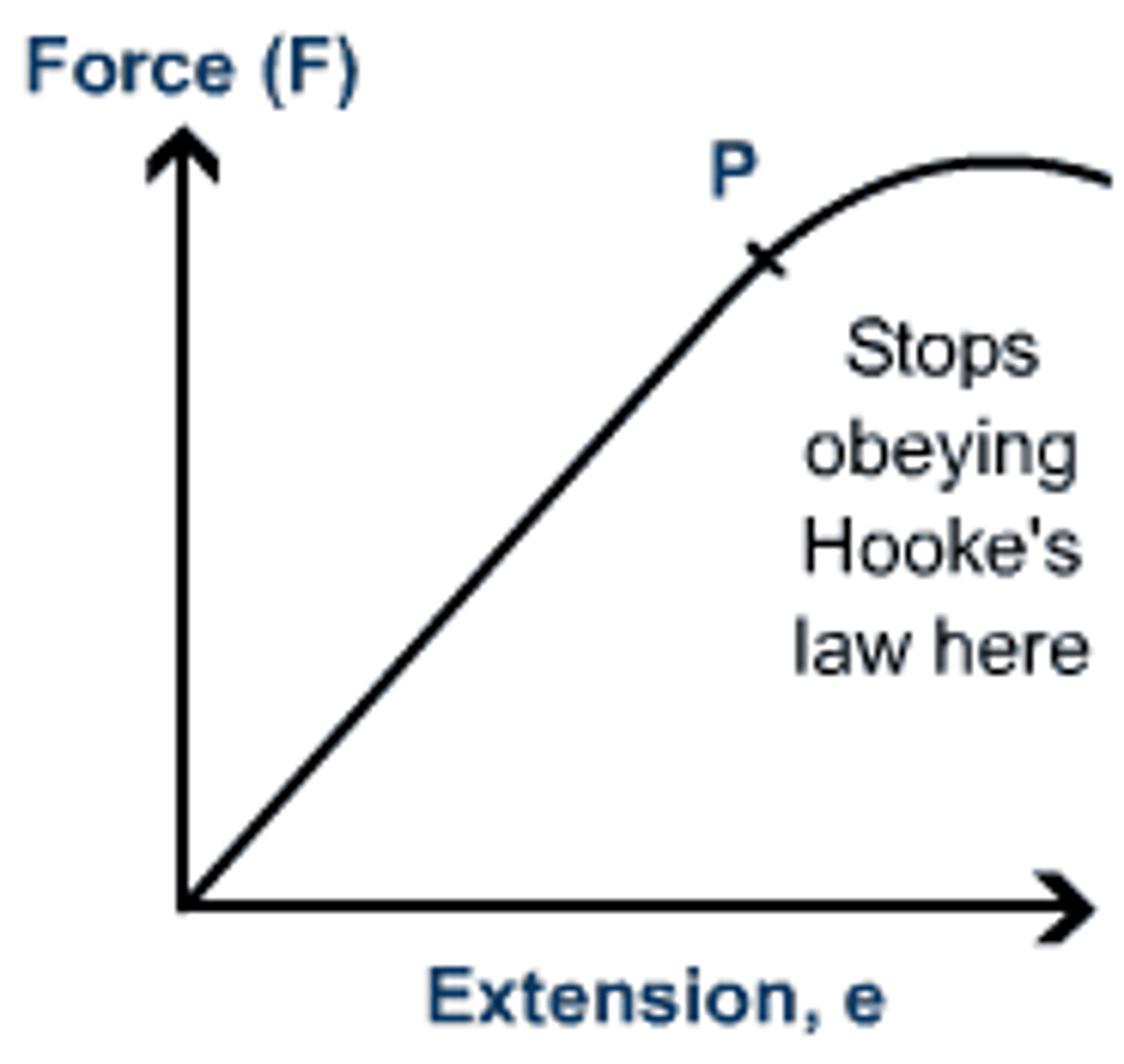
Extension is directly proportional to applied force until the spring reaches its elastic limit.
