Reactions of alkenes
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Electrophillic addition
A type of addition in which an electrophile ( electron pair acceptor) is attracted to an electron-rich centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
State the steps of halogenation of alkenes and draw diagrams
An induced dipole is formed at the halogen e.g. bromine, when they get closer to the double bond in the alkene. So the electrons in the bromine repel to one bromine atom of the element, which causes this induced dipole
The positively charged bromine of the halogen is then attracted to the electron dense double bond of the alkene, breaking the double bond and forming a new bond with the positive bromine
This then forms a carbocation as one of the carbons in the structure now only has 3 bonds around it meaning the the negative bromine which was left behind is then attracted to the carbocation
Forming the final product of 1,2-dibromoethane
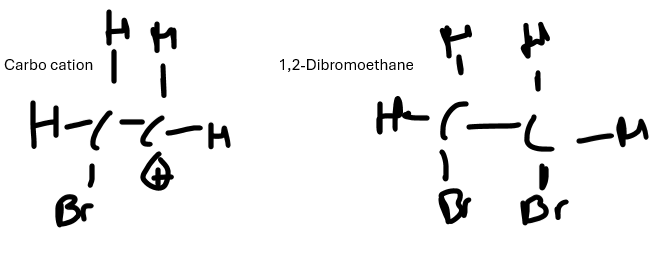
Why is halogenation an electrophilic reaction
This reaction is electrophilic as the pi bond a region of high electron density and attracts the δ⁺ bromine molecule which acts as an electrophile. It is an addition reaction because the carbon double bond breaks and a new halogen carbon bond is formed
Hydrogenation of alkenes
Conditions for hydrogenation is a nickel catalyst, hydrogen and a temperature of 150o
CH2=CHBr+H2 ⟶ Ni, 150 °CCH3−CH2Br
Hydration of alkenes
Conditions needed are in the presence of steam, phosphoric acid and a temperature of around 300 °C
CH2=CH2+H2O(g) ⟶CH3CH2OH