F = kx
Compressive
Describes a force that squeezes an object
Tensile
capable of being stretched
Stress
Force per unit cross-sectional area that acts perpendicular to the surface. (in Pascals)

Strain
Extension per unit length (no units but usually measured as a percent)
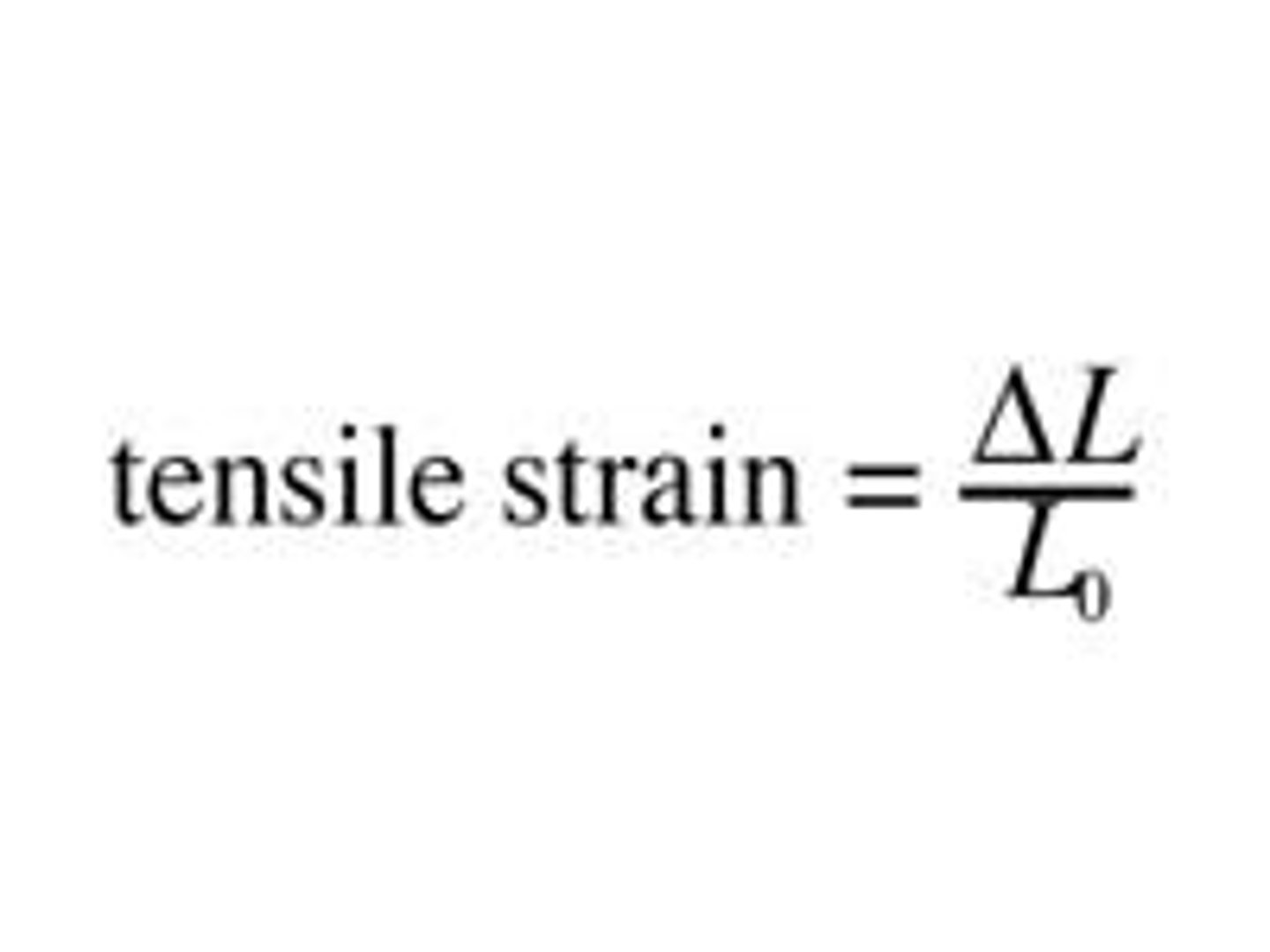
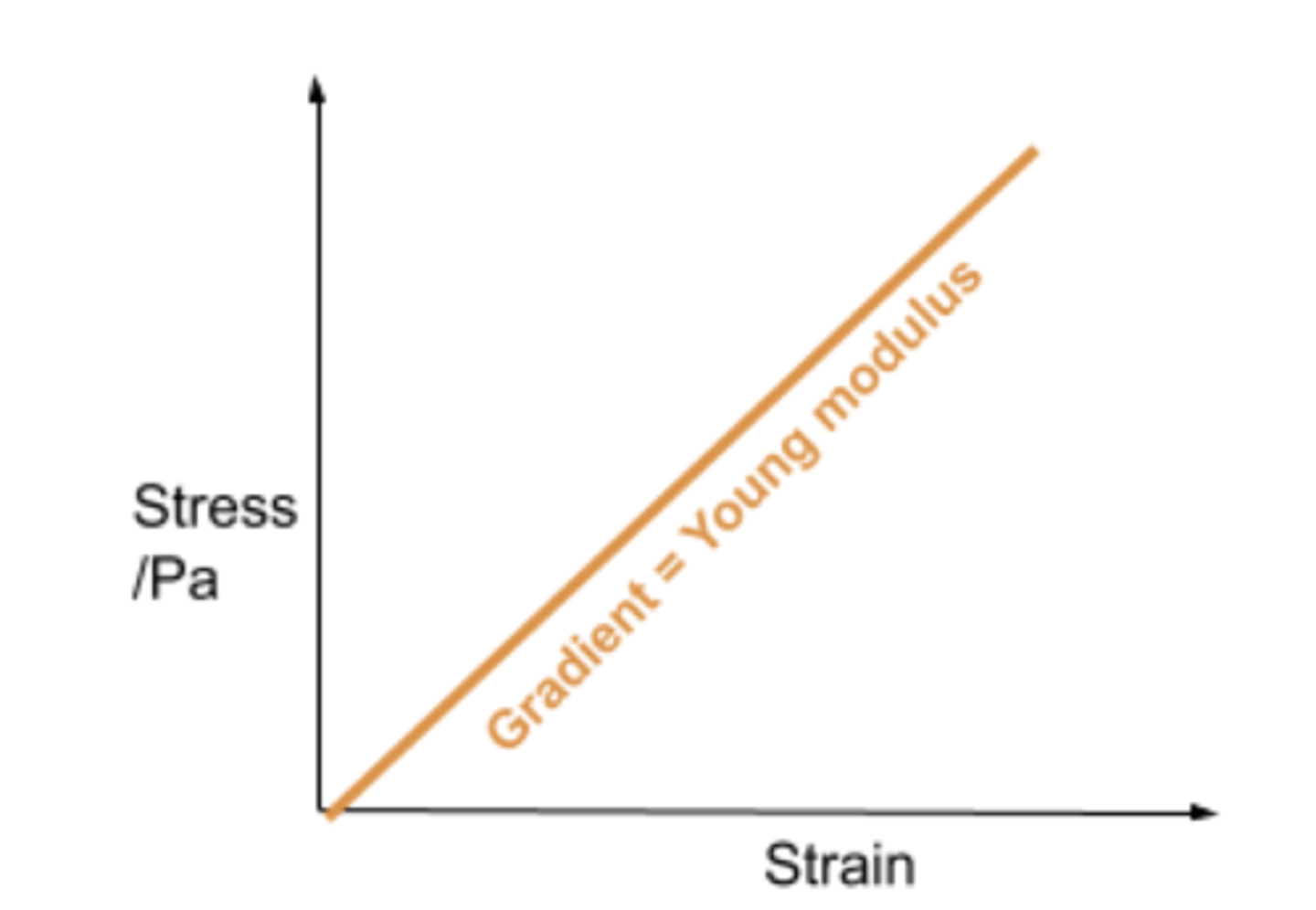
Young modulus
stress/strain
assuming limit of proportionality has not been exceeded

Strain energy
Stored energy in an object due to elastic deformation

Gradient of a stress strain graph
Young modulus
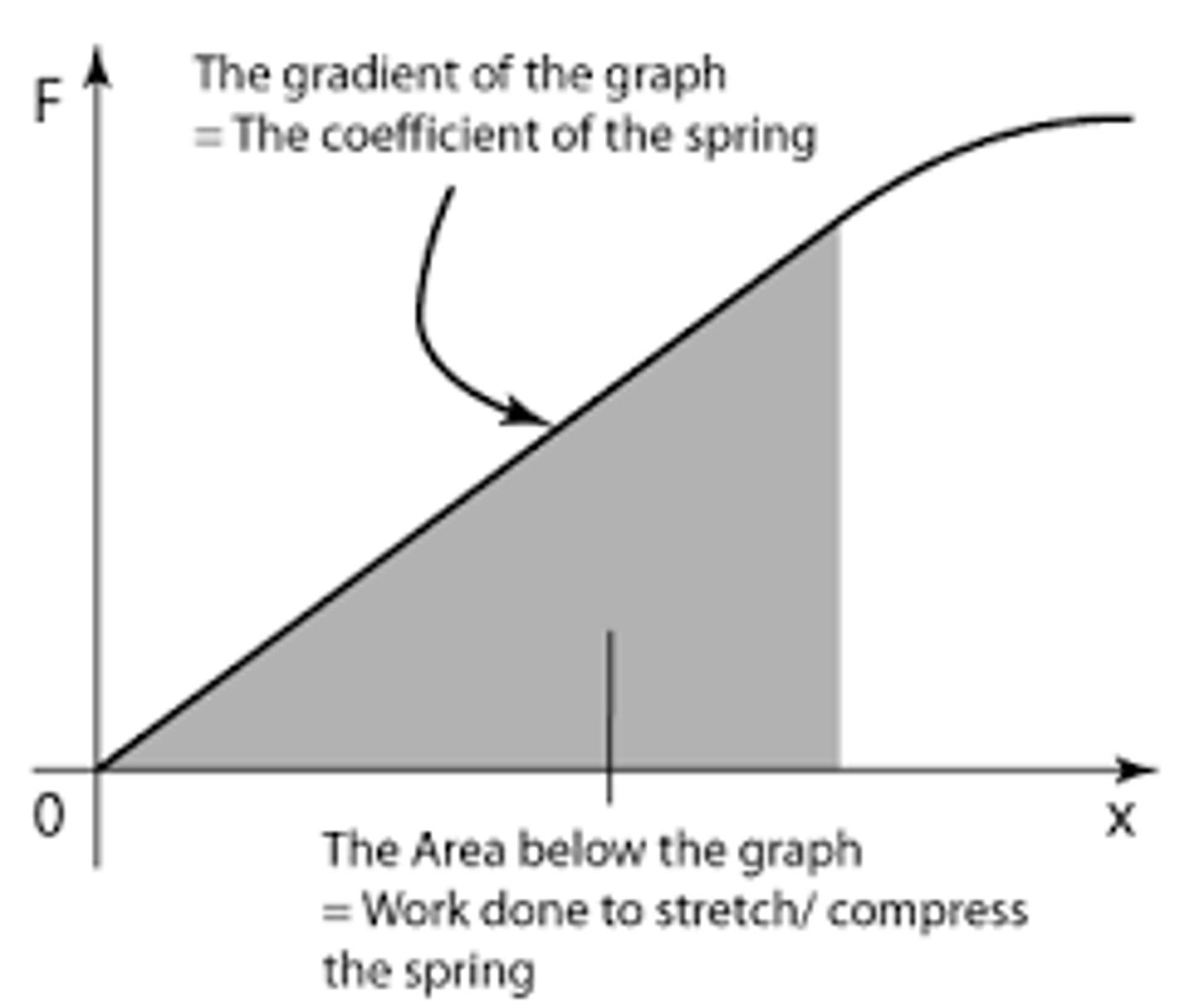
Gradient of a force-extension graph
spring constant k
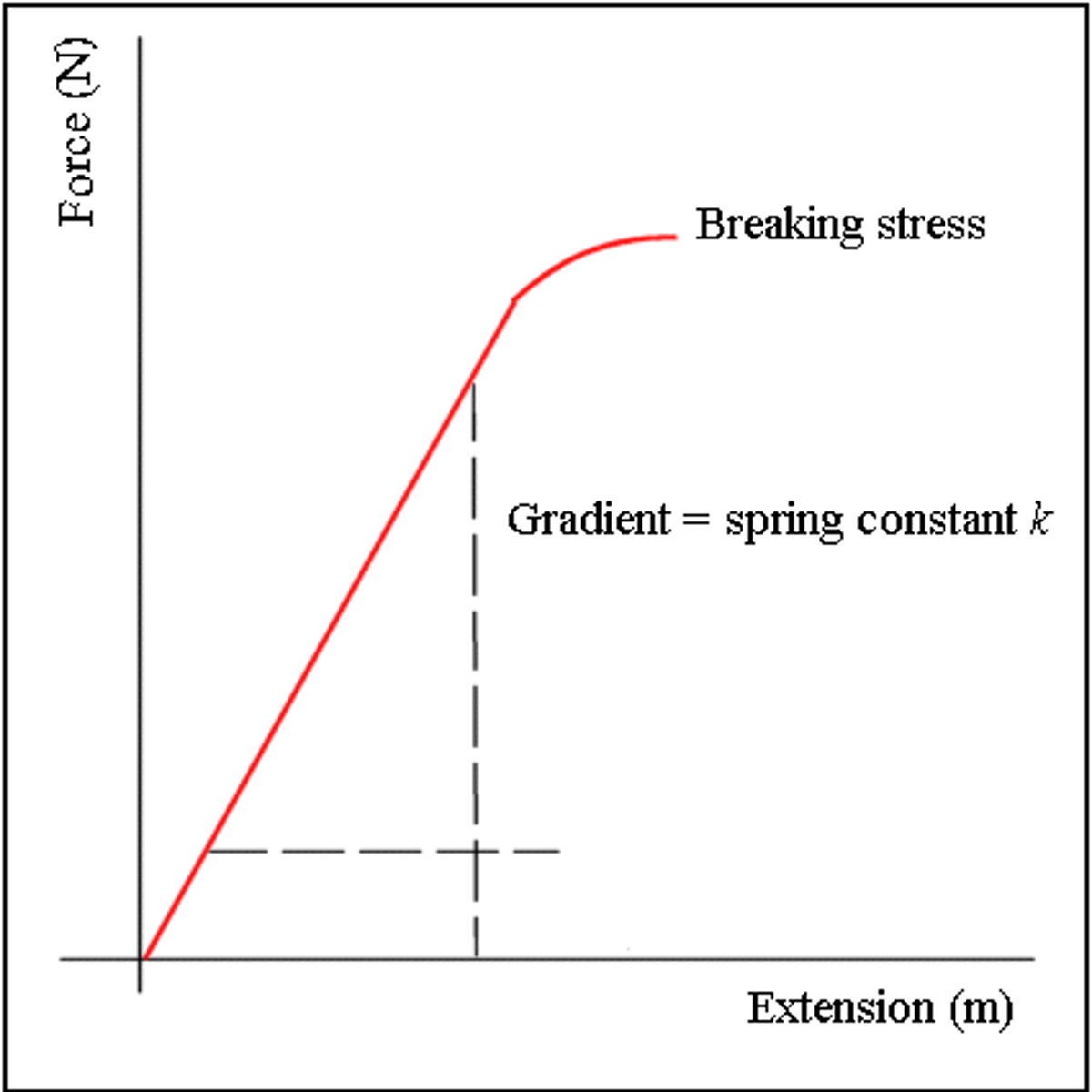
Area under a force-extension graph
Elastic strain energy
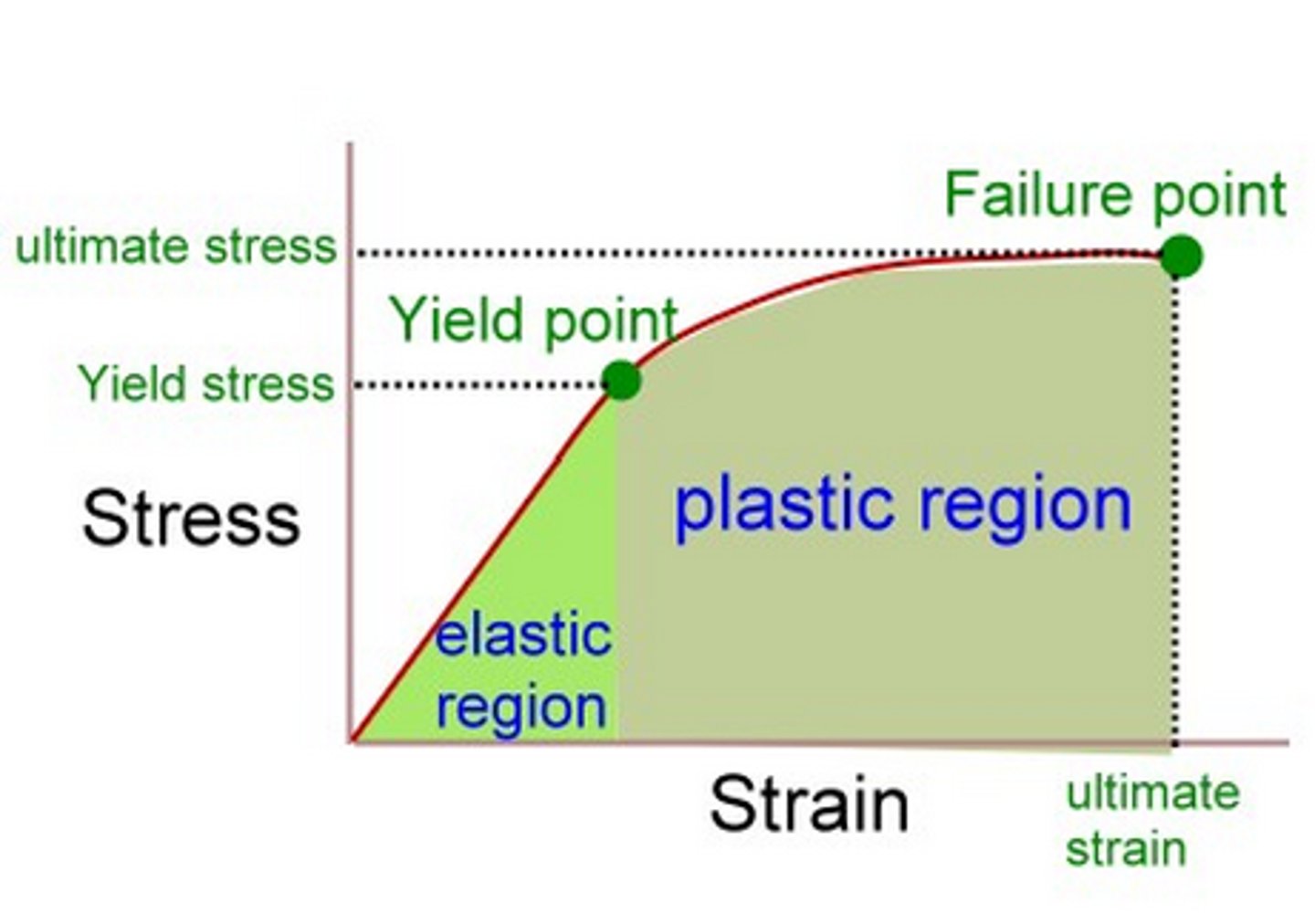
Elastic Limit
The value of stress beyond which an object will not return to its original dimensions.
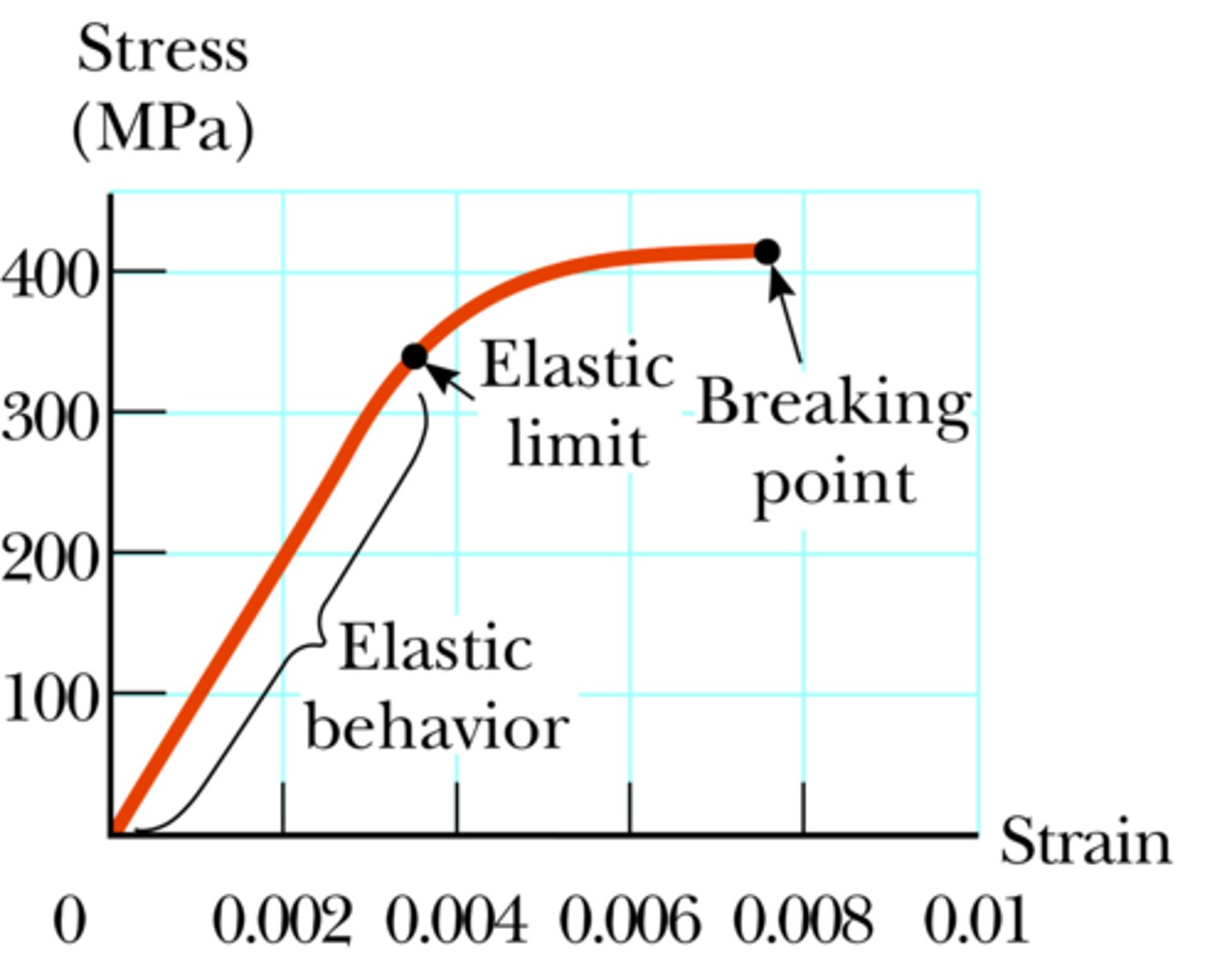
Elastic Deformation
An object that returns to its original length when the force is removed has deformed elastically.
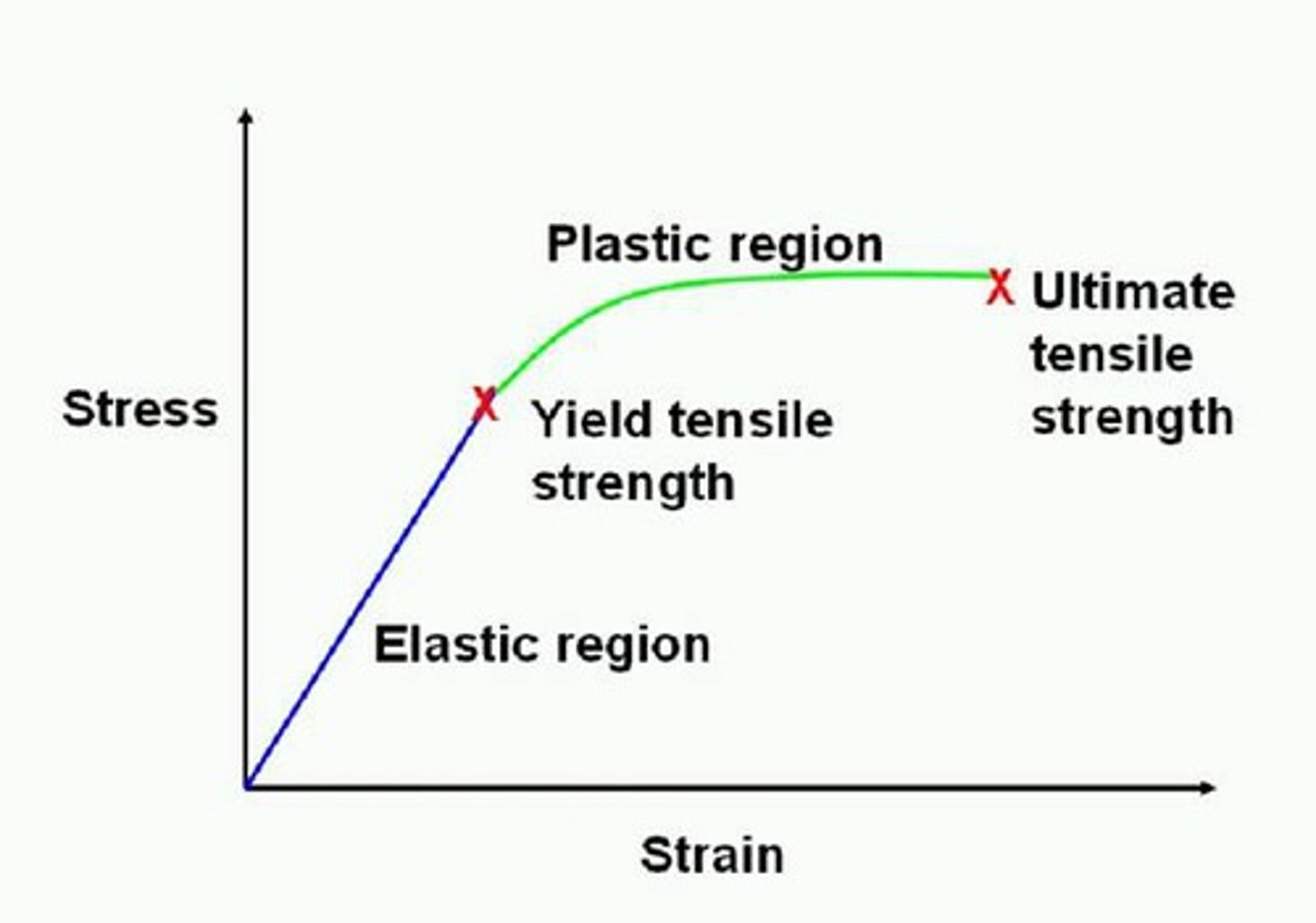
Plastic Deformation
An object that does NOT return to its original length when the force is removed.
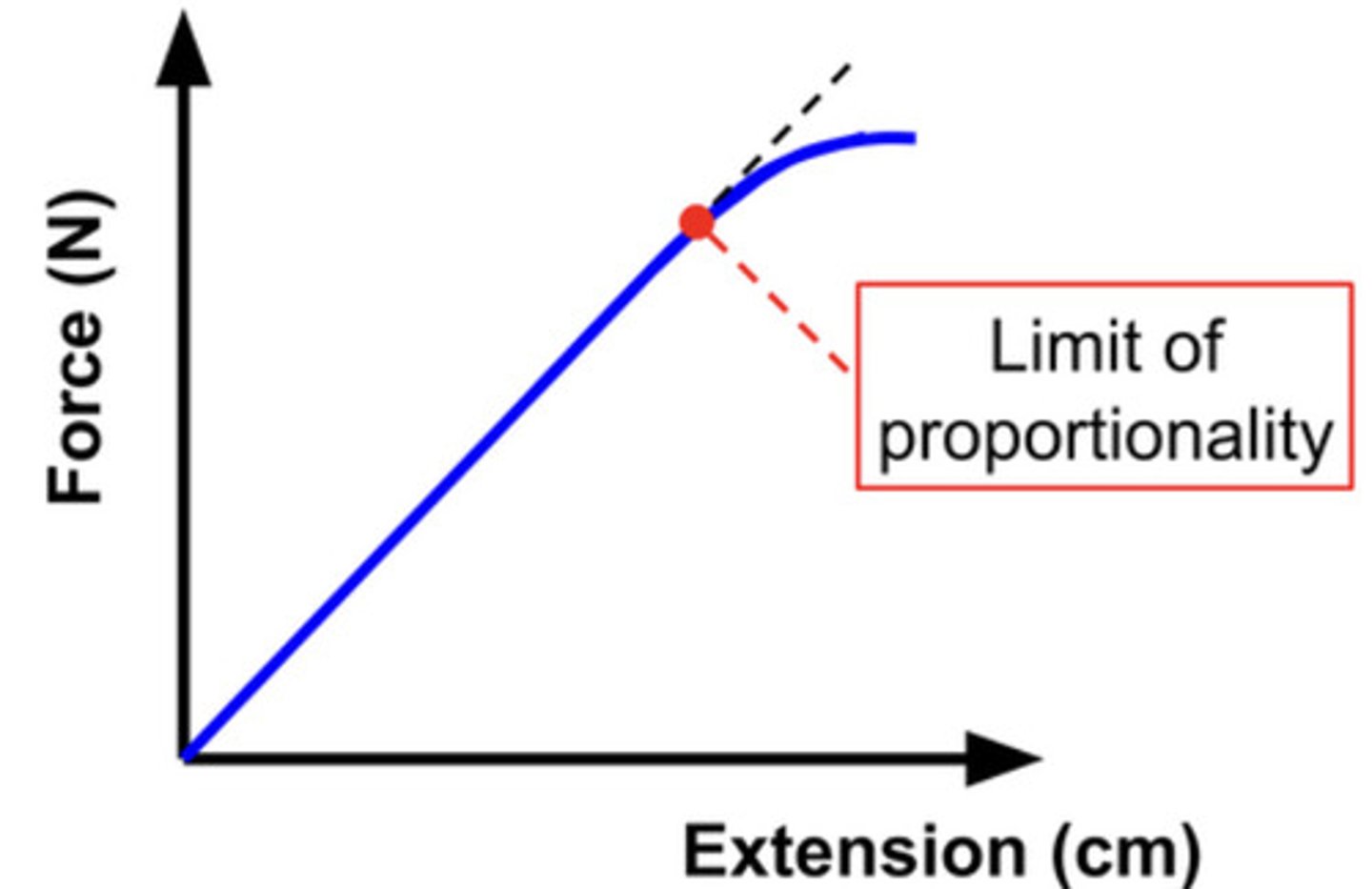
Limit of Proportionality
The point beyond which extension is no longer proportional to the force.
Springs in Series and Parallel.
Opposite of resistors (which is on formula sheet)